PsoralenCAS# 66-97-7 |
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 66-97-7 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 6199 | Appearance | White-pale yellow powder |
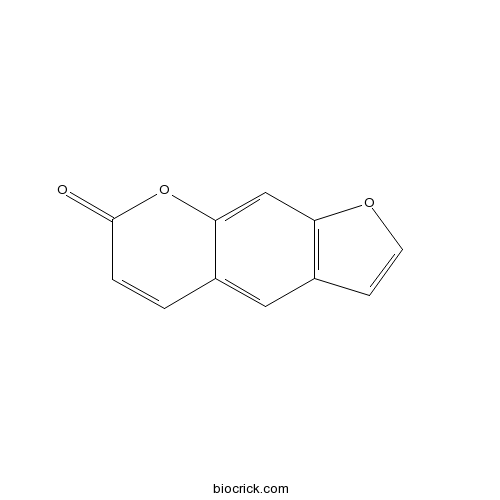
| Formula | C11H6O3 | M.Wt | 186.2 |
| Type of Compound | Coumarins | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Synonyms | Ficusin; Furocoumarin | ||
| Solubility | DMSO : ≥ 1.9 mg/mL (10.21 mM) *"≥" means soluble, but saturation unknown. | ||
| Chemical Name | furo[3,2-g]chromen-7-one | ||
| SMILES | C1=CC(=O)OC2=CC3=C(C=CO3)C=C21 | ||
| Standard InChIKey | ZCCUUQDIBDJBTK-UHFFFAOYSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C11H6O3/c12-11-2-1-7-5-8-3-4-13-9(8)6-10(7)14-11/h1-6H | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | Psoralen is a naturally occurring furocoumarin that intercalates with DNA, inhibiting DNA synthesis and cell division. Psoralen has immunomodulatory properties on Th2 response in vitro, it can remit the degeneration of lumbar intervertebral disc induced by IL-1β to some extent, and affect the related factors of IL-1β signaling pathway. Psoralen may be feasible for reversing the multidrug resistance by inhibiting ABCB1 gene and protein expression. Psoralen ultraviolet A is an effective treatment for psoriasis. |
| Targets | IL Receptor | HIV | EGFR | ABCB1 | GATA-3 |
| In vitro | Psoralen reverses docetaxel-induced multidrug resistance in A549/D16 human lung cancer cells lines.[Pubmed: 24703328]Phytomedicine. 2014 Jun 15;21(7):970-7.Chemotherapy is the recommended treatment for advanced-stage cancers. However, the emergence of multidrug resistance (MDR), the ability of cancer cells to become simultaneously resistant to different drugs, limits the efficacy of chemotherapy. Previous studies have shown that herbal medicine or natural food may be feasible for various cancers as potent chemopreventive drug. This study aims to explore the capablility of reversing the multidrug resistance of docetaxel (DOC)-resistant A549 cells (A549/D16) of Psoralen and the underlying mechanisms.
Effects of psoralen on chondrocyte degeneration in lumbar intervertebral disc of rats.[Pubmed: 25796142]Pak J Pharm Sci. 2015 Mar;28(2 Suppl):667-70.Discuss the internal mechanism of delaying degeneration of lumber intervertebral disc.
|
| In vivo | Evaluation of psoralen ethosomes for topical delivery in rats by using in vivo microdialysis.[Pubmed: 24489470]Int J Nanomedicine. 2014 Jan 23;9:669-78.This study aimed to improve skin permeation and deposition of Psoralen by using ethosomes and to investigate real-time drug release in the deep skin in rats.
|
| Kinase Assay | Psoralens potentiate ultraviolet light-induced inhibition of epidermal growth factor binding.[Pubmed: 3490664 ]Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Nov;83(21):8211-5.The Psoralens, when activated by ultraviolet light of 320-400 nm (UVA light), are potent modulators of epidermal cell growth and differentiation. Previously, we reported that, in mammalian cells, these compounds bind to specific saturable high-affinity cellular receptor sites.
|
| Animal Research | Effects of Psoraleae fructus and its major component psoralen on Th2 response in allergic asthma.[Pubmed: 24871658]Am J Chin Med. 2014;42(3):665-78.This study is aimed to evaluate the effects of Psoraleae fructus (PF) on Th2 responses in a rat model of asthma in vivo and Psoralen, a major constituent in PF, on Th2 responses in vitro.
|
| Structure Identification | Nucleic Acids Res. 1996 Feb 1; 24(3): 509–514.Psoralen crosslinking between human immunodeficiency virus type 1 RNA and primer tRNA3(Lys).[Reference: WebLink]Initiation of reverse transcription is a crucial step of retroviral infection. In HIV-1, it involves hybridization of the 18 3′-terminal nucleotides of the primer tRNA3Lys to the primer binding site (PBS) of the viral RNA. Moreover, additional interactions between the two RNAs were recently evidenced [Isel et al. (1995) J. Mol. Biol. 247, 25269–25272].
|

Psoralen Dilution Calculator

Psoralen Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 5.3706 mL | 26.8528 mL | 53.7057 mL | 107.4114 mL | 134.2642 mL |
| 5 mM | 1.0741 mL | 5.3706 mL | 10.7411 mL | 21.4823 mL | 26.8528 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.5371 mL | 2.6853 mL | 5.3706 mL | 10.7411 mL | 13.4264 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.1074 mL | 0.5371 mL | 1.0741 mL | 2.1482 mL | 2.6853 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0537 mL | 0.2685 mL | 0.5371 mL | 1.0741 mL | 1.3426 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
Psoralen(Furocoumarin) is an active ingredient from Fructus Psoraleae; has anticancer activity. IC50 value: Target: in vitro: Psoralen dosages of 1-10 μM exhibited low cytotoxicity toward chondrocytes. However, a dosage of 100 μM suppressed the proliferation of chondrocytes. Different concentrations of psoralen treatments on chondrocytes revealed that GAG and Type II collagen synthesis increased, especially at 100 μM, by 0.39-fold and 0.48-fold, respectively, on day 3, and by 0.51-fold and 0.56-fold, respectively, on day 9 [1]. in vivo: Tumor volume inhibition rates were 43.75% and 40.18%, respectively, in the psoralen and isopsoralen low-dose groups, and tumor weight inhibition rates were 38.83% and 37.77%. Tumor volume inhibition rates were 67.86% and 66.96%, respectively, in the psoralen and isopsoralen high-dose groups, and tumor weight inhibition rates were 49.47% and 47.87% [2]. psoralen can inhibit metastasis of breast cancer to bone in vivo. Histological, molecular biological, and imaging analyses revealed that psoralen inhibits bone metastases in mice [3].
References:
[1]. Xu K, et al. Psoralen activates cartilaginous cellular functions of rat chondrocytes in vitro. Pharm Biol. 2014 Dec 4:1-6.
[2]. Lu H, et al. Isolation and purification of psoralen and isopsoralen and their efficacy and safety in the treatment of osteosarcoma in nude rats. Afr Health Sci. 2014 Sep;14(3):641-7.
[3]. Wu C, et al. Psoralen inhibits bone metastasis of breast cancer in mice. Fitoterapia. 2013 Dec;91:205-10.
- D-Glucosamine hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCN5982
CAS No.:66-84-2
- Cycloheximide
Catalog No.:BCC3653
CAS No.:66-81-9
- Dicoumarol
Catalog No.:BCC9225
CAS No.:66-76-2
- Strophantidin
Catalog No.:BCC8255
CAS No.:66-28-4
- Uracil
Catalog No.:BCN4211
CAS No.:66-22-8
- Punicalin
Catalog No.:BCN4961
CAS No.:65995-64-4
- Punicalagin
Catalog No.:BCN1037
CAS No.:65995-63-3
- Isogarciniaxanthone E
Catalog No.:BCN4205
CAS No.:659747-28-1
- Micranoic acid A
Catalog No.:BCN4204
CAS No.:659738-08-6
- AMG-517
Catalog No.:BCC1052
CAS No.:659730-32-2
- Esculentoside C
Catalog No.:BCN5012
CAS No.:65931-92-2
- Dienogest
Catalog No.:BCC4489
CAS No.:65928-58-7
- H-Nva-OH
Catalog No.:BCC2643
CAS No.:6600-40-4
- Cirsimaritin
Catalog No.:BCN4206
CAS No.:6601-62-3
- 6-Demethoxytangeretin
Catalog No.:BCN3844
CAS No.:6601-66-7
- (5Z)-7-Oxozeaenol
Catalog No.:BCC7724
CAS No.:66018-38-0
- H-D-Arg(NO2)-OH
Catalog No.:BCC2871
CAS No.:66036-77-9
- Glycyrin
Catalog No.:BCN7681
CAS No.:66056-18-6
- Licoisoflavone A
Catalog No.:BCN2929
CAS No.:66056-19-7
- Gomisin H
Catalog No.:BCN3902
CAS No.:66056-20-0
- Angeloylgomisin H
Catalog No.:BCN2843
CAS No.:66056-22-2
- Benzoylgomisin H
Catalog No.:BCN7242
CAS No.:66056-23-3
- Licoisoflavone B
Catalog No.:BCN6695
CAS No.:66056-30-2
- Licoisoflavanone
Catalog No.:BCN6856
CAS No.:66067-26-3
Comparison of ethosomes and liposomes for skin delivery of psoralen for psoriasis therapy.[Pubmed:24907596]
Int J Pharm. 2014 Aug 25;471(1-2):449-52.
Recent reports have indicated that psoriasis may be caused by malfunctioning dermal immune cells, and Psoralen ultraviolet A (PUVA) is an effective treatment for this chronic disease. However, conventional topical formulations achieve poor drug delivery across patches of psoriasis to their target sites. The present study describes the development of a novel Psoralen transdermal delivery system employing ethosomes, flexible vesicles that can penetrate the stratum corneum and target deep skin layers. An in vitro skin permeation study showed that the permeability of Psoralen-loaded ethosomes was superior to that of liposomes. Using ethosomes, Psoralen transdermal flux and skin deposition were 38.89+/-0.32 mug/cm(2)/h and 3.87+/-1.74 mug/cm(2), respectively, 3.50 and 2.15 times those achieved using liposomes, respectively. The ethosomes and liposomes were found to be safe following daily application to rat skin in vivo, for 7 days. The ethosomes showed better biocompatibility with human embryonic skin fibroblasts than did an equivalent ethanol solution, indicating that the phosphatidylcholine present in ethosome vesicles improved their biocompatibility. These findings indicated that ethosomes could potentially improve the dermal and transdermal delivery of Psoralen and possibly of other drugs requiring deep skin delivery.
Psoralen reverses docetaxel-induced multidrug resistance in A549/D16 human lung cancer cells lines.[Pubmed:24703328]
Phytomedicine. 2014 Jun 15;21(7):970-7.
Chemotherapy is the recommended treatment for advanced-stage cancers. However, the emergence of multidrug resistance (MDR), the ability of cancer cells to become simultaneously resistant to different drugs, limits the efficacy of chemotherapy. Previous studies have shown that herbal medicine or natural food may be feasible for various cancers as potent chemopreventive drug. This study aims to explore the capablility of reversing the multidrug resistance of docetaxel (DOC)-resistant A549 cells (A549/D16) of Psoralen and the underlying mechanisms. In this study, results showed that the cell viability of A549/D16 subline is decreased when treated with Psoralen plus DOC, while Psoralen has no effect on the cell proliferation on A549 and A549/D16 cells. Furthermore, mRNA and proteins levels of ABCB1 were decreased in the presence of Psoralen, while decreased ABCB1 activity was also revealed by flow cytometry. Based on these results, we believe that Psoralen may be feasible for reversing the multidrug resistance by inhibiting ABCB1 gene and protein expression. Such inhibition will lead to a decrease in ABCB1 activity and anti-cancer drug efflux, which eventually result in drug resistance reversal and therefore, sensitizing drug-resistant cells to death in combination with chemotherapeutic drugs.
Effects of Psoraleae fructus and its major component psoralen on Th2 response in allergic asthma.[Pubmed:24871658]
Am J Chin Med. 2014;42(3):665-78.
This study is aimed to evaluate the effects of Psoraleae fructus (PF) on Th2 responses in a rat model of asthma in vivo and Psoralen, a major constituent in PF, on Th2 responses in vitro. A rat model of asthma was established by sensitization and challenged with ovalbumin (OVA). Airway hyperresponsiveness was detected by direct airway resistance analysis. Lung tissues were examined for cell infiltration and mucus hypersecretion. Bronchoalveolar lavage fluid (BALF) was assessed for cytokine levels. In vitro study, Th2 cytokine production was evaluated in the culture supernatant of D10.G4.1 (D10 cells) followed by the determination of cell viability, meanwhile Th2 transcription factor GATA-3 expression in D10 cells was also determined. The oral administration of PF significantly reduced airway hyperresponsiveness (AHR) to aerosolized methacholine and decreased IL-4 and IL-13 levels in the BALF. Histological studies showed that PF markedly inhibited inflammatory infiltration and mucus secretion in the lung tissues. In vitro study, Psoralen significantly suppressed Th2 cytokines of IL-4, IL-5 and IL-13 by ConA-stimulated D10 cells without inhibitory effect on cell viability. Furthermore, GATA-3 protein expression was also markedly reduced by Psoralen. This study demonstrated that PF exhibited inhibitory effects on hyperresponsiveness and airway inflammation in a rat model of asthma, which was associated with the suppression of Th2 response. Psoralen, a major constituent of PF, has immunomodulatory properties on Th2 response in vitro, which indicated that Psoralen might be a critical component of PF for its therapeutic effects.
Psoralens potentiate ultraviolet light-induced inhibition of epidermal growth factor binding.[Pubmed:3490664]
Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Nov;83(21):8211-5.
The Psoralens, when activated by ultraviolet light of 320-400 nm (UVA light), are potent modulators of epidermal cell growth and differentiation. Previously, we reported that, in mammalian cells, these compounds bind to specific saturable high-affinity cellular receptor sites. In the present studies, we demonstrate that binding of Psoralens to their receptors followed by UVA light activation is associated with inhibition of epidermal growth factor (EGF) receptor binding. Inhibition of EGF binding, which required UVA light, was rapid and dependent on the dose of UVA light (0.5-2.0 J/cm2), as well as the concentration of Psoralens (10 nM to 1 microM). Higher doses of UVA light (2.0-6.0 J/cm2) by themselves were also inhibitory, indicating that Psoralens potentiate the UVA-induced inhibition of EGF binding. A number of biologically active analogs of Psoralen, including 8-methoxyPsoralen, 5-methoxyPsoralen, and 4,5',8-trimethylPsoralen, when activated by UVA light, were found to be inhibitors of binding. Inhibition of EGF binding by Psoralens was observed in a variety of human and mouse cell culture lines known to possess Psoralen receptors. In the epidermal-derived line PAM 212, at least two populations of receptors with different affinities for EGF were found. Psoralens and UVA light selectively inhibited binding to the higher-affinity EGF receptors, an effect analogous to that of the phorbol ester tumor promoters. As observed with phorbol esters, photoactivated Psoralens appeared to inhibit EGF binding by an indirect mechanism. These data demonstrate that the Psoralens and UVA light have direct biological effects on cell-surface membranes. Since EGF is a growth-regulatory peptide, the ability of Psoralens and UVA light to inhibit EGF binding may underlie the biologic effects of these agents in the skin.
Effects of psoralen on chondrocyte degeneration in lumbar intervertebral disc of rats.[Pubmed:25796142]
Pak J Pharm Sci. 2015 Mar;28(2 Suppl):667-70.
Discuss the internal mechanism of delaying degeneration of lumber intervertebral disc. The cartilage of lumbar intervertebral disc of SD rats was selected in vitro, then cultured by tissue explant method, and identified by HE staining, toluidine blue staining and immunofluorescence. The optimal concentration of Psoralen was screened by cell proliferation assay and RT-PCR method. The cells in third generation with good growth situation is selected and placed in 6-well plate at concentration of 1x10(5)/well and its expression was tested. Compared to concentration of 0, the mRNA expression of Col2al (Collagen ) secreted by was up regulated chondrocyte of lumbar intervertebral disc at the concentration of 12.5 and 25muM (P<0.0 or P<0.01). The aggrecan mRNA of Psoralen group was higher than blank control group (P<0.01); compared with IL-1beta induced group, the mRNA expression of Col2al was significantly increased but the mRNA expression of ADAMTS-5 was significantly decreased in Psoralen group (P<0.01). These findings suggest that, Psoralen can remit the degeneration of lumbar intervertebral disc induced by IL-1beta to some extent, and affect the related factors of IL-1beta signaling pathway.
Evaluation of psoralen ethosomes for topical delivery in rats by using in vivo microdialysis.[Pubmed:24489470]
Int J Nanomedicine. 2014 Jan 23;9:669-78.
This study aimed to improve skin permeation and deposition of Psoralen by using ethosomes and to investigate real-time drug release in the deep skin in rats. We used a uniform design method to evaluate the effects of different ethosome formulations on entrapment efficiency and drug skin deposition. Using in vitro and in vivo methods, we investigated skin penetration and release from Psoralen-loaded ethosomes in comparison with an ethanol tincture. In in vitro studies, the use of ethosomes was associated with a 6.56-fold greater skin deposition of Psoralen than that achieved with the use of the tincture. In vivo skin microdialysis showed that the peak concentration and area under the curve of Psoralen from ethosomes were approximately 3.37 and 2.34 times higher, respectively, than those of Psoralen from the tincture. Moreover, it revealed that the percutaneous permeability of ethosomes was greater when applied to the abdomen than when applied to the chest or scapulas. Enhanced permeation and skin deposition of Psoralen delivered by ethosomes may help reduce toxicity and improve the efficacy of long-term Psoralen treatment.


