NothofaginCAS# 11023-94-2 |
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 11023-94-2 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 21722188 | Appearance | Powder |
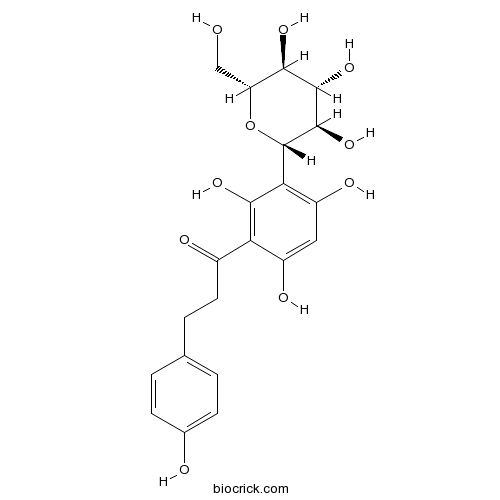
| Formula | C21H24O10 | M.Wt | 436.4 |
| Type of Compound | Chalcones | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Solubility | Soluble in Chloroform,Dichloromethane,Ethyl Acetate,DMSO,Acetone,etc. | ||
| Chemical Name | 3-(4-hydroxyphenyl)-1-[2,4,6-trihydroxy-3-[(2S,3R,4R,5S,6R)-3,4,5-trihydroxy-6-(hydroxymethyl)oxan-2-yl]phenyl]propan-1-one | ||
| SMILES | C1=CC(=CC=C1CCC(=O)C2=C(C(=C(C=C2O)O)C3C(C(C(C(O3)CO)O)O)O)O)O | ||
| Standard InChIKey | VZBPTZZTCBNBOZ-VJXVFPJBSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C21H24O10/c22-8-14-17(27)19(29)20(30)21(31-14)16-13(26)7-12(25)15(18(16)28)11(24)6-3-9-1-4-10(23)5-2-9/h1-2,4-5,7,14,17,19-23,25-30H,3,6,8H2/t14-,17-,19+,20-,21+/m1/s1 | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | 1. Nothofagin has antioxidant activity. 2. Nothofagin and Aspalathin may have significant benefits in the treatment of diabetic complications. 3. Nothofagin and Aspalathin possess antithrombotic activity and offers a basis for development of a novel anticoagulant. 4. Nothofagin and Aspalathin possess anti-inflammatory activity by inhibiting hyperpermeability, expression of CAMs, and adhesion and migration of leukocytes, thereby endorsing its usefulness as a therapy for vascular inflammatory diseases. 5. Nothofagin and Aspalathin have potential to as an anti-sendothelial cell protein C receptor shedding reagent against phorbol-12-myristate 13-acetate and cecal ligation and puncture -mediated endothelial cell protein C receptor shedding. |
| Targets | TNF-α | IL Receptor | ERK | p38MAPK | JNK | NF-kB | ROS |

Nothofagin Dilution Calculator

Nothofagin Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 2.2915 mL | 11.4574 mL | 22.9148 mL | 45.8295 mL | 57.2869 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.4583 mL | 2.2915 mL | 4.583 mL | 9.1659 mL | 11.4574 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.2291 mL | 1.1457 mL | 2.2915 mL | 4.583 mL | 5.7287 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0458 mL | 0.2291 mL | 0.4583 mL | 0.9166 mL | 1.1457 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0229 mL | 0.1146 mL | 0.2291 mL | 0.4583 mL | 0.5729 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
- Temocapril HCl
Catalog No.:BCC5016
CAS No.:110221-44-8
- Ginsenoside Rc
Catalog No.:BCN1072
CAS No.:11021-14-0
- Ginsenoside Rb2
Catalog No.:BCN1064
CAS No.:11021-13-9
- Cochliophilin A
Catalog No.:BCC8154
CAS No.:110204-45-0
- Malonylginsenoside Rb(1)
Catalog No.:BCC9230
CAS No.:88140-34-5
- 1,5,8-Trihydroxy-3-methoxy-2-prenylxanthone
Catalog No.:BCN1623
CAS No.:110187-11-6
- JZL184
Catalog No.:BCC4790
CAS No.:1101854-58-3
- Ouabain Octahydrate
Catalog No.:BCC5211
CAS No.:11018-89-6
- 4-Galloylquinic acid
Catalog No.:BCN3733
CAS No.:110170-37-1
- Methyl hesperidin
Catalog No.:BCN6341
CAS No.:11013-97-1
- Indoximod (NLG-8189)
Catalog No.:BCC5584
CAS No.:110117-83-4
- Ascomycin
Catalog No.:BCN8286
CAS No.:11011-38-4
- Digitonin
Catalog No.:BCN3734
CAS No.:11024-24-1
- (-)-beta-Peltatin-5-O-beta-D-glucopyranoside
Catalog No.:BCN3607
CAS No.:11024-59-2
- Ganoderic acid N
Catalog No.:BCN2438
CAS No.:110241-19-5
- Ganoderenic acid E
Catalog No.:BCN8241
CAS No.:110241-23-1
- Amrubicin
Catalog No.:BCC3640
CAS No.:110267-81-7
- Agnuside
Catalog No.:BCN5990
CAS No.:11027-63-7
- Bacoside A
Catalog No.:BCC8127
CAS No.:11028-00-5
- CI 966 hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC7010
CAS No.:110283-66-4
- Santalol
Catalog No.:BCN8352
CAS No.:11031-45-1
- α-Bungarotoxin
Catalog No.:BCC7264
CAS No.:11032-79-4
- FD-838
Catalog No.:BCN6396
CAS No.:110341-78-1
- CGS 19755
Catalog No.:BCC6986
CAS No.:110347-85-8
Antithrombotic activities of aspalathin and nothofagin via inhibiting platelet aggregation and FIIa/FXa.[Pubmed:25325928]
Arch Pharm Res. 2015 Jun;38(6):1080-9.
Aspalathin (Asp) and Nothofagin (Not) are two major active dihydrochalcones found in green rooibos tea (Aspalathus linearis; family, Fabaceae; tribe, Crotalarieae), which have been reported for their anti-oxidant activity. Here, the anticoagulant activities of Asp and Not were examined by monitoring activated partial thromboplastin time (aPTT), prothrombin time (PT), and the activities of thrombin (Factor IIa, FIIa) and activated factor X (FXa). And, the effects of Asp and Not on expression of plasminogen activator inhibitor type 1 (PAI-1) and tissue-type plasminogen activator (t-PA) were evaluated in tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-alpha activated human umbilical vein endothelial cells (HUVECs). Treatment with Asp and Not resulted in prolonged aPTT and PT and inhibition of the activities of thrombin and FXa, as well as inhibited production of thrombin and FXa in HUVECs. In addition, Asp and Not inhibited thrombin-catalyzed fibrin polymerization and platelet aggregation. Asp and Not also elicited anticoagulant effects in mice. In addition, treatment with Asp and Not resulted in significant reduction of the PAI-1 to t-PA ratio. Collectively, Asp and Not possesses antithrombotic activities and offers a basis for development of a novel anticoagulant.
Aspalathin and nothofagin from rooibos (Aspalathus linearis) inhibit endothelial protein C receptor shedding in vitro and in vivo.[Pubmed:25510322]
Fitoterapia. 2015 Jan;100:179-86.
Aspalathin (Asp) and Nothofagin (Not) are two major active dihydrochalcones found in green rooibos, which have been reported for their anti-oxidant activity. Increasing evidence has demonstrated that beyond its role in the activation of protein C, endothelial cell protein C receptor (EPCR) is also involved in vascular inflammation. EPCR activity is markedly changed by ectodomain cleavage and its release as the soluble EPCR. EPCR can be shed from the cell surface, which is mediated by tumor necrosis factor-alpha converting enzyme (TACE). However, little is known about the effects of Asp and Not on EPCR shedding. Our results demonstrated that Asp and Not induced potent inhibition of phorbol-12-myristate 13-acetate (PMA)-, tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-alpha-, interleukin (IL)-1beta, and cecal ligation and puncture (CLP)-induced EPCR shedding. Asp and Not also inhibited the expression and activity of PMA-induced TACE in endothelial cells. Asp and Not also suppressed CLP-induced protein C decrease in mice and thrombin generation in HUVECs. In addition, treatment with Asp and Not resulted in reduced PMA-stimulated phosphorylation of p38, extracellular regulated kinase (ERK) 1/2, and c-Jun N-terminal kinase (JNK). These results demonstrate the potential of Asp and Not as an anti-sEPCR shedding reagent against PMA and CLP-mediated EPCR shedding.
Aspalathin and Nothofagin from Rooibos (Aspalathus linearis) inhibits high glucose-induced inflammation in vitro and in vivo.[Pubmed:25338943]
Inflammation. 2015 Feb;38(1):445-55.
Vascular inflammation plays a key role in the initiation and progression of atherosclerosis, a major complication of diabetes mellitus. Aspalathin (Asp) and Nothofagin (Not) are two major active dihydrochalcones found in green rooibos, which have been reported for their antioxidant activity. In this study, we assessed whether Asp or Not can suppress vascular inflammation induced by high glucose (HG) in human umbilical vein endothelial cells (HUVECs) and mice. We monitored the effects of Asp or Not on HG-induced vascular hyperpermeability, expression of cell adhesion molecules (CAMs), formation of reactive oxygen species (ROS), and activation of nuclear factor (NF)-kappaB in vitro and in vivo. Our data indicate that HG markedly increased vascular permeability, monocyte adhesion, expression of CAMs, formation of ROS, and activation of NF-kappaB. Remarkably, treatment of Asp or Not inhibited HG-mediated vascular hyperpermeability, adhesion of monocytes toward HUVECs, and expression of CAMs. In addition, Asp or Not suppressed the formation of ROS and the activation of NF-kappaB. Since vascular inflammation induced by HG is critical in the development of diabetic complications, our results suggest that Asp or Not may have significant benefits in the treatment of diabetic complications.
Anti-inflammatory Effects of Aspalathin and Nothofagin from Rooibos (Aspalathus linearis) In Vitro and In Vivo.[Pubmed:25655391]
Inflammation. 2015 Aug;38(4):1502-16.
Aspalathin (Asp) and Nothofagin (Not) are two major active dihydrochalcones found in green rooibos, which have been reported for their anti-oxidant activity. Here, we investigated the anti-inflammatory effects and underlying mechanisms of Asp and Not against lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-mediated vascular inflammatory responses. The anti-inflammatory activities of Asp and Not were determined by measuring permeability, monocytes adhesion and migration, and activation of pro-inflammatory proteins in LPS-activated human umbilical vein endothelial cells (HUVECs) and mice. We found that each compound inhibited LPS-induced barrier disruption, expression of cell adhesion molecules (CAMs), and adhesion/transendothelial migration of neutrophils to human endothelial cells. Asp and Not also suppressed LPS-induced hyperpermeability and leukocyte migration in vivo. Furthermore, each compound suppressed the production of tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-alpha) or interleukin (IL)-6 and the activation of nuclear factor-kappaB (NF-kappaB) or extracellular regulated kinases (ERK) 1/2 by LPS. Moreover, treatment with each compound resulted in reduced LPS-induced lethal endotoxemia. These results suggest that Asp and Not posses anti-inflammatory functions by inhibiting hyperpermeability, expression of CAMs, and adhesion and migration of leukocytes, thereby endorsing its usefulness as a therapy for vascular inflammatory diseases.


