Viscidulin ICAS# 92519-95-4 |
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 92519-95-4 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 5320471 | Appearance | Yellow powder |
| Formula | C15H10O7 | M.Wt | 302.2 |
| Type of Compound | Flavonoids | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Solubility | Soluble in Chloroform,Dichloromethane,Ethyl Acetate,DMSO,Acetone,etc. | ||
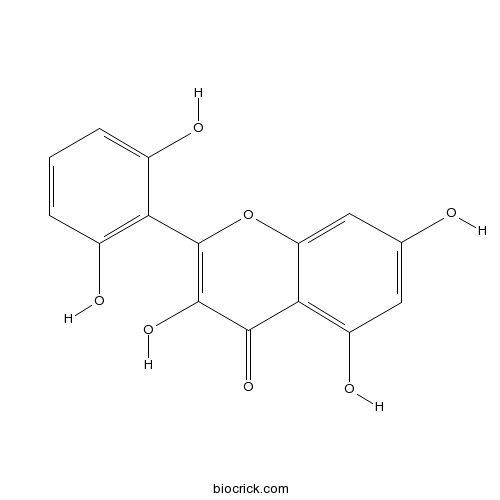
| Chemical Name | 2-(2,6-dihydroxyphenyl)-3,5,7-trihydroxychromen-4-one | ||
| SMILES | C1=CC(=C(C(=C1)O)C2=C(C(=O)C3=C(C=C(C=C3O2)O)O)O)O | ||
| Standard InChIKey | NULZZCUABWZIRV-UHFFFAOYSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C15H10O7/c16-6-4-9(19)12-10(5-6)22-15(14(21)13(12)20)11-7(17)2-1-3-8(11)18/h1-5,16-19,21H | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Structure Identification | Acta Physiologiae Plantarum, 2018, 40(9):161.Transcriptomic analysis and dynamic expression of genes reveal flavonoid synthesis in Scutellaria viscidula.[Reference: WebLink]Scutellaria viscidula Bunge (Labiatae), a perennial herb, is an important medicinal plant that possesses broad pharmacological actions. S. viscidula contains flavonoids with good bioactivities (e.g., baicalin, wogonoside, baicalein, and wogonin) mainly in its dry root, which is used as alternative to Scutellaria baicalensis in the north of China. Furthermore, S. viscidula also has flavones with interesting diverged structures such as panicolin, Viscidulin I, Viscidulin II, and Viscidulin III. Tracing the dynamic process of gene expression will help reveal the mechanism of flavonoid synthesis in S. viscidula, as well as the 4′-deoxyflavone biosynthesis in S. baicalensis. One way is to generate and analyze the expressed sequence tags (ESTs). However, little is known on the transcriptome information of S. viscidula, particularly the key genes involved in flavonoid biosynthesis. |

Viscidulin I Dilution Calculator

Viscidulin I Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 3.3091 mL | 16.5453 mL | 33.0907 mL | 66.1813 mL | 82.7267 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.6618 mL | 3.3091 mL | 6.6181 mL | 13.2363 mL | 16.5453 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.3309 mL | 1.6545 mL | 3.3091 mL | 6.6181 mL | 8.2727 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0662 mL | 0.3309 mL | 0.6618 mL | 1.3236 mL | 1.6545 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0331 mL | 0.1655 mL | 0.3309 mL | 0.6618 mL | 0.8273 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
- Viscidulin II
Catalog No.:BCN3187
CAS No.:92519-93-2
- Viscidulin III
Catalog No.:BCN4464
CAS No.:92519-91-0
- 21-Deoxyneridienone B
Catalog No.:BCN4463
CAS No.:924910-83-8
- Rupesin E
Catalog No.:BCN7009
CAS No.:924901-58-6
- 4,5-Epoxyartemisinic acid
Catalog No.:BCN4462
CAS No.:92466-31-4
- AZD-5597
Catalog No.:BCC6453
CAS No.:924641-59-8
- T 5601640
Catalog No.:BCC5617
CAS No.:924473-59-6
- AdipoRon
Catalog No.:BCC4756
CAS No.:924416-43-3
- HBX 41108
Catalog No.:BCC6137
CAS No.:924296-39-9
- DUBs-IN-2
Catalog No.:BCC5257
CAS No.:924296-19-5
- DUBs-IN-1
Catalog No.:BCC5256
CAS No.:924296-18-4
- DUBs-IN-3
Catalog No.:BCC5258
CAS No.:924296-17-3
- Jingzhaotoxin III
Catalog No.:BCC6327
CAS No.:925463-91-8
- 10-DEBC hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC7409
CAS No.:925681-41-0
- KU-60019
Catalog No.:BCC3699
CAS No.:925701-49-1
- Acitretin sodium
Catalog No.:BCC4299
CAS No.:925701-88-8
- 3-Isomangostin hydrate formate
Catalog No.:BCN4466
CAS No.:925705-36-8
- TG100713
Catalog No.:BCC4985
CAS No.:925705-73-3
- Secaubryenol
Catalog No.:BCN4467
CAS No.:925932-08-7
- Secaubrytriol
Catalog No.:BCN4468
CAS No.:925932-10-1
- Dayecrystal A
Catalog No.:BCN4859
CAS No.:926010-24-4
- AMTB hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC7834
CAS No.:926023-82-7
- Radotinib(IY-5511)
Catalog No.:BCC6398
CAS No.:926037-48-1
- O-Demethylforbexanthone
Catalog No.:BCN4469
CAS No.:92609-77-3
7-O-Methylwogonin from Scutellaria baicalensis Disturbs Mitotic Progression by Inhibiting Plk1 Activity in Hep3B Cells.[Pubmed:30199903]
Planta Med. 2019 Feb;85(3):217-224.
Polo-like kinase 1, a mitotic Ser/Thr kinase, has emerged as a molecular target for the development of anticancer drugs. In this study, we found that polo-like kinase 1 activity was inhibited by 7-O-methylwogonin and related flavones, including baicalein, dihydrobaicalein, and Viscidulin II, isolated from Scutellaria baicalensis. Although dihydrobaicalein exhibited the highest polo-like kinase 1 inhibitory activity among the four compounds, it also inhibited other kinases, such as vaccinia-related kinase 2 and polo-like kinase 2. Baicalein and Viscidulin II also showed low selectivity to polo-like kinase 1 since they inhibited polo-like kinase 3 and polo-like kinase 2, respectively. However, 7-O-methylwogonin exhibited selective polo-like kinase 1 inhibitory activity, as evidenced from in vitro kinase assays based on fluorescence resonance energy transfer assays and ADP-Glo kinase assays. In addition, examination of mitotic morphology and immunostaining using specific antibodies for the mitotic markers, p-histone H3 and mitotic protein monoclonal 2, in Hep3B cells showed that 7-O-methylwogonin treatment increased mitotic cell populations due to inhibition of mitotic progression as a result of polo-like kinase 1 inhibition. The pattern of 7-O-methylwogonin-induced mitotic arrest was similar to that of BI 2536, a specific polo-like kinase 1 inhibitor. Thus, it was suggested that 7-O-methylwogonin disturbed mitotic progression by inhibiting polo-like kinase 1 activity. These data suggest that 7-O-methylwogonin, a polo-like kinase 1 inhibitor, may be a useful anticancer agent because of its polo-like kinase 1 selectivity and effectiveness.
Flavones Isolated from Scutellariae radix Suppress Propionibacterium Acnes-Induced Cytokine Production In Vitro and In Vivo.[Pubmed:26712724]
Molecules. 2015 Dec 24;21(1):E15.
Scutellariae radix, the root of Scutellaria baicalensis, has long been applied in traditional formulations and modern herbal medications. Propionibacterium acnes (P. acnes) in follicles can trigger inflammation and lead to the symptom of inflammatory acnes vulgaris. This study was aimed at evaluating the effect of Scutellariae radix extract and purified components isolated from it on inflammation induced by P. acnes in vitro and in vivo. The results showed the ethyl acetate (EA) soluble fraction from the partition of crude ethanolic extract from Scutellariae radix inhibited P. acnes-induced interleukin IL-8 and IL-1beta production in human monocytic THP-1 cells. Seven flavones were isolated from the EA fraction by repeated chromatographies, and identified as 5,7-dihydroxy-6-methoxyflavone (FL1, oroxylin), 5,7-dihydroxy-8-methoxyflavone (FL2, wogonin), 5-hydroxy-7,8-dimethoxyflavone (FL3, 7-O-methylwogonin), 5,6'-dihydroxy-6,7,8,2'-tetramethoxy flavone (FL4, skullcapflavone II), 5,7,4'-trihydroxy-8-methoxyflavone (FL5), 5,2',6'-trihydroxy-7,8-dimethoxyflavone (FL6, Viscidulin II), and 5,7,2',5'-tetrahydroxy-8,6'-dimethoxyflavone (FL7, ganhuangenin). They all significantly suppressed P. acnes-induced IL-8 and IL-1beta production in THP-1 cells, and FL2 exerted the strongest effect with half maximal inhibition (IC50) values of 8.7 and 4.9 muM, respectively. Concomitant intradermal injection of each of the seven flavones (20 mug) with P. acnes effectively attenuated P. acnes-induced ear swelling, and decreased the production of IL-6 and tumor necrosis factor-alpha in ear homogenates. Our results suggested that all the seven flavones can be potential therapeutic agents against P. acnes-induced skin inflammation.
Triple aldose reductase/alpha-glucosidase/radical scavenging high-resolution profiling combined with high-performance liquid chromatography-high-resolution mass spectrometry-solid-phase extraction-nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy for identification of antidiabetic constituents in crude extract of Radix Scutellariae.[Pubmed:26187760]
J Chromatogr A. 2015 Aug 21;1408:125-32.
In this work, development of a new microplate-based high-resolution profiling assay using recombinant human aldose reductase is presented. Used together with high-resolution radical scavenging and high-resolution alpha-glucosidase assays, it provided the first report of a triple aldose reductase/alpha-glucosidase/radical scavenging high-resolution inhibition profile - allowing proof of concept with Radix Scutellariae crude extract as a polypharmacological herbal drug. The triple bioactivity high-resolution profiles were used to pinpoint bioactive compounds, and subsequent structure elucidation was performed with hyphenated high-performance liquid chromatography-high-resolution mass spectrometry-solid-phase extraction-nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy. The only alpha-glucosidase inhibitor was baicalein, whereas main aldose reductase inhibitors in the crude extract were baicalein and skullcapflavone II, and main radical scavengers were ganhuangemin, Viscidulin III, baicalin, oroxylin A 7-O-glucuronide, wogonoside, baicalein, wogonin, and skullcapflavone II.
[Flavonoids from Scutellaria baicalensis and their bioactivities].[Pubmed:19829679]
Beijing Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. 2009 Oct 18;41(5):578-84.
OBJECTIVE: To study the flavonoids of Scutellaria baicalensis and their bioactivities. METHODS: Chromatographic methods were used to separate compounds, spectral methods were used to determine the structures and bioactivities of the flavonoids were screened in several models in vitro. RESULTS: Nine compounds were isolated and identified as baicalein (1), wogonin (2), oroxylin A (3), 5, 7, 2', 6'-tetrahydroxyflavone (4), Viscidulin III (5), baicalin (6), wogonoside (7), oroxylin A-7-O-beta-D-glucuronide (8) and chrysin-6-C-alpha-L-arabinopyranosyl-8-C-beta-D-glucopyranoside (9). CONCLUSION: Baicalein had good anti-bacteria activity, and some compounds showed inhibiting activity against IL-1beta converting enzyme. The 13C NMR data of compounds 9 were assigned correctly by 2D nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR).
[Studies on ethyl acetate soluble constituents of Huanglian Jiedutang].[Pubmed:19160789]
Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 2008 Sep;33(18):2080-6.
OBJECTIVE: To study the ethyl acetate soluble constituents from the water extractive of Huanglian Jiedutang decoction, which are composed of Rhizoma Coptidis, Radix Scutellariae, Cortex Phellodendri and Fructus Gardeniae, and provide substances foundation for its pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic investigation. METHOD: The chemical constituents were isolated by various column chromatographic methods and structurally elucidated by NMR and MS techniques. RESULT: Thirty-five compounds were isolated, among which twenty compounds have been identified as beta-sitosterol (1), oroxylin A (2), wogonin (3), ursolic acid (4), skullcapflavone I (5), tenaxin I (6), skullcapflavone II (7), limonin (8), 5, 2'-dihydroxy-6, 7, 8, 3'-tetramethoxyflavone (9), chrysin (12), baicalein (17), tenaxin II (19), 5, 7, 2'-trihydroxy-6, 8-dimethoxyflavone (21), shihulimonin A (22), 6, 2'-dihydroxy-5, 7, 8, 6'-tetramethoxyflavone (26), Viscidulin II (28), 5, 7, 4'-trihydroxy-8-methoxyflavone (29), 5, 7, 2', 6'-tetrahydroxyflavone (30), wogonin-7-O-beta-D-glucuronide methyl ester (31) and daucosterol (34). CONCLUSION: On the basis of reported results of the chemical constituents of Rhizoma Coptidis, Radix Scutellariae, Cortex Phellodendri and Fructus Gardeniae, it was estimated that all flavonoid compounds rised from the Radix Scutellariae, and compounds 8 and 22 rised from Cortex Phellodendri. Compound 22 was identified in the Cortex Phellodendri for the first time.
Studies on the constituents of roots of Scutellaria planipes.[Pubmed:17252377]
Planta Med. 1997 Dec;63(6):536-9.
From the roots of Scutellaria planipes (L.), three new flavonoids, 5,7,3',6'-tetrahydroxy-6,8,2'-trimethoxyflavone, (2 R,3 R)-3,5,7,2',5'-pentahydroxyflavanone and 7,2'-dihydroxy-5-methoxyflavone were isolated, together with ten known flavonoids, skullcapflavone I, wogonin, baicalein, norwogonin, Viscidulin III, 5,7,2',6'-tetrahydroxy-flavone, 3,5,7,2',6'-pentahydroxyflavone, wogonin 7- O-beta- D-glucuronide, baicalin, baicalein 7- O-beta- D-glucopyranoside, and three phenethyl alcohol glycosides, acteoside, martynoside, and jionoside D. The structures were elucidated by spectroscopic methods.
Cytotoxic activities of flavonoids from two Scutellaria plants in Chinese medicine.[Pubmed:15036470]
J Ethnopharmacol. 2004 Mar;91(1):65-8.
The effects of 17 flavonoids, isolated from two flavonoid-rich Scutellaria species (Scutellaria baicalensis Georgi and Scutellaria rivularis Wall) used in traditional Chinese medicine, on HL-60 cells were assessed by WST-8. Ten of the flavonoids inhibited the proliferation of HL-60, as shown by IC50 values used as indexes of the inhibition. 2',3',5,7-tetrahydroxy flavone (IC50=9.5 microM), apigenin (15.0 microM), Viscidulin III (17.4 microM), wogonin (17.4 microM) and luteolin (18.4 microM) were more effective than baicalein (23.0 microM) which reportedly inhibits the proliferation of some cancer cell lines. Others were less effective, and oroxylin A stimulated the proliferation. Scutellaria rivularis, used for the treatment of tumors in the clinic, contained flavonoids that were more inhibitive than those in Scutellaria baicalensis. These results are demonstrative of some reasons for the use of Scutellaria rivularis as a crude antitumor drug.


