MagnoflorineCAS# 2141-09-5 |
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 2141-09-5 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 73337 | Appearance | Powder |
| Formula | C20H24NO4 | M.Wt | 342.4 |
| Type of Compound | Alkaloids | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Solubility | Soluble in Chloroform,Dichloromethane,Ethyl Acetate,DMSO,Acetone,etc. | ||
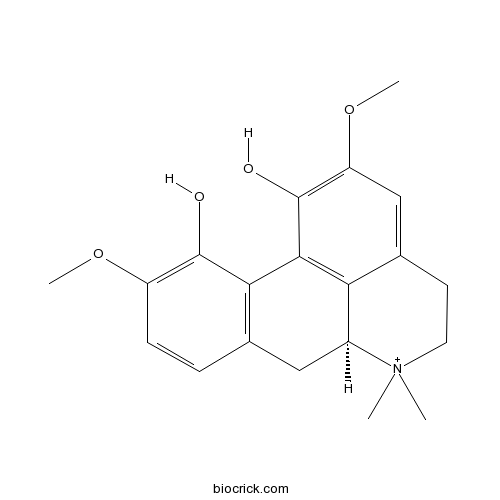
| Chemical Name | (6aS)-2,10-dimethoxy-6,6-dimethyl-5,6,6a,7-tetrahydro-4H-dibenzo[de,g]quinoline-6-ium-1,11-diol | ||
| SMILES | C[N+]1(CCC2=CC(=C(C3=C2C1CC4=C3C(=C(C=C4)OC)O)O)OC)C | ||
| Standard InChIKey | YLRXAIKMLINXQY-ZDUSSCGKSA-O | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C20H23NO4/c1-21(2)8-7-12-10-15(25-4)20(23)18-16(12)13(21)9-11-5-6-14(24-3)19(22)17(11)18/h5-6,10,13H,7-9H2,1-4H3,(H-,22,23)/p+1/t13-/m0/s1 | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | Magnoflorine possesses high activity as α-glucosidase inhibitor in vitro and in vivo, has antidiabetic potential activity; it also has sedative and anxiolytic effects, probably mediated by a GABAergic mechanism of action. Magnoflorine has protective effects, mediated by some mechanism other than prevention of micelle formation or protection of the erythrocyte membrane against osmotic imbalance. |
| Targets | LDL | GABA Receptor |
| In vitro | Sinomenine and magnoflorine, major constituents of Sinomeni Caulis et Rhizoma, show potent protective effects against membrane damage induced by lysophosphatidylcholine in rat erythrocytes.[Pubmed: 25840917 ]J Nat Med. 2015 Apr 4. The effects of the water extract of Sinomeni Caulis et Rhizoma (SCR-WE) and its major constituents, sinomenine (SIN) and Magnoflorine (MAG), on moderate hemolysis induced by lysophosphatidylcholine (LPC) were investigated in rat erythrocytes and compared with the anti-hemolytic effects of lidocaine (LID) and propranolol (PRO) as reference drugs. Magnoflorine from Coptidis Rhizoma protects high density lipoprotein during oxidant stress.[Pubmed: 17541173]Biol Pharm Bull. 2007 Jun;30(6):1157-60.The objective of the present study was to investigate the beneficial properties of Magnoflorine, an alkaloid isolated from coptidis rhizoma, on protecting human high density lipoprotein (HDL) against lipid peroxidation. |
| Kinase Assay | Magnoflorine from Tinospora cordifolia stem inhibits α-glucosidase and is antiglycemic in rats.[Reference: WebLink]J. Funct. Foods, 2012, 4(1):79-86.Antidiabetic potential of Tinospora cordifolia stem is well proven. In the course of screening of useful α-glucosidase inhibitors, we prepared alkaloid fraction (AFTC) and isolated three isoquinoline alkaloids, namely, jatrorrhizine, palmatine and Magnoflorine as active candidates for α-glucosidase inhibition.
|
| Animal Research | The involvement of magnoflorine in the sedative and anxiolytic effects of Sinomeni Caulis et Rhizoma in mice.[Pubmed: 23456265]J Nat Med. 2013 Oct;67(4):814-21.The present study seeks to evaluate the sedative and anxiolytic effects of the 70% ethanol extract of Sinomeni Caulis et Rhizoma (SR). |

Magnoflorine Dilution Calculator

Magnoflorine Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 2.9206 mL | 14.6028 mL | 29.2056 mL | 58.4112 mL | 73.014 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.5841 mL | 2.9206 mL | 5.8411 mL | 11.6822 mL | 14.6028 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.2921 mL | 1.4603 mL | 2.9206 mL | 5.8411 mL | 7.3014 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0584 mL | 0.2921 mL | 0.5841 mL | 1.1682 mL | 1.4603 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0292 mL | 0.146 mL | 0.2921 mL | 0.5841 mL | 0.7301 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
- CART (55-102) (human)
Catalog No.:BCC6007
CAS No.:214050-22-3
- Taxiphyllin
Catalog No.:BCN4922
CAS No.:21401-21-8
- Chrysin dimethylether
Catalog No.:BCN6799
CAS No.:21392-57-4
- Barbacarpan
Catalog No.:BCN4921
CAS No.:213912-46-0
- 1-Acetoxy-9,17-octadecadiene-12,14-diyne-11,16-diol
Catalog No.:BCN1493
CAS No.:213905-35-2
- Nifenazone
Catalog No.:BCC3822
CAS No.:2139-47-1
- Zedoarofuran
Catalog No.:BCN3527
CAS No.:213833-34-2
- 6,8-Cyclo-1,4-eudesmanediol
Catalog No.:BCN4920
CAS No.:213769-80-3
- 5-Iodo-A-85380, 5-trimethylstannyl N-BOC derivative
Catalog No.:BCC7102
CAS No.:213766-21-3
- Drim-7-ene-11,12-diol acetonide
Catalog No.:BCN4919
CAS No.:213552-47-7
- Flumethasone
Catalog No.:BCC8986
CAS No.:2135-17-3
- Ercalcidiol
Catalog No.:BCC1555
CAS No.:21343-40-8
- Glucoraphanin
Catalog No.:BCN3817
CAS No.:21414-41-5
- 26-Deoxycimicifugoside
Catalog No.:BCN2906
CAS No.:214146-75-5
- 1-Decarboxy-3-oxo-ceanothic acid
Catalog No.:BCN4924
CAS No.:214150-74-0
- Picrotin
Catalog No.:BCC8233
CAS No.:21416-53-5
- N-Benzylphthalimide
Catalog No.:BCC9096
CAS No.:2142-01-0
- 5,7-dimethoxy-2,2-dimethylchromene
Catalog No.:BCN8030
CAS No.:21421-66-9
- Demethylsuberosin
Catalog No.:BCN6508
CAS No.:21422-04-8
- Rosamultic acid
Catalog No.:BCN3516
CAS No.:214285-76-4
- 16alpha-Hydroxybauerenol
Catalog No.:BCN7724
CAS No.:214351-30-1
- 1400W dihydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC7057
CAS No.:214358-33-5
- (+)-Syringaresinol
Catalog No.:BCN7496
CAS No.:21453-69-0
- AMT hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC6823
CAS No.:21463-31-0
The involvement of magnoflorine in the sedative and anxiolytic effects of Sinomeni Caulis et Rhizoma in mice.[Pubmed:23456265]
J Nat Med. 2013 Oct;67(4):814-21.
The present study seeks to evaluate the sedative and anxiolytic effects of the 70% ethanol extract of Sinomeni Caulis et Rhizoma (SR). The extract was orally administered to mice at dosages of 25, 50, 100, 200 or 400 mg/kg. The mice were then subjected to an array of behavioral tests to assess the sedative (open-field, rota-rod, and thiopental sodium-induced sleeping test) and anxiolytic (elevated plus maze test) effects of the substance. SR (100, 200 mg/kg) significantly reduced locomotor activity, decreased rota-rod performance, and potentiated thiopental sodium-induced sleeping in mice, all indicative of its sedative effects. SR (50, 100 mg/kg) also produced anxiolytic effects, as shown by an increase in entries and staying time on the open arm of the plus maze. SR's sedative and anxiolytic effects were comparable to that of the benzodiazepine, diazepam. Moreover, to identify SR's probable mechanism of action, intracellular Cl(-) ion influx was observed in cultured human neuroblastoma cells. SR dose-dependently increased Cl(-) influx, which was blocked by co-administration of the GABAA receptor competitive antagonist, bicuculline. Among the major constituents of SR, only Magnoflorine showed a similar increment in Cl(-) influx, which was also blocked by bicuculline. Altogether, the present results suggest that SR has sedative and anxiolytic effects, probably mediated by Magnoflorine through a GABAergic mechanism of action.
Sinomenine and magnoflorine, major constituents of Sinomeni caulis et rhizoma, show potent protective effects against membrane damage induced by lysophosphatidylcholine in rat erythrocytes.[Pubmed:25840917]
J Nat Med. 2015 Jul;69(3):441-8.
The effects of the water extract of Sinomeni Caulis et Rhizoma (SCR-WE) and its major constituents, sinomenine (SIN) and Magnoflorine (MAG), on moderate hemolysis induced by lysophosphatidylcholine (LPC) were investigated in rat erythrocytes and compared with the anti-hemolytic effects of lidocaine (LID) and propranolol (PRO) as reference drugs. LPC caused hemolysis at concentrations above the critical micelle concentration (CMC), and the concentration of LPC producing moderate hemolysis (60 %) was approximately 10 muM. SCR-WE at 1 ng/mL-100 mug/mL significantly inhibited the hemolysis induced by LPC. SIN and MAG attenuated LPC-induced hemolysis in a concentration-dependent manner from very low to high concentrations (1 nM-100 muM and 10 nM-100 muM, respectively). In contrast, the inhibiting effects of LID and PRO on LPC-induced hemolysis were observed at higher concentrations (1-100 muM) but not at lower concentrations (1-100 nM). Neither SIN nor MAG affected micelle formation of LPC, nor, at concentrations of 1 nM-1 muM, did they attenuate the hemolysis induced by osmotic imbalance (hypotonic hemolysis). Similarly, SCR-WE also did not modify micelle formation or hypotonic hemolysis, except at the highest concentration. These results suggest that SIN and MAG potently protect the erythrocyte membrane from LPC-induced damage and contribute to the beneficial action of SCR-WE. The protective effects of SIN and MAG are mediated by some mechanism other than prevention of micelle formation or protection of the erythrocyte membrane against osmotic imbalance.
Magnoflorine from Coptidis Rhizoma protects high density lipoprotein during oxidant stress.[Pubmed:17541173]
Biol Pharm Bull. 2007 Jun;30(6):1157-60.
The objective of the present study was to investigate the beneficial properties of Magnoflorine, an alkaloid isolated from coptidis rhizoma, on protecting human high density lipoprotein (HDL) against lipid peroxidation. Magnoflorine exerts an inhibitory effect against Cu2+-induced lipid peroxidation of HDL, as showed by prolongation of lag time from 62 to 123 min at the concentration of 3.0 microM. It also inhibits the generation of thiobarbituric acid reactive substances (TBARS) in the dose-dependent manners with IC50 values of 2.3+/-0.2 microM and 6.2+/-0.5 microM since HDL oxidation mediated by either catalytic Cu2+ or thermo-labile radical initiator (AAPH), respectively. Separately, Cu2+ oxidized HDL lost the antioxidant action but the inclusion of Magnoflorine/Cu2+ oxidized HDL can protect LDL oxidation according to increasing Magnoflorine concentration. The results suggest that Magnoflorine may have a role to play in preventing the HDL oxidation.


