Lauryl-LF 11Analog of LF 11; antibiotic CAS# 832729-14-3 |
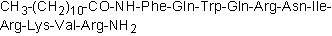
- CUDC-101
Catalog No.:BCC2149
CAS No.:1012054-59-9
- Valproic acid sodium salt (Sodium valproate)
Catalog No.:BCC2156
CAS No.:1069-66-5
- M344
Catalog No.:BCC2162
CAS No.:251456-60-7
- Belinostat (PXD101)
Catalog No.:BCC2153
CAS No.:414864-00-9
- Trichostatin A (TSA)
Catalog No.:BCC3605
CAS No.:58880-19-6
- JNJ-26481585
Catalog No.:BCC2147
CAS No.:875320-29-9
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 832729-14-3 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 90488941 | Appearance | Powder |
| Formula | C81H134N26O15 | M.Wt | 1712.11 |
| Type of Compound | N/A | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Solubility | Soluble to 2 mg/ml in 30% acetonitrile / water | ||
| Sequence | FQWQRNIRKVR (Modifications: Phe-1 = CH3-(CH2)10-CO-NH-Phe, Arg-11 = C-terminal amide) | ||
| Chemical Name | (2S)-N-[(2S)-1-[[(2S)-5-amino-1-[[(3S)-1-[[(2S,3S)-1-[[(2S)-1-[[(2S)-6-amino-1-[[(2S)-1-[[(2S)-1-amino-5-(diaminomethylideneamino)-1-oxopentan-2-yl]amino]-3-methyl-1-oxobutan-2-yl]amino]-1-oxohexan-2-yl]amino]-5-(diaminomethylideneamino)-1-oxopentan-2-yl]amino]-3-methyl-1-oxopentan-2-yl]amino]-6-(diaminomethylideneamino)-2-oxohexan-3-yl]amino]-1,5-dioxopentan-2-yl]amino]-3-(1H-indol-3-yl)-1-oxopropan-2-yl]-2-[[3-cyclohexyl-1-hydroxy-2-(undecylamino)propyl]amino]pentanediamide | ||
| SMILES | CCCCCCCCCCCNC(CC1CCCCC1)C(NC(CCC(=O)N)C(=O)NC(CC2=CNC3=CC=CC=C32)C(=O)NC(CCC(=O)N)C(=O)NC(CCCN=C(N)N)C(=O)CNC(C(C)CC)C(=O)NC(CCCN=C(N)N)C(=O)NC(CCCCN)C(=O)NC(C(C)C)C(=O)NC(CCCN=C(N)N)C(=O)N)O | ||
| Standard InChIKey | AUHGQKBFMDAWAQ-BSHYLFJSSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C77H138N24O12/c1-6-8-9-10-11-12-13-14-22-39-88-59(43-49-26-16-15-17-27-49)71(110)97-58(35-37-63(80)104)69(108)100-60(44-50-45-92-52-29-19-18-28-51(50)52)72(111)98-57(34-36-62(79)103)68(107)94-53(31-23-40-89-75(82)83)61(102)46-93-65(48(5)7-2)74(113)99-56(33-25-42-91-77(86)87)67(106)96-55(30-20-21-38-78)70(109)101-64(47(3)4)73(112)95-54(66(81)105)32-24-41-90-76(84)85/h18-19,28-29,45,47-49,53-60,64-65,71,88,92-93,97,110H,6-17,20-27,30-44,46,78H2,1-5H3,(H2,79,103)(H2,80,104)(H2,81,105)(H,94,107)(H,95,112)(H,96,106)(H,98,111)(H,99,113)(H,100,108)(H,101,109)(H4,82,83,89)(H4,84,85,90)(H4,86,87,91)/t48-,53-,54-,55-,56-,57-,58-,59?,60-,64-,65-,71?/m0/s1 | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | N-terminally acylated analog of LF 11. Displays enhanced antibacterial and LPS-binding activities. |

Lauryl-LF 11 Dilution Calculator

Lauryl-LF 11 Molarity Calculator

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
- LF 11
Catalog No.:BCC6174
CAS No.:832729-13-2
- APD668
Catalog No.:BCC5389
CAS No.:832714-46-2
- Angelol H
Catalog No.:BCN8047
CAS No.:83247-73-8
- Dehydrocavidine
Catalog No.:BCN2549
CAS No.:83218-34-2
- 1beta-Hydroxy-beta-eudesmol
Catalog No.:BCN7097
CAS No.:83217-89-4
- ISX 9
Catalog No.:BCC6181
CAS No.:832115-62-5
- Astragaloside A
Catalog No.:BCC6494
CAS No.:83207-58-3
- 2',4',6'-Trimethoxyacetophenone
Catalog No.:BCN4847
CAS No.:832-58-6
- Angelol G
Catalog No.:BCN7963
CAS No.:83199-38-6
- 8alpha-Tigloyloxyhirsutinolide 13-O-acetate
Catalog No.:BCN7108
CAS No.:83182-58-5
- Kaempferol 3-O-rhamninoside
Catalog No.:BCN6845
CAS No.:83170-31-4
- Bonducellin
Catalog No.:BCN6823
CAS No.:83162-84-9
- Napabucasin
Catalog No.:BCC6525
CAS No.:83280-65-3
- Menisporphine
Catalog No.:BCN7902
CAS No.:83287-02-9
- 7-Hydroxycoumarin-6-carboxylic acid
Catalog No.:BCN4375
CAS No.:833-52-3
- Bryostatin 1
Catalog No.:BCC7343
CAS No.:83314-01-6
- 8(17),13-Labdadien-15,16-olide
Catalog No.:BCN4374
CAS No.:83324-51-0
- (-)-Lariciresinol
Catalog No.:BCN3418
CAS No.:83327-19-9
- Dynorphin B
Catalog No.:BCC5987
CAS No.:83335-41-5
- 10-O-Caffeoyl-6-epiferetoside
Catalog No.:BCN4822
CAS No.:83348-22-5
- 25(R)-Hydroxyprotopanaxadiol
Catalog No.:BCN2493
CAS No.:83349-37-5
- D609
Catalog No.:BCC1509
CAS No.:83373-60-8
- Prenyl caffeate
Catalog No.:BCC8351
CAS No.:100884-13-7
- PL 017
Catalog No.:BCC5864
CAS No.:83397-56-2
Laparoscopic Silastic Ring Mini-Gastric Bypass (SR-MGBP): Up to 11-Year Results from a Single Centre.[Pubmed:28378207]
Obes Surg. 2017 Sep;27(9):2229-2234.
BACKGROUND: Bariatric surgery is well established as an effective method for treating obesity and its related comorbidities. The laparoscopic mini-gastric bypass (MGBP) represents a simpler alternative to a Roux-en-Y gastric bypass (RYGBP). The placement of a silastic ring (SR) may enhance excess weight loss and minimize weight regain. This study reports long-term results from a cohort of patients undergoing a SR-MGBP in a single centre. METHODS: Long-term outcomes (up to 11 years) in a cohort of 156 patients undergoing surgery between August 2005 and January 2008 were analysed. A combination of follow-up questionnaires and electronic hospital records were used to assess weight loss, comorbidity resolution and complications. RESULTS: A total of 156 patients (mean body mass index 46 kg/m(2)) underwent surgery. Ninety-two patients responded to the follow-up questionnaires. Computer-based hospital information was available on a total of 139 patients. Mean percent excess weight loss (%EWL) at 11 years was 84.3%. Comorbidity resolution, determined by medication use, showed a reduction in diabetes (21.8% to 7.1%), hypertension (37.2% to 21.4%) and hypercholesterolaemia (40.4% to 13.4%). Five of 139 patients (3.6%) had SR problems needing removal. Two other patients had the SR changed to a bigger size and a further two had endoscopic removal of the SR for erosion. Of the 139 patients, 9.4% required conversion to a Roux-en-Y gastric bypass (RYGBP). The number of patients on anti-reflux medications increased from 5.1% to 44.6% at 11 years. There were two deaths unrelated to surgery. CONCLUSIONS: SR-MGBP appears to be a safe and effective operation for the morbidly obese. It is durable, with good weight loss at up to 11 years post-surgery. The SR can easily be removed or exchanged for another size and is reasonable to consider when performing a MGBP. Concerns about bile reflux appear to be well founded, and some patients who are poorly controlled medically will require revision.
A prospective study on fetal posterior cranial fossa assessment for early detection of open spina bifida at 11-13 weeks.[Pubmed:28378426]
Congenit Anom (Kyoto). 2018 Jan;58(1):4-9.
The objective of this study was to test three measurements: brain stem (BS), intracranial translucency (IT) and brain stem to occipital bone distance (BSOB), as well as one landmark: cisterna magna (CM) visibility, for early diagnosis of open spina bifida (OSB) in a low risk population. A prospective observational study was undertaken in a university hospital. A sample of 1479 women consented to participate between 20 September 2013 and 30 June 2015. Measurements were performed from the mid-sagittal view, as is routinely used for nuchal thickness assessment. CM visibility was assessed qualitatively as the third anechoic band in the posterior cranial fossa (PCF). All pregnancies were screened with a combination of maternal serum alpha-fetoprotein and second trimester anomaly scan and followed until delivery. Predictive values were calculated for each marker. We were able to diagnose two OSB cases and highly suspect one Dandy-Walker malformation case at the first trimester scan by the observation of PCF. PCF characteristics of OSB cases were increased BS diameter, increased BS-BSOB ratio and non-visualization of the CM. All the markers demonstrated high sensitivity and specificity but CM visibility reached the highest positive predictive value. Due to relatively high false positive rates, PCF measurements could not reach a satisfactory performance to validate their clinical use as a single marker. CM visibility has the advantage of being a qualitative marker and reduces the need for sophisticated and time-consuming measurements. Intracranial translucency and BS-BSOB ratio measurements should be used when the CM visibility is absent or in doubt.
A cross-sectional study on HPV testing with type 16/18 genotyping for cervical cancer screening in 11,064 Chinese women.[Pubmed:28378404]
Cancer Med. 2017 May;6(5):1091-1101.
Cytology-based cervical cancer screening is restricted because of a lack of cytologists. Thus, HPV-based instead of cytology-based screening may be a more suitable strategy in China. Here, we assessed the effectiveness of HPV testing (Cobas((R)) 4800 Test, Roche) and HPV-based programs to detect high-grade cervical intraepithelial neoplasia (CIN) or cancer compared with cytology (Thinprep, Hologic) and cytology-based programs through a cross-sectional study in 11,064 Chinese women aged 21-65 years who were enrolled from Longyou County in Zhejiang Province, China. The rates of HPV positivity and cytology abnormality were 9.8% and 6.1%, respectively. The HPV positivity rate had two age peaks, 21-24 (15.4%) and 60-65 (14.4%) years. According to adjusted data, HPV testing demonstrated significantly higher sensitivity and negative predictive value (NPV) than cytology for detecting CIN2 or worse (90.0% vs. 66.7%, 99.9% vs. 99.5%), and there was an acceptable specificity (91.3%) and positive predictive value (PPV, 12.5%). Furthermore, primary HPV testing with type 16/18 genotyping showed the highest sensitivity (78.6%) and NPV (99.7%) among four screening strategies, and there was similar specificity (96.8%) and PPV (23.9%) compared with co-testing screening to detect CIN2+, while there were fewer colposcopies (4.2) and tests (106.3) performed than with co-testing and primary cytology screening to detect a case of high-grade CIN. The differences in effectiveness were approximately similar when CIN3+ was the identifying target. Our findings suggest that primary HPV testing with type 16/18 genotyping has a higher sensitivity and NPV, possesses optimal cost/effectiveness in the first round of screening and is a feasible strategy of cervical cancer screening for Chinese women.
GNG11 (G-protein subunit gamma 11) suppresses cell growth with induction of reactive oxygen species and abnormal nuclear morphology in human SUSM-1 cells.[Pubmed:28380310]
Biochem Cell Biol. 2017 Aug;95(4):517-523.
Enforced expression of GNG11, G-protein subunit gamma 11, induces cellular senescence in normal human diploid fibroblasts. We here examined the effect of the expression of GNG11 on the growth of immortalized human cell lines, and found that it suppressed the growth of SUSM-1 cells, but not of HeLa cells. We then compared these two cell lines to understand the molecular basis for the action of GNG11. We found that expression of GNG11 induced the generation of reactive oxygen species (ROS) and abnormal nuclear morphology in SUSM-1 cells but not in HeLa cells. Increased ROS generation by GNG11 would likely be caused by the down-regulation of the antioxidant enzymes in SUSM-1 cells. We also found that SUSM-1 cells, even under normal culture conditions, showed higher levels of ROS and higher incidence of abnormal nuclear morphology than HeLa cells, and that abnormal nuclear morphology was relevant to the increased ROS generation in SUSM-1 cells. Thus, SUSM-1 and HeLa cells showed differences in the regulation of ROS and nuclear morphology, which might account for their different responses to the expression of GNG11. Thus, SUSM-1 cells may provide a unique system to study the regulatory relationship between ROS generation, nuclear morphology, and G-protein signaling.
Effect of the hydrophobicity to net positive charge ratio on antibacterial and anti-endotoxin activities of structurally similar antimicrobial peptides.[Pubmed:20058937]
Biochemistry. 2010 Feb 9;49(5):853-61.
The interaction between host-defense antimicrobial peptides (AMPs) and the bacterial lipopolysaccharide (LPS) governs both the susceptibility of the bacteria to the peptide and the ability of the peptide to inhibit LPS activation of immune cells. Both functions depend on the biophysical properties of the peptides. However, the sequence and structural diversity of AMPs makes it difficult to determine common denominators required for antimicrobial and LPS neutralizing activities. Toward this end, we synthesized and investigated a series of nine 12-amino acid peptides and their fatty acid-conjugated analogues composed of both D- and L-isomers of Leu and Lys at various ratios. The positions of the D-amino acids were preserved. These peptides differ in their net positive charge and hydrophobicity. However, their overall structure in the membrane is similar, as determined by Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy. The peptides and their analogues were functionally tested for their antibacterial and hemolytic activity, their ability to permeate LPS vesicles, their ability to neutralize LPS activation of macrophages, and their effect on LPS morphology, determined by negative staining electron microscopy. The data revealed that increasing the ratio between hydrophobicity and the net positive charge increases both antimicrobial and LPS neutralization activities, but with different modes of contributions. Whereas antimicrobial activity increases linearly with the increase in the peptides' hydrophobicity, peptides with different hydrophobicities are endowed with similar LPS neutralizing activities. Besides adding important information regarding AMP parameters involved in antimicrobial and anti-LPS activities, this study suggests the use of such diastereomers as potential templates for the development of simple molecules that conduct both types of functions.
Influence of N-acylation of a peptide derived from human lactoferricin on membrane selectivity.[Pubmed:16616888]
Biochim Biophys Acta. 2006 Sep;1758(9):1426-35.
Increasing numbers of bacterial strains being resistant to conventional antibiotics emphasize the urgent need for new antimicrobial agents. One strategy is based on host defence peptides that can be found in every organism including humans. We have studied the antimicrobial peptide LF11, derived from the pepsin cleavage product of human lactoferrin, known for its antimicrobial and lipid A-binding activity, and peptide C12LF11, the N-lauryl-derivative of LF11, which has owing to the attached hydrocarbon chain an additional hydrophobic segment. The influence of this hydrocarbon chain on membrane selectivity was studied using model membranes composed of dipalmitoylphosphatidylglycerol (DPPG), mimicking bacterial plasma membranes, and of dipalmitoylphosphatidylcholine (DPPC), a model system for mammalian membranes. A variety of biophysical techniques was applied. Thereby, we found that LF11 did not affect DPPC bilayers and showed only moderate effects on DPPG membranes in accordance with its non-hemolytic and weak antimicrobial activity. In contrast, the introduction of the N-lauryl group caused significant changes in the phase behaviour and lipid chain packing in both model membrane systems. These findings correlate with the in vitro tests on methicillin resistant S. aureus, E. coli, P. aeruginosa and human red blood cells, showing increased biological activity of C12LF11 towards these test organisms. This provides evidence that both electrostatic and hydrophobic interactions are crucial for biological activity of antimicrobial peptides, whereas a certain balance between the two components has to be kept, in order not to loose the specificity for bacterial membranes.
Enhancement of endotoxin neutralization by coupling of a C12-alkyl chain to a lactoferricin-derived peptide.[Pubmed:15344905]
Biochem J. 2005 Jan 1;385(Pt 1):135-43.
Antibacterial peptide acylation, which mimics the structure of the natural lipopeptide polymyxin B, increases antimicrobial and endotoxin-neutralizing activities. The interaction of the lactoferricin-derived peptide LF11 and its N-terminally acylated analogue, lauryl-LF11, with different chemotypes of bacterial lipopolysaccharide (LPS Re, Ra and smooth S form) was investigated by biophysical means and was related to the peptides' biological activities. Both peptides exhibit high antibacterial activity against the three strains of Salmonella enterica differing in the LPS chemotype. Lauryl-LF11 has one order of magnitude higher activity against Re-type, but activity against Ra- and S-type bacteria is comparable with that of LF11. The alkyl derivative peptide lauryl-LF11 shows a much stronger inhibition of the LPS-induced cytokine induction in human mononuclear cells than LF11. Although peptide-LPS interaction is essentially of electrostatic nature, the lauryl-modified peptide displays a strong hydrophobic component. Such a feature might then explain the fact that saturation of the peptide binding takes place at a much lower peptide/LPS ratio for LF11 than for lauryl-LF11, and that an overcompensation of the negative LPS backbone charges is observed for lauryl-LF11. The influence of LF11 on the gel-to-liquid-crystalline phase-transition of LPS is negligible for LPS Re, but clearly fluidizing for LPS Ra. In contrast, lauryl-LF11 causes a cholesterol-like effect in the two chemotypes, fluidizing in the gel and rigidifying of the hydrocarbon chains in the liquid-crystalline phase. Both peptides convert the mixed unilamellar/non-lamellar aggregate structure of lipid A, the 'endotoxic principle' of LPS, into a multilamellar one. These data contribute to the understanding of the mechanisms of the peptide-mediated neutralization of endotoxin and effect of lipid modification of peptides.


