HellebrigeninCAS# 465-90-7 |
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 465-90-7 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 259577 | Appearance | Powder |
| Formula | C24H32O6 | M.Wt | 416.51 |
| Type of Compound | Miscellaneous | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Solubility | Soluble in Chloroform,Dichloromethane,Ethyl Acetate,DMSO,Acetone,etc. | ||
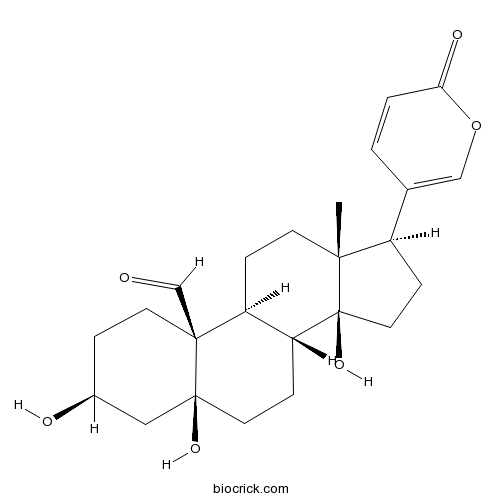
| Chemical Name | (3S,5S,8R,9S,10S,13R,14S,17R)-3,5,14-trihydroxy-13-methyl-17-(6-oxopyran-3-yl)-2,3,4,6,7,8,9,11,12,15,16,17-dodecahydro-1H-cyclopenta[a]phenanthrene-10-carbaldehyde | ||
| SMILES | CC12CCC3C(C1(CCC2C4=COC(=O)C=C4)O)CCC5(C3(CCC(C5)O)C=O)O | ||
| Standard InChIKey | TVKPTWJPKVSGJB-XHCIOXAKSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C24H32O6/c1-21-8-5-18-19(6-10-23(28)12-16(26)4-9-22(18,23)14-25)24(21,29)11-7-17(21)15-2-3-20(27)30-13-15/h2-3,13-14,16-19,26,28-29H,4-12H2,1H3/t16-,17+,18-,19+,21+,22-,23-,24-/m0/s1 | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | Hellebrigenin has anti-hepatoma activities, it induces cell cycle arrest and apoptosis in human hepatocellular carcinoma HepG2 cells through inhibition of Akt. Hellebrigenin exhibites moderate to strong activity against human HL-60, SF-295, MDA-MB-435, and HCT-8 cancer cell strains without hemolysis of mouse erythrocytes. |
| Targets | CDK | PARP | Akt | Caspase |
| In vitro | Cytotoxic profile of natural and some modified bufadienolides from toad Rhinella schneideri parotoid gland secretion[Reference: WebLink]Toxicon, 2010, 56(3):339-348.Cutaneous secretions of toad species are an important source of bufadienolides, compounds that exhibit interesting structural features and biopharmacological properties.
|
| Kinase Assay | Hellebrigenin induces cell cycle arrest and apoptosis in human hepatocellular carcinoma HepG2 cells through inhibition of Akt.[Pubmed: 24954031]Chem Biol Interact. 2014 Aug 5;219:184-94.Hellebrigenin, one of bufadienolides belonging to cardioactive steroids, was found in skin secretions of toads and plants of Helleborus and Kalanchoe genera.
|

Hellebrigenin Dilution Calculator

Hellebrigenin Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 2.4009 mL | 12.0045 mL | 24.009 mL | 48.0181 mL | 60.0226 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.4802 mL | 2.4009 mL | 4.8018 mL | 9.6036 mL | 12.0045 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.2401 mL | 1.2005 mL | 2.4009 mL | 4.8018 mL | 6.0023 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.048 mL | 0.2401 mL | 0.4802 mL | 0.9604 mL | 1.2005 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.024 mL | 0.12 mL | 0.2401 mL | 0.4802 mL | 0.6002 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
- Rhaponticin 6''-O-gallate
Catalog No.:BCN8856
CAS No.:94356-23-7
- Gardoside
Catalog No.:BCN8855
CAS No.:54835-76-6
- Rebaudioside E
Catalog No.:BCN8854
CAS No.:63279-14-1
- Neoastilbin
Catalog No.:BCN8853
CAS No.:54081-47-9
- 27-O-acetyl-withaferin A
Catalog No.:BCN8852
CAS No.:1214886-35-7
- Isorhamnetin 7-O-alpha-L-rhamnoside
Catalog No.:BCN8850
CAS No.:17331-72-5
- Hyperforin
Catalog No.:BCN8848
CAS No.:11079-53-1
- Bacopaside N2
Catalog No.:BCN8847
CAS No.:871706-75-1
- Sterebin E
Catalog No.:BCN8846
CAS No.:114343-74-7
- 4'-Methoxyagarotetrol
Catalog No.:BCN8845
CAS No.:123278-01-3
- Mulberrofuran Q
Catalog No.:BCN8844
CAS No.:101383-35-1
- Hydroxy-beta-sanshool
Catalog No.:BCN8841
CAS No.:97465-69-5
- 3beta-Methoxy-2,3-dihydrowithaferin A
Catalog No.:BCN8859
CAS No.:73365-94-3
- Pangelin
Catalog No.:BCN8861
CAS No.:33783-80-1
- Isoarnebin I
Catalog No.:BCN8862
CAS No.:24502-79-2
- 7-Methylcoumarin
Catalog No.:BCN8863
CAS No.:2445-83-2
- Isorhamnetin 7-O-glucoside
Catalog No.:BCN8864
CAS No.:6743-96-0
- 5,7,3',4',5'-Pentamethoxyflavone
Catalog No.:BCN8865
CAS No.:53350-26-8
- 7-Ethoxyrosmanol
Catalog No.:BCN8866
CAS No.:111200-01-2
- Piperlonguminine
Catalog No.:BCN8867
CAS No.:5950-12-9
- Cassiaside B
Catalog No.:BCN8868
CAS No.:119170-51-3
- Emodin-1-O-beta-gentiobioside
Catalog No.:BCN8869
CAS No.:849789-95-3
- N-(p-Coumaroyl) serotonin
Catalog No.:BCN8870
CAS No.:68573-24-0
- Quercetin 3-O-sophoroside-7-O-rhamnoside
Catalog No.:BCN8871
CAS No.:64828-40-6
Antiseizure potential of the ancient Greek medicinal plant Helleborus odorus subsp. cyclophyllus and identification of its main active principles.[Pubmed:32445663]
J Ethnopharmacol. 2020 May 20:112954.
ETHNOPHARMACOLOGICAL RELEVANCE: Ethnopharmacological data and ancient texts support the use of black hellebore (Helleborus odorus subsp. cyclophyllus, Ranunculaceae) for the management and treatment of epilepsy in ancient Greece. AIM OF THE STUDY: A pharmacological investigation of the root methanolic extract (RME) was conducted using the zebrafish epilepsy model to isolate and identify the compounds responsible for a potential antiseizure activity and to provide evidence of its historical use. In addition, a comprehensive metabolite profiling of this studied species was proposed. MATERIALS AND METHODS: The roots were extracted by solvents of increasing polarity and root decoction (RDE) was also prepared. The extracts were evaluated for antiseizure activity using a larval zebrafish epilepsy model with pentylenetetrazole (PTZ)-induced seizures. The RME exhibited the highest antiseizure activity and was therefore selected for bioactivity-guided fractionation. Isolated compounds were fully characterized by NMR and high-resolution tandem mass spectrometry (HRMS/MS). The UHPLC-HRMS/MS analyses of the RME and RDE were used for dereplication and metabolite profiling. RESULTS: The RME showed 80% inhibition of PTZ-induced locomotor activity (300mug/ml). This extract was fractionated and resulted in the isolation of a new glucopyranosyl-deoxyribonolactone (1) and a new furostanol saponin derivative (2), as well as 20-hydroxyecdysone (3), hellebrin (4), a spirostanol glycoside derivative (5) and deglucohellebrin (6). The antiseizure activity of RME was found to be due to the new furostanol saponin (2), hellebrin (4), which reduced 45% and 60% of PTZ-induced seizures (135muM, respectively). Besides, the aglycone of hellebrin, Hellebrigenin (S34), was also active (45% at 7muM). To further characterize the chemical composition of both RME and RDE, 30 compounds (A7-33, A35-37) were annotated based on UHPLC-HRMS/MS metabolite profiling. This revealed the presence of additional bufadienolides, furostanols and evidenced alkaloids. CONCLUSIONS: This study is the first to identify the molecular basis of the ethnopharmacological use of black hellebore for the treatment of epilepsy. This was achieved using a microscale zebrafish epilepsy model to rapidly quantify in vivo antiseizure activity. The UHPLC-HRMS/MS profile revealed the chemical diversity of the extracts and the presence of numerous bufadienolides, furostanols and ecdysteroids, also present in the decoction.
Hellebrigenin anti-pancreatic cancer effects based on apoptosis and autophage.[Pubmed:32426183]
PeerJ. 2020 May 8;8:e9011.
Hellebrigenin is a natural product found in the toad skin secretions and plants of Urginea, including Hellebores and Kalanchoe genera. It has been shown to be active against Leishmania chagasi promastigotes and Trypanosoma cruzi trypomastigotes and also reported to play an anti-tumor effect on several cancer cell lines in vitro, including pancreatic cancer. This study is aimed to investigate the effects of Hellebrigenin on pancreatic carcinoma cells, SW1990 and BxPC-3 in vitro and its molecular mechanism involved in antitumor activities. Our results showed that Hellebrigenin effectively inhibited the proliferation of SW1990 and BxPC-3 cells in dose- and time-dependent manner. Flow cytometry results showed that Hellebrigenin induced the G0/G1 arrest in both of SW1990 and BxPC-3 cells and promoted cell early apoptosis and autophagy according to morphological observation. Immunofluorescence staining results further confirmed that cell apoptosis and autophagy also increased upon the Hellebrigenin treatment. Moreover, higher dose of Hellebrigenin further increased the cell apoptosis rate while decrease the mitochondrial membrane potential 24 h after treatment. The autophagy rate increased 48 h after treatment with significant difference (P < 0.05). Western blot analysis showed that the expression of caspase 3, 7, cleaved caspase 7, Atg 12, LC3 proteins were increased in SW1990 cell after treatment with Hellebrigenin. In addition, increasing expression of caspase 3, 7, 9, PARP, cleaved caspase 3, 7, 9, PARP, the sub basic protein of the PI3K family, Beclin-1, LC 3, Atg 3, 5, 12, 16 L were also observed after BxPC-3 cells treated with Hellebrigenin. In summary, this study reported for the first time that Hellebrigenin effectively induced autophagy and apoptosis especially the early apoptosis in SW1990 and BxPC-3 cells.
Cytotoxicity and antimitotic activity of Rhinella schneideri and Rhinella marina venoms.[Pubmed:31265888]
J Ethnopharmacol. 2019 Oct 5;242:112049.
ETHNOPHARMACOLOGICAL RELEVANCE: Rhinella schneideri and Rhinella marina are toad venoms distributed in different parts of the world, including Brazil, Columbia and amazon. Venoms extracted from different species have many clinical applications such as antimicrobial cardiotonics and treatment of cancer. Aim of the study; In this study, we aim to investigate the effect of venoms extracted from R. schneideri and R. marina on cancer cells and verify possible mechanism of action. MATERIAL AND METHOD: Cytotoxicity analyses was performed using the resazurin reduction assay, where different concentrations of venoms were tested against sensitive CCRF-CEM and P-gp overexpressing ADR/CEM5000 leukemia cells. Programmed cell death was investigated using the flow cytometric annexin V/propidium iodide apoptosis assay. Furthermore, we analyzed flow cytometric cell cycle analyses of CCRF-CEM cells. Effect on tubulin formation was tested using molecular docking and fluorescence microscopy of U2OS-GFP-alpha-tubulin osteosarcoma cells treated for 24h with venoms. RESULTS: Cytotoxicity assays revealed a strong activity towards wild-type CCRF-CEM cells (IC50 values of 0.202+/-0.005mug/ml and 0.18+/-0.007mug/ml for R. schneideri and R. marina, respectively) and multidrug-resistant CEM/ADR5000cells (IC50 0.403+/-0.084mug/ml and 0.32+/-0.077mug/ml for R. schneideri and R. marina, respectively). The venoms induced apoptosis as major mechanism of cell death. The venoms induced strong G2/M cell arrest in CCRF-CEM cells. We suggested tubulin as a major target for the venoms. In silico molecular docking of the major constituents of the venoms, i.e. bufalin, marinobufagin, telocinbufagin, Hellebrigenin, showed strong binding affinities to tubulin. This result was verified in vitro. The venoms dysregulated microtubule arrangement of U2OS cells expressing GFP-labeled tubulin. Toxicity predictions by QSAR methodology highlighted the toxic features of bufadienolides. CONCLUSION: Our study demonstrated the importance of toad venoms as source of cytotoxic compounds that may serve as lead compounds for the development of novel anticancer drugs.
New cytotoxic bufadienolides from the roots and rhizomes of Helleborus thibetanus Franch.[Pubmed:30587014]
Nat Prod Res. 2020 Apr;34(7):950-957.
Three new bufadienolides 14beta, 16beta-dihydroxy-3beta-[beta-D-glucopyranosyl-(1-->6)-(beta-D-glucopyranosyl)oxy] -5alpha-bufa-20, 22-dienolide (1), 14beta-hydroxy-3beta-[beta-D-glucopyranosyl-(1-->4)-(beta-D-glucopyranosyl)oxy]-5 alpha-bufa-20, 22-dienolide (2) and Hellebrigenin-3-O-beta-D-glucosyl-(1-->4)-beta-D-glucoside (3), together with eight known bufadienolides (4-11) were isolated from the roots and rhizomes of Helleborus thibetanus. Their structures were elucidated by extensive spectroscopic methods and acid hydrolysis. Compounds 1-7 were evaluated for their cytotoxic activity against HCT116, A549 and HepG2 tumor cell lines. Compound 1 exhibited moderate cytotoxicity against HepG2 cells with IC50 value of 15.1 +/- 1.72 muM. Compounds 5 and 6 exhibited moderate cytotoxicity against HCT116 cells with IC50 values of 15.12 +/- 0.58 muM and 13.17 +/- 2.34 muM, respectively.
Cytocidal effects of arenobufagin and hellebrigenin, two active bufadienolide compounds, against human glioblastoma cell line U-87.[Pubmed:30272276]
Int J Oncol. 2018 Dec;53(6):2488-2502.
Glioblastoma is the most common and lethal intracranial tumor type, characterized by high angiogenic and infiltrative capacities. To provide a novel insight into therapeutic strategies against glioblastoma, the cytotoxicity of arenobufagin and Hellebrigenin was investigated in the human glioblastoma cell line, U-87. Similar dose-dependent cytotoxicity was observed in the cells, whereas no detectable toxicity was confirmed in mouse primary astrocytes. Treatment with each drug downregulated the expression levels of Cdc25C, Cyclin B1 and survivin, which occurred in parallel with G2/M phase arrest. Necrotic-like cell death was only observed in the cells treated with a relatively high concentration (>100 ng/ml). These results indicate that the two drugs exhibited distinct cytotoxicity against cancerous glial cells with high potency and selectivity, suggesting that growth inhibition associated with G2/M phase arrest and/or necrosis were attributed to their toxicities. Activation of the p38 mitogen activated protein kinase (MAPK) signaling pathway was also observed in treated cells. Notably, a specific inhibitor of p38 MAPK, SB203580, itself caused a significant decrease in cell viability, and further enhanced the cytotoxicity of the two drugs, suggesting an important pro-survival role for p38 MAPK. Given that p38 MAPK serves an essential role in promoting glioblastoma cell survival, developing a novel combination regimen of arenobufagin/Hellebrigenin plus a p38 MAPK inhibitor may improve the efficacy of the two drugs, and may provide more therapeutic benefits to patients with glioblastoma. The qualitative assessment demonstrated the existence of arenobufagin in the cerebrospinal fluid of arenobufagin-treated rats, supporting its clinical application.
[Study on quality control method of toad venom based on characteristic chromatogram and QAMS].[Pubmed:30111043]
Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 2018 Jul;43(14):2863-2871.
Toad venom (Chansu) is prepared from the dried secretion of parotid gland and skin gland from Bufo bufo gargarizans or B. melanostictus. Up to now, much attention shall be paid to the poor quality of commercial toad venom because of the adulteration. So, it is urgent to establish a scientific and perfect quality control method to improve the quality of toad venom and guarantee its safety and effectiveness in clinical application. The different batches of toad venom samples were assayed by high performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) and the quantitative analysis of multi-components by single marker (QAMS) was used to detect the contents of five bufagenins. As a result, the reference characteristic chromatogram was established, displaying serotonin, gamabufotalin, arenobufagin, Hellebrigenin, telocinobufagin, bufotalin, cinobufotalin, bufalin, cinobufagin and resibufogenin as characteristic peaks. Taking cinobufagin as an internal reference substance, QAMS was verified for the determination of five bufagenins (gamabufotalin, bufotalin, bufalin, cinobufagin, resibufogenin) in toad venom samples. The durability and applicability of the relative correction factor (RCF) were also studied systematically. RCFs of cinobufagin to gamabufotalin, bufotalin, bufalin and resibufogenin were determined as 1.05, 0.895, 1.09 and 0.913, respectively. The characteristic chromatogram and QAMS established in this study could effectively control the quality of toad venom and provide scientific evidence for the improvement of the quality standard of the toad venom to be described in Chinese Pharmacopoeia (2020 edition).
Antiproliferative activity and chemical composition of the venom from the Amazonian toad Rhinella marina (Anura: Bufonidae).[Pubmed:27616454]
Toxicon. 2016 Oct;121:119-129.
Little is known on the composition of Peruvian Amazon toad venoms. The large toad Rhinella marina is common in the cleared tropical forests of the Iquitos region and is regarded as poisonous. The venom from two different populations of R. marina was collected in the Departamento de Loreto, Peru. The samples were assessed for antiproliferative effect and composition. Some 29 compounds were identified or tentatively identified from the venom by spectroscopic and spectrometric means. The main free bufadienolide was marinobufagin 7 while marinobufotoxin 15 and bufalitoxin 9 were the main bufadienolide argininyl diacid derivatives. The alkaloids dehydrobufotenin 28 and bufotenidin 29 were present in both venoms. The main difference in the venoms was the relative ratio of argininyl diacids from bufadienolides to free bufadienolides. The argininyl diacids included derivatives from bufalin, marinobufagin, telocinobufagin, Hellebrigenin, resibufogenin and bufotalinin. Four compounds, including undecadienoyl aginine 6 and three argininyl diacids from bufadienolides were tentatively identified for the first time in the samples. The venom showed a strong antiproliferative effect towards MRC-5 normal human lung fibroblasts (0.063-0.247 mug/mL), AGS human gastric adenocarcinoma cells (0.076-0.272 mug/mL), SK-MES-1 human lung cancer cells (0.154-0.296 mug/mL), J82 human bladder carcinoma cells (0.169-0.212 mug/mL), and HL-60 human promyelocytic leukemia (0.071-0.283 mug/mL). The antiproliferative effect is mediated by ROS production and cell cycle arrest in human breast cancer cells (MCF7 and MDA-MB-231). This is the first report on the composition of R. marina venom from the Peruvian Amazon pointing out the need to include different venom samples to get a better picture from the activity and composition of South American toad defense substances.
Metabolites profiling of 10 bufadienolides in human liver microsomes and their cytotoxicity variation in HepG2 cell.[Pubmed:26869342]
Anal Bioanal Chem. 2016 Apr;408(10):2485-95.
Bufadienolides, a class of polyhydroxy steroids, exhibit significant antitumor activity. In this study, a total of 39 metabolites from 10 bufadienolides were detected and identified by ultrahigh-performance liquid chromatography (UHPLC) coupled with an LTQ Orbitrap mass spectrometer. The results showed that hydroxylation and dehydrogenation were the major metabolic pathways of bufadienolides in human liver microsomes (HLMs). CYP3A4 was found to be the major metabolic enzyme and CYP2D6 only mediated the dehydrogenation reaction. A systematic validated cytotoxicity evaluation method for bufadienolide metabolites at equal equivalents was established. Hellebrigenin (1), hellebrigenol (2), arenobufagin (3), bufotalin (5), and bufalin (6) were selected to determine their cytotoxicity against HepG2 cells before and after incubation in HLMs. All the test samples were enriched by a validated solid-phase extraction (SPE) method. Although the cytotoxicities of metabolites were weaker than those of the parent compounds to different degrees, their effects were still strong.
[Bufadienolides from venom of Bufo bufo gargarizans].[Pubmed:25204176]
Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 2014 Mar;39(5):841-5.
Twelve compounds were isolated from the venom of Bufo bufo gargarizans. On the basis of their physical and chemical properties and spectral data, their structures were identified as resibufagenin (1), bufotalin (2), desacetylcinobufagin (3), 19-oxodesacetylcinobufotalin (4), cinobufotalin (5), 1beta-hydroxylbufalin (6), 12alpha-hydroxybufalin (7), bufotalinin (8), Hellebrigenin (9), telocinobufagin (10), hellebrigenol (11) and cinobufagin-3-hemisuberate methyl ester (12), respectively. Compounds 7 and 12 are new natural products.
Hellebrigenin induces cell cycle arrest and apoptosis in human hepatocellular carcinoma HepG2 cells through inhibition of Akt.[Pubmed:24954031]
Chem Biol Interact. 2014 Aug 5;219:184-94.
Hellebrigenin, one of bufadienolides belonging to cardioactive steroids, was found in skin secretions of toads and plants of Helleborus and Kalanchoe genera. In searching for natural constituents with anti-hepatoma activities, we found that Hellebrigenin, isolated from traditional Chinese medicine Venenum Bufonis, potently reduced the viability and colony formation of human hepatocellular carcinoma cells HepG2, and went on to explore the underlying molecular mechanisms. Our results demonstrated that Hellebrigenin triggered DNA damage through DNA double-stranded breaks and subsequently induced cell cycle G2/M arrest associated with up-regulation of p-ATM (Ser(1981)), p-Chk2 (Tyr(68)), p-CDK1 (Tyr(15)) and Cyclin B1, and down-regulation of p-CDC25C (Ser(216)). It was also found that Hellebrigenin induced mitochondrial apoptosis, characterized by Bax translocation to mitochondria, disruption of mitochondrial membrane potential, release of cytochrome c into cytosol and sequential activation of caspases and PARP. In addition, Akt expression and phosphorylation were inhibited by Hellebrigenin, whereas Akt silencing with siRNA significantly blocked cell cycle arrest but enhanced apoptosis induced by Hellebrigenin. Activation of Akt by human insulin-like growth factor I (hIGF-I) could obviously attenuate Hellebrigenin-induced cell death. In summary, our study is the first to report the efficacy of Hellebrigenin against HepG2 and elucidated its molecular mechanisms including DNA damage, mitochondria collapse, cell cycle arrest and apoptosis, which will contribute to the development of Hellebrigenin into a chemotherapeutic agent in the treatment of liver cancer.
Structure-activity relationship analysis of bufadienolide-induced in vitro growth inhibitory effects on mouse and human cancer cells.[Pubmed:23706005]
J Nat Prod. 2013 Jun 28;76(6):1078-84.
The in vitro growth inhibitory effects of 27 bufadienolides and eight degradation products, with two cardenolides (ouabain and digoxin) chosen as reference compounds, were analyzed by means of an MTT colorimetric assay in six human and two mouse cancer cell lines. A structure-activity analysis was then performed to highlight the most important substituents relating to the in vitro growth inhibitory activity of bufadienolides in cancer cells. Thus, the current study revealed that various bufadienolides, including gamabufotalin rhamnoside (1a), bufotalin (2a), and hellebrin (3a), displayed higher growth inhibitory activities for various human cancer cell lines when compared to ouabain and digoxin. Gamabufotalin rhamnoside (1a) was the only compound that displayed growth inhibitory effects of <1 muM in mouse cancer cells that expressed mutated forms of the Na(+),K(+)-ATPase alpha-1 subunit. In addition, all genins and degradation products displayed weaker (if any) in vitro growth inhibitory effects on cancer cells when compared to their respective glycosylated homologue, with the exception of Hellebrigenin (3b), which was as active as hellebrin (3a).
14,15-Didehydro-hellebrigenin.[Pubmed:22719419]
Acta Crystallogr Sect E Struct Rep Online. 2012 Jun 1;68(Pt 6):o1614-5.
The title compound, C(24)H(30)O(5), is the didehydro product of the steroid Hellebrigenin (systematic name: 3beta,5,14-trihy-droxy-19-oxo-5beta-bufa-20,22-dienolide). It consists of three cyclo-hexane rings (A, B and C), a five-membered ring (D) and a six-membered lactone ring (E). The stereochemistry of the ring junctions are A/B cis, B/C trans and C/D cis. Cyclo-hexane rings A, B and C have normal chair conformations. The five-membered ring D with the C=C bond adopts an envelope conformation. Lactone ring E is essentially planar with a mean derivation of 0.006 (4) A and is beta-oriented at the C atom of ring D to which it is attached. There is an O-Hcdots, three dots, centeredO hydrogen bond in the mol-ecule involving the hy-droxy groups. In the crystal, O-Hcdots, three dots, centeredO hydrogen bonds link the mol-ecules into chains propagating along [010]. The chains are linked by C-Hcdots, three dots, centeredO contacts into a three-dimensional network.
Secohellebrigeninamide.[Pubmed:22412577]
Acta Crystallogr Sect E Struct Rep Online. 2012 Mar 1;68(Pt 3):o682.
The title compound, C(26)H(37)NO(5), was the reaction product of Hellebrigenin with N,N-dimethyl-formamide. It consists of three cyclo-hexane rings (A, B and C), one five-membered ring (D) and one dihydro-pyran ring (E). The stereochemistry of the ring junctions is is A/B cis, B/C trans, C/D cis and C/E trans. The cyclo-hexane rings A, B and C have chair conformations. Both the five-membered ring D and the dihydro-pyran ring adopt an envelope conformation. Two orientations are found for the aldehyde group with occupancies of 0.608 (10) and 0.392 (10). In the crystal, short O-Hcdots, three dots, centeredO hydrogen bonds and short C-Hcdots, three dots, centeredO contacts involving the hy-droxy group, terminal methyl group and carbonyl group link the mol-ecules into a three-dimensional network.


