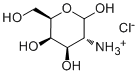
D-Galactosamine hydrochlorideCAS# 1772-03-8 |
Quality Control & MSDS
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 1772-03-8 | SDF | File under preparation. |
| PubChem ID | N/A | Appearance | Powder |
| Formula | C6H14ClNO5 | M.Wt | 215.63 |
| Type of Compound | Impurities | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Solubility | Soluble in Chloroform,Dichloromethane,Ethyl Acetate,DMSO,Acetone,etc. | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||

D-Galactosamine hydrochloride Dilution Calculator

D-Galactosamine hydrochloride Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 4.6376 mL | 23.1879 mL | 46.3757 mL | 92.7515 mL | 115.9393 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.9275 mL | 4.6376 mL | 9.2751 mL | 18.5503 mL | 23.1879 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.4638 mL | 2.3188 mL | 4.6376 mL | 9.2751 mL | 11.5939 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0928 mL | 0.4638 mL | 0.9275 mL | 1.855 mL | 2.3188 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0464 mL | 0.2319 mL | 0.4638 mL | 0.9275 mL | 1.1594 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
- D-Mannosamine hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCX0510
CAS No.:5505-63-5
- Moracin N
Catalog No.:BCX0509
CAS No.:135248-05-4
- (S)-5-Hydroxy-1-(4-hydroxy-3-methoxyphenyl)-7-phenylheptan-3-one
Catalog No.:BCX0508
CAS No.:1220110-76-8
- 1β-Hydroxy-8α-methoxyeremophila-7(11),9-dien-12,8β-olide
Catalog No.:BCX0507
CAS No.:849700-45-4
- Methylconiferin
Catalog No.:BCX0506
CAS No.:883150-46-7
- Iristectorin B
Catalog No.:BCX0505
CAS No.:94396-09-5
- Vavain
Catalog No.:BCX0504
CAS No.:199996-77-5
- 6-Demethoxyirigenin
Catalog No.:BCX0503
CAS No.:1348833-10-2
- Oxyphyllenodiol A
Catalog No.:BCX0502
CAS No.:363610-30-4
- Teuhetenone A
Catalog No.:BCX0501
CAS No.:152481-80-6
- Isocrenatoside
Catalog No.:BCX0500
CAS No.:221895-09-6
- Erythrinin E
Catalog No.:BCX0499
CAS No.:2731101-51-0
- N-acetyl-D-galactosamine
Catalog No.:BCX0512
CAS No.:1811-31-0
- N-Acetyl-D-mannosamine
Catalog No.:BCX0513
CAS No.:7772-94-3
- Xanthomicrol
Catalog No.:BCX0514
CAS No.:16545-23-6
- 5,7-Dihydroxy-3,8,3',4'-tetramethoxyflavone
Catalog No.:BCX0515
CAS No.:42923-42-2
- 5,4'-Dihydroxy-6,7,8,3'-tetramethoxyflavone
Catalog No.:BCX0516
CAS No.:16520-78-8
- Tetrahydroauroglaucin
Catalog No.:BCX0517
CAS No.:40434-07-9
- Sanggenon F
Catalog No.:BCX0518
CAS No.:85889-03-8
- 4-Hydroxyphenylpyruvic acid
Catalog No.:BCX0519
CAS No.:156-39-8
- Isodihydroauroglaucin
Catalog No.:BCX0520
CAS No.:74886-31-0
- Demethoxysudachitin
Catalog No.:BCX0521
CAS No.:4323-80-2
- Oxyphyllenodiol B
Catalog No.:BCX0522
CAS No.:363610-32-6
- Labda-12E,14-dien-16,15-olid-17-oic acid
Catalog No.:BCX0523
CAS No.:1855905-16-6
Active AKT2 stimulation of SREBP1/SCD1-mediated lipid metabolism boosts hepatosteatosis and cancer.[Pubmed:38244769]
Transl Res. 2024 Jan 18;268:51-62.
Due to soared obesity population worldwide, hepatosteatosis is becoming a major risk factor for hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). Undertaken molecular events during the progression of steatosis to liver cancer are thus under intensive investigation. In this study, we demonstrated that high-fat diet potentiated mouse liver AKT2. Hepatic AKT2 hyperactivation through gain-of-function mutation of Akt2 (Akt2E17K) caused spontaneous hepatosteatosis, injury, inflammation, fibrosis, and eventually HCC in mice. AKT2 activation also exacerbated lipopolysaccharide and D-Galactosamine hydrochloride-induced injury/inflammation and N-Nitrosodiethylamine (DEN)-induced HCC. A positive correlation between AKT2 activity and SCD1 expression was observed in human HCC samples. Activated AKT2 enhanced the production of monounsaturated fatty acid which was dependent on SREBP1 upregulation of SCD1. Blockage of active SREBP1 and ablation of SCD1 reduced steatosis, inflammation, and tumor burden in DEN-treated Akt2(E17K) mice. Therefore, AKT2 activation is crucial for the development of steatosis-associated HCC which can be treated with blockage of AKT2-SREBP1-SCD1 signaling cascade.
Levosimendan Increases Survival in a D-Galactosamine and Lipopolysaccharide Rat Model.[Pubmed:36551917]
Biomedicines. 2022 Dec 7;10(12):3161.
Levosimendan, a calcium sensitizer, has an organ protective profile through the inhibition of inflammatory mediators and cytokines in critical conditions, such as heart failure, ischemia-reperfusion injury, and sepsis. The survival effect of levosimendan for acute liver failure has not been examined yet. Male Sprague-Dawley rats were examined in the D-Galactosamine hydrochloride and lipopolysaccharide (GalN/LPS) model. Levosimendan was injected intraperitoneally before GalN/LPS treatment. Survival was monitored for 7 days. For biochemical analyses, liver and blood samples were collected from the rats at 1 and 8 h after GaIN/LPS treatment. The pretreatment of levosimendan at 4 mg/kg significantly increased survival in GalN/LPS rats. In the liver specimen, levosimendan significantly inhibited the activation of nuclear factor-kappaB (NF-kappaB) at 1 h, and significantly decreased the mRNA expression of inflammatory mediators, including inducible nitric oxide synthase and tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-alpha), at 8 h. In serum, levosimendan decreased the levels of nitrite, a metabolite of nitric oxide, and TNF-alpha protein, as well as aspartate aminotransferase and alanine aminotransferase. These results indicated that Levosimendan ameliorated liver dysfunction and survival in acute liver failure model rats through the suppression of NF-kappaB activation.
Studies on the Antiliver Injury of Effective Parts from Saururus chinensis by Rats and Mice Model In Vivo.[Pubmed:35518346]
Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2022 Apr 26;2022:7821724.
The aim of this study was to evaluate the pharmacodynamics of the effective parts from Saururus chinensis (EPS) in vivo. The antihepatic fibrosis and injury effects of EPS were investigated with the following four model animals including the effect on Wistar rats with liver fibrosis induced by complex factors, mice with acute liver injury induced, respectively, by carbon tetrachloride and alcohol, and Sprague-Dawley (SD) rats with acute liver injury caused by D-Galactosamine hydrochloride. The pharmacodynamics results showed that the rats' oral administration of EPS can significantly inhibit the formation of liver fibrosis in rats caused by complex factors and has significant preventive and therapeutic effects on acute liver injury caused by various factors as shown by decreased levels of serum biochemical indicators and improved pathological grade. Taken all together, our findings showed that EPS exhibits potent activities and should be considered a good option and an additional source of natural compounds for the treatment of hepatic fibrosis and hepatic injury.
D-Mannosamine hydrochloride (2-amino-2-deoxy-D-mannose hydrochloride): ionic hydrogen bonding in saccharides involving chloride and aminium ions.[Pubmed:35380125]
Acta Crystallogr C Struct Chem. 2022 Apr 1;78(Pt 4):223-230.
D-Mannosamine hydrochloride (2-amino-2-deoxy-D-mannose hydrochloride), C(6)H(14)NO(5)(+).Cl(-), (I), crystallized from a methanol/ethyl acetate/n-hexane solvent mixture at room temperature in a (4)C(1) chair conformation that is slightly distorted towards the (C3,O5)B form. A comparison of the structural parameters of (I) with the corresponding parameters in alpha-D-glucosamine hydrochloride, (II), and beta-D-Galactosamine hydrochloride, (III)/(III'), was undertaken to evaluate the effects of ionic hydrogen bonding on structural properties. Three types of ionic hydrogen bonds are present in the crystals of (I)-(III)/(III'), i.e. N(+)-H...O, N(+)-H...Cl(-), and O-H...Cl(-). The exocyclic structural parameters in (I), (II), and (III)/(III') appear to be most influenced by this bonding, especially the exocyclic hydroxy groups, which adopt eclipsed conformations enabled by ionic hydrogen bonding to the chloride anion. Anomeric disorder was observed in crystals of (I), with an alpha:beta ratio of 37:63. However, anomeric configuration appears to exert minimal structural effects; that is, bond lengths, bond angles, and torsion angles are essentially identical in both anomers. The observed disorder at the anomeric C atom of (I) appears to be caused by the presence of the chloride anion and atom O3 or O4 in proximal voids, which provide opportunities for hydrogen bonding to atom O1 in both axial and equatorial orientations.
Blockade of Dopamine D2 Receptors as a Novel Approach to Stimulation of Notch1(+) Endothelial Progenitor Cells and Angiogenesis in C57BL/6 Mice with Pulmonary Emphysema Induced by Proteases and Deficiency of alpha1-Antitrypsin.[Pubmed:32328949]
Bull Exp Biol Med. 2020 Apr;168(6):718-723.
We studied the effects of spiperone, a selective blocker of dopamine D2 receptors, on the model of pulmonary emphysema provoked by administration of elastase and D-Galactosamine hydrochloride to female C57BL/6 mice and characterized by activation of proteases in the lungs and systemic deficiency of its inhibitor alpha1-antitrypsin. In this model, spiperone prevented the development of inflammatory reaction and reduced the area of emphysematous expanded alveolar tissue. The expression of angiogenic marker CD31 in the lungs increased under these conditions. Regeneration of the damaged microvascular bed under the action of spiperone resulted from recruiting of Notch1(+) endothelial progenitor cells (CD45(-)CD31(+)CD34(+)) into the lungs and blockade of the inhibitory effect of dopamine on phosphorylation of VEGF-2 receptors in endothelial cells of different maturity. In addition, spiperone produced a protective effect on hepatocytes and restored the production and secretion of alpha1-antitrypsin by these cells.
Cathelicidin deficiency exacerbates cardiac dysfunction in lipopolysaccharide-induced endotoxaemic mice.[Pubmed:31868940]
Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol. 2020 Apr;47(4):677-686.
The therapeutic potential of the antimicrobial peptide cathelicidin (Camp) administration in sepsis has been widely investigated. However, little is known about the pathophysiological roles of cathelicidin in septic cardiomyopathy. In a lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-induced endotoxaemic model, we found that the mRNA and protein expression of cardiac cathelicidin were induced in C57BL/6J wild-type (WT) mice upon LPS challenge, accompanied by increased circulating cathelicidin levels. We showed that this peptide was mainly derived from neutrophils and monocytes/macrophages. Camp deficiency exacerbated LPS-induced myocardial depression, while the administration of CRAMP (the mature form of mouse cathelicidin) decreased the LPS-induced mortality in a D-Galactosamine hydrochloride (D-GalN)-sensitized endotoxin shock model. In vivo, LPS-treated Camp knockout mice had a significant higher protein level of myocardial and circulating tumour necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-alpha), a major contributing factor to septic cardiomyopathy, compared to LPS-treated WT mice, while CRAMP administration inhibited LPS-induced TNF-alpha production in the heart and plasma in D-GalN-sensitized endotoxaemic mice. In vitro, CRAMP treatment suppressed LPS-induced Tnf-alpha mRNA expression in cultured neonatal mouse cardiomyocytes and reduced TNF-alpha secretion in the culture supernatant. The inhibitory effects of CRAMP on TNF-alpha production may be related to its neutralizing ability of LPS, since CRAMP application had no effects on another toll-like receptor 4 ligand paclitaxel-induced Tnf-alpha mRNA expression in cardiomyocytes. These findings suggest that LPS-induced cathelicidin protects the heart against myocardial depression partly through the inhibition of TNF-alpha production via neutralizing LPS.
Platelet Factor 4 Attenuates Experimental Acute Liver Injury in Mice.[Pubmed:30971954]
Front Physiol. 2019 Mar 26;10:326.
Platelet factor 4 (PF4) is a pleiotropic inflammatory chemokine, which has been implicated in various inflammatory disorders including liver fibrosis. However, its role in acute liver diseases has not yet been elucidated. Here we describe an unexpected, anti-inflammatory role of PF4. Serum concentrations of PF4 were measured in patients and mice with acute liver diseases. Acute liver injury in mice was induced either by carbon tetrachloride or by D-Galactosamine hydrochloride and lipopolysaccharide. Serum levels of PF4 were decreased in patients and mice with acute liver diseases. PF4(-/-) mice displayed increased liver damage in both models compared to control which was associated with increased apoptosis of hepatocytes and an enhanced pro-inflammatory response of liver macrophages. In this experimental setting, PF4(-/-) mice were unable to generate activated Protein C (APC), a protein with anti-inflammatory activities on monocytes/macrophages. In vitro, PF4 limited the activation of liver resident macrophages. Hence, the systemic application of PF4 led to a strong amelioration of experimental liver injury. Along with reduced liver injury, PF4 improved the severity of the pro-inflammatory response of liver macrophages and induced increased levels of APC. PF4 has a yet unidentified direct anti-inflammatory effect in two models of acute liver injury. Thus, attenuation of acute liver injury by systemic administration of PF4 might offer a novel therapeutic approach for acute liver diseases.
Endothelial Progenitor Cells and Notch-1 Signaling as Markers of Alveolar Endothelium Regeneration in Pulmonary Emphysema.[Pubmed:30488216]
Bull Exp Biol Med. 2018 Dec;166(2):201-206.
We studied the effects of elastase, cigarette smoke extract, D-Galactosamine hydrochloride, and tyrosine kinase inhibitor SU5416 on endothelial progenitor cells and angiogenesis precursors, as well as on Notch-1 expression by immature endothelial cells. Simultaneously with pulmonary emphysema, different damaging factors with diverse mechanisms of action caused pathological changes in the microvascular network of the lungs and destroyed the alveolar endothelium in female C57Bl/6 mice. D-Galactosamine hydrochloride disturbed mobilization of endothelial progenitor cells expressing VEGFR (CD45-CD309(+)) and angiogenesis progenitors (CD45(-)CD309(+)CD117(+)) and their migration into emphysema expanded lungs. Elastase inhibited VEGFR-expressing endothelial progenitor cells, while cigarette smoke extract inhibited cells with CD45(-)CD31(+)CD34(+) phenotype. In pulmonary emphysema provoked by elastase or D-Galactosamine hydrochloride, angiogenesis was provided by endothelial cells with CD45(-)CD31(+)CD34(+) phenotype, whereas in emphysema modeled with SU5416 or cigarette smoke extract, it was provided by the endothelial VEGFR-expressing cells and mature CD31(+) endothelial cells, respectively. Replenishment of immature endothelial cells damaged by elastase and SU5416 involved Notch-1(+) angiogenesis precursors and Notch-1(+) endothelial progenitor cells with VEGFR.


