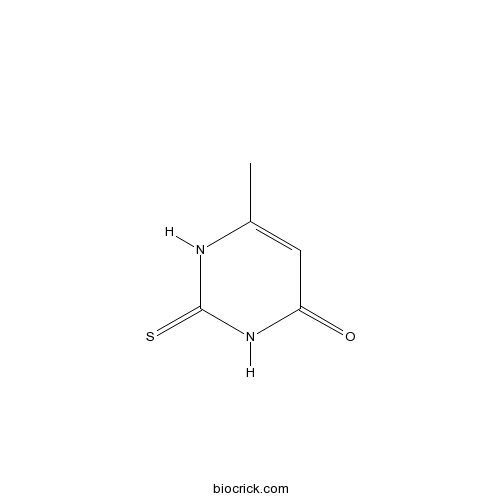
MethylthiouracilCAS# 56-04-2 |
- Meprednisone
Catalog No.:BCC4893
CAS No.:1247-42-3
- Hydrocortisone
Catalog No.:BCN2192
CAS No.:50-23-7
- Prednisolone
Catalog No.:BCC4830
CAS No.:50-24-8
- Desonide
Catalog No.:BCC4967
CAS No.:638-94-8
- Fluticasone propionate
Catalog No.:BCC4907
CAS No.:80474-14-2
- Methylprednisolone
Catalog No.:BCC2256
CAS No.:83-43-2
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 56-04-2 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 667493 | Appearance | Powder |
| Formula | C5H6N2OS | M.Wt | 142.18 |
| Type of Compound | N/A | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Synonyms | MTU | ||
| Solubility | DMSO : ≥ 50 mg/mL (351.67 mM) H2O : < 0.1 mg/mL (insoluble) *"≥" means soluble, but saturation unknown. | ||
| Chemical Name | 6-methyl-2-sulfanylidene-1H-pyrimidin-4-one | ||
| SMILES | CC1=CC(=O)NC(=S)N1 | ||
| Standard InChIKey | HWGBHCRJGXAGEU-UHFFFAOYSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C5H6N2OS/c1-3-2-4(8)7-5(9)6-3/h2H,1H3,(H2,6,7,8,9) | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | Methylthiouracil is an antithyroid agent. Methylthiouracil suppresses the production TNF-α and IL-6, and the activation of NF-κB and ERK1/2.In Vitro:HUVECs are treated with various concentrations of MTU (0-20 μM) for 6 h after the addition of LPS (100 ng/mL) for 4 h. MTU inhibits LPS-mediated hyperpermeability in endothelial cells, with the optimal effect occurring at a concentration above 5 μM. The effects of MTU are examined on HUVEC actin cytoskeletal arrangement by immunofluorescence staining of HUVEC monolayers with F-actin labeled fluorescein phalloidin. Control HUVECs exhibit a random distribution of F-actin throughout the cells, with some localization of actin filament bundles at the cell boundaries. Barrier disruption by LPS (100 ng/mL) is manifested by the formation of paracellular gaps in HUVECs. In addition, post-treatment with MTU (10 or 20 μM) results in inhibited formation of LPS-induced paracellular gaps with the formation of dense F-actin rings. To test the cytotoxicity of MTU, cellular viability assays are performed in HUVECs treated with MTU for 24 h. At concentrations up to 20 μM, MTU does not affect cell viability[1].In Vivo:MTU treatment results in marked inhibition of the peritoneal leakage of dye induced by LPS. The average circulating blood volume for mice is 72 mL/kg. Because the average mouse weight in this study is 27 g, and the average blood volume is 2 mL, the injected MTU (142 or 284 μg/kg) results in a maximum concentration of 10 or 20 μM in the peripheral blood[1]. References: | |||||

Methylthiouracil Dilution Calculator

Methylthiouracil Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 7.0333 mL | 35.1667 mL | 70.3334 mL | 140.6668 mL | 175.8335 mL |
| 5 mM | 1.4067 mL | 7.0333 mL | 14.0667 mL | 28.1334 mL | 35.1667 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.7033 mL | 3.5167 mL | 7.0333 mL | 14.0667 mL | 17.5833 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.1407 mL | 0.7033 mL | 1.4067 mL | 2.8133 mL | 3.5167 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0703 mL | 0.3517 mL | 0.7033 mL | 1.4067 mL | 1.7583 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
Methylthiouracil is an antithyroid preparation.
- Nitazoxanide
Catalog No.:BCC3824
CAS No.:55981-09-4
- ARC 239 dihydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC6851
CAS No.:55974-42-0
- Pseudohypericin
Catalog No.:BCN6348
CAS No.:55954-61-5
- Methylpheophorbide A
Catalog No.:BCN7998
CAS No.:5594-30-9
- Betamethasone 17,21-dipropionate
Catalog No.:BCC8875
CAS No.:5593-20-4
- Pennogenin 3-O-beta-chacotrioside
Catalog No.:BCN6707
CAS No.:55916-52-4
- Polyphyllin VI
Catalog No.:BCN1053
CAS No.:55916-51-3
- Cucurbitacin R
Catalog No.:BCN7877
CAS No.:55903-92-9
- Friedelin
Catalog No.:BCN5747
CAS No.:559-74-0
- beta-Amyrin
Catalog No.:BCN5746
CAS No.:559-70-6
- Morolic acid
Catalog No.:BCN7475
CAS No.:559-68-2
- 6-Hydroxysugiol
Catalog No.:BCN3154
CAS No.:55898-07-2
- 2,4-Diamino-6-hydroxypyrimidine
Catalog No.:BCC6658
CAS No.:56-06-4
- 4-Aminobutanoic acid
Catalog No.:BCN2187
CAS No.:56-12-2
- Cystamine dihydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC6344
CAS No.:56-17-7
- Cantharidin
Catalog No.:BCN1280
CAS No.:56-25-7
- Tetraethylammonium chloride
Catalog No.:BCC7554
CAS No.:56-34-8
- H-Gly-OH
Catalog No.:BCC2946
CAS No.:56-40-6
- H-Ala-OH
Catalog No.:BCC3190
CAS No.:56-41-7
- H-Ser-OH
Catalog No.:BCC3028
CAS No.:56-45-1
- Deoxycorticosterone acetate
Catalog No.:BCC4655
CAS No.:56-47-3
- Diethylstilbestrol
Catalog No.:BCC4900
CAS No.:56-53-1
- Quinidine
Catalog No.:BCC7863
CAS No.:56-54-2
- DL-5-Hydroxytryptophan
Catalog No.:BCN1232
CAS No.:56-69-9
Suppressive effects of methylthiouracil on polyphosphate-mediated vascular inflammatory responses.[Pubmed:27421058]
J Cell Mol Med. 2016 Dec;20(12):2333-2340.
Drug repositioning is used to discover drug candidates to treat human diseases, through the application of drugs or compounds that are approved for the treatment of other diseases. This method can significantly reduce the time required and cost of discovering new drug candidates for human diseases. Previous studies have reported pro-inflammatory responses of endothelial cells to the release of polyphosphate (PolyP). In this study, we examined the anti-inflammatory responses and mechanisms of Methylthiouracil (MTU), which is an antithyroid drug, and its effects on PolyP-induced septic activities in human umbilical vein endothelial cells (HUVECs) and mice. The survival rates, septic biomarker levels, behaviour of human neutrophils and vascular permeability were determined in PolyP-activated HUVECs and mice. MTU suppressed the PolyP-mediated vascular barrier permeability, up-regulation of inflammatory biomarkers, adhesion/migration of leucocytes, and activation and/or production of nuclear factor-kappaB, tumour necrosis factor-alpha and interleukin-6. Furthermore, MTU demonstrated protective effects on PolyP-mediated lethal death and the levels of the related septic biomarkers. Therefore, these results indicated the therapeutic potential of MTU on various systemic inflammatory diseases, such as sepsis or septic shock.
Novel insight into drug repositioning: Methylthiouracil as a case in point.[Pubmed:26117428]
Pharmacol Res. 2015 Sep;99:185-93.
Drug repositioning refers to the development of existing drugs for new indications. These drugs may have (I) failed to show efficacy in late stage clinical trials without safety issues; (II) stalled in the development for commercial reasons; (III) passed the point of patent expiry; or (IV) are being explored in new geographic markets. Over the past decade, pressure on the pharmaceutical industry caused by the 'innovation gap' owing to rising development costs and stagnant product output have become major reasons for the growing interest in drug repositioning. Companies that offer a variety of broad platforms for identifying new indications have emerged; some have been successful in building their own pipelines of candidates with reduced risks and timelines associated with further clinical development. The business models and platforms offered by these companies will be validated if they are able to generate positive proof-of-concept clinical data for their repositioned compounds. This review describes the strategy of biomarker-guided repositioning of chemotherapeutic drugs for inflammation therapy, considering the repositioning of Methylthiouracil (MTU), an antithyroid drug, as a potential anti-inflammatory reagent.
Methylthiouracil, a new treatment option for sepsis.[Pubmed:26239884]
Vascul Pharmacol. 2017 Jan;88:1-10.
The screening of bioactive compound libraries can be an effective approach for repositioning FDA-approved drugs or discovering new treatments for human diseases. Inhibition of high mobility group box 1 (HMGB1) and restoration of endothelial integrity are emerging as an attractive therapeutic strategies in the management of severe sepsis or septic shock. Here, we examined the effects of Methylthiouracil (MTU), used as antithyroid drug, by monitoring the effects on lipopolysaccharide (LPS)- or cecal ligation and puncture (CLP)-mediated release of HMGB1, and on the modulation of HMGB1-mediated inflammatory responses. The anti-inflammatory activities of MTU were determined by measuring permeability, leukocyte adhesion and migration, and the activation of pro-inflammatory proteins in HMGB1-activated HUVECs and mice. MTU inhibited the release of HMGB1 and downregulated HMGB1-dependent inflammatory responses in human endothelial cells. MTU also inhibited HMGB1-mediated hyperpermeability and leukocyte migration in mice. In addition, treatment with MTU reduced CLP-induced release of HMGB1 and sepsis-related mortality and pulmonary injury. Our results indicate that MTUs could be candidate therapeutic agents for various severe vascular inflammatory diseases via the inhibition of the HMGB1 signaling pathway.
Anti-inflammatory effects of methylthiouracil in vitro and in vivo.[Pubmed:26298005]
Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 2015 Nov 1;288(3):374-86.
The screening of bioactive compound libraries can be an effective approach for repositioning FDA-approved drugs or discovering new treatments for human diseases. Here, Methylthiouracil (MTU), an antithyroid drug, was examined for its effects on lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-mediated vascular inflammatory responses. The anti-inflammatory activities of MTU were determined by measuring permeability, human neutrophil adhesion and migration, and activation of pro-inflammatory proteins in LPS-activated human umbilical vein endothelial cells and mice. We found that post-treatment with MTU inhibited LPS-induced barrier disruption, expression of cell adhesion molecules (CAMs), and adhesion/transendothelial migration of human neutrophils to human endothelial cells. MTU induced potent inhibition of LPS-induced endothelial cell protein C receptor (EPCR) shedding. It also suppressed LPS-induced hyperpermeability and neutrophil migration in vivo. Furthermore, MTU suppressed the production of tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-alpha) and interleukin (IL)-6, and the activation of nuclear factor-kappaB (NF-kappaB) and extracellular regulated kinases (ERK) 1/2 by LPS. Moreover, post-treatment with MTU resulted in reduced LPS-induced lethal endotoxemia. These results suggest that MTU exerts anti-inflammatory effects by inhibiting hyperpermeability, expression of CAMs, and adhesion and migration of leukocytes, thereby endorsing its usefulness as a therapy for vascular inflammatory diseases.


