SulfamonomethoxineCAS# 1220-83-3 |
Quality Control & MSDS
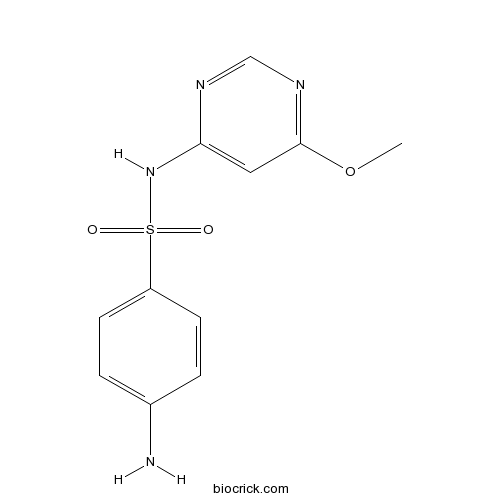
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 1220-83-3 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 5332 | Appearance | Powder |
| Formula | C11H12N4O3S | M.Wt | 280.3 |
| Type of Compound | N/A | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Solubility | DMSO : 100 mg/mL (356.76 mM; Need ultrasonic) H2O : < 0.1 mg/mL (insoluble) | ||
| Chemical Name | 4-amino-N-(6-methoxypyrimidin-4-yl)benzenesulfonamide | ||
| SMILES | COC1=NC=NC(=C1)NS(=O)(=O)C2=CC=C(C=C2)N | ||
| Standard InChIKey | WMPXPUYPYQKQCX-UHFFFAOYSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C11H12N4O3S/c1-18-11-6-10(13-7-14-11)15-19(16,17)9-4-2-8(12)3-5-9/h2-7H,12H2,1H3,(H,13,14,15) | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||

Sulfamonomethoxine Dilution Calculator

Sulfamonomethoxine Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 3.5676 mL | 17.838 mL | 35.6761 mL | 71.3521 mL | 89.1902 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.7135 mL | 3.5676 mL | 7.1352 mL | 14.2704 mL | 17.838 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.3568 mL | 1.7838 mL | 3.5676 mL | 7.1352 mL | 8.919 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0714 mL | 0.3568 mL | 0.7135 mL | 1.427 mL | 1.7838 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0357 mL | 0.1784 mL | 0.3568 mL | 0.7135 mL | 0.8919 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
Sulfamonomethoxine is a long acting sulfonamide antibacterial agent, used in blood kinetic studies,and blocks the synthesis of folic acid by inhibiting synthetase of dihydropteroate.
- 3-Phenyl-1-propanol
Catalog No.:BCC8102
CAS No.:122-97-4
- Phenylacetaldehyde
Catalog No.:BCN3819
CAS No.:122-78-1
- Cinnamyl cinnamate
Catalog No.:BCN4722
CAS No.:122-69-0
- (-)-Ampelopsin H
Catalog No.:BCC8842
CAS No.:
- Zingerone
Catalog No.:BCN1192
CAS No.:122-48-5
- Glycerine trioleate
Catalog No.:BCN2287
CAS No.:122-32-7
- Tetraethoxypropane
Catalog No.:BCN2221
CAS No.:122-31-6
- Sulfadimethoxine
Catalog No.:BCC5159
CAS No.:122-11-2
- (±)-Anatoxin A fumarate
Catalog No.:BCC6796
CAS No.:1219922-30-1
- PF 4778574
Catalog No.:BCC6322
CAS No.:1219633-99-4
- 4,5-Diepipsidial A
Catalog No.:BCN3920
CAS No.:1219603-97-0
- PKA inhibitor fragment (6-22) amide
Catalog No.:BCC1042
CAS No.:121932-06-7
- Niazirin
Catalog No.:BCN7300
CAS No.:122001-32-5
- Cyhalofop
Catalog No.:BCC5474
CAS No.:122008-78-0
- PLP (139-151)
Catalog No.:BCC5920
CAS No.:122018-58-0
- Monomethyl lithospermate B
Catalog No.:BCN2533
CAS No.:122021-74-3
- Khayalenoid E
Catalog No.:BCN6111
CAS No.:1220508-29-1
- [bAla8]-Neurokinin A(4-10)
Catalog No.:BCC7137
CAS No.:122063-01-8
- 2'-O-Acetylsprengerinin C
Catalog No.:BCN6655
CAS No.:1220707-33-4
- Charantadiol A
Catalog No.:BCN3483
CAS No.:1220890-23-2
- 3,4-Dihydro-3,4-dihydroxynaphthalen-1(2H)-one
Catalog No.:BCN1602
CAS No.:1220891-22-4
- Auraptenol
Catalog No.:BCN6113
CAS No.:1221-43-8
- 2-Deoxy-2,2-difluoro-D-erythro-pentafuranous-1-ulose-3,5-dibenzoate
Catalog No.:BCC8575
CAS No.:122111-01-7
- Gemcitabine HCl
Catalog No.:BCC1076
CAS No.:122111-03-9
Molecularly imprinted silica gel incorporated with agarose polymer matrix as mixed matrix membrane for separation and preconcentration of sulfonamide antibiotics in water samples.[Pubmed:30952293]
Talanta. 2019 Jul 1;199:522-531.
Molecularly imprinted silica gel (MISG) was incorporated through dispersion in agarose polymer matrix to form a mixed matrix membrane (MMM) and was applied for the determination of three sulfonamide antibiotic compounds (i.e. sulfamethoxazole (SMX), Sulfamonomethoxine (SMM), and sulfadiazine (SDZ)) from environmental water samples. Several important microextraction conditions, such as type of desorption solvent, extraction time, amount of sorbent, sample volume, pH, and effect of desorption time, were comprehensively optimized. A preconcentration factors of >/=20 was achieved by the extraction of 12.5mL of water samples using the developed method. This microextraction-HPLC method demonstrated good linearity (1-500mugL(-1)) with a coefficient of determination (R(2)) of 0.9959-0.9999, low limits of detection (0.06-0.17mugL(-1)) and limits of quantification (0.20-0.56mugL(-1)), good analyte recoveries (80-96%), and acceptable relative standard deviations (< 10%) under the optimized conditions. The method is systematically compared to those reported in the literature.
Using ionic liquid monomer to improve the selective recognition performance of surface imprinted polymer for sulfamonomethoxine in strong polar medium.[Pubmed:30709623]
J Chromatogr A. 2019 May 10;1592:38-46.
Molecularly imprinted polymers (MIPs) synthesized by conventional functional monomers have poor specific recognition ability in strong polar solvent, which is not favorable to their applications in separation and analysis. In this work, an ionic liquid functional monomer, 1-allyl-3-vinylimidazolium chloridize, is introduced to prepare Sulfamonomethoxine imprinted polymer on the surface of silica carriers in methanol. (1)H NMR and (35)Cl NMR spectroscopy is performed to discuss the interactions between template and the functional monomer. The rebinding experiments show that the MIP has excellent selectivity towards sulfonamide antibiotic (Sulfamonomethoxine, sulfamethoxazole and sulfadiazine) in methanol. From (1)H NMR and (35)Cl NMR analysis and selective adsorption results, it was inferred that hydrogen bond, electrostatic and pi-pi interactions are the driving force for the selective recognition of MIP in methanol. Combined solid phase extraction (SPE) with HPLC detection, 98.0-108.0% of Sulfamonomethoxine have been extracted by MIP-SPE cartridge from the mixture of Sulfamonomethoxine, diphenylamine and N-butylpyridinium chloride. Under optimal condition, the proposed MIP-SPE column can response Sulfamonomethoxine linearly in the concentration range from 3.0-1.0x10(4) mug L(-1), and the established MIP-SPE-HPLC system has been successfully applied for extraction and analysis of Sulfamonomethoxine in soil and sediment with recoveries ranging from 95.0% to 105.0%.
A Class-Selective Immunoassay for Sulfonamides Residue Detection in Milk Using a Superior Polyclonal Antibody with Broad Specificity and Highly Uniform Affinity.[Pubmed:30691168]
Molecules. 2019 Jan 26;24(3). pii: molecules24030443.
The development of multianalyte immunoassays with an emphasis on food safety has attracted increasing interest, due to its high target throughput, short detection time, reduced sample consumption, and low overall cost. In this study, a superior polyclonal antibody (pAb) against sulfonamides (SAs) was raised by using a bioconjugate of bovine serum albumin with a rationally designed hapten 4-[(4-aminophenyl) sulfonyl-amino]-2-methoxybenzoic acid (SA10-X). The results showed that the pAb could recognize 19 SAs with 50% inhibition (IC50) below 100 microg L(-1) and a recognition profile for SAs containing, either a five-atom ring or a six-atom ring, with highly uniform affinity. A three-dimensional quantitative structure-activity relationship analysis indicated that the electrostatic features of SAs play a considerably important role, during recognition with pAb than stereochemical effects. Skimmed milk samples were directly diluted five times before analysis. After optimization, the limit of detection for Sulfamonomethoxine, sulfamethoxazole, sulfaquinoxaline, sulfadimethoxine, and sulfamethazine were 1.00, 1.25, 2.95, 3.35, and 6.10 microg L(-1), respectively. The average recoveries for these 5 SAs were 72.0(-)107.5% with coefficients of variation less than 14.1%. The established method, based on pAb, with broad specificity and uniform affinity, offered a simple, sensitive, and high-throughput screening tool for the detection of multi-SAs in milk samples.
Chitosan Grafted With beta-Cyclodextrin: Synthesis, Characterization, Antimicrobial Activity, and Role as Absorbefacient and Solubilizer.[Pubmed:30687698]
Front Chem. 2019 Jan 10;6:657.
We synthesized chitosan grafted with beta-cyclodextrin (CD-g-CS) from mono-6-deoxy-6-(p-toluenesulfonyl)-beta-cyclodextrin and chitosan. Two different amounts of immobilized beta-cyclodextrin (beta-CD) on CD-g-CS (QCD: 0.643 x 10(3) and 0.6 x 10(2) mumol/g) were investigated. The results showed that the amino contents of CD-g-CS with QCD = 0.643 x 10(3) and 0.6 x 10(2) mumol/g were 6.34 +/- 0.072 and 9.41 +/- 0.055%, respectively. Agar diffusion bioassay revealed that CD-g-CS (QCD = 0.6 x 10(2) mumol/g) was more active against Staphylococcus xylosus and Escherichia coli than CD-g-CS (QCD = 0.643 x 10(3) mumol/g). Cell membrane integrity tests and scanning electron microscopy observation revealed that the antimicrobial activity of CD-g-CS was attributed to membrane disruption and cell lysis. Uptake tests showed that CD-g-CS promoted the uptake of doxorubicin hydrochloride by S. xylosus, particularly for CD-g-CS with QCD = 0.6 x 10(2) mumol/g, and the effect was concentration dependent. CD-g-CS (QCD = 0.6 x 10(2) and 0.643 x 10(3) mumol/g) also improved the aqueous solubilities of sulfadiazine, Sulfamonomethoxine, and sulfamethoxazole. These findings provide a clear understanding of CD-g-CS and are of great importance for reducing the dosage of antibiotics and antibiotic residues in animal-derived foods. The results also provide a reliable, direct, and scientific theoretical basis for its wide application in the livestock industry.
Determination of sulfamonomethoxine in tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus x Oreochromis mossambicus) by liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry and its application pharmacokinetics study.[Pubmed:30648589]
J Food Drug Anal. 2019 Jan;27(1):339-346.
A precise and reliable analytical method to measure trace levels of Sulfamonomethoxine (SMM) and N(4)-acetyl metabolite in tilapia samples using liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry was developed. Optimized chromatographic separation was performed on C18 reversed-phase columns using gradient elution with methanol and 5 mmol/L of an ammonium acetate aqueous solution (adjusted to pH 3.5 using formic acid). This study investigated the pharmacokinetic properties and tissue distribution of SMM and its major metabolite N(4)-acetyl Sulfamonomethoxine (AC-SMM) in tilapia after a single dose of 100 mg kg(-1) body weight of orally administered SMM. Blood and tissues were collected between 0.5 and 192 h with 14 total sampling time points. SMM was rapidly absorbed, and extensively distributed in the bile and liver through systemic circulation. Enterohepatic circulation of SMM was observed in the tilapia body. Acetylation percentages were 45% (blood), 90% (liver), 62% (kidney), 98% (bile), and 52% (muscle). High concentrations of AC-SMM accumulated in the tilapia bile. At 192 h, AC-SMM concentration in the bile remained at 4710 mug kg(-1). The ke value of AC-SMM (0.015 h(-1)) in the blood was lower than that of SMM (0.032 h(-1)). This study demonstrated effective residue monitoring and determined the pharmacokinetic properties of SMM and AC-SMM in tilapia.
A new ionic liquid surface-imprinted polymer for selective solid-phase-extraction and determination of sulfonamides in environmental samples.[Pubmed:30488649]
J Sep Sci. 2019 Feb;42(3):725-735.
Toward improving the selective adsorption performance of molecularly imprinted polymers in strong polar solvents, in this work, a new ionic liquid functional monomer, 1-butyl-3-vinylimidazolium bromide, was used to synthesize sulfamethoxazole imprinted polymer in methanol. The resulting molecularly imprinted polymer was characterized by Fourier transform infrared spectra and scanning electron microscopy, and the rebinding mechanism of the molecularly imprinted polymer for sulfonamides was studied. A static equilibrium experiment revealed that the as-obtained molecularly imprinted polymer had higher molecular recognition for sulfonamides (e.g., sulfamethoxazole, Sulfamonomethoxine, and sulfadiazine) in methanol; however, its adsorption of interferent (e.g., diphenylamine, metronidazole, 2,4-dichlorophenol, and m-dihydroxybenzene) was quite low. (1) H NMR spectroscopy indicated that the excellent recognition performance of the imprinted polymer was based primarily on hydrogen bond, electrostatic and pi-pi interactions. Furthermore, the molecularly imprinted polymer can be employed as a solid phase extraction sorbent to effectively extract sulfamethoxazole from a mixed solution. Combined with high-performance liquid chromatography analysis, a valid molecularly imprinted polymer-solid phase extraction protocol was established for extraction and detection of trace sulfamethoxazole in spiked soil and sediment samples, and with a recovery that ranged from 93-107%, and a relative standard deviation of lower than 9.7%.
Occurrence, fate and mass loadings of antibiotics in two swine wastewater treatment systems.[Pubmed:29929305]
Sci Total Environ. 2018 Oct 15;639:1421-1431.
Antibiotics are widely applied in livestock industry to prevent or treat animal diseases. However, those antibiotics are poorly metabolized in livestock animals, most of them being excreted via feces or urine. Hence we need to understand the removal of antibiotics in swine farm wastewater treatment systems. This study investigated occurrence and fate of various antibiotics in two full-scale swine farm wastewater treatment systems (Farm A: anaerobic digester-A(2)/O-lagoon; Farm B: upflow anaerobic sludge blanket (UASB)-(A/O)(2)-lagoon). The results showed the presence of 25 antibiotics out of 40 target antibiotics in the wastewater and sludge samples from the two farms. In Farm A, Sulfamonomethoxine, sulfachlorpyridazine, oxytetracycline and lincomycin were predominant in the influent with concentrations up to 166+/-3.64mug/L, while in the dewatered sludge chlortetracycline, oxytetracycline, tetracycline and norfloxacin were the predominant target compounds with concentrations up to 29.2+/-3.74mug/g. In Farm B, high concentrations (up to 3630+/-1040mug/L) of sulfachlorpyridazine, Sulfamonomethoxine and lincomycin were detected in the influent, and the predominant target antibiotics detected in the dewater sludge were similar to those in Farm A, with concentrations up to 28.6+/-0.592mug/g. The aqueous removal rates for the total antibiotics were >99.0% in the wastewater treatment plants of both farms. Among a series of treatment units, the anaerobic digester in Farm A and UASB in Farm B made a significant contribution to the elimination of the target antibiotics from the animal wastewater. The daily mass loadings of total antibiotics in the manure, influent, dewatered sludge and effluent were 17.1, 28.0, 2.53, and 0.0730g/d for Farm A and 24.5, 354, 3.17, and 0.293g/d for Farm B. The full-scale swine wastewater treatment facilities could effectively remove antibiotics from swine wastewater, but the dewatered sludge needs to be further treated before disposal on land.
Source estimation of pharmaceuticals based on catchment population and in-stream attenuation in Yodo River watershed, Japan.[Pubmed:29751447]
Sci Total Environ. 2018 Feb 15;615:964-971.
Fifty-five pharmaceuticals were monitored at four rivers and inlets and/or outlets of three sewage treatment plants (STPs) in Yodo River watershed, Japan over 17 sampling events. Twenty-six quantified pharmaceuticals were classified by source and fate. The load per person (LPP) of nine pharmaceuticals, including six with observed mass balance in studied river stretch of <80%, was appreciably lower in river water (RW) than in the effluent (EF) of STPs (RW/EF <0.5), indicating that they were susceptible to in-stream attenuation in the study area, while the others were relatively conservative. The LPP of 12 pharmaceuticals in RW were within +/-50% of that in EF. Because their mass loadings in rivers were correlated with human population in the catchment and most people use the sewer system, the major source of the 12 pharmaceuticals was considered to be STPs. The LPP of the three most labile pharmaceuticals in STPs (caffeine, theophylline, and acetaminophen) was >1.5 in RW/EF and <1.0 in RW/influent (IF) of STPs. Poorly treated sewage discharged from households without using the sewer system was considered to be influential source of the three pharmaceuticals. The LPP (RW/EF) of caffeine, a pharmaceutical contained in food and beverage, was considerably higher than that of the other two, and this is attributable to untreated gray water discharged at households using the night-soil treatment system. The LPP of two veterinary drugs (Sulfamonomethoxine and lincomycin) were >1.5 (RW/EF) and >1.0 (RW/IF). Their mass loadings in rivers showed a positive correlation with swine population in the catchment, although Sulfamonomethoxine is equally used in both cattle and swine farming. This was attributable to application of cattle excrement as manure, and lability of Sulfamonomethoxine during composting processes. The major source of the two veterinary drugs was considered to be on-site treatment facilities of swine urine.
Freeze-thaw approach: A practical sample preparation strategy for residue analysis of multi-class veterinary drugs in chicken muscle.[Pubmed:29573149]
J Sep Sci. 2018 Jun;41(11):2461-2472.
Seven drugs from different classes, namely, fluoroquinolones (enrofloxacin, ciprofloxacin, sarafloxacin), sulfonamides (sulfadimidine, Sulfamonomethoxine), and macrolides (tilmicosin, tylosin), were used as test compounds in chickens by oral administration, a simple extraction step after cryogenic freezing might allow the effective extraction of multi-class veterinary drug residues from minced chicken muscles by mix vortexing. On basis of the optimized freeze-thaw approach, a convenient, selective, and reproducible liquid chromatography with tandem mass spectrometry method was developed. At three spiking levels in blank chicken and medicated chicken muscles, average recoveries of the analytes were in the range of 71-106 and 63-119%, respectively. All the relative standard deviations were <20%. The limits of quantification of analytes were 0.2-5.0 ng/g. Regardless of the chicken levels, there were no significant differences (P > 0.05) in the average contents of almost any of the analytes in medicated chickens between this method and specific methods in the literature for the determination of specific analytes. Finally, the developed method was successfully extended to the monitoring of residues of 55 common veterinary drugs in food animal muscles.
Antibiotics in Crab Ponds of Lake Guchenghu Basin, China: Occurrence, Temporal Variations, and Ecological Risks.[Pubmed:29562694]
Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2018 Mar 19;15(3). pii: ijerph15030548.
Antibiotics are widely used in aquaculture, however, this often results in undesirable ecological effects. To evaluate the occurrence, temporal variations, and ecological risk of antibiotics in five crab ponds of Lake Guchenghu Basin, China, 44 antibiotics from nine classes were analyzed by rapid resolution liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry (RRLC-MS/MS). Twelve antibiotics belonging to six classes were detected in the aqueous phase of five crab ponds, among which sulfonamides and macrolides were the predominant classes, and six compounds (Sulfamonomethoxine, sulfadiazine, trimethoprim, erythromycin-H(2)O, monensin, and florfenicol) were frequently detected at high concentrations. In general, the antibiotic levels varied between different crab ponds, with the average concentrations ranging from 122 to 1440 ng/L. The antibiotic concentrations in crab ponds exhibited obvious seasonal variations, with the highest concentration and detection frequency detected in summer. Multivariate analysis showed that antibiotic concentrations were significantly correlated with environmental variables, such as total organic carbon, phosphate, ammonia nitrogen, and pH. Sulfadiazine, clarithromycin, erythromycin-H(2)O, and ciprofloxacin posed a high risk to algae, while the mixture of antibiotics could pose a high risk to aquatic organisms in the crab ponds. Overall, the usage of antibiotics in farming ponds should be comprehensively investigated and controlled to preserve a healthy aquaculture ecosystem.
Ultrasensitive Immunochromatographic Strip for Fast Screening of 27 Sulfonamides in Honey and Pork Liver Samples Based on a Monoclonal Antibody.[Pubmed:28844139]
J Agric Food Chem. 2017 Sep 20;65(37):8248-8255.
Group-specific monoclonal antibodies (Mabs) with selectivity for 27 sulfonamides were developed based on new combinations of immunogen and coating antigen. The Mab was able to recognize 27 sulfonamides with 50% inhibition concentration (IC50) values ranging from 0.15 to 15.38 mug/L. In particular, the IC50 values for five sulfonamides (sulfamethazine, sulfaquinoxaline, Sulfamonomethoxine, sulfadimethoxine, and sulfamethoxazole) were 0.51, 0.15, 0.56, 0.54, and 2.14 mug/L, respectively. On the basis of the Mab, an immunochromatographic lateral flow strip test was established for rapid screening of sulfonamides in honey samples. The visual limit of detection of the strip test for most sulfonamides in spiked honey samples was below 10 mug/kg, satisfying the requirements of authorities. Positive honey and pork liver samples, which had been confirmed by high-performance liquid chromatography/mass spectrometry, were used to validate the reliability of the proposed strip test. The immunochromatographic lateral flow strip test provides a rapid and convenient method for fast screening of sulfonamides in honey samples.
Removal behaviors of sulfamonomethoxine and its degradation intermediates in fresh aquaculture wastewater using zeolite/TiO2 composites.[Pubmed:28750362]
J Hazard Mater. 2017 Oct 15;340:427-434.
Removal efficiencies of Sulfamonomethoxine (SMM) and its degradation intermediates formed by treatment with zeolite/TiO2 composites through adsorption and photocatalysis were investigated in fresh aquaculture wastewater (FAWW). Coexistent substances in the FAWW showed no inhibitory effects against SMM adsorption. Although coexistent substances in the FAWW inhibited the photocatalytic decomposition of SMM, the composites mitigated the inhibition, possibly because of concentration of SMM on their surface by adsorption. LC/MS/MS analyses revealed that hydroxylation of amino phenyl and pyrimidinyl portions, transformation of the amino group in the amino phenyl portion into a nitroso group, and substitution of the methoxy group with a hydroxyl group occurring in the initial reaction resulted in the formation of various intermediates during the photocatalysis of SMM. All detected intermediates had a ring structure, and almost all intermediates disappeared at the same time SMM was completely decomposed. Ph-OH formed by hydroxylation of the phenyl portion was detected upon decomposition of SMM during photocatalysis. The removal of Ph-OH by the composites proceeded more rapidly than that by TiO2 alone under ultraviolet irradiation. The SMM and Ph-OH were completely degraded by the composites within 30min, showing that the zeolite/TiO2 composites were effective in removing SMM and its intermediates from FAWW.
Occurrence and human dietary assessment of sulfonamide antibiotics in cultured fish around Tai Lake, China.[Pubmed:28593547]
Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2017 Jul;24(21):17493-17499.
As the most important fishery medicines, sulfonamides are widely used to prevent diseases caused by pathogens in aquaculture. However, relatively little is known about the residues and dietary risks associated with cultured fish around Tai Lake. In the present study, a sampling strategy for a complete aquaculture period was conducted. Specifically, 12 selected sulfonamide antibiotics were measured among 116 fish samples recruited from four sampling periods, four species, four areas, and 18 fish ponds. All 12 antibiotics were detected at detection frequencies of 4.31-28.45%. Total sulfonamides were detected in 77.59% of the fish samples, with 57.76% of fish samples containing from 0.1 to 10 mug kg(-1). Sulfadiazine (SDZ), sulfamethoxazole (SMZ), sulfamethazine (SDD), and Sulfamonomethoxine (SMM) were the main types of antibiotics used, and these were present at high concentrations (>100 mug kg(-1)) with high occurrences, especially in the middle of the aquaculture season. Dietary assessment showed that residual antibiotics in all fish that were being sent to market were far below the maximum residue limit (MRL) of total sulfonamides and that there was almost no risk associated with fish consumption. The results of the present study will facilitate development of effective measures to produce safe aquatic products and meaningful suggestions for consuming aquatic products.
Removal of antibiotics from piggery wastewater by biological aerated filter system: Treatment efficiency and biodegradation kinetics.[Pubmed:28432952]
Bioresour Technol. 2017 Aug;238:70-77.
This study aimed to investigate the removal efficiency and mechanism for antibiotics in swine wastewater by a biological aerated filter system (BAF system) in combination with laboratory aerobic and anaerobic incubation experiments. Nine antibiotics including Sulfamonomethoxine, sulfachloropyridazine, sulfamethazine, trimethoprim, norfloxacin, ofloxacin, lincomycin, leucomycin and oxytetracycline were detected in the wastewater with concentrations up to 192,000ng/L. The results from this pilot study showed efficient removals (>82%) of the conventional wastewater pollutants (BOD5, COD, TN and NH3-N) and the detected nine antibiotics by the BAF system. Laboratory simulation experiment showed first-order dissipation kinetics for the nine antibiotics in the wastewater under aerobic and anaerobic conditions. The biodegradation kinetic parameters successfully predicted the fate of the nine antibiotics in the BAF system. This suggests that biodegradation was the dominant process for antibiotic removal in the BAF system.
Prevalence and drug resistance of avian Eimeria species in broiler chicken farms of Zhejiang province, China.[Pubmed:28339722]
Poult Sci. 2017 Jul 1;96(7):2104-2109.
In this study, coccidia were isolated and identified from 5 main poultry farms located in Zhejiang province, eastern China. The overall prevalence of Eimeria spp. was 30.7% (95 of 310). Five common species were observed: E. tenella, E. acervulina, E. maxima, E. necatrix, and E. mitis. Two isolates (HZ and QZ) were tested for sensitivity to 8 anticoccidial drugs using 4 indexes including anticoccidial index (ACI), percent of optimum anticoccidial activity (POAA), reduction of lesion scores (RLS), and relative oocyst production (ROP): sulfachloropyrazine, toltrazuril, diclazuril, Sulfamonomethoxine/trimethoprim, and amprolium; sulfaquinoxaline/sulfadimethoxine, nicarbazin, and halofuginone. The results showed that the 2 isolates have developed various degrees of resistance to most of the tested drugs. The multi-resistance coccidia are a potential threat to local poultry farming. Rotation of anticoccidial drugs and shuttle programs are recommended to prevent further economic losses caused by coccidiosis.


