JZL184MAGL inhibitor, potent and selective CAS# 1101854-58-3 |
- AM630
Catalog No.:BCC1353
CAS No.:164178-33-0
- Nepicastat
Catalog No.:BCC1795
CAS No.:173997-05-2
- Otenabant
Catalog No.:BCC1828
CAS No.:686344-29-6
- CP-945598 HCl
Catalog No.:BCC1082
CAS No.:686347-12-6
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 1101854-58-3 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 25021165 | Appearance | Powder |
| Formula | C27H24N2O9 | M.Wt | 520.49 |
| Type of Compound | N/A | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Solubility | DMSO : ≥ 35 mg/mL (67.24 mM) H2O : < 0.1 mg/mL (insoluble) *"≥" means soluble, but saturation unknown. | ||
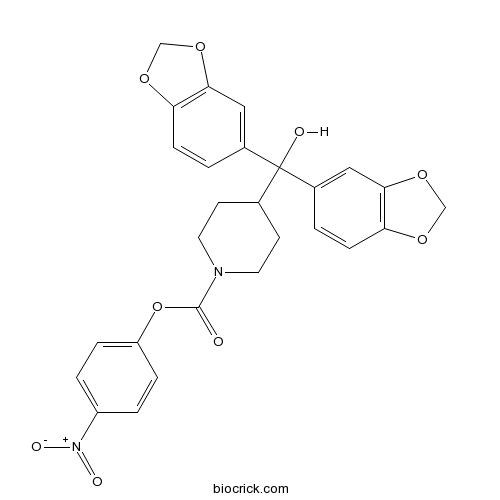
| Chemical Name | (4-nitrophenyl) 4-[bis(1,3-benzodioxol-5-yl)-hydroxymethyl]piperidine-1-carboxylate | ||
| SMILES | C1CN(CCC1C(C2=CC3=C(C=C2)OCO3)(C4=CC5=C(C=C4)OCO5)O)C(=O)OC6=CC=C(C=C6)[N+](=O)[O-] | ||
| Standard InChIKey | SEGYOKHGGFKMCX-UHFFFAOYSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C27H24N2O9/c30-26(38-21-5-3-20(4-6-21)29(32)33)28-11-9-17(10-12-28)27(31,18-1-7-22-24(13-18)36-15-34-22)19-2-8-23-25(14-19)37-16-35-23/h1-8,13-14,17,31H,9-12,15-16H2 | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | Potent and selective MAGL inhibitor. Blocks hydrolysis of the endocannabinoid 2-arachidonyl glycerol (2-AG) in vivo in the mouse brain (IC50 = 8 nM). Potentiates depolarization-induced suppression of excitability in cerebellar Purkinje neurons. Exhibits >300-fold selectivity for MAGL over FAAH in vitro. Attenuates nociception in neuropathic and inflammatory pain models. Also reduces free fatty acid levels in primary tumors. |

JZL184 Dilution Calculator

JZL184 Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 1.9213 mL | 9.6063 mL | 19.2127 mL | 38.4253 mL | 48.0317 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.3843 mL | 1.9213 mL | 3.8425 mL | 7.6851 mL | 9.6063 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.1921 mL | 0.9606 mL | 1.9213 mL | 3.8425 mL | 4.8032 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0384 mL | 0.1921 mL | 0.3843 mL | 0.7685 mL | 0.9606 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0192 mL | 0.0961 mL | 0.1921 mL | 0.3843 mL | 0.4803 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
JZL184 is a potent and selective inhibitor of MAGL [1].
Monoacylglycerol lipase (MAGL) is a membrane-associated member of the serine hydrolase superfamily and hydrolyzes endocannabinoid 2-arachidonoylglycerol (2-AG) and intracellular triglyceride stores.
JZL184 is a potent and selective MAGL inhibitor. In cerebellar Purkinje neurons, JZL184 (40-120 min) prolonged depolarization-induced suppression of excitation (DSE) in a dose-dependent way, which was mediated by CB1 receptor. In hippocampal CA1 pyramidal neurons, JZL184 (100 nM) significantly prolonged depolarization-induced suppression of inhibition (DSI), which was mediated by CB1 receptor activation. In mouse cerebellar slices, JZL184 (100 nM) significantly enhanced 2-AG (10 μM)-induced depression of EPSCs in Purkinje neurons. These results suggested that MAGL is the primary mechanism by which 2-AG is metabolized [1].
In mice, JZL184 inhibited 2-AG hydrolysis with IC50 value of 8 nM and increased brain 2-AG by 8-fold. The JZL184-treated mice exhibited CB1-dependent behaviors including analgesia, hypomotility and hypothermia [2]. In rats, JZL184 (8 mg/kg) exhibited anxiolytic-like effects via inhibition of MGL mediated 2-AG hydrolysis under high levels of environmental aversiveness [3]. In rats, JZL184 produced antinociception with ED50 values of 0.06 and 0.03 μM in the early phase and the late phase of formalin pain, respectively [4].
References:
[1]. Pan B, Wang W, Long JZ, et al. Blockade of 2-arachidonoylglycerol hydrolysis by selective monoacylglycerol lipase inhibitor 4-nitrophenyl 4-(dibenzo[d][1,3]dioxol-5-yl(hydroxy)methyl)piperidine-1-carboxylate (JZL184) Enhances retrograde endocannabinoid signaling. J Pharmacol Exp Ther, 2009, 331(2): 591-597.
[2]. Long JZ, Li W, Booker L, et al. Selective blockade of 2-arachidonoylglycerol hydrolysis produces cannabinoid behavioral effects. Nat Chem Biol, 2009, 5(1): 37-44.
[3]. Sciolino NR, Zhou W, Hohmann AG. Enhancement of endocannabinoid signaling with JZL184, an inhibitor of the 2-arachidonoylglycerol hydrolyzing enzyme monoacylglycerol lipase, produces anxiolytic effects under conditions of high environmental aversiveness in rats. Pharmacol Res, 2011, 64(3): 226-234.
[4]. Guindon J, Guijarro A, Piomelli D, et al. Peripheral antinociceptive effects of inhibitors of monoacylglycerol lipase in a rat model of inflammatory pain. Br J Pharmacol, 2011, 163(7): 1464-1478.
- Ouabain Octahydrate
Catalog No.:BCC5211
CAS No.:11018-89-6
- 4-Galloylquinic acid
Catalog No.:BCN3733
CAS No.:110170-37-1
- Methyl hesperidin
Catalog No.:BCN6341
CAS No.:11013-97-1
- Indoximod (NLG-8189)
Catalog No.:BCC5584
CAS No.:110117-83-4
- Ascomycin
Catalog No.:BCN8286
CAS No.:11011-38-4
- des-His1-[Glu9]-Glucagon (1-29) amide
Catalog No.:BCC5885
CAS No.:110084-95-2
- Plerixafor (AMD3100)
Catalog No.:BCC1158
CAS No.:110078-46-1
- 12-Epinapelline
Catalog No.:BCN2800
CAS No.:110064-71-6
- 7-Hydroxy-3-(4-hydroxybenzylidene)chroman-4-one
Catalog No.:BCN1624
CAS No.:110064-50-1
- Strophantin K (mixture)
Catalog No.:BCC8256
CAS No.:11005-63-3
- Calpain Inhibitor I, ALLN
Catalog No.:BCC1233
CAS No.:110044-82-1
- Tussilagonone
Catalog No.:BCC8365
CAS No.:110042-38-1
- 1,5,8-Trihydroxy-3-methoxy-2-prenylxanthone
Catalog No.:BCN1623
CAS No.:110187-11-6
- Malonylginsenoside Rb(1)
Catalog No.:BCC9230
CAS No.:88140-34-5
- Cochliophilin A
Catalog No.:BCC8154
CAS No.:110204-45-0
- Ginsenoside Rb2
Catalog No.:BCN1064
CAS No.:11021-13-9
- Ginsenoside Rc
Catalog No.:BCN1072
CAS No.:11021-14-0
- Temocapril HCl
Catalog No.:BCC5016
CAS No.:110221-44-8
- Nothofagin
Catalog No.:BCN3787
CAS No.:11023-94-2
- Digitonin
Catalog No.:BCN3734
CAS No.:11024-24-1
- (-)-beta-Peltatin-5-O-beta-D-glucopyranoside
Catalog No.:BCN3607
CAS No.:11024-59-2
- Ganoderic acid N
Catalog No.:BCN2438
CAS No.:110241-19-5
- Ganoderenic acid E
Catalog No.:BCN8241
CAS No.:110241-23-1
- Amrubicin
Catalog No.:BCC3640
CAS No.:110267-81-7
Monoacylglycerol lipase inhibitor JZL184 reduces neuroinflammatory response in APdE9 mice and in adult mouse glial cells.[Pubmed:25927213]
J Neuroinflammation. 2015 Apr 28;12:81.
BACKGROUND: Recently, the role of monoacylglycerol lipase (MAGL) as the principal regulator of simultaneous prostaglandin synthesis and endocannabinoid receptor activation in the CNS was demonstrated. To expand upon previously published research in the field, we observed the effect of the MAGL inhibitor JZL184 during the early-stage proinflammatory response and formation of beta-amyloid (Abeta) in the Alzheimer's disease mouse model APdE9. We also investigated its effects in proinflammatory agent - induced astrocytes and microglia isolated from adult mice. FINDINGS: Transgenic APdE9 mice (5 months old) were treated with JZL184 (40 mg/kg) or vehicle every day for 1 month. In vivo binding of the neuroinflammation-related, microglia-specific translocator protein (TSPO) targeting radioligand [(18) F]GE-180 decreased slightly but statistically non-significantly in multiple brain areas compared to vehicle-treated mice. JZL184 treatment induced a significant decrease in expression levels of inflammation-induced, Iba1-immunoreactive microglia in the hippocampus (P < 0.01) and temporal and parietal (P < 0.05) cortices. JZL184 also induced a marked decrease in total Abeta burden in the temporal (P < 0.001) and parietal (P < 0.01) cortices and, to some extent, in the hippocampus. Adult microglial and astrocyte cultures pre-treated with JZL184 and then exposed to the neuroinflammation-inducing agents lipopolysaccharide (LPS), interferon-gamma (IFN-gamma), and Abeta42 had significantly reduced proinflammatory responses compared to cells without JZL184 treatment. CONCLUSIONS: JZL184 decreased the proinflammatory reactions of microglia and reduced the total Abeta burden and its precursors in the APdE9 mouse model. It also reduced the proinflammatory responses of microglia and astrocytes isolated from adult mice.
Neuroprotective Effect of JZL184 in MPP(+)-Treated SH-SY5Y Cells Through CB2 Receptors.[Pubmed:25976369]
Mol Neurobiol. 2016 May;53(4):2312-9.
Growing evidence suggests that the endocannabinoid system plays a role in neuroprotection in Parkinson's disease. Recently, we have shown the neuroprotective effect of monoacylglycerol lipase (MAGL) inhibition with JZL184 in the chronic 1-methyl-4-phenyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridine (MPTP) mouse model. However, further investigation is needed to determine the neuroprotective mechanisms of the endocannabinoid system on the nigrostriatal pathway. The aim of this work was to investigate whether the neuroprotective effect of JZL184 in mice could be extended to an in vitro cellular model to further understand the mechanism of action of the drug. The SH-SY5Y cell line was selected based on its dopaminergic-like phenotype and its susceptibility to 1-methyl-4-phenylpyridinium iodide (MPP(+)) toxicity. Furthermore, SH-SY5Y cells express both cannabinoid receptors, CB1 and CB2. The present study describes the neuroprotective effect of MAGL inhibition with JZL184 in SH-SY5Y cells treated with MPP(+). The effect of JZL184 in cell survival was blocked by AM630, a CB2 receptor antagonist, and it was mimicked with JWH133, a CB2 receptor agonist. Rimonabant, a CB1 receptor antagonist, did not affect JZL184-induced cell survival. These results demonstrate that the neuroprotective effect of MAGL inhibition with JZL184 described in animal models of Parkinson's disease could be extended to in vitro models such as SH-SY5Y cells treated with MPP(+). This represents a useful tool to study mechanisms of neuroprotection mediated by MAGL inhibition, and we provide evidence for the possible involvement of CB2 receptors in the improvement of cell survival.
The monoacylglycerol lipase inhibitor JZL184 decreases inflammatory response in skeletal muscle contusion in rats.[Pubmed:25912803]
Eur J Pharmacol. 2015 Aug 15;761:1-10.
Muscle wound healing process is a typical inflammation-evoked event. The monoacylglycerol lipase (MAGL) inhibitor (4-nitrophenyl)4-[bis(1,3-benzodioxol -5-yl)-hydroxymethyl]piperidine-1-carboxylate (JZL184) has been previously reported to reduce inflammation in colitis and acute lung injury in mice, which provide a new strategy for primary care of skeletal muscle injury. We investigated the effect of JZL184 on inflammation in rat muscle contusion model, and found decreased neutrophil and macrophage infiltration and pro-inflammatory cytokine expression. With extension of post-traumatic interval, myofiber regeneration was significantly hindered with increased collagen types I and capital I, Ukrainiancapital I, Ukrainiancapital I, Ukrainian mRNAfibroblast infiltration as well as promoted fibrosis. Furthermore, 1-(2,4-dichlorophenyl)-5-(4-iodophenyl)-4-methyl-N-morpholin-4-ylpyrazole-3-carbo xamide (AM281, a selective cannabinoid CB1 receptor antagonist) and [6-iodo-2-methyl-1-(2-morpholin-4-ylethyl)indol-3-yl]-(4-methoxyphenyl)methanone (AM630, a selective cannabinoid CB2 receptor antagonist) treatment alleviated the anti-inflammatory effect of JZL184. Our findings demonstrate that JZL184 is able to inhibit the inflammatory response and interfere with contused muscle healing, in which the anti-inflammatory action may be mediated through cannabinoid CB1 and CB2 receptors.
Monoacylglycerol lipase inhibitor JZL184 regulates apoptosis and migration of colorectal cancer cells.[Pubmed:26847687]
Mol Med Rep. 2016 Mar;13(3):2850-6.
Monoacylglycerol lipase (MAGL) is involved in the degradation of triacylglycerol. Previous studies have demonstrated that MAGL regulates tumor growth and metastasis via fatty acid networks, and is associated with colorectal cancer. JZL184 is a MAGL inhibitor, which in the present study was administered to colorectal cancer cell lines, resulting in decreased tumor proliferation, increased apoptosis and increased tumor cell sensitivity to 5-fluorouracil. Bcell lymphoma 2 (Bcl2) and Bcl2associated X protein (Bax) are key proteins in apoptosis. The expression levels of Bcl2/Bax were determined in colorectal cancer cell lines following JZL184 administration, and it was observed that the mRNA and protein expression levels of Bcl2 were decreased, whereas the expression levels of Bax were increased. These results indicated that JZL184 may induce tumor cell apoptosis by regulating the expression of Bcl2 and Bax. Epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT) is closely associated with metastasis. Administration of JZL184 in various malignant colorectal cancer cell lines suppressed migration and altered the expression of EMT markers; Ecadherin was increased, whereas the expression levels of vimentin and zinc finger protein SNAI1 were decreased. These results suggested that JZL184 was able to regulate the EMT process, in order to control the migration of colorectal cancer cells, particularly in tumors with a stronger metastatic capability. Therefore, in colorectal cancer, MAGL may be considered a potential therapeutic target and JZL184 may be a possible therapeutic agent.
Repeated low-dose administration of the monoacylglycerol lipase inhibitor JZL184 retains cannabinoid receptor type 1-mediated antinociceptive and gastroprotective effects.[Pubmed:23412396]
J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2013 Jun;345(3):492-501.
The monoacylglycerol lipase (MAGL) inhibitor 4-nitrophenyl 4-(dibenzo[d][1,3]dioxol-5-yl(hydroxy)methyl)piperidine-1-carboxylate (JZL184) produces antinociceptive and anti-inflammatory effects. However, repeated administration of high-dose JZL184 (40 mg/kg) causes dependence, antinociceptive tolerance, cross-tolerance to the pharmacological effects of cannabinoid receptor agonists, and cannabinoid receptor type 1 (CB1) downregulation and desensitization. This functional CB1 receptor tolerance poses a hurdle in the development of MAGL inhibitors for therapeutic use. Consequently, the present study tested whether repeated administration of low-dose JZL184 maintains its antinociceptive actions in the chronic constriction injury of the sciatic nerve neuropathic pain model and protective effects in a model of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug-induced gastric hemorrhages. Mice given daily injections of high-dose JZL184 (>/=16 mg/kg) for 6 days displayed decreased CB1 receptor density and function in the brain, as assessed in [(3)H]SR141716A binding and CP55,940 [(-)-cis-3-[2-hydroxy-4-(1,1-dimethylheptyl)phenyl]-trans-4-(3-hydroxypropyl) cyclohexanol]-stimulated guanosine 5'-O-(3-[(35)S]thio)triphosphate binding assays, respectively. In contrast, normal CB1 receptor expression and function were maintained following repeated administration of low-dose JZL184 (JZL184 underwent tolerance following repeated administration, but these effects were maintained following repeated low-dose JZL184 treatment. Consistent with these observations, repeated high-dose JZL184, but not repeated low-dose JZL184, elicited cross-tolerance to the common pharmacological effects of Delta(9)-tetrahydrocannabinol. This same pattern of effects was found in a rimonabant [(5-(4-chlorophenyl)-1-(2,4-dichloro-phenyl)-4-methyl-N-(piperidin-1-yl)-1H-pyraz ole-3-carboxamide)]-precipitated withdrawal model of cannabinoid dependence. Taken together, these results indicate that prolonged, partial MAGL inhibition maintains potentially beneficial antinociceptive and anti-inflammatory effects, without producing functional CB1 receptor tachyphylaxis/tolerance or cannabinoid dependence.
Dysregulated lipid metabolism in cancer.[Pubmed:22937213]
World J Biol Chem. 2012 Aug 26;3(8):167-74.
Alteration of lipid metabolism has been increasingly recognized as a hallmark of cancer cells. The changes of expression and activity of lipid metabolizing enzymes are directly regulated by the activity of oncogenic signals. The dependence of tumor cells on the dysregulated lipid metabolism suggests that proteins involved in this process are excellent chemotherapeutic targets for cancer treatment. There are currently several drugs under development or in clinical trials that are based on specifically targeting the altered lipid metabolic pathways in cancer cells. Further understanding of dysregulated lipid metabolism and its associated signaling pathways will help us to better design efficient cancer therapeutic strategy.
Selective blockade of 2-arachidonoylglycerol hydrolysis produces cannabinoid behavioral effects.[Pubmed:19029917]
Nat Chem Biol. 2009 Jan;5(1):37-44.
2-Arachidonoylglycerol (2-AG) and anandamide are endocannabinoids that activate the cannabinoid receptors CB1 and CB2. Endocannabinoid signaling is terminated by enzymatic hydrolysis, a process that for anandamide is mediated by fatty acid amide hydrolase (FAAH), and for 2-AG is thought to involve monoacylglycerol lipase (MAGL). FAAH inhibitors produce a select subset of the behavioral effects observed with CB1 agonists, which suggests a functional segregation of endocannabinoid signaling pathways in vivo. Testing this hypothesis, however, requires specific tools to independently block anandamide and 2-AG metabolism. Here, we report a potent and selective inhibitor of MAGL called JZL184 that, upon administration to mice, raises brain 2-AG by eight-fold without altering anandamide. JZL184-treated mice exhibited a broad array of CB1-dependent behavioral effects, including analgesia, hypothermia and hypomotility. These data indicate that 2-AG endogenously modulates several behavioral processes classically associated with the pharmacology of cannabinoids and point to overlapping and unique functions for 2-AG and anandamide in vivo.
Blockade of 2-arachidonoylglycerol hydrolysis by selective monoacylglycerol lipase inhibitor 4-nitrophenyl 4-(dibenzo[d][1,3]dioxol-5-yl(hydroxy)methyl)piperidine-1-carboxylate (JZL184) Enhances retrograde endocannabinoid signaling.[Pubmed:19666749]
J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2009 Nov;331(2):591-7.
Endocannabinoid (eCB) signaling mediates depolarization-induced suppression of excitation (DSE) and inhibition (DSI), two prominent forms of retrograde synaptic depression. N-Arachidonoylethanolamine (AEA) and 2-arachidonoylglycerol (2-AG), two known eCBs, are degraded by fatty acid amide hydrolase (FAAH) and monoacylglycerol lipase (MAGL), respectively. Selective blockade of FAAH and MAGL is critical for determining the roles of the eCBs in DSE/DSI and understanding how their action is regulated. 4-Nitrophenyl 4-(dibenzo[d][1,3]dioxol-5-yl(hydroxy)methyl)piperidine-1-carboxylate (JZL184) is a recently developed, highly selective, and potent MAGL inhibitor that increases 2-AG but not AEA concentrations in mouse brain. Here, we report that JZL184 prolongs DSE in Purkinje neurons in cerebellar slices and DSI in CA1 pyramidal neurons in hippocampal slices. The effect of JZL184 on DSE/DSI is mimicked by the nonselective MAGL inhibitor methyl arachidonyl fluorophosphonate. In contrast, neither the selective FAAH inhibitor cyclohexylcarbamic acid 3'-carbomoylbiphenyl-3-yl ester (URB597) nor FAAH knockout has a significant effect on DSE/DSI. JZL184 produces greater enhancement of DSE/DSI in mouse neurons than that in rat neurons. The latter finding is consistent with biochemical studies showing that JZL184 is more potent in inhibiting mouse MAGL than rat MAGL. These results indicate that the degradation of 2-AG by MAGL is the rate-limiting step that determines the time course of DSE/DSI and that JZL184 is a useful tool for the study of 2-AG-mediated signaling.


