OxymatrineCAS# 16837-52-8 |
- Oxysophoridine
Catalog No.:BCX0913
CAS No.:54809-74-4
Quality Control & MSDS
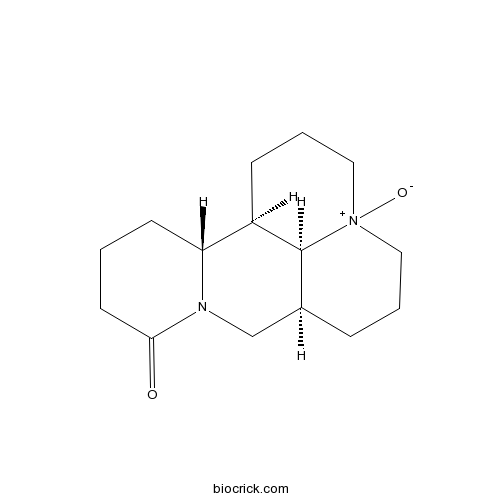
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 16837-52-8 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 114850 | Appearance | White-beige powder |
| Formula | C15H24N2O2 | M.Wt | 264.4 |
| Type of Compound | Alkaloids | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Synonyms | Oxysophoridine;54809-74-4;Matrine N-oxide;Matrine oxide | ||
| Solubility | H2O : 100 mg/mL (378.27 mM; Need ultrasonic) DMSO : 100 mg/mL (378.27 mM; Need ultrasonic) | ||
| SMILES | C1CC2C3CCC[N+]4(C3C(CCC4)CN2C(=O)C1)[O-] | ||
| Standard InChIKey | XVPBINOPNYFXID-LHDUFFHYSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C15H24N2O2/c18-14-7-1-6-13-12-5-3-9-17(19)8-2-4-11(15(12)17)10-16(13)14/h11-13,15H,1-10H2/t11-,12+,13+,15-,17?/m0/s1 | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | 1. Oxysophoridine has a protective effect on focal cerebral ischemic injury through antioxidant and anti-apoptotic mechanisms. 2. Oxysophoridine ameliorates cardiac damage in a rat model of AMI and that this cardioprotection may be linked with its anti-oxidative, anti-apoptotic and anti-inflammatory properties. 3. Oxysophoridine may be a potential neuroprotective agent for cerebral ischemia injury, that the effect may be due to its ability to inhibit oxidative stress and expression of the N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor subunit NR1.4.Oxymatrine has exhibited anti-hepatitis virus infection, anti-hepatic fibrosis, anti-inflammation, anti-anaphylaxis and other immune-regulation, it induces human pancreatic cancer PANC-1 cells apoptosis via regulating expression of Bcl-2 and IAP families, and releasing of cytochrome C. It can attenuate diabetes-associated cognitive deficits in rats, which is associated with oxidative stress, inflammation and apoptotic cascades, it is proven to protect ischemic and reperfusion injury in liver, intestine and heart. |
| Targets | Bcl-2/Bax | Caspase | IAP | NF-kB | IL Receptor | TNF-α | p38MAPK | p65 | Wnt/β-catenin | P450 (e.g. CYP17) | Bcl-2/Bax | Caspase | NO | SOD | p65 | NF-kB | IL Receptor | TNF-α |
| In vitro | Oxymatrine induces human pancreatic cancer PANC-1 cells apoptosis via regulating expression of Bcl-2 and IAP families, and releasing of cytochrome c[Pubmed: 21714853]J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2011; 30(1): 66.Oxymatrine, an isolated extract from traditional Chinese herb Sophora Flavescens Ait, has been traditionally used for therapy of anti-hepatitis B virus, anti-inflammation and anti-anaphylaxis. The present study was to investigate the anti-cancer effect of Oxymatrine on human pancreatic cancer PANC-1 cells, and its possible molecular mechanism.
Oxymatrine diminishes the side population and inhibits the expression of β-catenin in MCF-7 breast cancer cells.[Pubmed: 21069479 ]Med Oncol. 2011 Dec;28 Suppl 1:S99-107.Cancer stem cells (CSCs) play a critical role in both cancer initiation and relapse as they are resistant to most cytotoxic agents and able to proliferate indefinitely. The plant alkaloid Oxymatrine has many biological activities including the ability to induce cell cycle arrest and apoptosis, which makes it a potentially useful agent for targeting cancer cells.
|
| In vivo | Oxymatrine protects rat brains against permanent focal ischemia and downregulates NF-kappaB expression.[Pubmed: 19285049 ]Brain Res. 2009 May 1;1268:174-80.
Study on the anti-inflammatory mechanism of oxymatrine in dextran sulfate sodium induced colitis of rats[Reference: WebLink]Chinese Journal of Digestion, 2003, 11(31):4912-5.
Oxymatrine attenuates diabetes-associated cognitive deficits in rats.[Pubmed: 24442148]Acta Pharmacol. Sin., 2014, 35(3):331-8.Oxymatrine (OMT) is the major quinolizidine alkaloid extracted from the root of Sophora flavescens Ait (the Chinese herb Kushen) and exhibits diverse pharmacological actions.
Astragalus polysaccharide and oxymatrine can synergistically improve the immune efficacy of Newcastle disease vaccine in chicken.[Pubmed: 20149818]Int J Biol Macromol. 2010 May 1;46(4):425-8.
|
| Animal Research | Inhibition of hepatitis B virus by oxymatrine in vivo.[Pubmed: 11819732 ]Attenuation of acute lung injury in mice by oxymatrine is associated with inhibition of phosphorylated p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase.[Pubmed: 15763380 ]J Ethnopharmacol. 2005 Apr 8;98(1-2):177-83.Oxymatrine is one of the alkaloids extracted from Chinese herb Sophora japonica (Sophora flavescens Ait.) with activities of anti-inflammation, inhibiting immune reaction, antivirus, protecting hepatocytes and antihepatic fibrosis. However, the effect of Oxymatrine on acute lung injury (ALI) has not been known yet.
World J Gastroenterol. 2001 Feb;7(1):49-52.To investigate the anti-HBV effect of Oxymatrine (oxy) in vivo.
|

Oxymatrine Dilution Calculator

Oxymatrine Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 3.7821 mL | 18.9107 mL | 37.8215 mL | 75.643 mL | 94.5537 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.7564 mL | 3.7821 mL | 7.5643 mL | 15.1286 mL | 18.9107 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.3782 mL | 1.8911 mL | 3.7821 mL | 7.5643 mL | 9.4554 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0756 mL | 0.3782 mL | 0.7564 mL | 1.5129 mL | 1.8911 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0378 mL | 0.1891 mL | 0.3782 mL | 0.7564 mL | 0.9455 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
Oxymatrine, an alkaloid from the roots of Sophora species, with anti-inflammatory, antifibrosis, and antitumor effects, inhibits the iNOS expression and TGF-β/Smad pathway.
In Vitro:Oxymatrine, an alkaloid component extracted from the roots of Sophora species, has been shown to have antiinflammatory, antifibrosis, and antitumor effects and the ability to protect against myocardial damage, etc. The potential signaling pathways involved in the clinical application of oxymatrine might include the TGF-β/Smad, tolllike receptor 4/nuclear factor kappa-light-chain-enhancer of activated B cells, toll-like receptor9/TRAF6, Janus kinase/signal transduction and activator of transcription, phosphatidylinositol-3 kinase/Akt, delta-opioid receptorarrestinl-Bcl-2, CD40, epidermal growth factor receptor, nuclear factor erythroid-2-related factor 2/hemeoxygenase-1 signaling pathways, and dimethylarginine dimethylaminohydrolase/asymmetric dimethylarginine metabolism pathway[1]. Oxymatrine significantly inhibits the proliferation of DU145 and PC-3 cell lines in a time- and dose-dependent manner. By contrast, following treatment with oxymatrine, PNT1B healthy human prostate cell proliferation is not inhibited[2].
In Vivo:The volume and weight of tumors in mice significantly decreased in a dose-dependent manner. Oxymatrine may reduce prostate cancer cell growth by promoting cell apoptosis in vivo[2]. Oxymatrine is effective in reducing the production and deposition of collagen in the liver tissue of experimental rats. Oxymatrine could promote the expression of Smad 7 and inhibit the expression of Smad 3 and CBP in CCl4-induced hepatic fibrosis in SD rats, could modulate the fibrogenic signal transduction of TGFβ-Smad pathway[3].
References:
[1]. Lu ML, et al. Potential Signaling Pathways Involved in the Clinical Application of Oxymatrine. Phytother Res. 2016 Jul;30(7):1104-12.
[2]. Wu C, et al. Oxymatrine inhibits the proliferation of prostate cancer cells in vitro and in vivo. Mol Med Rep. 2015 Jun;11(6):4129-34.
[3]. Wu XL, et al. Effect of Oxymatrine on the TGFbeta-Smad signaling pathway in rats with CCl4-induced hepatic fibrosis. World J Gastroenterol. 2008 Apr 7;14(13):2100-5.
- Asiaticoside
Catalog No.:BCN1011
CAS No.:16830-15-2
- 3-Epidehydropachymic acid
Catalog No.:BCN3644
CAS No.:168293-15-0
- 3-O-Acetyl-16 alpha-hydroxydehydrotrametenolic acid
Catalog No.:BCN1531
CAS No.:168293-14-9
- 3-O-Acetyl-16 alpha-hydroxytrametenolic acid
Catalog No.:BCN1532
CAS No.:168293-13-8
- C-Veratroylglycol
Catalog No.:BCN1102
CAS No.:168293-10-5
- 3,5-Dimethoxy-3'-hydroxybibenzyl
Catalog No.:BCN8112
CAS No.:168281-05-8
- Rimonabant
Catalog No.:BCC4414
CAS No.:168273-06-1
- Evofolin B
Catalog No.:BCN1101
CAS No.:168254-96-4
- Wilforol C
Catalog No.:BCN1100
CAS No.:168254-95-3
- Nortenuazonic acid
Catalog No.:BCN1847
CAS No.:16820-44-3
- Agitoxin 2
Catalog No.:BCC8026
CAS No.:168147-41-9
- Taxin B
Catalog No.:BCN6945
CAS No.:168109-52-2
- Tacrine hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC6869
CAS No.:1684-40-8
- Compound 401
Catalog No.:BCC7622
CAS No.:168425-64-7
- Rhodiocyanoside A
Catalog No.:BCN7852
CAS No.:168433-86-1
- Epifriedelanol
Catalog No.:BCN1104
CAS No.:16844-71-6
- SHU 9119
Catalog No.:BCC6019
CAS No.:168482-23-3
- Z-D-Val-OH
Catalog No.:BCC2732
CAS No.:1685-33-2
- Dehydrogeijerin
Catalog No.:BCN7531
CAS No.:16850-91-2
- Fosbretabulin (Combretastatin A4 Phosphate (CA4P)) Disodium
Catalog No.:BCC4600
CAS No.:168555-66-6
- H-Asp(OMe)-OH.HCl
Catalog No.:BCC2889
CAS No.:16856-13-6
- AIDA
Catalog No.:BCC6841
CAS No.:168560-79-0
- TPEN
Catalog No.:BCC7913
CAS No.:16858-02-9
- Conivaptan HCl
Catalog No.:BCC3756
CAS No.:168626-94-6
Attenuation of acute lung injury in mice by oxymatrine is associated with inhibition of phosphorylated p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase.[Pubmed:15763380]
J Ethnopharmacol. 2005 Apr 8;98(1-2):177-83.
Oxymatrine is one of the alkaloids extracted from Chinese herb Sophora japonica (Sophora flavescens Ait.) with activities of anti-inflammation, inhibiting immune reaction, antivirus, protecting hepatocytes and antihepatic fibrosis. However, the effect of Oxymatrine on acute lung injury (ALI) has not been known yet. In this study, the effect of Oxymatrine on ALI was investigated using an oleic acid-induced ALI mouse model. Morphological findings showed that the oleic acid group demonstrated a marked lung injury represented by prominent atelectasis, intraalveolar and interstitial patchy hemorrhage, edema, thickened alveolar septum, formation of hyaline membranes and the existence of inflammatory cells in alveolar spaces. While in the Oxymatrine/dexamethasone group, these changes were less severe and in the vicinity of the control group. Furthermore, pretreatment with Oxymatrine significantly alleviated oleic acid-induced lung injury accompanied by reduction of lung index and wet-to-dry weight ratio, decreases in serum TNF-alpha level and inhibition of phosphorylated p38 MAPK. These findings suggest that Oxymatrine has a beneficial effect on acute lung injury induced by oleic acid in mice and may inhibit the production of proinflammatory cytokine, TNF-alpha, by means of the inhibition of p38 MAPK.
Oxymatrine attenuates diabetes-associated cognitive deficits in rats.[Pubmed:24442148]
Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2014 Mar;35(3):331-8.
AIM: Oxymatrine (OMT) is the major quinolizidine alkaloid extracted from the root of Sophora flavescens Ait (the Chinese herb Kushen) and exhibits diverse pharmacological actions. In this work we investigated the effects of OMT on diabetes-associated cognitive decline (DACD) in a rat model of diabetes and explored the mechanisms of action. METHODS: Male Wistar rats were injected with streptozotocin (65 mg/kg, ip) once to induce diabetes. The rats were then treated with vehicle or OMT (60 or 120 mg/kg per day, ip) for 7 weeks. Memory function was assessed using Morris water maze test. The levels of malondialdehyde (MDA), superoxide dismutase (SOD), glutathione (GSH), NF-kappaB p65 unit, TNF-alpha, IL-1beta and caspase-3 in the cerebral cortex and hippocampus were quantified. RESULTS: The diabetic rats exhibited markedly reduced body weight and increased plasma glucose level. The memory function of the rats assessed using Morris water maze test showed significant reduction in the percentage of time spent in the target quadrant and the number of times crossing the platform, coupled with markedly prolongation of escape latency and mean path length. Moreover, the rats showed oxidative stress (significantly increased MDA, decreased SOD and reduced GSH levels), as well as significant increases of NF-kappaB p65 unit, TNF-alpha, IL-1beta and caspase-3 levels in the cerebral cortex and hippocampus. Chronic treatment with OMT dose-dependently reversed these behavioral, biochemical and molecular changes in the diabetic rats. However, the swimming speed had no significant difference among the control, diabetic and OMT-treated diabetic rats. CONCLUSION: Chronic treatment with OMT alleviates diabetes-associated cognitive decline in rats, which is associated with oxidative stress, inflammation and apoptotic cascades.
Oxysophoridine attenuates the injury caused by acute myocardial infarction in rats through anti-oxidative, anti-inflammatory and anti-apoptotic pathways.[Pubmed:25338622]
Mol Med Rep. 2015 Jan;11(1):527-32.
Oxysophoridine (OSR), a natural alkaloid derived from the traditional Chinese medicinal plant sophora alopecuroides, can perform a variety of pharmacological actions. The aim of the present study was to assess the cardioprotective effect of OSR against acute myocardial infarction (AMI) in rats. OSR markedly reduced infarction size and levels of specific myocardial enzymes, including creatine kinase, the MB isoenzyme of creatine kinase, lactate dehydrogenase and cardiac troponin T. A reduced level of malondialdehyde was observed, and elevated catalase, Cu/Zn-superoxide dismutase (SOD), Mn-SOD, non-enzymatic scavenger glutathione and glutathione peroxidase activity were also identified in the OSR-treated rats. Additionally, OSR inhibited the activities of various inflammatory cytokines in a dose-dependent manner. These included nuclear factor-kappaB p65, tumor necrosis factor-alpha, and interleukin-1beta, -6 and -10. Furthermore, OSR treatment suppressed caspase-3 activity in a dose-dependent manner. These results demonstrate that OSR ameliorates cardiac damage in a rat model of AMI and that this cardioprotection may be linked with its anti-oxidative, anti-apoptotic and anti-inflammatory properties.
Oxymatrine diminishes the side population and inhibits the expression of beta-catenin in MCF-7 breast cancer cells.[Pubmed:21069479]
Med Oncol. 2011 Dec;28 Suppl 1:S99-107.
Cancer stem cells (CSCs) play a critical role in both cancer initiation and relapse as they are resistant to most cytotoxic agents and able to proliferate indefinitely. The plant alkaloid Oxymatrine has many biological activities including the ability to induce cell cycle arrest and apoptosis, which makes it a potentially useful agent for targeting cancer cells. In order to determine whether it has beneficial pharmacological properties to eradicate CSCs, we analyzed the effects of Oxymatrine on MCF-7 breast cancer cells. Cancer stem-like cells' (side population, SP) identification and sorting were performed. The inhibitory effect of Oxymatrine was evaluated on the sorted SP and non-SP cells. The results indicated that Oxymatrine caused a dose-dependent reduction in the proliferation of MCF-7 cells and a decrease in SP cells. Wnt/beta-catenin signaling pathway was also examined by analyzing the expression of total beta-catenin and phosphorylated beta-catenin in cytoplasm, and the results showed that the growth inhibitory effects of Oxymatrine treatment on MCF-7 cells may be due to the inhibition of SP and Wnt/beta-catenin signaling pathway. Further work is warranted to explore whether Oxymatrine may be a useful novel therapeutic drug for targeting breast CSCs.
Oxysophoridine protects against focal cerebral ischemic injury by inhibiting oxidative stress and apoptosis in mice.[Pubmed:24078262]
Neurochem Res. 2013 Nov;38(11):2408-17.
Our previous studies have demonstrated that oxysophoridine (OSR) has protective effects on cerebral neurons damage in vitro induced by oxygen and glucose deprivation. In this study, we further investigated whether OSR could reduce ischemic cerebral injury in vivo and its possible mechanism. Male Institute of cancer research mice were intraperitoneally injected with OSR (62.5, 125 and 250 mg/kg) for seven successive days, then subjected to brain ischemia induced by the model of middle cerebral artery occlusion. After reperfusion, neurological scores and infarct volume were estimated. Morphological examination of tissues was performed. Apoptotic neurons were detected by terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase mediated dUTP nick end labeling staining. Oxidative stress levels were assessed by measurement of malondialdehyde (MDA), superoxide dismutase (SOD) and glutathione peroxidase (GSH-Px) levels. The expression of various apoptotic markers as Caspase-3, Bax and Bcl-2 were investigated by immunohistochemistry and Western-blot analysis. OSR pretreatment groups significantly reduced infract volume and neurological deficit scores. OSR decreased the percentage of apoptotic neurons, relieved neuronal morphological damage. Moreover, OSR markedly decreased MDA content, and increased SOD, GSH-Px activities. Administration of OSR (250 mg/kg) significantly suppressed overexpression of Caspase-3 and Bax, and increased Bcl-2 expression. These findings indicate that OSR has a protective effect on focal cerebral ischemic injury through antioxidant and anti-apoptotic mechanisms.
Inhibition of hepatitis B virus by oxymatrine in vivo.[Pubmed:11819732]
World J Gastroenterol. 2001 Feb;7(1):49-52.
AIM: To investigate the anti-HBV effect of Oxymatrine (oxy) in vivo. METHODS: HBV transgenic mice were produced by micro-injection of a 4.2 kb fragment containing the complete HBV genomes. Expression level of HBsAg and HBcAg in the transgenic mice liver was determined by immunohistochemical assay. RESULTS: Four groups (6 mice in each group) were injected intraperitoneally with oxy at the dosage of 100, 200, and 300 mg/kg or with saline once a day for 30 days. Both HBsAg and HBcAg were positive in livers of all the six mice in the control group (injected with saline), and were positive in livers of two mice in 100mg/kg group and 300 mg/kg group. In 200 mg/kg group, HBsAg and HBcAg were negative in livers of all the six mice. Based on the results, 200mg/kg is the ideal dosage to explore the effect of oxy at different time points. According to the oxy treatment time, mice were divided into four groups: 10 d, 20 d, 30 d and 60 d (4 mice in each group). Each mouse underwent liver biopsy two weeks before the treatment of oxy. Down-regulation of HBsAg and HBcAg appeared after treatment of Oxymatrine for 10 d and 20 d, Dane-like particles disappeared after the treatment of oxy for 20 d under electron microscopy, however, the expression level of HBsAg and HBcAg returned to normal 60 d later after oxy treatment. CONCLUSION: Oxymatrine can reduce the contents of HBsAg and HBcAg in transgenic mice liver,longer treatment time and larger dosage do not yield better effects.
Oxymatrine protects rat brains against permanent focal ischemia and downregulates NF-kappaB expression.[Pubmed:19285049]
Brain Res. 2009 May 1;1268:174-180.
BACKGROUND: Oxymatrine is proven to protect ischemic and reperfusion injury in liver, intestine and heart, this effect is via anti-inflammation and anti-apoptosis. Whether this protective effect applies to ischemic injury in brain, we therefore investigate the potential neuroprotective role of Oxymatrine and the underlying mechanisms. METHODS: Male, Sprague-Dawley rats were randomly assigned to four groups: permanent middle cerebral artery occlusion (pMCAO), high dose (pMCAO+Oxymatrine 120 mg/kg), low dose (pMCAO+Oxymatrine 60 mg/kg) and sham operated group. We used a permanent middle cerebral artery occlusion model and administered Oxymatrine intraperitoneally immediately after cerebral ischemia and once daily on the following days. At 24 h after MCAO, neurological deficit was evaluated using a modified six point scale; brain water content was measured; NF-kappaB expression was measured by immunohistochemistry, Western blotting and RT-PCR. Infarct volume was analyzed with 2, 3, 5-triphenyltetrazolium chloride (TTC) staining at 72 h. RESULTS: Compared with pMCAO group, neurological deficit in high dose group was improved (P<0.05), infarct volume was decreased (P<0.001) and cerebral edema was alleviated (P<0.05). Consistent with these indices, immunohistochemistry, Western blot and RT-PCR analysis indicated that NF-kappaB expression was significantly decreased in high dose group. Low dose of Oxymatrine did not affect NF-kappaB expression in pMCAO rats. CONCLUSIONS: Oxymatrine reduced infarct volume induced by pMCAO, this effect may be through the decreasing of NF-kappaB expression.
Oxymatrine induces human pancreatic cancer PANC-1 cells apoptosis via regulating expression of Bcl-2 and IAP families, and releasing of cytochrome c.[Pubmed:21714853]
J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2011 Jun 29;30:66.
BACKGROUND: Oxymatrine, an isolated extract from traditional Chinese herb Sophora Flavescens Ait, has been traditionally used for therapy of anti-hepatitis B virus, anti-inflammation and anti-anaphylaxis. The present study was to investigate the anti-cancer effect of Oxymatrine on human pancreatic cancer PANC-1 cells, and its possible molecular mechanism. METHODS: The effect of Oxymatrine on the viability and apoptosis was examined by methyl thiazolyl tetrazolium and flow cytometry analysis. The expression of Bax, Bcl-2, Bcl-x (L/S), Bid, Bad, HIAP-1, HIAP-2, XIAP, NAIP, Livin and Survivin genes was accessed by RT-PCR. The levels of cytochrome c and caspase 3 protein were assessed by Western blotting. RESULTS: Oxymatrine inhibited cell viability and induced apoptosis of PANC-1 cells in a time- and dose-dependent manner. This was accompanied by down-regulated expression of Livin and Survivin genes while the Bax/Bcl-2 ratio was upregulated. Furthermore, Oxymatrine treatment led to the release of cytochrome c and activation of caspase-3 proteins. CONCLUSION: Oxymatrine can induce apoptotic cell death of human pancreatic cancer, which might be attributed to the regulation of Bcl-2 and IAP families, release of mitochondrial cytochrome c and activation of caspase-3.
Oxysophoridine suppresses the growth of hepatocellular carcinoma in mice: in vivo and cDNA microarray studies.[Pubmed:22466946]
Chin J Integr Med. 2012 Mar;18(3):209-13.
OBJECTIVE: To observe the in vivo effects of oxysophoridine on hepatocellular carcinoma in mice and to study the related mechanisms. METHODS: C57BL mice were inoculated with mouse hepatoma H22 cells subcutaneously, then divided into 5 groups (14 per group), and treated with oxysophoridine (50, 100, or 150 mg/kg) or cisplatin (4 mg/kg) for 10 days. Inhibitory rate of tumor, body weight gain, and influence indices on internal organs (liver, spleen and thymus) were evaluated. The differentially expressed genes between the oxysophoridine-treated group, and the control group were analyzed using cDNA microarray and quantitative real-time PCR (qRT-PCR) experiments. RESULTS: Compared with the tumor weight of the control group (2.75+/-0.66 g), oxysophoridine significantly suppressed hepatocellular carcinoma growth in mice (P <0.01), with 0.82+/-0.36 g, 0.57+/-0.22 g, and 1.22+/-0.67 g for the tumor weight in the low, moderate, and high dose treatment group, respectively. The moderate dose led to the highest inhibitory rate, 79.3%. Observation of body weight gain and influence on three organs showed that compared with cisplatin, oxysophoridine produced fewer side effects in vivo. cDNA microarray and qRT-PCR showed that the most significant differentially expressed genes in the tumor samples of oxysophoridine-treated mice were mostly involved in regulating apoptosis, with the Tnfrsf11b (osteoprotegerin) gene being the most significantly affected. CONCLUSION: Oxysophoridine was a promising compound for developing drugs against hepatocellular carcinoma, and its anti-hepatoma effect was probably related to osteoprotegerin activation.
Anti-apoptotic and neuroprotective effects of oxysophoridine on cerebral ischemia both in vivo and in vitro.[Pubmed:23807812]
Planta Med. 2013 Jul;79(11):916-23.
In this study, we investigated the neuroprotective effect of oxysophoridine on ischemia and ischemia-like insults. Protection by oxysophoridine was studied at the in vivo level using a model of middle cerebral artery occlusion in mice and at the in vitro level using primary rat hippocampal neuronal cultures exposed to oxygen-glucose deprivation, a model of ischemia-like injury. The behavioral test was performed by using the neurological scores. The infarction volume of brain was assessed in the brain slices stained with 2,3,5-triphenyl tetrazolium chloride. The neuron apoptosis was evaluated by Hoechst 33342 staining. The morphological change in the neurons was examined using a Transmission Electron Microscope (TEM or EM). To evaluate neuron apoptosis, caspase-3, -9, and - 8 activities were measured using assay kits with an ELISA reader. The Western blotting assay was used to evaluate the release of cytochrome c and expression of caspase-3, Bcl-2, and Bax proteins. The quantitative real-time PCR assay was used to evaluate the release of cytochrome c and the expression of caspase-3 mRNA. Oxysophoridine-treated groups (62.5, 125, 250 mg/kg) markedly reduced neurological deficit scores and infarct volumes. Treatment with oxysophoridine (5, 20, 80 micromol/L) significantly attenuated neuronal damage, with evidence of decreased cell apoptosis and decreased cell morphologic impairment. Furthermore, treatment with oxysophoridine could effectively downregulate the expression of cytochrome c and caspase-3 in both mRNA and protein levels, and Bax in the protein level, and induce an increase of Bcl-2 in the protein level. The caspase-3, -9, and -8 activities were also inhibited. These findings suggested that oxysophoridine may be a potential neuroprotective agent for cerebral ischemia injury.
Astragalus polysaccharide and oxymatrine can synergistically improve the immune efficacy of Newcastle disease vaccine in chicken.[Pubmed:20149818]
Int J Biol Macromol. 2010 May 1;46(4):425-8.
Three hundred and sixty 14-day-old chickens were divided into seven groups. The chickens, except for blank control group, were vaccinated with Newcastle disease vaccine, repeated at 28 days old. At the same time of the first vaccination, the chickens in three astragalus polysaccharide-Oxymatrine (AP-OM) groups were orally administrated respectively with the mixture of AP-OM at high, medium and low concentrations, in astragalus polysaccharide (AP) group and Oxymatrine (OM) group, with corresponding medicine, in non-medicine (NM) control group, with equal volume of physiological saline, once a day for 3 successive days. On 14, 21, 28, 35 and 42 days after the first vaccination, the changes of peripheral lymphocyte proliferation and serum antibody titers of the chickens were determined by MTT method and hemagglutination inhibition test. On 14, 28 and 42 days after the first vaccination, the serum IL-2 concentration was determined by Enzyme-linked Immunosorbent Assay (ELISA). The results showed that at most time points, the lymphocyte proliferation, antibody titers and IL-2 concentrations of 5 medicine-administrating groups were significantly higher than that of corresponding NM group. At some time points, the lymphocyte proliferation, antibody titers and IL-2 concentrations in high and medium doses of AP-OM groups were significantly or numberly higher than those in AP group and OM group. It indicated that AP-OM could significantly improve the immune efficacy of Newcastle disease vaccine, astragalus polysaccharide and Oxymatrine possessed synergistical immunoenhancement.
Protective effect of oxysophoridine on cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injury in mice.[Pubmed:25206429]
Neural Regen Res. 2013 May 25;8(15):1349-59.
Oxysophoridine, a new alkaloid extracted from Sophora alopecuroides L., has been shown to have a protective effect against ischemic brain damage. In this study, a focal cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injury model was established using middle cerebral artery occlusion in mice. Both 62.5, 125, and 250 mg/kg oxysophoridine, via intraperitoneal injection, and 6 mg/kg nimodipine, via intragastric administration, were administered daily for 7 days before modeling. After 24 hours of reperfusion, mice were tested for neurological deficit, cerebral infarct size was assessed and brain tissue was collected. Results showed that oxysophoridine at 125, 250 mg/kg and 6 mg/kg nimodipine could reduce neurological deficit scores, cerebral infarct size and brain water content in mice. These results provided evidence that oxysophoridine plays a protective role in cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injury. In addition, oxysophoridine at 62.5, 125, and 250 mg/kg and 6 mg/kg nimodipine increased adenosine-triphosphate content, and decreased malondialdehyde and nitric oxide content. These compounds enhanced the activities of glutathione-peroxidase, superoxide dismutase, catalase, and lactate dehydrogenase, and decreased the activity of nitric oxide synthase. Protein and mRNA expression levels of N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor subunit NR1 were markedly inhibited in the presence of 250 mg/kg oxysophoridine and 6 mg/kg nimodipine. Our experimental findings indicated that oxysophoridine has a neuroprotective effect against cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injury in mice, and that the effect may be due to its ability to inhibit oxidative stress and expression of the N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor subunit NR1.


