Vanillic acidCAS# 121-34-6 |
Quality Control & MSDS
Number of papers citing our products

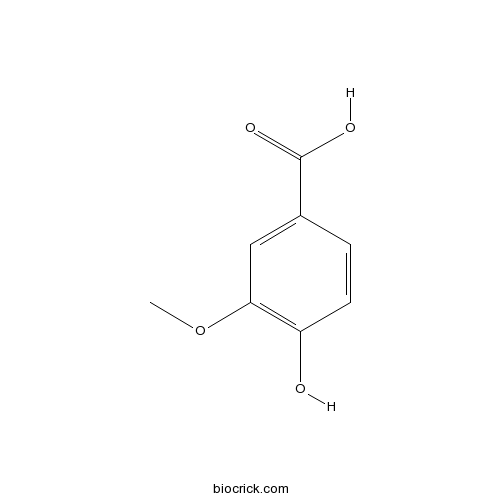
Chemical structure

3D structure
| Cas No. | 121-34-6 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 8468 | Appearance | White to light yellow powder |
| Formula | C8H8O4 | M.Wt | 168.2 |
| Type of Compound | Phenols | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Synonyms | 4-Hydroxy 3-methoxybenzoic acid | ||
| Solubility | DMSO : ≥ 100 mg/mL (594.71 mM) *"≥" means soluble, but saturation unknown. | ||
| Chemical Name | 4-hydroxy-3-methoxybenzoic acid | ||
| SMILES | COC1=C(C=CC(=C1)C(=O)O)O | ||
| Standard InChIKey | WKOLLVMJNQIZCI-UHFFFAOYSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C8H8O4/c1-12-7-4-5(8(10)11)2-3-6(7)9/h2-4,9H,1H3,(H,10,11) | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | Vanillic acid is a flavoring agent which has hepatoprotective, free radical scavenging, antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties. It exerts protective effects in isoproterenol induced cardiotoxic rats, has inhibitory effect on methylglyoxal-mediated glycation in apoptotic Neuro-2A cells via inhibition of glycation mechanisms including ROS, p38 and JNK, PKC and p47(phox). |
| Targets | TNF-α | ROS | p38MAPK | JNK | PKC | p47(phox) | IL Receptor | Fas | Caspase |
| In vitro | Inhibitory effect of vanillic acid on methylglyoxal-mediated glycation in apoptotic Neuro-2A cells[Pubmed: 18706441]Neurotoxicology. 2008 Nov;29(6):1016-22.Methylglyoxal is a reactive dicarbonyl compound generated as an intermediate of glycolysis during the physical glycation in the diabetic condition. It is considered to be a potent precursor of advanced glycation end products (AGEs) formation. Methylglyoxal itself and methylglyoxal-derived AGEs have been commonly implicated in the development of diabetic neuropathy. Our previous study indicated that Vanillic acid showed an inhibitory effect against methylglyoxal-mediated Neuro-2A cell apoptosis, suggesting that Vanillic acid might possess cytoprotective properties in the prevention of diabetic neuropathy complication.
|
| In vivo | Protective effects of vanillic acid on electrocardiogram, lipid peroxidation, antioxidants, proinflammatory markers and histopathology in isoproterenol induced cardiotoxic rats.[Pubmed: 21763302 ]Eur J Pharmacol. 2011 Oct 1;668(1-2):233-40.Myocardial infarction affects a large proportion in the world. This study aims to evaluate the protective effects of Vanillic acid in isoproterenol induced cardiotoxic rats.
Hepatoprotective effect of syringic acid and vanillic acid on CCl4-induced liver injury.[Pubmed: 20522963]Biol Pharm Bull. 2010;33(6):983-7.The mycelia of the edible mushroom Lentinula edodes can be cultured in solid medium containing lignin, and the hot-water extracts (L.E.M.) is commercially available as a nutritional supplement. During the cultivation, phenolic compounds, such as syringic acid and Vanillic acid, were produced by lignin-degrading peroxidase secreted from L. edodes mycelia. Since these compounds have radical scavenging activity, we examined their protective effect on oxidative stress in mice with CCl(4)-induced liver injury.
|
| Kinase Assay | Effect of vanillic acid on COQ6 mutants identified in patients with coenzyme Q10 deficiency.[Pubmed: 24140869]Biochim Biophys Acta. 2014 Jan;1842(1):1-6.Human COQ6 encodes a monooxygenase which is responsible for the C5-hydroxylation of the quinone ring of coenzyme Q (CoQ). Mutations in COQ6 cause primary CoQ deficiency, a condition responsive to oral CoQ10 supplementation. Treatment is however still problematic given the poor bioavailability of CoQ10.
|
| Animal Research | Vanillic acid prevents altered ion pumps, ions, inhibits Fas-receptor and caspase mediated apoptosis-signaling pathway and cardiomyocyte death in myocardial infarcted rats.[Pubmed: 25794854]Chem Biol Interact. 2015 May 5;232:68-76.Animal Models: Male albino Wistar rats |

Vanillic acid Dilution Calculator

Vanillic acid Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 5.9453 mL | 29.7265 mL | 59.453 mL | 118.9061 mL | 148.6326 mL |
| 5 mM | 1.1891 mL | 5.9453 mL | 11.8906 mL | 23.7812 mL | 29.7265 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.5945 mL | 2.9727 mL | 5.9453 mL | 11.8906 mL | 14.8633 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.1189 mL | 0.5945 mL | 1.1891 mL | 2.3781 mL | 2.9727 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0595 mL | 0.2973 mL | 0.5945 mL | 1.1891 mL | 1.4863 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
- Vanillin
Catalog No.:BCN2605
CAS No.:121-33-5
- 3-Deazaneplanocin A (DZNep) hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC3604
CAS No.:120964-45-6
- FPL 64176
Catalog No.:BCC7050
CAS No.:120934-96-5
- Isoliquiritin apioside
Catalog No.:BCN2914
CAS No.:120926-46-7
- PF-03394197(Oclacitinib)
Catalog No.:BCC6474
CAS No.:1208319-26-9
- N6022
Catalog No.:BCC4127
CAS No.:1208315-24-5
- Ketone Ester
Catalog No.:BCC1677
CAS No.:1208313-97-6
- VU 0365114
Catalog No.:BCC6164
CAS No.:1208222-39-2
- CaMKII-IN-1
Catalog No.:BCC5530
CAS No.:1208123-85-6
- Quassidine B
Catalog No.:BCN7022
CAS No.:1207862-37-0
- Gynosaponin I
Catalog No.:BCN4078
CAS No.:1207861-69-5
- Huperzine A
Catalog No.:BCN1058
CAS No.:120786-18-7
- (-)-Terreic acid
Catalog No.:BCC7051
CAS No.:121-40-4
- Benzethonium Chloride
Catalog No.:BCC4635
CAS No.:121-54-0
- N-Acetylsulfanilyl chloride
Catalog No.:BCC9084
CAS No.:121-60-8
- 2-Amino-5-nitrothiazole
Catalog No.:BCC8538
CAS No.:121-66-4
- Propyl gallate
Catalog No.:BCN8431
CAS No.:121-79-9
- 3'-Nitroacetophenone
Catalog No.:BCN2256
CAS No.:121-89-1
- ST 1936 oxalate
Catalog No.:BCC7919
CAS No.:1210-81-7
- N-Acetyl-5-Hydroxytryptamine
Catalog No.:BCC9080
CAS No.:1210-83-9
- JZL 195
Catalog No.:BCC7966
CAS No.:1210004-12-8
- Secretin (rat)
Catalog No.:BCC5848
CAS No.:121028-49-7
- Nelarabine
Catalog No.:BCC1072
CAS No.:121032-29-9
- IEM 1460
Catalog No.:BCC7135
CAS No.:121034-89-7
A rapid colorimetric screening method for vanillic acid and vanillin-producing bacterial strains.[Pubmed:24314059]
J Appl Microbiol. 2014 Apr;116(4):903-10.
AIM: To isolate a bacterial strain capable of biotransforming ferulic acid, a major component of lignin, into vanillin and Vanillic acid by a rapid colorimetric screening method. METHODS AND RESULTS: For the production of vanillin, a natural aroma compound, we attempted to isolate a potential strain using a simple screening method based on pH change resulting from the degradation of ferulic acid. The strain Pseudomonas sp. AZ10 UPM exhibited a significant result because of colour changes observed on the assay plate on day 1 with a high intensity of yellow colour. The biotransformation of ferulic acid into Vanillic acid by the AZ10 strain provided the yield (Yp/s ) and productivity (Pr ) of 1.08 mg mg(-1) and 53.1 mg L(-1) h(-1) , respectively. In fact, new investigations regarding lignin degradation revealed that the strain was not able to produce vanillin and Vanillic acid directly from lignin; however, partially digested lignin by mixed enzymatic treatment allowed the strain to produce 30.7 mg l(-1) and 1.94 mg l(-1) of Vanillic acid and biovanillin, respectively. CONCLUSIONS: (i) The rapid colorimetric screening method allowed the isolation of a biovanillin producer using ferulic acid as the sole carbon source. (ii) Enzymatic treatment partially digested lignin, which could then be utilized by the strain to produce biovanillin and Vanillic acid. SIGNIFICANCE AND IMPACT OF THE STUDY: To the best of our knowledge, this is the first study reporting the use of a rapid colorimetric screening method for bacterial strains producing vanillin and Vanillic acid from ferulic acid.
Effect of vanillic acid on COQ6 mutants identified in patients with coenzyme Q10 deficiency.[Pubmed:24140869]
Biochim Biophys Acta. 2014 Jan;1842(1):1-6.
Human COQ6 encodes a monooxygenase which is responsible for the C5-hydroxylation of the quinone ring of coenzyme Q (CoQ). Mutations in COQ6 cause primary CoQ deficiency, a condition responsive to oral CoQ10 supplementation. Treatment is however still problematic given the poor bioavailability of CoQ10. We employed S. cerevisiae lacking the orthologous gene to characterize the two different human COQ6 isoforms and the mutations found in patients. COQ6 isoform a can partially complement the defective yeast, while isoform b, which lacks part of the FAD-binding domain, is inactive but partially stable, and could have a regulatory/inhibitory function in CoQ10 biosynthesis. Most mutations identified in patients, including the frameshift Q461fs478X mutation, retain residual enzymatic activity, and all patients carry at least one hypomorphic allele, confirming that the complete block of CoQ biosynthesis is lethal. These mutants are also partially stable and allow the assembly of the CoQ biosynthetic complex. In fact treatment with two hydroxylated analogues of 4-hydroxybenzoic acid, namely, Vanillic acid or 3-4-hydroxybenzoic acid, restored the respiratory growth of yeast Deltacoq6 cells expressing the mutant huCOQ6-isoa proteins. These compounds, and particularly Vanillic acid, could therefore represent an interesting therapeutic option for COQ6 patients.
Vanillic acid prevents altered ion pumps, ions, inhibits Fas-receptor and caspase mediated apoptosis-signaling pathway and cardiomyocyte death in myocardial infarcted rats.[Pubmed:25794854]
Chem Biol Interact. 2015 May 5;232:68-76.
The present study aims to evaluate the preventive effects of Vanillic acid on altered ion pumps, ions and Fas-receptor and caspase mediated apoptosis-signaling pathway and cardiomyocyte death in isoproterenol induced myocardial infarcted rats. Male albino Wistar rats were pretreated with Vanillic acid (5 mg/kg and 10 mg/kg body weight) daily for 10 days. After the pretreatment, isoproterenol (100 mg/kg body weight) was injected into rats at an interval of 24h for 2 days to induce myocardial infarction. Isoproterenol induced rats significantly increased activities/levels of serum cardiac markers, plasma lipid peroxidation products, serum uric acid and significantly decreased plasma non-enzymatic antioxidants. Furthermore, isoproterenol significantly altered the activities/levels of ion pumps and ions in the heart. The myocardial expressions of apoptotic genes such as Fas-receptor, caspases-8, -9, and -3 were increased in isoproterenol induced rats. There was a significant increase in cardiomyocyte apoptosis observed in isoproterenol induced rats. Pretreatment with Vanillic acid (5 mg/kg and 10 mg/kg body weight) to isoproterenol induced rats showed significant effects on all the biochemical and molecular parameters evaluated. Isolated cardiomyocyte viability by trypan blue exclusion staining also correlated with these biochemical findings. Thus, Vanillic acid prevented altered ion pumps, ions and inhibited Fas-receptor and caspase mediated apoptosis-signaling pathway and cardiomyocyte death in isoproterenol induced myocardial infarcted rats. Our study also revealed that pretreatment with Vanillic acid at the dose of 10 mg/kg body weight was more effective than 5 mg/kg body weight. The cardioprotective effects of Vanillic acid are associated with its antioxidant mechanisms.
Evaluation of vanillic acid as inhibitor of carbonic anhydrase isozyme III by using a modified Hummel-Dreyer method: approach for drug discovery.[Pubmed:23605884]
Biomed Chromatogr. 2013 Sep;27(9):1157-61.
alpha-3 carbonic anhydrase isozyme (CAIII) is the most abundant protein in adipocytes and considered insensitive to sulfonamide inhibitors. It was reported recently that the knock-down of CAIII is attributed with controlling lipogenesis. Thus inhibition of this target may lead to the discovery of new therapies against obesity and insulin resistance. Vanillic acid as a small molecule with coordinating groups and has a potential to bind zinc atoms in CA binding sites. Inhibition of CAIII by Vanillic acid was evaluated by Hummel-Dreyer chromatography because it provides free interaction between ligand and macromolecule and introduces solution for faulty results obtained by current colorimetric assays. HPLC system of Vanillic acid produces vacancy (negative) peak representing the amount of attached Vanillic acid with CAIII. It was found that Vanillic acid is able to bind with CAIII through two equilibria, one at equimolar ratio and another at 2:1 (Vanillic acid-CAIII) ratio. The affinity constant of equimolar binding between CAIII and Vanillic acid was found to be 14,400 m(-1) . It was found that Vanillic acid binding with CAIII is much stronger than phenol and acetazolamide (positive controls).


