Dynorphin BEndogenous κ agonist CAS# 83335-41-5 |
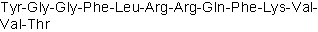
- Amyloid β-Protein (1-15)
Catalog No.:BCC1003
CAS No.:183745-81-5
- Endomorphin-1
Catalog No.:BCC1008
CAS No.:189388-22-5
- Beta-Amyloid (1-11)
Catalog No.:BCC1002
CAS No.:190436-05-6
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 83335-41-5 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 25078106 | Appearance | Powder |
| Formula | C74H115N21O17 | M.Wt | 1570.85 |
| Type of Compound | N/A | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Solubility | H2O Peptide Solubility and Storage Guidelines: 1. Calculate the length of the peptide. 2. Calculate the overall charge of the entire peptide according to the following table: 3. Recommended solution: | ||
| Sequence | YGGFLRRQFKVVT | ||
| Chemical Name | (2R,3S)-2-[[(2R)-2-[[(2R)-2-[[(2S)-6-amino-2-[[2-[[(2R)-5-amino-2-[[(2S)-2-[[2-[[(2S)-2-[[(2S)-2-[[2-[[2-[[(2S)-2-amino-3-(4-hydroxyphenyl)propanoyl]amino]acetyl]amino]acetyl]amino]-3-phenylpropanoyl]amino]-4-methylpentanoyl]amino]-5-(diaminomethylideneamino)pentanoyl]amino]-5-(diaminomethylideneamino)pentanoyl]amino]-5-oxopentanoyl]amino]-3-phenylpropanoyl]amino]hexanoyl]amino]-3-methylbutanoyl]amino]-3-methylbutanoyl]amino]-3-hydroxybutanoic acid | ||
| SMILES | CC(C)CC(C(=O)NC(CCCN=C(N)N)C(=O)NC(CCCN=C(N)N)C(=O)NC(CCC(=O)N)C(=O)NC(CC1=CC=CC=C1)C(=O)NC(CCCCN)C(=O)NC(C(C)C)C(=O)NC(C(C)C)C(=O)NC(C(C)O)C(=O)O)NC(=O)C(CC2=CC=CC=C2)NC(=O)CNC(=O)CNC(=O)C(CC3=CC=C(C=C3)O)N | ||
| Standard InChIKey | AGTSSZRZBSNTGQ-LWZMOALMSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C74H115N21O17/c1-40(2)34-53(91-68(107)54(36-44-18-10-8-11-19-44)86-58(100)39-84-57(99)38-85-62(101)48(76)35-46-25-27-47(97)28-26-46)67(106)89-51(24-17-33-83-74(80)81)63(102)87-50(23-16-32-82-73(78)79)64(103)90-52(29-30-56(77)98)65(104)92-55(37-45-20-12-9-13-21-45)69(108)88-49(22-14-15-31-75)66(105)93-59(41(3)4)70(109)94-60(42(5)6)71(110)95-61(43(7)96)72(111)112/h8-13,18-21,25-28,40-43,48-55,59-61,96-97H,14-17,22-24,29-39,75-76H2,1-7H3,(H2,77,98)(H,84,99)(H,85,101)(H,86,100)(H,87,102)(H,88,108)(H,89,106)(H,90,103)(H,91,107)(H,92,104)(H,93,105)(H,94,109)(H,95,110)(H,111,112)(H4,78,79,82)(H4,80,81,83)/t43-,48-,49-,50-,51?,52+,53-,54-,55?,59+,60+,61+/m0/s1 | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | Opioid peptide that is the preferred endogenous agonist for the kappa opioid receptor. Displays moderate selectivity for κ1b. |

Dynorphin B Dilution Calculator

Dynorphin B Molarity Calculator

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
- (-)-Lariciresinol
Catalog No.:BCN3418
CAS No.:83327-19-9
- 8(17),13-Labdadien-15,16-olide
Catalog No.:BCN4374
CAS No.:83324-51-0
- Bryostatin 1
Catalog No.:BCC7343
CAS No.:83314-01-6
- 7-Hydroxycoumarin-6-carboxylic acid
Catalog No.:BCN4375
CAS No.:833-52-3
- Menisporphine
Catalog No.:BCN7902
CAS No.:83287-02-9
- Napabucasin
Catalog No.:BCC6525
CAS No.:83280-65-3
- Lauryl-LF 11
Catalog No.:BCC6175
CAS No.:832729-14-3
- LF 11
Catalog No.:BCC6174
CAS No.:832729-13-2
- APD668
Catalog No.:BCC5389
CAS No.:832714-46-2
- Angelol H
Catalog No.:BCN8047
CAS No.:83247-73-8
- Dehydrocavidine
Catalog No.:BCN2549
CAS No.:83218-34-2
- 1beta-Hydroxy-beta-eudesmol
Catalog No.:BCN7097
CAS No.:83217-89-4
- 10-O-Caffeoyl-6-epiferetoside
Catalog No.:BCN4822
CAS No.:83348-22-5
- 25(R)-Hydroxyprotopanaxadiol
Catalog No.:BCN2493
CAS No.:83349-37-5
- D609
Catalog No.:BCC1509
CAS No.:83373-60-8
- Prenyl caffeate
Catalog No.:BCC8351
CAS No.:100884-13-7
- PL 017
Catalog No.:BCC5864
CAS No.:83397-56-2
- Phenformin HCl
Catalog No.:BCC4362
CAS No.:834-28-6
- ICI 154,129
Catalog No.:BCC5677
CAS No.:83420-94-4
- Boc-D-Prolinol
Catalog No.:BCC2707
CAS No.:83435-58-9
- Ebracteolata cpd B
Catalog No.:BCN3781
CAS No.:83459-37-4
- Ginsenoside Ra1
Catalog No.:BCN8392
CAS No.:83459-41-0
- Mifamurtide
Catalog No.:BCC5241
CAS No.:83461-56-7
- Voglibose
Catalog No.:BCC4750
CAS No.:83480-29-9
Effects of Orchidectomy and Testosterone Replacement on Numbers of Kisspeptin-, Neurokinin B-, and Dynorphin A-Immunoreactive Neurones in the Arcuate Nucleus of the Hypothalamus in Obese and Diabetic Rats.[Pubmed:28009489]
J Neuroendocrinol. 2017 Feb;29(2).
Neurones expressing kisspeptin, neurokinin B and dynorphin A, located in the arcuate nucleus of the hypothalamus (ARC), are important regulators of reproduction. Their functions depend on metabolic and hormonal status. We hypothesised that male rats with high-fat diet-induced obesity (DIO) and/or streptozotocin-induced diabetes mellitus type 1 (DM1) and type 2 (DM2) will have alterations in numbers of immunoreactive (-IR) cells: kisspeptin-IR and/or neurokinin B-IR and dynorphin A-IR neurones in the ARC in the sham condition. In addition, orchidectomy alone (ORX) and with testosterone treatment (ORX+T) will unmask possible deficits in the response of these neurones in DIO, and/or DM1 and DM2 rats. Rats were assigned to four groups: a control (C) and one diabetic group (DM1) were fed a regular chow diet, whereas the obese group (DIO) and the other diabetic group (DM2) were fed a high-fat diet. To induce diabetes, streptozotocin was injected. After 6 weeks, each group was divided into three subgroups: ORX, ORX+T and sham. After another 2 weeks, metabolic and hormonal profiles were assessed and immunocytochemistry was performed. We found that: (1) under sham conditions: (i) DM1 and DM2 animals had higher numbers of kisspeptin-IR cells than controls and (ii) DM2 rats had increased numbers of neurokinin B-IR and dynorphin A-IR cells compared to C animals; (2) ORX and ORX+T treatments unmasked deficits of the studied neurones in DM1 and DM2 but not in DIO animals; and (3) DIO, DM1 and DM2 rats had altered metabolic and hormonal profiles, in particular decreased levels of testosterone. We concluded that alterations in numbers of kisspeptin-IR and neurokinin B-IR neurones in the ARC and their response to ORX and ORX+T may account for disruptions of metabolic and reproductive functions in diabetic but not in obese rats.
Age-related alterations in hypothalamic kisspeptin, neurokinin B, and dynorphin neurons and in pulsatile LH release in female and male rats.[Pubmed:27842268]
Neurobiol Aging. 2017 Feb;50:30-38.
Pulsatile secretion of gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GnRH)/luteinizing hormone (LH) decreases during aging. Kisspeptin (encoded by Kiss1) neurons in the arcuate nucleus coexpress neurokinin B (Tac3) and dynorphin (Pdyn) and are critical for regulating the GnRH/LH pulse. We therefore examined kisspeptin neurons by histochemistry and pulsatile LH release in rats aged 2-3 (Young), 12-13 (Young-Middle), 19-22 (Late-Middle), and 24-26 (Old) months. Total LH concentrations, sampled for 3 hours, decreased in both sexes with aging. In females, numbers of Tac3 and Pdyn neurons were significantly reduced in all aging rats, and numbers of Kiss1 neurons were significantly reduced in Late-Middle and Old rats. In males, numbers of all 3 neuron-types were significantly decreased in all aging rats. GnRH agonist induced LH release in all animals; however, the increased LH concentration in all aging rats was less than that in Young rats. These results suggest that expression of each gene in kisspeptin neurons may be controlled individually during aging, and that reduction of their expression or change in pituitary responsiveness may cause attenuated pulsatile LH secretion.
Prenatal testosterone exposure decreases colocalization of insulin receptors in kisspeptin/neurokinin B/dynorphin and agouti-related peptide neurons of the adult ewe.[Pubmed:27543746]
Eur J Neurosci. 2016 Oct;44(8):2557-2568.
Insulin serves as a link between the metabolic and reproductive systems, communicating energy availability to the hypothalamus and enabling reproductive mechanisms. Adult Suffolk ewes prenatally exposed to testosterone (T) display an array of reproductive and metabolic dysfunctions similar to those seen in women with polycystic ovarian syndrome (PCOS), including insulin resistance. Moreover, prenatal T treatment alters neuropeptide expression in KNDy (co-expressing kisspeptin, neurokinin B/dynorphin) and agouti-related peptide (AgRP) neurons in the arcuate nucleus, two populations that play key roles in the control of reproduction and metabolism, respectively. In this study, we determined whether prenatal T treatment also altered insulin receptors in KNDy and AgRP neurons, as well as in preoptic area (POA) kisspeptin, pro-opiomelanocortin (POMC), and gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GnRH) neurons of the adult sheep brain. Immunofluorescent detection of the beta subunit of insulin receptor (IRbeta) revealed that KNDy, AgRP and POMC neurons, but not GnRH or POA kisspeptin neurons, colocalize IRbeta in control females. Moreover, prenatal T treatment decreased the percentage of KNDy and AgRP neurons that colocalized IRbeta, consistent with reduced insulin sensitivity. Administration of the anti-androgen drug, Flutamide, during prenatal T treatment, prevented the reduction in IRbeta colocalization in AgRP, but not in KNDy neurons, suggesting that these effects are programmed by androgenic and oestrogenic actions, respectively. These findings provide novel insight into the effects of prenatal T treatment on hypothalamic insulin sensitivity and raise the possibility that decreased insulin receptors, specifically within KNDy and AgRP neurons, may contribute to the PCOS-like phenotype of this animal model.
Immunohistochemical characterization of the arcuate kisspeptin/neurokinin B/dynorphin (KNDy) and preoptic kisspeptin neuronal populations in the hypothalamus during the estrous cycle in heifers.[Pubmed:27349533]
J Reprod Dev. 2016 Oct 18;62(5):471-477.
Elucidating the physiological mechanisms that control reproduction is an obvious strategy for improving the fertility of cattle and developing new agents to control reproductive functions. The present study aimed to identify kisspeptin neurons in the bovine hypothalamus, clarifying that a central mechanism is also present in the cattle brain, as kisspeptin is known to play an important role in the stimulation of gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GnRH)/gonadotropin secretion in other mammals. To characterize kisspeptin neurons in the bovine hypothalamus, the co-localizations of kisspeptin and neurokinin B (NKB) or kisspeptin and dynorphin A (Dyn) were examined. Hypothalamic tissue was collected from Japanese Black or Japanese Black x Holstein crossbred cows during the follicular and luteal phases. Brain sections, including the arcuate nucleus (ARC) and the preoptic area (POA), were dual immunostained with kisspeptin and either NKB or Dyn. In the ARC, both NKB and Dyn were co-localized in kisspeptin neurons during both the follicular and luteal phases, demonstrating the presence of kisspeptin/NKB/Dyn-containing neurons, referred to as KNDy neurons, in cows. In the POA, no co-localization of kisspeptin with either NKB or Dyn was detected. Kisspeptin expression in the follicular phase was higher than that in the luteal phase, suggesting that kisspeptin expression in the POA is positively controlled by estrogen in cows. The kisspeptin neuronal populations in the ARC and POA likely play important roles in regulating the GnRH pulse and surge, respectively, in cows.
Cysteine protease inhibitors suppress the development of tolerance to morphine antinociception.[Pubmed:18440066]
Neuropeptides. 2008 Jun;42(3):239-44.
The effects of various protease inhibitors on the development of antinociceptive tolerance to morphine were examined in mice. Intrathecal (i.t.) administration of morphine (0.01-1 nmol) produced a dose-dependent and significant antinociceptive effect in the 0.5% formalin test. When the doses of morphine (mg/kg, s.c. per injection) were given as pretreatment twice daily for two days [first day (30) and second day (60)], i.t. administration of morphine (0.1 nmol) was inactive due to antinociceptive tolerance on the third day. Tolerance to i.t. morphine was significantly suppressed by the i.t. injection of N-ethylmaleimide or Boc-Tyr-Gly-NHO-Bz, inhibitors of cysteine proteases involved in dynorphin degradation, as well as by dynorphin A, Dynorphin B and (-) U-50,488, a selective kappa-opioid receptor agonist. On the other hand, amastatin, an aminopeptidase inhibitor, phosphoramidon, an endopeptidase 24.11 inhibitor, lisinopril, an angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitor, and phenylmethanesulfonyl fluoride, a serine protease inhibitor, were inactive. These results suggest that cysteine protease inhibitors suppress the development of morphine tolerance presumably through the inhibition of dynorphin degradation.
Antisense mapping KOR-1: evidence for multiple kappa analgesic mechanisms.[Pubmed:10224306]
Brain Res. 1999 May 1;826(2):289-92.
In binding assays, both Dynorphin B and alpha-neoendorphin are relatively selective for the kappa1b site, unlike U50,488H which has high affinity for both kappa1a and kappa1b sites. In vivo, U50,488H, Dynorphin B and alpha-neoendorphin analgesia are reversed by the kappa1-selective antagonist, nor-binaltorphimine (norBNI). Antisense mapping the three exons of KOR-1 revealed that probes targeting all three exons blocked U50,488H analgesia, as expected. However, the selectivity profile of Dynorphin B and alpha-neoendorphin analgesia towards the various antisense oligodeoxynucleotides differed markedly from U50,488H, implying a different receptor mechanism of action.


