DelavirdineHIV-1 reverse transcriptase inhibitor CAS# 136817-59-9 |
- Azelnidipine
Catalog No.:BCC4400
CAS No.:123524-52-7
- Verapamil HCl
Catalog No.:BCC4747
CAS No.:152-11-4
- Gabapentin HCl
Catalog No.:BCC4502
CAS No.:60142-95-2
- Zonisamide sodium
Catalog No.:BCC4240
CAS No.:68291-98-5
- Felodipine
Catalog No.:BCC4402
CAS No.:72509-76-3
- Manidipine
Catalog No.:BCC4404
CAS No.:89226-50-6
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 136817-59-9 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 5625 | Appearance | Powder |
| Formula | C22H28N6O3S | M.Wt | 456.56 |
| Type of Compound | N/A | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Synonyms | U 90152; BHAP-U 90152 | ||
| Solubility | Soluble in DMSO | ||
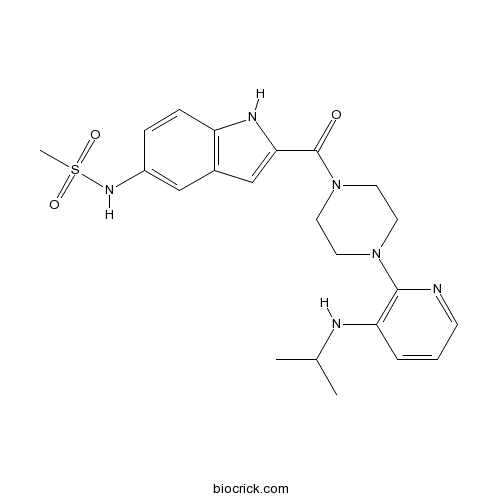
| Chemical Name | N-[2-[4-[3-(propan-2-ylamino)pyridin-2-yl]piperazine-1-carbonyl]-1H-indol-5-yl]methanesulfonamide | ||
| SMILES | CC(C)NC1=C(N=CC=C1)N2CCN(CC2)C(=O)C3=CC4=C(N3)C=CC(=C4)NS(=O)(=O)C | ||
| Standard InChIKey | WHBIGIKBNXZKFE-UHFFFAOYSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C22H28N6O3S/c1-15(2)24-19-5-4-8-23-21(19)27-9-11-28(12-10-27)22(29)20-14-16-13-17(26-32(3,30)31)6-7-18(16)25-20/h4-8,13-15,24-26H,9-12H2,1-3H3 | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | Delavirdine(U 90152) is a potent non-nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitor (NNRTI).
IC50 Value: 0.26 uM (Recombinant HIV-1 RT) [1]
Target: HIV-1 reverse transcriptase; NNRTI
in vitro: U-90152 [1-(5-methanesulfonamido-1H-indol-2-yl-carbonyl)-4-[3-(1-methyl eth yl-amino)pyridinyl]piperazine], which inhibited recombinant HIV-1 RT at a 50% inhibitory concentration (IC50) of 0.26 microM (compared with IC50s of > 440 microM for DNA polymerases alpha and delta). U-90152 blocked the replication in peripheral blood lymphocytes of 25 primary HIV-1 isolates, including variants that were highly resistant to 3'-azido-2',3'-dideoxythymidine (AZT) or 2',3'-dideoxyinosine, with a mean 50% effective dose of 0.066 +/- 0.137 microM. U-90152 had low cellular cytotoxicity, causing less than 8% reduction in peripheral blood lymphocyte viability at 100 microM. In experiments assessing inhibition of the spread of HIV-1IIIB in cell cultures, U-90152 was much more effective than AZT. When approximately 500 HIV-1IIIB-infected MT-4 cells were mixed 1:1,000 with uninfected cells, 3 microM AZT delayed the evidence of rapid viral growth for 7 days. In contrast, 3 microM U-90152 totally prevented the spread of HIV-1, and death and/or dilution of the original inoculum of infected cells prevented renewed viral growth after U-90152 was removed at day 24 [1]. Asdelavirdine concentration was increased from 0 to 100 microM, the K(M) for diclofenac metabolism rose from 4.5+/-0.5 to 21+/-6 microM, and V(max) declined from 4.2+/-0.1 to 0.54+/-0.08 nmol/min/mg of protein, characteristic of mixed-type inhibition [2].
in vivo: The mean values (+/- standard deviations) for the maximum concentration in serum (C(max)) of ritonavir, the area under the concentration-time curve from 0 to 12 h (AUC(0-12)), and the minimum concentration in serum (C(min)) of ritonavir before the addition of delavirdine were 14.8 +/- 6.7 micro M, 94 +/- 36 micro M. h, and 3.6 +/- 2.1 micro M, respectively. These same parameters were increased to 24.6 +/- 13.9 micro M, 154 +/- 83 micro M. h, and 6.52 +/- 4.85 micro M, respectively, after the addition of delavirdine(P is <0.05 for all comparisons). Delavirdine pharmacokinetic parameters in the presence of ritonavir included a C(max) of 23 +/- 16 micro M, an AUC(0-8) of 114 +/- 75 micro M. h, and a C(min) of 9.1 +/- 7.5 micro M [3].
Toxicity:
Clinical trial: Quality of Life of HIV-infected Participants Switched to Raltegravir Versus Other Antiretroviral Regimens. Phase 4 References: | |||||

Delavirdine Dilution Calculator

Delavirdine Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 2.1903 mL | 10.9515 mL | 21.9029 mL | 43.8059 mL | 54.7573 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.4381 mL | 2.1903 mL | 4.3806 mL | 8.7612 mL | 10.9515 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.219 mL | 1.0951 mL | 2.1903 mL | 4.3806 mL | 5.4757 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0438 mL | 0.219 mL | 0.4381 mL | 0.8761 mL | 1.0951 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0219 mL | 0.1095 mL | 0.219 mL | 0.4381 mL | 0.5476 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
Delavirdine is a non-nucleoside inhibitor of HIV-1 reverse transcriptase [1].
Delavirdine prevents HIV-1 replication by noncompetitively inhibiting reverse transcriptase. It allosteric binds to the enzyme and changes the conformation of the polymerase site. Delavirdine inhibits both RNA- and DNA-directed DNA polymerase functions of the enzyme. Delavirdine is highly selective against HIV-1 reverse transcriptase. It shows negligible effects on HIV-2 reverse transcriptase and human DNA polymerases. Delavirdine exerts potent antiviral activity in CD4+ H9, MT-2, MT-4 and PBMCs cell lines infected with HIV-1 with IC50 values ranged from 0.008μM to 0.9μM. It also effectively inhibits the replication of 25 primary clinical isolates of HIV-1 in PBMCs with a mean IC50 value of 66nM [1].
References:
[1] Scott L J, Perry C M. Delavirdine[J]. Drugs, 2000, 60(6): 1411-1444.
- 6-O-Cinnamoylcatalpol
Catalog No.:BCN6193
CAS No.:136807-41-5
- [Ser25] Protein Kinase C (19-31)
Catalog No.:BCC1022
CAS No.:136795-05-6
- Lubiprostone
Catalog No.:BCC4918
CAS No.:136790-76-6
- Goniodiol diacetate
Catalog No.:BCN3956
CAS No.:136778-40-0
- Retinyl glucoside
Catalog No.:BCC1891
CAS No.:136778-12-6
- Gallic aldehyde
Catalog No.:BCN7859
CAS No.:13677-79-7
- 4,4'-Bismaleimidodiphenylmethane
Catalog No.:BCC8662
CAS No.:13676-54-5
- Minimolide F
Catalog No.:BCN6424
CAS No.:1367351-41-4
- 2-Mercaptoethanesulfonic acid
Catalog No.:BCC1789
CAS No.:3375-50-6
- NB-598 hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC1787
CAS No.:136719-25-0
- 9-Deoxygoniopypyrone
Catalog No.:BCN3931
CAS No.:136685-37-5
- PD 123319 ditrifluoroacetate
Catalog No.:BCC1841
CAS No.:136676-91-0
- 1-Dehydro-10-gingerdione
Catalog No.:BCN3338
CAS No.:136826-50-1
- TOTU
Catalog No.:BCC2826
CAS No.:136849-72-4
- Macranthoidin B
Catalog No.:BCN5938
CAS No.:136849-88-2
- AHU-377 hemicalcium salt
Catalog No.:BCC5141
CAS No.:1369773-39-6
- (-)-Syringaresnol-4-O-beta-D-apiofuranosyl-(1->2)-beta-D-glucopyranoside
Catalog No.:BCN1578
CAS No.:136997-64-3
- Sophoraflavanone H
Catalog No.:BCN6864
CAS No.:136997-68-7
- Sophoraflavanone I
Catalog No.:BCN6863
CAS No.:136997-69-8
- Calcium pantothenate
Catalog No.:BCN8503
CAS No.:137-08-6
- Lidocaine
Catalog No.:BCC1084
CAS No.:137-58-6
- L-Ascorbyl 6-palmitate
Catalog No.:BCC4915
CAS No.:137-66-6
- Amprolium HCl
Catalog No.:BCC4626
CAS No.:137-88-2
- 3',4'-Di-O-acetyl-2',6'-di-O-p-coumaroylastragalin
Catalog No.:BCN6610
CAS No.:137018-33-8
Solid lipid nanoparticles comprising internal Compritol 888 ATO, tripalmitin and cacao butter for encapsulating and releasing stavudine, delavirdine and saquinavir.[Pubmed:21865017]
Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces. 2011 Dec 1;88(2):682-90.
Solid lipid nanoparticles (SLNs) with complex internal phase were fabricated for formulating stavudine (D4T), Delavirdine (DLV), and saquinavir (SQV). The lipids including Compritol 888 ATO, tripalmitin, and cacao butter were stabilized by L-alpha-phospatidylcholine, cholesteryl hemisuccinate, and taurocholate to form SLNs. The results revealed that the morphology of SLNs was spheroidal with shallow surface pits. An increase in the weight percentage of Compritol 888 ATO increased the average diameter of D4T-entrapping SLNs and decreased that of DLV- and SQV-entrapping SLNs. Preservation at 4 degrees C over 6 weeks slightly enhanced the size of SLNs. For a specific drug, an increase in the entrapment efficiency enlarged the nanocarriers. The order of drug in the average particle diameter and in the entrapment efficiency was SQV>DLV>D4T, in general. In addition, the dissolution of the three drugs from SLNs showed the characteristics of sustained release. The order of drug in the cumulative release percentage was D4T>DLV>SQV. SLNs containing Compritol 888 ATO, tripalmitin, and cacao butter are efficient in carrying antiretroviral agents for medicinal application.
Effect of six antiretroviral drugs (delavirdine, stavudine, lamivudine, nelfinavir, amprenavir and lopinavir/ritonavir in association) on albino pregnant rats (Rattus norvegicus Albinus, Rodentia, Mammalia): biological assay.[Pubmed:25398151]
Ceska Gynekol. 2014 Aug;79(4):295-304.
OBJECTIVE: To compare the chronic effects of antiretrovirals (lamivudine, stavudine, Delavirdine, nelfinavir, amprenavir and an association of lopinavir/ritonavir) on albino pregnant rats. DESIGN: Review. SETTING: Department of Obstetrics, Federal University of Sao Paulo (UNIFESP), Sao Paulo, SP, Brazil. METHODS: This was a comparative retrospective study formed by 18 groups of 10 pregnant rats each, which were nearly three months of age and weighed 200 g. All of them were medicated every day using a stomach probe, while the control group was given 1 mL of distilled water. The study groups received lamivudine (at 5, 15 and 45 mg/kg/day); stavudine (at 1, 3 and 9 mg/kg/day); nelfinavir (at 40, 120 and 360 mg/kg/day); amprenavir (at 46, 138 and 414 mg/kg/day); lopinavir/ritonavir (at 12.8/3.2, 38.4/9.6 and 115/28.8 mg/kg/day) and Delavirdine (at 20 and 60 mg/kg/day). These represented 1, 3 and 9 times the human therapeutic dose, except for the last drug, for which the 9-times dose was not used. Maternal, litter and placental weights, implantation and reabsorption numbers, major external fetal malformations and fetal and maternal deaths were evaluated. The Kruskal-Wallis test was used to compare quantitative variables and the chi-square test was used to compare qualitative variables. RESULTS: At all three doses, stavudine increased the maternal weight (p=0.001), while lamivudine at 3- and 9-times doses reduced it (p<0.001). Amprenavir at all of the doses, and lopinavir/ritonavir at 3- and 9-times doses, caused higher rates of maternal death (p<0.001). Regarding the fetuses, none of the antiretroviral drugs studied were harmful with regard to implantation, reabsorption, teratogenity and mortality (p>0.05). Stavudine at all doses reduced the litter weights (p<0.001); however, lamivudine at the usual and 3-times doses, Delavirdine at 3-times dose, and amprenavir at 3-times dose increased the litter weight (p<0.001). CONCLUSION: In the maternal compartment, we observed lethal toxicity in the pregnant rats that received amprenavir and ritonavir/lopinavir; and maternal weight change with lamivudine and stavudine. In the fetal compartment, adverse effects were observed in relation to litter weight from stavudine, lamivudine, Delavirdine and amprenavir.
Design and synthesis of dual inhibitors of HIV reverse transcriptase and integrase: introducing a diketoacid functionality into delavirdine.[Pubmed:18314335]
Bioorg Med Chem. 2008 Apr 1;16(7):3587-95.
Cost and toxicity problems associated with highly active antiretroviral therapy (HAART) in HIV/AIDS treatment could be alleviated by using designed multiple ligands (DMLs). Dual inhibitors of HIV reverse transcriptase (RT) and integrase (IN) were rationally designed by introducing a diketoacid (DKA) functionality into the tolerant C-5 site of RT inhibitor Delavirdine. The resulting compounds all demonstrate good activity against both RT and IN in enzymatic assays and HIV in cell-based assay, whereas their C-7 regioisomers are all inactive in these assays. Balanced activities were observed with C-3 halogenated inhibitors.
Multiple-Dose Pharmacokinetics of Delavirdine Mesylate and Didanosine in HIV-Infected Patients.[Pubmed:17535044]
Clin Drug Investig. 2003;23(5):323-8.
BACKGROUND: Delavirdine is a non-nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitor with pH-dependent absorption characteristics that has received accelerated approval for the treatment of patients with HIV-1 infection. In a prior single-dose study concurrent administration of Delavirdine mesylate and didanosine (buffered formulation) resulted in up to a 31% decrease in the area under the plasma Delavirdine concentration versus time curve (AUC) compared with when both drugs were taken separately. OBJECTIVE: To evaluate the interaction of these two agents at steady state. STUDY DESIGN AND PATIENTS: A total of 11 HIV-infected subjects who were previously stabilised on didanosine were enrolled into a randomised, open-labelled crossover study. Nine subjects continued to receive their prescribed dose and schedule of didanosine, with each dose of didanosine taken either together with or 1 hour after Delavirdine mesylate (400mg every 8 hours). Pharmacokinetic studies at baseline, day 14 and day 28 were conducted and the plasma concentrations of Delavirdine and didanosine were determined. RESULTS: A lower Delavirdine maximum plasma concentration (C(max)) [22.4 +/- 11 vs 35.5 +/- 17muM; p = 0.045] was noted when Delavirdine and didanosine were taken together. However, no significant difference was noted for Delavirdine AUC (114 +/- 56 muM.h compared with 153 +/- 79 muM.h [p = 0.181]). In addition, no differences were noted for didanosine pharmacokinetic parameters between treatments. CONCLUSION: These data indicate that patients receiving didanosine and Delavirdine as part of a combination regimen during long-term therapy can be instructed to take them together in an attempt to enhance adherence to treatment with both antiretroviral agents.


