alpha-BisabololCAS# 23089-26-1 |
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

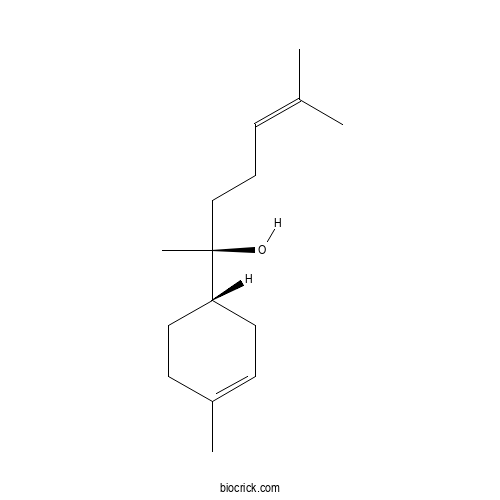
| Cas No. | 23089-26-1 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 442343 | Appearance | Colorless liquid |
| Formula | C15H26O | M.Wt | 222.4 |
| Type of Compound | Sesquiterpenoids | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Synonyms | Levomenol | ||
| Solubility | Soluble in chloroform | ||
| Chemical Name | (2S)-6-methyl-2-[(1S)-4-methylcyclohex-3-en-1-yl]hept-5-en-2-ol | ||
| SMILES | CC1=CCC(CC1)C(C)(CCC=C(C)C)O | ||
| Standard InChIKey | RGZSQWQPBWRIAQ-CABCVRRESA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C15H26O/c1-12(2)6-5-11-15(4,16)14-9-7-13(3)8-10-14/h6-7,14,16H,5,8-11H2,1-4H3/t14-,15+/m1/s1 | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | alpha-Bisabolol has antitumorous and antimicrobial activities. Halitosis-associated bacterium S. moorei is susceptible to the antimicrobial agents tea tree oil and alpha-bisabolol, they might be beneficial in oral healthcare products. (-)-alpha-Bisabolol has gastroprotective effect on ethanol and indomethacin-induced ulcer | |||||

alpha-Bisabolol Dilution Calculator

alpha-Bisabolol Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 4.4964 mL | 22.482 mL | 44.964 mL | 89.9281 mL | 112.4101 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.8993 mL | 4.4964 mL | 8.9928 mL | 17.9856 mL | 22.482 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.4496 mL | 2.2482 mL | 4.4964 mL | 8.9928 mL | 11.241 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0899 mL | 0.4496 mL | 0.8993 mL | 1.7986 mL | 2.2482 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.045 mL | 0.2248 mL | 0.4496 mL | 0.8993 mL | 1.1241 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
- 7-Hydroxyflavonol
Catalog No.:BCN0141
CAS No.:492-00-2
- (+/-)-2-Methyl-1-butanol
Catalog No.:BCN0140
CAS No.:137-32-6
- Syringetin 3-O-galactoside
Catalog No.:BCN0139
CAS No.:55025-56-4
- Cynatratoside E
Catalog No.:BCN0138
CAS No.:
- Bidenoside C
Catalog No.:BCN0137
CAS No.:700877-55-0
- 5,7-Dihydroxy-3',4',5'-trimethoxyflavanone
Catalog No.:BCN0136
CAS No.:62252-10-2
- Protocetraric acid
Catalog No.:BCN0135
CAS No.:489-51-0
- Castalin
Catalog No.:BCN0134
CAS No.:19086-75-0
- 3',4',7,8-Tetramethoxyflavone
Catalog No.:BCN0133
CAS No.:65548-55-2
- (+)-Lariciresinol 4'-O-beta-D-Glucopyranosyl-(1->3)-beta-D-glucopyranoside
Catalog No.:BCN0132
CAS No.:639857-95-7
- (-)-Cadin-4,10(15)-dien-11-oic acid
Catalog No.:BCN0131
CAS No.:1124353-23-6
- 2,3-Dehydrosilybin A
Catalog No.:BCN0130
CAS No.:25166-14-7
- cis-Aconitic acid
Catalog No.:BCN0143
CAS No.:585-84-2
- Ergocristine
Catalog No.:BCN0144
CAS No.:511-08-0
- 3',4',7,8-Tetrahydroxyflavone
Catalog No.:BCN0145
CAS No.:3440-24-2
- Daphnin
Catalog No.:BCN0146
CAS No.:486-55-5
- 2',6'-Dihydroxy 4',4-dimethoxydihydrochalcone
Catalog No.:BCN0147
CAS No.:35241-54-4
- 2'-Hydroxyflavanone
Catalog No.:BCN0148
CAS No.:17348-76-4
- 3',4',7-Trihydroxyisoflavone
Catalog No.:BCN0149
CAS No.:485-63-2
- Maritimein
Catalog No.:BCN0150
CAS No.:490-54-0
- Candicine
Catalog No.:BCN0151
CAS No.:6656-13-9
- Comanthosid B
Catalog No.:BCN0153
CAS No.:70938-60-2
- Helenien
Catalog No.:BCN0154
CAS No.:547-17-1
- N-trans-caffeoyltyramine
Catalog No.:BCN0155
CAS No.:103188-48-3
The Sensitivity Modifying Activity of Nerolidol and alpha-Bisabolol Against Trichophyton spp.[Pubmed:33088000]
Indian J Microbiol. 2020 Dec;60(4):505-510.
Trichophyton spp. is one of the main causative agents of dermatophytosis such as tinea ungium and tinea pedis. Resistance to antifungal drugs is a significant clinical problem in dermatophytosis. The main molecular mechanism of antifungal resistance to conventional therapy in dermatophytes is the expression of efflux pumps. Efforts aimed at improving the efficacy of current antifungals such as griseofulvin are relevant. Given this, sesquiterpenes such as alpha-Bisabolol and nerolidol found in essential oils represent promissing alternatives. Griseofulvin sensitivity modulation activity in T. rubrum, T. interdigitale H6, and T. interdigitale Deltamdr2 (mutant strain of T. interdigitale) promoted by alpha-Bisabolol and nerolidol were investigated. The minimum inhibitory concentration (MIC) of the test drugs were determined by microdilution. Subsequently, the effect of the drugs tested on plasma membrane functionality (K(+) release) was analyzed. The MIC of griseofulvin was determined at sub-inhibitory sesquiterpene concentrations (modulation assay). An association study was performed with griseofulvin and sesquiterpenes (checkerboard). alpha-Bisabolol was more potent than nerolidol; presenting lower MIC values. All of the fungi were sensitive to griseofulvin, starting at 8 microg/mL. With the exception of griseofulvin, all of the test drugs increased K(+) release (p < 0.05). Nerolidol modulated the sensitivity of all strains to griseofulvin; alpha-Bisabolol sensitivity modulation was limited to T. interdigitale H6 and T. interdigitale Deltamdr2. In association with griseofulvin: nerolidol and alpha-Bisabolol respectively presented synergism and additivity. Finally, the results of our study suggest using alpha-Bisabolol and nerolidol compounds as potential antifungal agents and griseofulvin sensitivity modulators for Trichophyton spp.
alpha-Bisabolol, a Dietary Bioactive Phytochemical Attenuates Dopaminergic Neurodegeneration through Modulation of Oxidative Stress, Neuroinflammation and Apoptosis in Rotenone-Induced Rat Model of Parkinson's disease.[Pubmed:33049992]
Biomolecules. 2020 Oct 8;10(10). pii: biom10101421.
Rotenone (ROT), a plant-derived pesticide is a well-known environmental neurotoxin associated with causation of Parkinson's disease (PD). ROT impairs mitochondrial dysfunction being mitochondrial complex-I (MC-1) inhibitor and perturbs antioxidant-oxidant balance that contributes to the onset and development of neuroinflammation and neurodegeneration in PD. Due to the scarcity of agents to prevent the disease or to cure or halt the progression of symptoms of PD, the focus is on exploring agents from naturally occurring dietary phytochemicals. Among numerous phytochemicals, alpha-Bisabolol (BSB), natural monocyclic sesquiterpene alcohol found in many ornamental flowers and edible plants garnered attention due to its potent pharmacological properties and therapeutic potential. Therefore, the present study investigated the neuroprotective effects of BSB in a rat model of ROT-induced dopaminergic neurodegeneration, a pathogenic feature of PD and underlying mechanism targeting oxidative stress, inflammation and apoptosis. BSB treatment significantly prevented ROT-induced loss of dopaminergic neurons and fibers in the substantia nigra and striatum respectively. BSB treatment also attenuated ROT-induced oxidative stress evidenced by inhibition of MDA formation and GSH depletion as well as improvement in antioxidant enzymes, SOD and catalase. BSB treatment also attenuated ROT-induced activation of the glial cells as well as the induction and release of proinflammatory cytokines (IL-1beta, IL-6 and TNF-alpha) and inflammatory mediators (iNOS and COX-2) in the striatum. In addition to countering oxidative stress and inflammation, BSB also attenuated apoptosis of dopaminergic neurons by attenuating downregulation of anti-apoptotic protein Bcl-2 and upregulation of pro-apoptotic proteins Bax, cleaved caspases-3 and 9. Further, BSB was observed to attenuate mitochondrial dysfunction by inhibiting mitochondrial lipid peroxidation, cytochrome-C release and reinstates the levels/activity of ATP and MC-I. The findings of the study demonstrate that BSB treatment salvaged dopaminergic neurons, attenuated microglia and astrocyte activation, induction of inflammatory mediators, proinflammatory cytokines and reduced the expression of pro-apoptotic markers. The in vitro study on ABTS radical revealed the antioxidant potential of BSB. The results of the present study are clearly suggestive of the neuroprotective effects of BSB through antioxidant, anti-inflammatory and anti-apoptotic properties in ROT-induced model of PD.
Antileishmanial activity of the essential oils of Myrcia ovata Cambess. and Eremanthus erythropappus (DC) McLeisch leads to parasite mitochondrial damage.[Pubmed:33030053]
Nat Prod Res. 2020 Oct 8:1-5.
Leishmania amazonensis is a species causative of cutaneous and anergic diffuse cutaneous leishmaniasis, treatment-resistant form, in the New World. Plants essential oils exhibit great potential as microbicide agents. We described the composition of the essential oils of two plants native from Brazil, Myrcia ovata, with geranial and neral as major constituents, and Eremanthus erythropappus, with alpha-Bisabolol. In vitro effects of these essential oils on L. amazonensis promastigotes growth and ultrastructure were analysed as well as their cytotoxicity to murine macrophages. Both oils were highly active with IC50/96 h of 8.69 and 9.53 microg/mL for M. ovata and E. erythropappus against promastigotes and caused ultrastructural alterations including mitochondrial enlargement. Cytotoxicity for murine macrophages varied with the oil concentrations. The IC50 low values of both M. ovata and E. erythropappus oils against L. amazonensis and their relative low cytotoxicity to mammal host cells support their potential use against cutaneous leishmaniasis.
Acaricidal activity of (E)-cinnamaldehyde and alpha-bisabolol on populations of Rhipicephalus microplus (Acari: Ixodidae) with different resistance profiles.[Pubmed:32979684]
Vet Parasitol. 2020 Oct;286:109226.
This study aimed to investigate the acaricidal activity of (E)-cinnamaldehyde and alpha-Bisabolol on populations of Rhipicephalus microplus with different resistance profiles. The adult immersion test (AIT) was used to characterize the susceptibility of tick populations (50 field populations) to synthetic acaricides: deltamethrin, amitraz, and chlorfenvinphos. The larval packet test (LPT) was used to determine the LC50 values for (E)-cinnamaldehyde (populations 1-25) and alpha-Bisabolol (populations 26-50) at the concentrations of 0.31, 0.62, 1.25, 2.0, 2.5, 5.0 and 10.0mg/mL. The susceptible strain Porto Alegre (POA) was used as a reference for calculating the resistance ratio (RR). In the AIT, deltamethrin did not show efficacy >95 % for any of the populations, whereas amitraz and chlorfenvinphos have presented efficacy >95 % for three (6 %) and 15 (30 %) populations, respectively. In the LPT, the LC50 values of (E)-cinnamaldehyde and alpha-Bisabolol varied from 0.23 to 2.36mg/mL and 1.57-3.01mg/mL, respectively. The RR50 for (E)-cinnamaldehyde showed 20 (80 %) populations with values <1.0 and no population with values>1.5. As for alpha-Bisabolol, only two (8%) populations have presented RR50 <1.0, whereas three (12 %) populations showed incipient resistance to this sesquiterpene (RR50 between 1.5 and 2.0). The results indicate that all studied tick populations showed low susceptibility to at least one of the commercial acaricides tested. In addition, comparison between the LC50 values of (E)-cinnamaldehyde and alpha-Bisabolol for the field populations and the susceptible strain POA suggests that there is no cross-resistance of (E)-cinnamaldehyde and alpha-Bisabolol for the tick populations evaluated, and that the differences in the LC50 values are due to population variations.
Anti-trichomonad activities of different compounds from foods, marine products, and medicinal plants: a review.[Pubmed:32907567]
BMC Complement Med Ther. 2020 Sep 9;20(1):271.
Human trichomoniasis, caused by the pathogenic parasitic protozoan Trichomonas vaginalis, is the most common non-viral sexually transmitted disease that contributes to reproductive morbidity in affected women and possibly to prostate cancer in men. Tritrichomonas foetus strains cause the disease trichomoniasis in farm animals (cattle, bulls, pigs) and diarrhea in domestic animals (cats and dogs). Because some T. vaginalis strains have become resistant to the widely used drug metronidazole, there is a need to develop alternative treatments, based on safe natural products that have the potential to replace and/or enhance the activity of lower doses of metronidazole. To help meet this need, this overview collates and interprets worldwide reported studies on the efficacy of structurally different classes of food, marine, and medicinal plant extracts and some of their bioactive pure compounds against T. vaginalis and T. foetus in vitro and in infected mice and women. Active food extracts include potato peels and their glycoalkaloids alpha-chaconine and alpha-solanine, caffeic and chlorogenic acids, and quercetin; the tomato glycoalkaloid alpha-tomatine; theaflavin-rich black tea extracts and bioactive theaflavins; plant essential oils and their compounds (+)-alpha-Bisabolol and eugenol; the grape skin compound resveratrol; the kidney bean lectin, marine extracts from algae, seaweeds, and fungi and compounds that are derived from fungi; medicinal extracts and about 30 isolated pure compounds. Also covered are the inactivation of drug-resistant T. vaginalis and T. foetus strains by sensitized light; anti-trichomonad effects in mice and women; beneficial effects of probiotics in women; and mechanisms that govern cell death. The summarized findings will hopefully stimulate additional research, including molecular-mechanism-guided inactivations and human clinical studies, that will help ameliorate adverse effects of pathogenic protozoa.
Grinding and Fractionation during Distillation Alter Hemp Essential Oil Profile and Its Antimicrobial Activity.[Pubmed:32872359]
Molecules. 2020 Aug 28;25(17). pii: molecules25173943.
The hypothesis of this study was that we can modify the essential oil (EO) profile of hemp (Cannabis sativa L.) and obtain fractions with differential composition and antimicrobial activity. Therefore, the objective was to evaluate the effects of grinding of hemp biomass before EO extraction and fractionation during distillation on EO profile and antimicrobial activity. The study generated a several EO fractions with a diversity of chemical profile and antimicrobial activity. The highest concentrations of beta-pinene and myrcene in the EO can be obtained in the 5-10 min distillation time (DT) of ground material or in the 80-120 min DT of nonground material. High delta-3-carene and limonene EO can be obtained from 0-5 min DT fraction of nonground material. High eucalyptol EO can be sampled either in the 0-5 min DT of the ground material or in the 80-120 min of nonground material. Overall, the highest concentrations of beta-caryophyllene, alpha-(E)-bergamotene, (Z)-beta-farnesene, alpha-humulene, caryophyllenyl alcohol, germacrene D-4-ol, spathulenol, caryophyllene oxide, humulene epoxide 2, beta-bisabolol, alpha-Bisabolol, sesquiterpenes, and cannabidiol (CBD) can be obtained when EO is sampled in the 80-120 min DT and the material is nonground. Monoterpenes in the hemp EO can be increased twofold to 85% by grinding the material prior to distillation and collecting the EO in the first 10 min. However, grinding resulted in a slight but significant decrease in the CBD concentration of the EO. CBD-rich oil can be produced by collecting at 120-180 min DT. Different EO fractions had differential antimicrobial activity. The highest antimicrobial activity of EO fraction was found against Staphylococcus aureus subsp. aureus. THC-free EO can be obtained if the EO distillation is limited to 120 min. The results can be utilized by the hemp processing industry and by companies developing new hemp EO-infused products, including perfumery, cosmetics, dietary supplements, food, and pharmaceutical industries.
In Vitro Scolicidal Activity of the Sesquiterpenes Isofuranodiene, alpha-Bisabolol and Farnesol on Echinococcus granulosus Protoscoleces.[Pubmed:32784679]
Molecules. 2020 Aug 7;25(16). pii: molecules25163593.
Cystic echinococcosis (CE) remains an important challenge both in humans and animals. There is no safe and suitable remedy for CE, so the discovery of new compounds with promising scolicidal effects, particularly from herbal sources, is of great importance for therapeutic uses in the treatment and prevention of CE reappearance. Sesquiterpenes are C15 organic compounds made up of three isoprene units and mostly occurring as fragrant components of essential oils. They are of economic importance for the cosmetic and pharmaceutical industry, and recently attracted the attention of the scientific community for their remarkable parasiticidal properties. In the present study, we have focused on three known sesquiterpenes, isofuranodiene (IFD), alpha-Bisabolol (BSB), and farnesol (FOH), as important phytoconstituents of the essential oils of wild celery (Smyrnium olusatrum), chamomile (Matricaria chamomilla), and acacia farnese (Vachellia farnesiana), respectively. Protoscoleces were recovered from fertile hydatid cysts and were exposed to different concentrations of the three tested compounds for different exposure times. The viability of protoscoleces was confirmed by 0.1% eosin staining. Results of scolicidal activity evaluations showed that IFD possessed the best effect against Echinococcus granulosus protoscoleces (LC50 and LC90 values of 8.87 and 25.48 microg/mL, respectively), followed by BSB (LC50 of 103.2 microg/mL) and FOH (LC50 of 113.68 microg/mL). The overall toxicity of IFD differed significantly from those of FOH and BSB, while there was no significant difference in toxicity between the latter compounds (p > 0.05). The present study showed that IFD seems to be a promising scolicidal agent and can be further tested to become a candidate for CE treatment.
An Assay on the Possible Effect of Essential Oil Constituents on Receptors Involved in Women's Hormonal Health and Reproductive System Diseases.[Pubmed:32567329]
J Evid Based Integr Med. 2020 Jan-Dec;25:2515690X20932527.
Aromatic herbal remedies, hydrosols, and essential oils are widely used for women's hormonal health. Scientific investigation of their major constituents may prevent unwanted infertility cases, fetal abnormalities, and drug-herb interactions. It also may lead to development of new medications. A list of 265 volatile molecules (mainly monoterpenes and sesquiterpenes) were prepared from a literature survey in Scopus and PubMed (2000-2019) on hydrosols and essential oils that are used for women's hormonal and reproductive health conditions. The PDB (protein data bank) files of the receptors (136 native PDB files) that involve with oxytocin, progesterone, estrogen, prolactin, acetyl choline, androgen, dopamine, human chorionic gonadotropin, luteinizing hormone, follicle-stimulating hormone, aromatase, and HER2 receptors were downloaded from Protein Data Bank. An in silico study using AutoDock 4.2 and Vina in parallel mode was performed to investigate possible interactions of the ligands with the receptors. Drug likeliness was investigated for the most active molecules using DruLiTo software. Aristola-1(10),8-diene, bergapten (5-methoxypsoralen), alpha-bergamotene, bicyclogermacrene, alpha-Bisabolol oxide A, alpha-bisabolone oxide, p-cymen-8-ol, 10-epi elemol, alpha-elemol, beta-eudesmol, 7-epi-beta-eudesmol, ficusin, beta-humulene, methyl jasmonate, nerolidol, pinocarvone, (+)-spathulenol, and thujone had better interactions with some androgen, aromatase, estrogen, progesterone, HER2, AChR, and/or dopamine receptors. Most of these molecules had an acceptable drug likeliness except for alpha-bergamotene, bicyclogermacrene, beta-humulene, and aristola-1(10),8-diene. Some volatile natural molecules can be considered as lead compound for drug development to treat hormonal conditions.
Antinociceptive Activity of Chemical Components of Essential Oils That Involves Docking Studies: A Review.[Pubmed:32547391]
Front Pharmacol. 2020 May 29;11:777.
Introduction: Pain is considered an unpleasant sensory and emotional experience, being considered as one of the most important causes of human suffering. Computational chemistry associated with bioinformatics has stood out in the process of developing new drugs, through natural products, to manage this condition. Objective: To analyze, through literature data, recent molecular coupling studies on the antinociceptive activity of essential oils and monoterpenes. Data source: Systematic search of the literature considering the years of publications between 2005 and December 2019, in the electronic databases PubMed and Science Direct. Eligibility Criteria: Were considered as criteria of 1) Biological activity: non-clinical effects of an OE and/or monoterpenes on antinociceptive activity based on animal models and in silico analysis, 2) studies with plant material: chemically characterized essential oils and/or their constituents isolated, 3) clinical and non-clinical studies with in silico analysis to assess antinociceptive activity, 4) articles published in English. Exclusion criteria were literature review, report or case series, meta-analysis, theses, dissertations, and book chapter. Results: Of 16,006 articles, 16 articles fulfilled all the criteria. All selected studies were non-clinical. The most prominent plant families used were Asteraceae, Euphorbiaceae, Verbenaceae, Lamiaceae, and Lauraceae. Among the phytochemicals studied were alpha-Terpineol, 3-(5-substituted-1,3,4-oxadiazol-2-yl)-N'-[2-oxo-1,2-dihydro-3H-indol-3-ylidene] propane hydrazide, beta-cyclodextrin complexed with citronellal, (-)-alpha-Bisabolol, beta-cyclodextrin complexed with farnesol, and p-Cymene. The softwares used for docking studies were Molegro Virtual Docker, Sybyl((R))X, Vlife MDS, AutoDock Vina, Hex Protein Docking, and AutoDock 4.2 in PyRx 0.9. The molecular targets/complexes used were Nitric Oxide Synthase, COX-2, GluR2-S1S2, TRPV1, beta-CD complex, CaV1, CaV2.1, CaV2.2, and CaV2.3, 5-HT receptor, delta receptor, kappa receptor, and MU (mu) receptor, alpha adrenergic, opioid, and serotonergic receptors, muscarinic receptors and GABAA opioid and serotonin receptors, 5-HT3 and M2 receptors. Many of the covered studies used molecular coupling to investigate the mechanism of action of various compounds, as well as molecular dynamics to investigate the stability of protein-ligand complexes. Conclusions: The studies revealed that through the advancement of more robust computational techniques that complement the experimental studies, they may allow some notes on the identification of a new candidate molecule for therapeutic use.
Chemical Diversity and Biological Activities of Essential Oils from Licaria, Nectrandra and Ocotea Species (Lauraceae) with Occurrence in Brazilian Biomes.[Pubmed:32517106]
Biomolecules. 2020 Jun 5;10(6). pii: biom10060869.
Lauraceae species are known as excellent essential oil (EO) producers, and their taxa are distributed throughout the territory of Brazil. This study presents a systematic review of chemical composition, seasonal studies, occurrence of chemical profiles, and biological activities to EOs of species of Licaria, Nectandra, and Ocotea genera collected in different Brazilian biomes. Based on our survey, 39 species were studied, with a total of 86 oils extracted from seeds, leaves, stem barks, and twigs. The most representative geographic area in specimens was the Atlantic Forest (14 spp., 30 samples) followed by the Amazon (13 spp., 30 samples), Cerrado (6 spp., 14 samples), Pampa (4 spp., 10 samples), and Caatinga (2 spp., 2 samples) forests. The majority of compound classes identified in the oils were sesquiterpene hydrocarbons and oxygenated sesquiterpenoids. Among them, beta-caryophyllene, germacrene D, bicyclogermacrene, caryophyllene oxide, alpha-Bisabolol, and bicyclogermacrenal were the main constituents. Additionally, large amounts of phenylpropanoids and monoterpenes such as safrole, 6-methoxyelemicin, apiole, limonene, alpha-pinene, beta-pinene, 1,8-cineole, and camphor were reported. Nectandra megatopomica showed considerable variation with the occurrence of fourteen chemical profiles according to seasonality and collection site. Several biological activities have been attributed to these oils, especially cytotoxic, antibacterial, antioxidant and antifungal potential, among other pharmacological applications.
alpha-Bisabolol suppresses the inflammatory response and ECM catabolism in advanced glycation end products-treated chondrocytes and attenuates murine osteoarthritis.[Pubmed:32334386]
Int Immunopharmacol. 2020 Jul;84:106530.
As a chronic musculoskeletal degeneration disease, osteoarthritis (OA) clinically manifests as joint pain, stiffness and a limited range of movement. OA has affected the life quality of at least one-tenth of the population but lacks satisfactory treatments. alpha-Bisabolol (BISA) is a small oily sesquiterpene alcohol widely found in essential oils of chamomile (Matricaria recutita), salvia and wood of Candeia and has multiple biological properties, particularly an anti-inflammatory effect. The purpose of this study is to assess the anti-inflammatory and chondroprotective effect of BISA in OA progression and explore its underlying mechanism. We isolated human chondrocytes and treated them with advanced glycation end products (AGEs) to imitate OA progression in vitro. BISA pretreatment suppressed the AGE-induced inflammatory reaction and extracellular matrix (ECM) degeneration by blocking nuclear factor kappa B (NF-kappaB), p38 and c-Jun N-terminal kinase (JNK) signaling. Moreover, a mouse destabilization of the medial meniscus (DMM) model was established by surgery to investigate BISA protection in vivo. BISA administration attenuated DMM-induced radiological and histopathological changes relative to the DMM group and resulted in lower OARSI scores. Taken together, the results of our study indicate the potential of BISA in OA therapy.
High density cultivation for efficient sesquiterpenoid biosynthesis in Synechocystis sp. PCC 6803.[Pubmed:32246065]
Sci Rep. 2020 Apr 3;10(1):5932.
Cyanobacteria and microalgae are attractive photoautotrophic host systems for climate-friendly production of fuels and other value-added biochemicals. However, for economic applications further development and implementation of efficient and sustainable cultivation strategies are essential. Here, we present a comparative study on cyanobacterial sesquiterpenoid biosynthesis in Synechocystis sp. PCC 6803 using a commercial lab-scale High Density Cultivation (HDC) platform in the presence of dodecane as in-situ extractant. Operating in a two-step semi-batch mode over a period of eight days, volumetric yields of (E)-alpha-bisabolene were more than two orders of magnitude higher than previously reported for cyanobacteria, with final titers of 179.4 +/- 20.7 mg * L(-1). Likewise, yields of the sesquiterpene alcohols (-)-patchoulol and (-)-alpha-Bisabolol were many times higher than under reference conditions, with final titers of 17.3 +/- 1.85 mg * L(-1) and 96.3 +/- 2.2 mg * L(-1), respectively. While specific productivity was compromised particularly for (E)-alpha-bisabolene in the HDC system during phases of high biomass accumulation rates, volumetric productivity enhancements during linear growth at high densities were more pronounced for (E)-alpha-bisabolene than for the hydroxylated terpenoids. Together, this study provides additional insights into cell density-related process characteristics, introducing HDC as highly efficient strategy for phototrophic terpenoid production in cyanobacteria.
Direct Identification of alpha-Bisabolol Enantiomers in an Essential Oil Using a Combined Ion Mobility-Mass Spectrometry/Quantum Chemistry Approach.[Pubmed:32212660]
J Nat Prod. 2020 Mar 26.
Enantiomer-specific identification of chiral molecules in natural extracts is a challenging task, as many routine analytical techniques fail to provide selectivity in multicomponent mixtures. Here we describe an alternative approach, based on the combination of ion mobility-mass spectrometry (IM-MS) and quantum chemistry (QM), for the direct enantiomers differentiation in crude essential oils. The identification of alpha-Bisabolol enantiomers contained in the raw essential oil (EO) from the Corsican Xanthium italicum fruits is reported as a proof-of-concept. Accordingly, IM-MS experiments performed in Ag(+)-doped methanol revealed the presence of both (+)- and (-)-alpha-Bisabolol in the EO, while molecular simulations provided the structures of the two alpha-Bisabolol enantiomer silver(I) adducts.


