LupenoneCAS# 1617-70-5 |
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 1617-70-5 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 92158 | Appearance | White powder |
| Formula | C30H48O | M.Wt | 424.7 |
| Type of Compound | Triterpenoids | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Solubility | Ethanol : 3.33 mg/mL (7.84 mM; Need ultrasonic) | ||
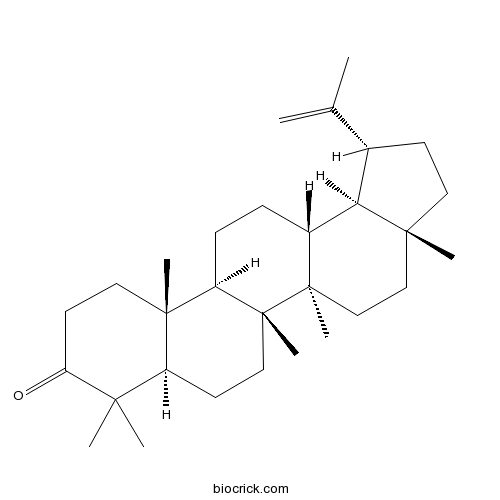
| Chemical Name | (1R,3aR,5aR,5bR,7aR,11aR,11bR,13aR,13bR)-3a,5a,5b,8,8,11a-hexamethyl-1-prop-1-en-2-yl-2,3,4,5,6,7,7a,10,11,11b,12,13,13a,13b-tetradecahydro-1H-cyclopenta[a]chrysen-9-one | ||
| SMILES | CC(=C)C1CCC2(C1C3CCC4C5(CCC(=O)C(C5CCC4(C3(CC2)C)C)(C)C)C)C | ||
| Standard InChIKey | GRBHNQFQFHLCHO-BHMAJAPKSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C30H48O/c1-19(2)20-11-14-27(5)17-18-29(7)21(25(20)27)9-10-23-28(6)15-13-24(31)26(3,4)22(28)12-16-30(23,29)8/h20-23,25H,1,9-18H2,2-8H3/t20-,21+,22-,23+,25+,27+,28-,29+,30+/m0/s1 | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | Lupenone and lupeol inhibit protein tyrosine phosphatase 1B (PTP1B) with IC50 values of 13.7 ± 2.1 and 5.6 ± 0.9 uM, respectively, they are non−competitive inhibitors of PTP1B, and PTP1B appears to be an attractive target for the development of new drugs for type 2 diabetes and obesity. Lupenone stimulates melanogenesis by increasing the tyrosinase enzyme expression via mitogen-activated protein kinase phosphorylated extracellular signal-regulated kinases 1 and 2 phosphorylation inhibition. A 1 : 4 mixture of Lupenone and caryophyllene oxide shows trypanocidal activity. |
| Targets | PPAR | ERK | MAPK | Antifection | PTP1B |
| In vitro | Lupenone isolated from Adenophora triphylla var. japonica extract inhibits adipogenic differentiation through the downregulation of PPARγ in 3T3-L1 cells.[Pubmed: 22848028]Phytother Res. 2013 May;27(5):761-6.Adenophora triphylla var. japonica (Campanulaceae) is known to have anti-inflammatory and anti-tussive effects. Dysfunction of adipocytes and adipose tissue in obesity is related to various inflammatory cytokines or adipokines. Synergistic Effect of Lupenone and Caryophyllene Oxide against Trypanosoma cruzi.[Pubmed: 23762135]Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2013;2013:435398.The in vitro trypanocidal activity of a 1 : 4 mixture of Lupenone and caryophyllene oxide confirmed a synergistic effect of the terpenoids against epimastigotes forms of T. cruzi (IC50 = 10.4 μ g/mL, FIC = 0.46). In addition, testing of the terpenoid mixture for its capacity to reduce the number of amastigote nests in cardiac tissue and skeletal muscle of infected mice showed a reduction of more than 80% at a dose level of 20.8 mg·kg(-1)·day(-1). |
| Kinase Assay | Inhibition of protein tyrosine phosphatase 1B by lupeol and lupenone isolated from Sorbus commixta.[Pubmed: 19548777 ]Lupenone from Erica multiflora leaf extract stimulates melanogenesis in B16 murine melanoma cells through the inhibition of ERK1/2 activation.[Pubmed: 23408272]Planta Med. 2013 Mar;79(3-4):236-43.Hypopigmentation diseases are usually managed using UVB light which increases the patients' risk for skin cancer. Here, we evaluated the melanogenesis stimulatory effects of leaf extracts of Erica multiflora, a medicinal plant from the Mediterranean region, and its active component, lup-20(29)-en-3-one, as possible therapeutic agents to address hypopigmentation disorders. J Enzyme Inhib Med Chem. 2009 Aug;24(4):1056-9.Protein tyrosine phosphatase 1B (PTP1B) appears to be an attractive target for the development of new drugs for type 2 diabetes and obesity. |

Lupenone Dilution Calculator

Lupenone Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 2.3546 mL | 11.773 mL | 23.546 mL | 47.0921 mL | 58.8651 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.4709 mL | 2.3546 mL | 4.7092 mL | 9.4184 mL | 11.773 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.2355 mL | 1.1773 mL | 2.3546 mL | 4.7092 mL | 5.8865 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0471 mL | 0.2355 mL | 0.4709 mL | 0.9418 mL | 1.1773 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0235 mL | 0.1177 mL | 0.2355 mL | 0.4709 mL | 0.5887 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
- Lupeol acetate
Catalog No.:BCN6893
CAS No.:1617-68-1
- Amentoflavone
Catalog No.:BCN6283
CAS No.:1617-53-4
- 2,3,8-Tri-O-methylellagic acid
Catalog No.:BCN1716
CAS No.:1617-49-8
- Caesalpine B
Catalog No.:BCN7377
CAS No.:1616757-60-8
- Caesalpine A
Catalog No.:BCN7376
CAS No.:1616757-59-5
- Dodovislactone B
Catalog No.:BCN7398
CAS No.:1616683-55-6
- Dodovislactone A
Catalog No.:BCN7399
CAS No.:1616683-54-5
- Dodovisone D
Catalog No.:BCN6871
CAS No.:1616683-53-4
- Dodovisone C
Catalog No.:BCN6872
CAS No.:1616683-52-3
- Dodovisone B
Catalog No.:BCN6867
CAS No.:1616683-51-2
- Dodovisone A
Catalog No.:BCN6839
CAS No.:1616683-50-1
- ONC201
Catalog No.:BCC3989
CAS No.:1616632-77-9
- Vincamine
Catalog No.:BCN2606
CAS No.:1617-90-9
- Z-Ile-Leu-aldehyde
Catalog No.:BCC5591
CAS No.:161710-10-7
- Tebipenem
Catalog No.:BCC5550
CAS No.:161715-21-5
- Tebipenempivoxil
Catalog No.:BCC3861
CAS No.:161715-24-8
- Rasagiline mesylate
Catalog No.:BCN2166
CAS No.:161735-79-1
- GLP-1 (9-36) amide
Catalog No.:BCC6001
CAS No.:161748-29-4
- 12-Oxocalanolide A
Catalog No.:BCN4699
CAS No.:161753-49-7
- Palmatrubine
Catalog No.:BCN2647
CAS No.:16176-68-4
- Esomeprazole Sodium
Catalog No.:BCC4376
CAS No.:161796-78-7
- Ethyl 2-(4-hydroxyphenyl)-4-methylthiazole-5-carboxylate
Catalog No.:BCC8969
CAS No.:161797-99-5
- Ethyl 2-(3-formyl-4-hydroxyphenyl)-4-methylthiazole-5-carboxylate
Catalog No.:BCC8968
CAS No.:161798-01-2
- Ethyl 2-(3-cyano-4-hydroxyphenyl)-4-methyl-1,3-thiazole-5-carboxylate
Catalog No.:BCC8966
CAS No.:161798-02-3
Synergistic Effect of Lupenone and Caryophyllene Oxide against Trypanosoma cruzi.[Pubmed:23762135]
Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2013;2013:435398.
The in vitro trypanocidal activity of a 1 : 4 mixture of Lupenone and caryophyllene oxide confirmed a synergistic effect of the terpenoids against epimastigotes forms of T. cruzi (IC50 = 10.4 mu g/mL, FIC = 0.46). In addition, testing of the terpenoid mixture for its capacity to reduce the number of amastigote nests in cardiac tissue and skeletal muscle of infected mice showed a reduction of more than 80% at a dose level of 20.8 mg.kg(-1).day(-1).
Lupenone isolated from Adenophora triphylla var. japonica extract inhibits adipogenic differentiation through the downregulation of PPARgamma in 3T3-L1 cells.[Pubmed:22848028]
Phytother Res. 2013 May;27(5):761-6.
Adenophora triphylla var. japonica (Campanulaceae) is known to have anti-inflammatory and anti-tussive effects. Dysfunction of adipocytes and adipose tissue in obesity is related to various inflammatory cytokines or adipokines. In this study, we investigated whether Lupenone isolated from A. triphylla var. japonica extract inhibits adipocyte differentiation and expression of adipogenic marker genes in 3T3-L1 preadipocytes. We demonstrated that Lupenone resulted in a significant reduction in lipid accumulation and expression of adipogenic marker genes in a dose-dependent manner. In addition, Lupenone decreased the transcriptional activity of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma (PPARgamma) induced by troglitazone, and we also demonstrated that Lupenone suppressed the PPARgamma and CCAAT-enhancer-binding protein alpha (C/EBPalpha) protein levels. These findings demonstrated that Lupenone isolated from A. triphylla var. japonica extract effectively inhibited adipocyte differentiation through downregulation of related transcription factor, particularly the PPARgamma gene.
Lupenone from Erica multiflora leaf extract stimulates melanogenesis in B16 murine melanoma cells through the inhibition of ERK1/2 activation.[Pubmed:23408272]
Planta Med. 2013 Mar;79(3-4):236-43.
Hypopigmentation diseases are usually managed using UVB light which increases the patients' risk for skin cancer. Here, we evaluated the melanogenesis stimulatory effects of leaf extracts of Erica multiflora, a medicinal plant from the Mediterranean region, and its active component, lup-20(29)-en-3-one, as possible therapeutic agents to address hypopigmentation disorders. B16 murine melanoma cells were treated with E. multiflora extracts or its active component Lupenone to evaluate their effects on melanin biosynthesis. The mechanism underlying the observed effects was also determined. Bioactivity-guided fractionation of fifteen ethyl acetate fractions identified fraction 2 to have melanogenesis stimulatory effects due to its ability to decrease mitogen-activated protein kinase phosphorylated extracellular signal-regulated kinases 1 and 2 activation. Preparative TLC of ethyl acetate fraction 2 revealed the presence of lup-20(29)-en-3-one as the major bioactive component. B16 cells treated with lup-20(29)-en-3-one increased melanin content without cytotoxicity. To determine the mechanism for the observed effects of lup-20(29)-en-3-one, the tyrosinase enzyme activity, the tyrosinase protein expression, and the activation of phosphorylated extracellular signal-regulated kinases 1 and 2 were determined. In addition, the expression of the tyrosinase mRNA was quantified using real-time PCR. Results showed that lup-20(29)-en-3-one has no effect on the tyrosinase enzyme activity but can increase tyrosinase expression at both the transcriptional and translational levels. The increase in the tyrosinase mRNA expression was most likely due to the inhibited mitogen-activated protein kinase phosphorylated extracellular signal-regulated kinases 1 and 2 activation. We report for the first time that E. multiflora ethyl acetate extract and its active compound lup-20(29)-en-3-one stimulate melanogenesis by increasing the tyrosinase enzyme expression via mitogen-activated protein kinase phosphorylated extracellular signal-regulated kinases 1 and 2 phosphorylation inhibition, making it a possible treatment for hypopigmentation diseases.
Inhibition of protein tyrosine phosphatase 1B by lupeol and lupenone isolated from Sorbus commixta.[Pubmed:19548777]
J Enzyme Inhib Med Chem. 2009 Aug;24(4):1056-9.
Protein tyrosine phosphatase 1B (PTP1B) appears to be an attractive target for the development of new drugs for type 2 diabetes and obesity. In our preliminary test, a MeOH extract of the stem barks of Sorbus commixta Hedl. (Rosaceae) showed strong PTP1B inhibitory activity. Bioassay-guided fractionation of the MeOH extract resulted in the isolation of two lupane-type triterpenes, Lupenone (1) and lupeol (2). Compounds 1 and 2 inhibited PTP1B with IC(50) values of 13.7 +/- 2.1 and 5.6 +/- 0.9 microM, respectively. Kinetic studies revealed that both the compounds 1 and 2 are non-competitive inhibitors of PTP1B that decrease V(max) values with no effect on K(m) values.


