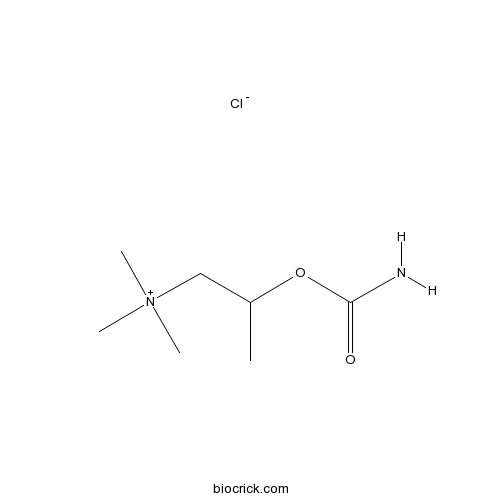
Bethanechol chlorideMuscarinic receptor agonist CAS# 590-63-6 |
- Amyloid β-Peptide (10-20) (human)
Catalog No.:BCC1026
CAS No.:152286-31-2
- Amyloid β-Protein (1-15)
Catalog No.:BCC1003
CAS No.:183745-81-5
- Beta-Amyloid (1-11)
Catalog No.:BCC1002
CAS No.:190436-05-6
- Myelin Basic Protein (68-82), guinea pig
Catalog No.:BCC1020
CAS No.:98474-59-0
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 590-63-6 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 11548 | Appearance | Powder |
| Formula | C7H17ClN2O2 | M.Wt | 196.68 |
| Type of Compound | N/A | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Synonyms | Carbamyl-β-methylcholine chloride | ||
| Solubility | H2O : ≥ 50 mg/mL (254.22 mM) DMSO : 11.11 mg/mL (56.49 mM; Need ultrasonic) *"≥" means soluble, but saturation unknown. | ||
| Chemical Name | 2-carbamoyloxypropyl(trimethyl)azanium;chloride | ||
| SMILES | [Cl-].CC(C[N+](C)(C)C)OC(N)=O | ||
| Standard InChIKey | XXRMYXBSBOVVBH-UHFFFAOYSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C7H16N2O2.ClH/c1-6(11-7(8)10)5-9(2,3)4;/h6H,5H2,1-4H3,(H-,8,10);1H | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | Bethanechol Chloride is a selective muscarinic receptor agonist without any effect on nicotinic receptors.
Target: mAChR
Bethanechol is a parasympathomimetic choline carbamate that selectively stimulates muscarinic receptors without any effect on nicotinic receptors. Unlike acetylcholine, bethanechol is not hydrolyzed by cholinesterase and will therefore have a long duration of action. Oral bethanechol significantly improves contraction pressures and bolus transit in the smooth muscle portion of the esophagus in patients with severe IEM [1]. Bethanechol has potential benefit in the treatment of cerebral palsy [2]. References: | |||||

Bethanechol chloride Dilution Calculator

Bethanechol chloride Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 5.0844 mL | 25.422 mL | 50.844 mL | 101.688 mL | 127.11 mL |
| 5 mM | 1.0169 mL | 5.0844 mL | 10.1688 mL | 20.3376 mL | 25.422 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.5084 mL | 2.5422 mL | 5.0844 mL | 10.1688 mL | 12.711 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.1017 mL | 0.5084 mL | 1.0169 mL | 2.0338 mL | 2.5422 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0508 mL | 0.2542 mL | 0.5084 mL | 1.0169 mL | 1.2711 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
Bethanechol Chloride is a selective muscarinic receptor agonist without any effect on nicotinic receptors.Bethanechol is a parasympathomimetic choline carbamate that selectively stimulates muscarinic receptors without any effect on nicotinic receptors. Un
- Betaine hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCN6304
CAS No.:590-46-5
- Tolazoline HCl
Catalog No.:BCC4321
CAS No.:59-97-2
- Levodopa
Catalog No.:BCN1098
CAS No.:59-92-7
- Nitrofurazone
Catalog No.:BCC3825
CAS No.:59-87-0
- Nicotinic acid
Catalog No.:BCN8328
CAS No.:59-67-6
- DL-Methionine
Catalog No.:BCC8318
CAS No.:59-51-8
- Oxindole
Catalog No.:BCN4050
CAS No.:59-48-3
- Procaine
Catalog No.:BCC5210
CAS No.:59-46-1
- Thiamine chloride
Catalog No.:BCN8344
CAS No.:59-43-8
- Sulfaquinoxaline
Catalog No.:BCC9158
CAS No.:59-40-5
- Mepyramine maleate
Catalog No.:BCC6740
CAS No.:59-33-6
- Folic acid
Catalog No.:BCN5375
CAS No.:59-30-3
- alpha-Endorphin
Catalog No.:BCC1010
CAS No.:59004-96-5
- 8-Hydroxyhyperforin 8,1-hemiacetal
Catalog No.:BCN4091
CAS No.:59014-02-7
- Atropine sulfate monohydrate
Catalog No.:BCC3728
CAS No.:5908-99-6
- Dehydrotoxicarol
Catalog No.:BCN3991
CAS No.:59086-93-0
- Albaspidin AP
Catalog No.:BCN2398
CAS No.:59092-91-0
- (+)-Rhododendrol
Catalog No.:BCN7091
CAS No.:59092-94-3
- Alpha-Angelica lactone
Catalog No.:BCN5001
CAS No.:591-12-8
- Misoprostol
Catalog No.:BCC5240
CAS No.:59122-46-2
- Neoisoliquiritin
Catalog No.:BCN2936
CAS No.:59122-93-9
- PSB 10 hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC7238
CAS No.:591771-91-4
- Sulforaphene
Catalog No.:BCN8179
CAS No.:592-95-0
- beta-Dihydroplumericinic acid
Catalog No.:BCN4092
CAS No.:59204-61-4
Pharmacological discrimination between muscarinic receptor signal transduction cascades with bethanechol chloride.[Pubmed:12711626]
Br J Pharmacol. 2003 Apr;138(7):1259-70.
1. Muscarinic agonist specificity is limited, making it difficult to match receptor subtypes with signal transduction cascades that mediate ion channel modulation. We have characterized the inhibitory effects of two muscarinic agonists, oxotremorine-M (Oxo-M) and Bethanechol chloride (BeCh), on Ca(2+) currents in neonatal rat superior cervical ganglion neurons. 2. Oxo-M-mediated (10 micro M) inhibition occurred via two signaling pathways. The first pathway inhibited whole cell peak currents, consisting primarily of N-type current, but not FPL 64176-induced, long-lasting tail currents, comprised entirely of L-type current. Inhibited currents displayed slowed activation kinetics and voltage dependence, characteristics of membrane-delimited inhibition. Current inhibition was blocked by the selective M(2) receptor antagonist, methoctramine (METH; 100 nM), or following pertussis toxin (PTX) pretreatment. 3. Activation of the second pathway inhibited both peak and long-lasting tail currents. This pathway was voltage-independent, PTX-insensitive, but sensitive to internal Ca(2+) chelator concentration. Muscarinic toxin 7 (MT-7, 100 nM), an irreversible M(1) receptor antagonist, eliminated this inhibition. Oxo-M (100 micro M) decreased L- and N-type channel activities in cell-attached patches, indicating that a diffusible second messenger is involved. 4. BeCh (100 micro M) also inhibited whole cell currents via the membrane-delimited pathway. Blocking M(4) receptors with 100 nM pirenzepine (in the presence of MT-7) had no effect, while antagonizing M(2) receptors with METH abolished inhibition. Concentrations of BeCh as high as 3 mM failed to inhibit either peak or long-lasting tail currents following PTX pretreatment. 5. These results indicate that BeCh may be an effective tool for selectively activating M(2) receptor stimulation of the membrane-delimited pathway.
Modulation of urethral alpha-sympathetic by parasympathetic before and following bethanechol chloride injection.[Pubmed:15745502]
Int Braz J Urol. 2003 Mar-Apr;29(2):162-5.
INTRODUCTION AND OBJECTIVES: Chagas' disease causes specific parasympathetic denervation and in its digestive clinic form promotes also functional alterations in bladder. Thus, the aim was to investigate the existence of balance between sympathetic and parasympathetic systems in lower urinary tract, as occurs in other organs. We verified the urethral closing pressure before and following parasympathetic stimulus. PATIENTS AND METHODS: For that, the urethral closure pressure was studied before and after the injection of 5 mg of Bethanechol chloride subcutaneously in 28 voluntary female patients, divided into 4 groups. The constitution of theses groups was: A) normal control = 6 patients; B) Chagas' disease with positive serology only = 5 patients; C) Chagas' disease with cardiac disease = 6 patients, and D) Chagas' disease with digestive disease and vesical hyporeflexia = 11 patients. Urethral profilometry was performed through perfusion urethral catheter with a 6.5 ml/minute flow and a traction rate of 5 mm/minute. RESULTS: Means and standard deviations for urethral closure pressure before Bethanechol chloride were respectively: group A = 67.3 +/- 7.1; group B = 69.2 +/- 7.4; group C = 95.8 +/- 5.1; group D = 82.1 +/- 8.4. After Bethanechol chloride they were: group A = 66.0 +/- 6.6; group B = 77.0 +/- 7.6; group C = 98.3 +/- 8.8; group D = 45.9 +/- 6.2. The Kruskal Wallis statistical test did not show statistically significance difference between groups A, B, C. However, it was statistically significant between groups C and D with p = 0.003. Wilcoxon test showed p = 0.001, only for values in group D before and following Bethanechol chloride. CONCLUSIONS: Chagas' disease in its intestinal form seems to alter urethral function as well. Parasympathetic stimulation decreased urethral pressure, indicating potential modulation by the parasympathetic system over the sympathetic system.
Effects of bethanechol chloride and distigmine bromide on postvoiding residual volume in patients with underactive bladder.[Pubmed:25531193]
Minerva Urol Nefrol. 2014 Dec;66(4):241-7.
AIM: The efficacy of cholinergic drugs for reduction of post-voiding residual volume (PVR) in patients with underactive bladder is still controversial. This study was performed to examine whether cholinergic drugs have such an effect on PVR. METHODS: Patients with underactive bladder treated for more than two months with cholinergic drugs, which were later discontinued, were extracted retrospectively based on their charts. The changes in PVR, cholinesterase activity (ChE), renal function, and voiding function before and after discontinuation of cholinergic drugs were reviewed and analyzed. RESULTS: Twenty-nine patients were included in this study. In multiple linear regression analysis, the discontinuation of distigmine bromide (DB) was indicated as a significant covariate for PVR increase and ChE increase, while Bethanechol chloride (BC) was not a significant covariate. The increase in ChE was significantly correlated with both PVR and voided volume after discontinuation of cholinergic drugs. CONCLUSION: DB could reduce PVR via a decrease in ChE. However, BC at doses up to 60 mg did not reduce PVR. DB may be recommended for the reduction of PVR in patients with underactive bladder.
Bethanechol chloride for the prevention of bladder dysfunction after radical hysterectomy in gynecologic cancer patients: a randomized controlled trial study.[Pubmed:21546875]
Int J Gynecol Cancer. 2011 May;21(4):730-6.
BACKGROUND: Bethanechol chloride is considered as a treatment in patients with high postvoid residual urine (PVR). It enhances detrusor muscle contraction, resulting in higher maximum flow rate, higher detrusor pressure at maximum flow, and lower PVR. The efficacy of this agent in patients after radical hysterectomy is unclear. We aim to evaluate the efficacy of Bethanechol chloride compared with placebo for the prevention of bladder dysfunction after type III radical hysterectomy. METHODS: Gynecologic cancer patients who underwent type III radical hysterectomy were randomized by computer-generated schedule to assign patients in a 1:1 ratio into 2 groups. The treatment group received Bethanechol chloride (Ucholine 20 mg 3 times a day on the third to seventh postoperative day), and the control group received placebo. Patients and physicians were masked to treatment allocation. The primary end point was the rate of urethral catheter removal at 1 week postoperatively. If PVR was more than 30% of voided volume, the urethral catheter was reinserted, and medication would be continued but not for more than 1 month. This study was registered as ISRCTN92687416. FINDINGS: There were 31 patients in each group without significant difference in baseline characteristics. Twenty-one patients (67.7%) in the treatment group and 12 patients (38.7%) in the control group had the urethral catheter removed at 1 week postoperatively (P = 0.04). Median duration of urethral catheterization was shorter in the treatment group (7 and 14 days, P = 0.03). However, the PVR and the incidence of urinary tract infection at 1 month postoperatively were not significantly different. Nine patients (29%) in the treatment group had adverse events such as nausea, abdominal distension, and abdominal cramping, which was higher than the control group (1 patient, 3.2%; P = 0.01). However, no patients required any medical treatments. CONCLUSIONS: Bethanechol chloride decreases the duration of urethral catheterization in patients who underwent type III radical hysterectomy with manageable adverse events.


