VX-702P38α MAPK inhibitor,highly selective and ATP-competitive CAS# 479543-46-9 |
- Skepinone-L
Catalog No.:BCC1953
CAS No.:1221485-83-1
- SB202190 (FHPI)
Catalog No.:BCC1093
CAS No.:152121-30-7
- SB 239063
Catalog No.:BCC1923
CAS No.:193551-21-2
- SD-06
Catalog No.:BCC1937
CAS No.:271576-80-8
- LY2228820
Catalog No.:BCC2528
CAS No.:862507-23-1
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 479543-46-9 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 10341154 | Appearance | Powder |
| Formula | C19H12F4N4O2 | M.Wt | 404.3 |
| Type of Compound | Inhibitors | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Synonyms | 745833-23-2 | ||
| Solubility | Soluble to 100 mM in DMSO | ||
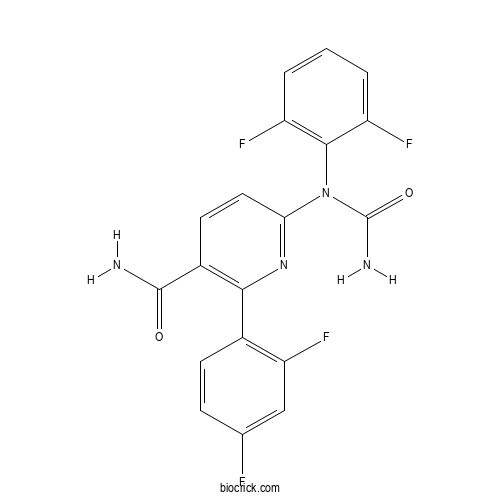
| Chemical Name | 6-(N-carbamoyl-2,6-difluoroanilino)-2-(2,4-difluorophenyl)pyridine-3-carboxamide | ||
| SMILES | C1=CC(=C(C(=C1)F)N(C2=NC(=C(C=C2)C(=O)N)C3=C(C=C(C=C3)F)F)C(=O)N)F | ||
| Standard InChIKey | FYSRKRZDBHOFAY-UHFFFAOYSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C19H12F4N4O2/c20-9-4-5-10(14(23)8-9)16-11(18(24)28)6-7-15(26-16)27(19(25)29)17-12(21)2-1-3-13(17)22/h1-8H,(H2,24,28)(H2,25,29) | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||

VX-702 Dilution Calculator

VX-702 Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 2.4734 mL | 12.3671 mL | 24.7341 mL | 49.4682 mL | 61.8353 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.4947 mL | 2.4734 mL | 4.9468 mL | 9.8936 mL | 12.3671 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.2473 mL | 1.2367 mL | 2.4734 mL | 4.9468 mL | 6.1835 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0495 mL | 0.2473 mL | 0.4947 mL | 0.9894 mL | 1.2367 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0247 mL | 0.1237 mL | 0.2473 mL | 0.4947 mL | 0.6184 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
VX-702 is a selective inhibitor of p38α MAPK with IC50 value ranges from 4 nM to 20 nM [1].
P38 mitogen-activated protein kinases (p38 MAPK), also named as MAPK14, are a class of mitogen-activated protein kinases and play an important role in a signaling cascade controlling cellular responses to cytokines and stress [1-3].
VX-702 is a potent p38α MAPK inhibitor and is designed as for greater affinity and greater selectivity compared with the first reported p38α MAPK inhibitors. When tested with PLTs (platelets), VX-702 caused better maintenance of PLT mitochondrial, functional, structural and metabolic parameters during 7 days storage and restored PLTs properties following an extended interruption of agitation to levels of continuously agitated PLTs [2, 4].
In the isolated perfused rat kidney (IPRK) model, administration of VX-702 at a range of doses between 100 and 600 ng/mL showed linear excretion and the clearance data were consistent with net reabsorption by the kidney. Further, VX-702 was showed not a substrate for renal organic anion and organic cation transport systems [3].
References:
[1]. Kuliopulos, A., R. Mohanlal, and L. Covic, Effect of selective inhibition of the p38 MAP kinase pathway on platelet aggregation. Thromb Haemost, 2004. 92(6): p. 1387-93.
[2]. Skripchenko, A., et al., An inhibition of p38 mitogen activated protein kinase delays the platelet storage lesion. PLoS One, 2013. 8(8): p. e70732.
[3]. Tamhane, M., et al., Comparative renal excretion of VX-702, a novel p38 MAPK inhibitor, and methotrexate in the perfused rat kidney model. Drug Dev Ind Pharm, 2010. 36(3): p. 315-22.
[4]. Wagner, S.J., et al., Amelioration of lesions associated with 24-hour suboptimal platelet storage at 16 degrees C by a p38MAPK inhibitor, VX-702. Vox Sang, 2015. 108(3): p. 226-32.
- Lactupicrin
Catalog No.:BCN0118
CAS No.:65725-11-3
- Tricetinidin chloride
Catalog No.:BCN0117
CAS No.:65618-21-5
- (-)-Carveol
Catalog No.:BCN0116
CAS No.:99-48-9
- Sempervirine nitrate
Catalog No.:BCN0115
CAS No.:17994-15-9
- (+)-Isocorydine hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCN0114
CAS No.:13552-72-2
- alpha-Pinene oxide
Catalog No.:BCN0113
CAS No.:1686-14-2
- Dehydroascorbic acid
Catalog No.:BCN0112
CAS No.:490-83-5
- Eupatorin-5-methylether
Catalog No.:BCN0111
CAS No.:21764-09-0
- Furfuryl acetate
Catalog No.:BCN0110
CAS No.:623-17-6
- DL-Threonine
Catalog No.:BCN0109
CAS No.:80-68-2
- 3-Hydroxybenzaldehyde
Catalog No.:BCN0108
CAS No.:100-83-4
- 1-Heptacosanol
Catalog No.:BCN0107
CAS No.:2004-39-9
- (+)-Longifolene
Catalog No.:BCN0120
CAS No.:475-20-7
- k-Strophanthoside
Catalog No.:BCN0121
CAS No.:33279-57-1
- Gomisin U
Catalog No.:BCN0122
CAS No.:135095-46-4
- Acetoxyvalerenic acid
Catalog No.:BCN0123
CAS No.:84638-55-1
- Vitexin 2''-glucoside
Catalog No.:BCN0124
CAS No.:61360-94-9
- Fortunellin
Catalog No.:BCN0125
CAS No.:20633-93-6
- 3',5'-Dimethoxy-4'-hydroxyacetophenone
Catalog No.:BCN0126
CAS No.:2478-38-8
- Bacosine
Catalog No.:BCN0127
CAS No.:198014-94-7
- Laudanosine
Catalog No.:BCN0128
CAS No.:1699-51-0
- Negundoside
Catalog No.:BCN0129
CAS No.:82451-20-5
- 2,3-Dehydrosilybin A
Catalog No.:BCN0130
CAS No.:25166-14-7
- (-)-Cadin-4,10(15)-dien-11-oic acid
Catalog No.:BCN0131
CAS No.:1124353-23-6
Berberine inhibits epithelial-mesenchymal transition and promotes apoptosis of tumour-associated fibroblast-induced colonic epithelial cells through regulation of TGF-beta signalling.[Pubmed:31399854]
J Cell Commun Signal. 2020 Mar;14(1):53-66.
Tumour-associated fibroblasts (TAFs) mediate the differentiation of adjacent stromal cells. Berberine (BBR), a monomer of traditional Chinese herbs, exhibits a potent therapeutic effect against cancer. However, the effects of BBR on the differentiation of normal colonic epithelial cells induced by TAFs have not been determined. In the present study, we selected the TAF-like myofibroblast cell line CCD-18Co. CCD-18Co-derived conditioned medium (CM) and co-culture induced epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT) changes in colonic epithelial HCoEpiC cells with decreased E-cadherin and increased vimentin and alpha-SMA expression. In addition, CCD-18Co stimulated the expression of ZEB1 and Snail and promoted motility. We used LY364947, a TGF-beta receptor kinase type I (TbetaRI) inhibitor, and BBR. Our results showed that LY364947 and BBR inhibited these phenomena. BBR decreased the expression of ZEB1 and Snail, and this effect was concentration dependent. BBR also downregulated the expression of TbetaRI, TbetaRII, Smad2/p-Smad2 and Smad3/p-Smad3. In addition, BBR induced apoptosis in EMT-like HCoEpiC cells in a concentration-dependent manner with upregulation of Bax and downregulation of Bcl-2. However, VX-702, an inhibitor of p38 MAPK, significantly suppressed the apoptosis rate. BBR promoted the expression of p38 MAPK and phosphorylated p38 MAPK. In conclusion, berberine inhibits EMT and promotes apoptosis in TAF-induced colonic epithelial cells through mediation of the Smad-dependent and SMAD-independent TGF-beta signalling pathways.
Trichostatin a inhibits phenotypic transition and induces apoptosis of the TAF-treated normal colonic epithelial cells through regulation of TGF-beta pathway.[Pubmed:31278993]
Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2019 Sep;114:105565.
Tumor-associated fibroblasts (TAFs) contribute to transdifferentiation of stromal cells in tumor microenvironment. Epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT) is a procedure of phenotypic remodeling of epithelial cells and extensively exists in local tumoral stroma. Histone deacetylase (HDAC) inhibitor Tricostatin A (TSA) and sodium butyrate (SB) are reported to play important roles in the regulation of biological behaviour of cancer cells. However, whether TSA or SB is involved in control of EMT in colon epithelial cells induced by TAFs remains unidentified. In present study, we used conditioned medium (CM) form TAF-like CCD-18Co cells to stimulate 2D- and 3D-cultured colon epithelial HCoEpiC cells for 24 h and 4 d. We found that the CCD-18Co CM triggered multiple morphological changes in HCoEpiCs including prolonged cell diameters, down-regulation of E-cadherin and up-regulation of vimentin and alpha-SMA. Besides, ZEB1 and Snail expression and migration were also promoted by the CM. These phenomena were abolised by 5 mug/ml LY364947, a TGF-beta receptor inhibitor. CCD-18Co induced up-regulation of HDAC1 and HDAC2 in the 2D and 3D models, while no change of HDAC4 exprerssion was found. Treatment of 2 mug/ml TSA reversed the CCD-18Co-induced morphological changes and migration of the HCoEpiCs, and suppressed the downregulation of E-cadherin and upregulation of vimentin, alpha-SMA, ZEB1 and Snail. However, the suppressive effect of 4 mg/ml SB on the EMT was not observed. TSA down-regulated the expressions of Smad2/3, p-Smad2/3 amd HDAC4. Besides, TSA promoted the apoptosis rate (36.84 +/- 6.52%) comparing with the CCD-18Co-treated HCoEpiCs (3.52 +/- 0.85%, P < 0.05), with promotion of Bax (0.5893+/-0.0498 in 2D and 0.8867+/-0.0916 in 3D) and reduction of Bcl-2 (0.0476+/-0.0053 in 2D and 0.0294+/-0.0075 in 3D). TSA stimulated expression of phosphorylated-p38 MAPK in 2D (0.3472+/-0.0249) and 3D (0.3188+/-0.0248). After pre-treatment with p38 MAPK inhibitor VX-702 (0.5 mg/ml), the apoptosis rate of TSA was decreased in 2D (10.32%) and 3D (5.26%). Our observations demonstrate that epigenetic treatment with HDAC inhibitor TSA may be a useful therapeutic tool for the reversion of TAF-induced EMT in colon epithelium through mediating canonical Smads pathway and non-canonical p38 MAPK signalling.
MicroRNA-105 promotes epithelial-mesenchymal transition of nonsmall lung cancer cells through upregulating Mcl-1.[Pubmed:30317672]
J Cell Biochem. 2019 Apr;120(4):5880-5888.
BACKGROUND: A growing number of microRNAs have been proved to play significant roles in limiting tumor growth and the epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT) process of nonsmall cell lung cancer (NSCLC). Present work aims to study the function of microRNA (miR)-105 in EMT of NSCLC cells, which is unrevealed yet. METHODS: Two NSCLC cell lines A549 and Calu-3 were transfected with miR-105 mimic, inhibitor, or scrambled control. And then the effects of miR-105 were evaluated by performing trypan blue staining, transwell assay, ANNEXIN-FITC/propidium iodide (PI) double staining and Western blot analysis. The expression levels of myeloid cell leukemia-1 (Mcl-1) after transfection were tested by real-time quantitative polymerase chain reaction and Western blot analysis. Whether Mcl-1 was a downstream effector of miR-105, and the involvement of mammalian target of Rapamycin (mTOR) and p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase (p38MAPK) signaling pathways were assessed. RESULTS: The overexpression of miR-105 significantly increased the viability and migration of A549 and Calu-3, but had no impacts on cell apoptosis. Meanwhile, E-cadherin was remarkably downregulated, and N-cadherin, Vimentin, ZEB1, and Snail were upregulated by miR-105 overexpression. Mcl-1 was positively regulated by miR-105, and the effects of miR-105 overexpression on A549 and Calu-3 cells viability, migration and EMT were all flattened by Mcl-1 silence. Both mTOR and p38MAPK pathways were activated in miR-105-overexpressing and Mcl-1-overexpressing cells. Besides, inhibition of mTOR and p38MAPK pathways by using Rapamycin and VX-702 abolished the regulatory effects of Mcl-1 on EMT. CONCLUSION: Our study underlines the importance of miR-105 in modulating NSCLC cells EMT. miR-105 promoted the EMT of NSCLC cells possibly via upregulation of Mcl-1 and thereby activation of mTOR and p38MAPK signaling.
Phosphoinositide 3-kinase p110alpha negatively regulates thrombopoietin-mediated platelet activation and thrombus formation.[Pubmed:29793021]
Cell Signal. 2018 Oct;50:111-120.
Phosphoinositide 3-kinase (PI3K) plays an important role in platelet function and contributes to platelet hyperreactivity induced by elevated levels of circulating peptide hormones, including thrombopoietin (TPO). Previous work established an important role for the PI3K isoform; p110beta in platelet function, however the role of p110alpha is still largely unexplored. Here we sought to investigate the role of p110alpha in TPO-mediated hyperactivity by using a conditional p110alpha knockout (KO) murine model in conjunction with platelet functional assays. We found that TPO-mediated enhancement of collagen-related peptide (CRP-XL)-induced platelet aggregation and adenosine triphosphate (ATP) secretion were significantly increased in p110alpha KO platelets. Furthermore, TPO-mediated enhancement of thrombus formation by p110alpha KO platelets was elevated over wild-type (WT) platelets, suggesting that p110alpha negatively regulates TPO-mediated priming of platelet function. The enhancements were not due to increased flow through the PI3K pathway as phosphatidylinositol 3,4,5-trisphosphate (PI(3,4,5)P3) formation and phosphorylation of Akt and glycogen synthase kinase 3 (GSK3) were comparable between WT and p110alpha KO platelets. In contrast, extracellular responsive kinase (ERK) phosphorylation and thromboxane (TxA2) formation were significantly enhanced in p110alpha KO platelets, both of which were blocked by the MEK inhibitor PD184352, whereas the p38 MAPK inhibitor VX-702 and p110alpha inhibitor PIK-75 had no effect. Acetylsalicylic acid (ASA) blocked the enhancement of thrombus formation by TPO in both WT and p110alpha KO mice. Together, these results demonstrate that p110alpha negatively regulates TPO-mediated enhancement of platelet function by restricting ERK phosphorylation and TxA2 synthesis in a manner independent of its kinase activity.
Blockade of p38 Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinase Inhibits Murine Sclerodermatous Chronic Graft-versus-Host Disease.[Pubmed:28189565]
Am J Pathol. 2017 Apr;187(4):841-850.
Bone marrow transplantation (BMT) of B10.D2 mice into sublethally irradiated BALB/c mice across minor histocompatibility loci is a well-established animal model for human sclerodermatous chronic graft-versus-host disease (Scl-cGVHD) and systemic sclerosis (SSc). The p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) pathway is a key regulator of inflammation and cytokine production. Furthermore, the activation of p38 MAPK plays an important role in collagen production in SSc. We investigated the effects of p38 MAPK inhibitor, VX-702, on Scl-cGVHD mice. VX-702 was orally administered to Scl-cGVHD mice from day 7 to 35 after BMT. We compared skin fibrosis of Scl-cGVHD mice between the VX-702-treated group and control group. Allogeneic BMT increased the phosphorylation of p38 MAPK in the skin. The administration of VX-702 attenuated the skin fibrosis of Scl-cGVHD compared to the control mice. Immunohistochemical staining showed that VX-702 suppressed the infiltration of CD4(+) T cells, CD8(+) T cells, and CD11b(+) cells into the dermis of Scl-cGVHD mice compared to the control mice. VX-702 attenuated the mRNA expression of extracellular matrix and fibrogenic cytokines, such as IL-6 and IL-13, in the skin of Scl-cGVHD mice. In addition, VX-702 directly inhibited collagen production from fibroblasts in vitro. VX-702 was shown to be a promising candidate for use in treating patients with Scl-cGVHD and SSc.
Amelioration of lesions associated with 24-hour suboptimal platelet storage at 16 degrees C by a p38MAPK inhibitor, VX-702.[Pubmed:25471280]
Vox Sang. 2015 Apr;108(3):226-32.
BACKGROUND AND OBJECTIVES: Previous studies with p38MAPK inhibitors at room temperature demonstrated that they improve a large number of platelet storage parameters, but cannot substantially inhibit p38MAPK activation nor protect against widespread decrements in platelet quality parameters during 4 degrees C storage. In this study, platelet quality parameters and inhibition of p38MAPK by VX-702 were studied after incubation of platelets at 16 degrees C without agitation, suboptimal storage conditions which produce moderate platelet decrements. MATERIALS AND METHODS: Trima apheresis units were collected and aliquoted into three 60-ml CLX storage bags: (i) a control aliquot which was held at 20-24 degrees C with constant agitation; (ii) a test aliquot which was held at 20-24 degrees C with agitation until Day 2, when it was reincubated at 16 +/- 1 degrees C for 24 +/- 0.5 h without agitation and then returned 20-24 degrees C with agitation; (iii) a test aliquot containing 1 mum VX-702 stored in an identical fashion as aliquot 2. Aliquots were tested for an array of platelet storage parameters and p38MAPK activation on Days 1, 4 and 7. RESULTS: Many platelet storage parameters and p38MAPK activation were adversely affected by 24-h incubation at 16 degrees C without agitation. With the exception of ESC, addition of VX-702 prevented p38MAPK activation and the decrements in most observed parameters. CONCLUSION: Unlike 4 degrees C storage, VX-702 prevents activation of p38MAPK and decrements in many platelet storage parameters after exposure to 16 degrees C without agitation for 24 h.
An inhibition of p38 mitogen activated protein kinase delays the platelet storage lesion.[Pubmed:23967093]
PLoS One. 2013 Aug 13;8(8):e70732.
BACKGROUND AND OBJECTIVES: Platelets during storage undergo diverse alterations collectively known as the platelet storage lesion, including metabolic, morphological, functional and structural changes. Some changes correlate with activation of p38 mitogen activated protein kinase (p38 MAPK). Another MAPK, extracellular signal-related kinase (ERK), is involved in PLT activation. The aim of this study was to compare the properties of platelets stored in plasma in the presence or absence of p38 and ERK MAPK inhibitors. MATERIALS AND METHODS: A single Trima apheresis platelet unit (n = 12) was aliquoted into five CLX storage bags. Two aliquots were continuously agitated with or without MAPK inhibitors. Two aliquots were subjected to 48 hours of interruption of agitation with or without MAPK inhibitors. One aliquot contained the same amount of solvent vehicle used to deliver the inhibitor. Platelets were stored at 20-24 degrees C for 7 days and sampled on Days 1, 4, and 7 for 18 in vitro parameters. RESULTS: Inhibition of p38 MAPK by VX-702 leads to better maintenance of all platelet in vitro storage parameters including platelet mitochondrial function. Accelerated by interruption of agitation, the platelet storage lesion of units stored with VX-702 was diminished to that of platelets stored with continuous agitation. Inhibition of ERK MAPK did not ameliorate decrements in any in vitro platelet properties. CONCLUSION: Signaling through p38 MAPK, but not ERK, is associated with platelet deterioration during storage.
Comparative renal excretion of VX-702, a novel p38 MAPK inhibitor, and methotrexate in the perfused rat kidney model.[Pubmed:20170280]
Drug Dev Ind Pharm. 2010 Mar;36(3):315-22.
CONTEXT: VX-702 is a novel p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase inhibitor being developed to treat rheumatoid arthritis. OBJECTIVE: To characterize the renal excretion profile of VX-702 using the isolated perfused rat kidney (IPRK) model. METHODS: Studies were performed to assess the dose linearity of VX-702 excretion and to evaluate the effect of inhibitors of organic anion (probenecid) and organic cation (cimetidine) transport systems on VX-702 disposition. VX-702 excretion was studied over a range of doses targeting concentrations between 100 and 600 ng/mL. VX-702 (600 ng/mL) was also co-perfused with probenecid (1 mM) and cimetidine (2 mM). The results were compared to parallel experiments performed with methotrexate (MTX). RESULTS: VX-702 excretion was linear over the range of doses studied, and clearance data were consistent with net reabsorption by the kidney. Transport inhibition studies indicate that VX-702 is not a substrate for renal organic anion and organic cation transport systems. MTX (500 ng/mL) also displayed net reabsorption in the IPRK, but secretory transport was inhibited upon co-administration with probenecid. This finding is consistent with previous IPRK studies that demonstrated inhibitory effects of NSAIDS on MTX excretion. CONCLUSION: Overall, this study suggests that a renal drug-drug interaction between VX-702 and MTX would be unlikely if these medications were co-administered.
Kinase inhibitors: a new approach to rheumatoid arthritis treatment.[Pubmed:20164774]
Curr Opin Rheumatol. 2010 May;22(3):330-5.
PURPOSE OF REVIEW: Due to the cost and parenteral mode of administration of biologics, efforts to develop oral small molecule inhibitors to protein kinases involved in cellular signaling that impact inflammatory cytokine production have been ongoing. This article will review the recent publications on these efforts. RECENT FINDINGS: On preclinical work, p38 mitogen-activated kinases were considered attractive targets to suppress cytokine production. Three different molecules (SCIO_469, Pamapimod, VX-702) that target the p38alpha isoform have been evaluated in phase 2 trials. Unfortunately, clinical efficacy was not observed, and dose-related toxicity was seen. The future of this approach is unclear. Targeting more upstream protein tyrosine kinases such as spleen tyrosine kinase (SyK) and the JAK family of kinases has been associated with greater success in clinical trials, with efficacy demonstrated. Adverse events occurred in a dose-dependent fashion with the SyK inhibitor, such as diarrhea and hypertension. Neutropenia, elevated liver-function tests, serum creatinine elevations and lipid elevations have occurred with JAK-kinase inhibition. Dose modifications have been made based on the phase 2 trial results; phase 3 clinical trials are ongoing. SUMMARY: Inhibiting downstream proteins involved in cellular signaling, such as p38, has not been successful to date. Inhibitors of more upstream protein-tyrosine kinases involved in cellular signaling appear to be viable molecular candidates for rheumatoid arthritis. If the results seen in phase 2 studies are confirmed in larger phase 3 studies, we may soon have new, oral DMARD therapies available.
Efficacy, pharmacodynamics, and safety of VX-702, a novel p38 MAPK inhibitor, in rheumatoid arthritis: results of two randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled clinical studies.[Pubmed:19404957]
Arthritis Rheum. 2009 May;60(5):1232-41.
OBJECTIVE: To assess the efficacy and safety of VX-702, a p38 MAPK inhibitor, in patients with active, moderate-to-severe rheumatoid arthritis (RA). METHODS: Two 12-week, double-blind, placebo-controlled studies of VX-702 were conducted in patients with active, moderate-to-severe RA. In the VeRA study, 313 patients received placebo or 2 daily doses of VX-702. In Study 304, 117 patients received placebo, daily VX-702, or twice weekly VX-702 in addition to concomitant methotrexate (MTX). Study end points included the proportion of patients meeting the American College of Rheumatology 20% improvement criteria (an ACR20 response), ACR50 and ACR70 responses, changes in the serum levels of biomarkers of inflammation, and safety assessments. RESULTS: The numerically superior ACR20 response rates among patients receiving VX-702 compared with those receiving placebo in both studies did not reach pairwise statistical significance at the highest doses in either study. At week 12 in the VeRA study, ACR20 response rates were 40%, 36%, and 28% among patients receiving 10 mg of VX-702, 5 mg of VX-702, and placebo, respectively. In Study 304, the response rates were 40%, 44%, and 22% for patients receiving 10 mg VX-702 daily plus MTX, 10 mg VX-702 twice weekly plus MTX, and placebo, respectively. Reductions in the levels of C-reactive protein, soluble tumor necrosis factor receptor p55, and serum amyloid A were observed as early as week 1 in both studies, but these levels rapidly returned to baseline values by week 4. The overall frequency of adverse events was similar between the VX-702 and placebo groups. In the VeRA study, serious infections were more frequent in the VX-702 groups compared with the placebo group (2.4% versus 0%) but not in Study 304 (2.6% versus 4.9%). CONCLUSION: The modest clinical efficacy plus the transient suppression of biomarkers of inflammation observed in this study suggest that p38 MAPK inhibition may not provide meaningful, sustained suppression of the chronic inflammation seen in RA.
Drug evaluation: VX-702, a MAP kinase inhibitor for rheumatoid arthritis and acute coronary syndrome.[Pubmed:17117592]
Curr Opin Investig Drugs. 2006 Nov;7(11):1020-5.
Vertex Pharmaceuticals Inc, in collaboration with Kissei Pharmaceutical Co Ltd, is developing VX-702, one of a series of second-generation, orally active p38 MAP kinase inhibitors, for the potential treatment of inflammation, rheumatoid arthritis and cardiovascular diseases. In June 2005, a phase II clinical trial of VX-702 was initiated in rheumatoid arthritis. In July 2006, Vertex was planning to file an IND in the second half of 2006.


