4-Methoxyphenylacetic acidCAS# 104-01-8 |
Quality Control & MSDS
Number of papers citing our products

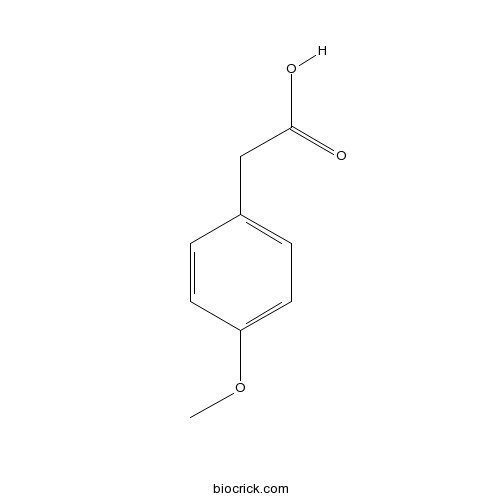
Chemical structure

3D structure
| Cas No. | 104-01-8 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 7690 | Appearance | White powder |
| Formula | C9H10O3 | M.Wt | 166.17 |
| Type of Compound | N/A | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Solubility | Soluble in Chloroform,Dichloromethane,Ethyl Acetate,DMSO,Acetone,etc. | ||
| Chemical Name | 2-(4-methoxyphenyl)acetic acid | ||
| SMILES | COC1=CC=C(C=C1)CC(=O)O | ||
| Standard InChIKey | NRPFNQUDKRYCNX-UHFFFAOYSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C9H10O3/c1-12-8-4-2-7(3-5-8)6-9(10)11/h2-5H,6H2,1H3,(H,10,11) | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||

4-Methoxyphenylacetic acid Dilution Calculator

4-Methoxyphenylacetic acid Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 6.0179 mL | 30.0897 mL | 60.1793 mL | 120.3587 mL | 150.4483 mL |
| 5 mM | 1.2036 mL | 6.0179 mL | 12.0359 mL | 24.0717 mL | 30.0897 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.6018 mL | 3.009 mL | 6.0179 mL | 12.0359 mL | 15.0448 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.1204 mL | 0.6018 mL | 1.2036 mL | 2.4072 mL | 3.009 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0602 mL | 0.3009 mL | 0.6018 mL | 1.2036 mL | 1.5045 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
- 4'-Hydroxypiptocarphin A
Catalog No.:BCN7113
CAS No.:103994-39-4
- 13-Hydroxygermacrone
Catalog No.:BCN3556
CAS No.:103994-29-2
- Ceftiofur hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC8911
CAS No.:103980-44-5
- Esculentic acid
Catalog No.:BCN5856
CAS No.:103974-74-9
- 15-Nor-14-oxolabda-8(17),12-dien-18-oic acid
Catalog No.:BCN1637
CAS No.:1039673-32-9
- Oleanolic acid 3-O-beta-D-glucosyl-(1->3)-alpha-L-rhamnosyl(1->2)-alpha-L-arabinoside
Catalog No.:BCN8132
CAS No.:103956-33-8
- Lupeol caffeate
Catalog No.:BCN5855
CAS No.:103917-26-6
- Nodosin
Catalog No.:BCN5854
CAS No.:10391-09-0
- (-)-Isodocarpin
Catalog No.:BCN3280
CAS No.:10391-08-9
- Maxacalcitol
Catalog No.:BCC1730
CAS No.:103909-75-7
- 17β-Hydroxy-17-methylandrosta-4,9(11)-dien-3-one
Catalog No.:BCC8444
CAS No.:1039-17-4
- Mannioside A
Catalog No.:BCN5853
CAS No.:1038922-95-0
- Anethole
Catalog No.:BCN5373
CAS No.:104-46-1
- Cinnamyl alcohol
Catalog No.:BCN4967
CAS No.:104-54-1
- Cinnamaldehyde
Catalog No.:BCN6241
CAS No.:104-55-2
- Tussilagone
Catalog No.:BCN2770
CAS No.:104012-37-5
- 8alpha-Methacryloyloxybalchanin
Catalog No.:BCN4756
CAS No.:104021-39-8
- Trospium chloride
Catalog No.:BCC4582
CAS No.:10405-02-4
- LP533401 hcl
Catalog No.:BCC6377
CAS No.:1040526-12-2
- Quinovic acid 3-O-alpha-L-rhamnopyranoside
Catalog No.:BCN1636
CAS No.:104055-76-7
- Dihydroobovatin
Catalog No.:BCN3982
CAS No.:104055-79-0
- 3',5'-Diprenylgenistein
Catalog No.:BCN3572
CAS No.:104055-80-3
- Rehmapicroside
Catalog No.:BCN2884
CAS No.:104056-82-8
- Cyclo(Ile-Val)
Catalog No.:BCN2410
CAS No.:104068-43-1
LC-MS-based serum metabolomics reveals a distinctive signature in patients with rheumatoid arthritis.[Pubmed:29442259]
Clin Rheumatol. 2018 Jun;37(6):1493-1502.
Metabolomics has been applied to explore altered metabolite profiles in disease and identify unique metabolic signatures in recent years. We aim to characterize the metabolic profile of rheumatoid arthritis patients and explore its underlying pathological processes using metabolomics approach. Serum samples from 30 rheumatoid arthritis (RA) patients, 30 primary Sjogren's syndrome (pSS) patients, and 32 healthy controls (HC) were collected. The sample was analyzed by ultra-high-performance liquid chromatography coupled with high-resolution mass spectrometry (UPLC-HRMS). Potential biomarkers were screened from orthogonal projection to latent structure discriminate analysis (OPLS-DA) and further evaluated by receiver operating characteristic analysis (ROC). Compared with HC and pSS patients, the RA patients had increased serum levels of 4-Methoxyphenylacetic acid, glutamic acid, L-leucine, L-phenylalanine, L-tryptophan, L-proline, glyceraldehyde, fumaric acid, and cholesterol as well as decreased capric acid, argininosuccinic acid, and billirubin. A total of eight potential biomarkers were screened and tentatively identified for RA. A panel of three metabolites (4-Methoxyphenylacetic acid, L-phenylalanine, and L-leucine) was identified as specific biomarkers of RA. ROC analysis showed that the panel had a sensitivity of 93.30% with a specificity of 95.20% in discrimination RA from other groups. UPLC-HRMS-based quantification of circulating metabolites was a useful tool for identifying RA patients from pSS patients and healthy controls. The potential biomarkers indicated that the RA metabolic disturbance might be associated with inflammation injury, amino acid metabolism, oxidative stress, and phospholipid metabolism.
Design and synthesis of 4-methoxyphenylacetic acid esters as 15-lipoxygenase inhibitors and SAR comparative studies of them.[Pubmed:19251422]
Bioorg Med Chem. 2009 Mar 15;17(6):2327-35.
A group of 4-Methoxyphenylacetic acid esters were designed, synthesized and evaluated as potential inhibitors of soybean 15-lipoxygenase (SLO) on the basis of eugenol and esteragol structures. Compounds 7d-e showed the best IC(50) in SLO inhibition (IC(50)=3.8 and 1.9 microM, respectively). All compounds were docked in SLO active site and showed that carbonyl group of compounds is oriented toward the Fe(III)-OH moiety in the active site of enzyme and fixed by hydrogen bonding with hydroxyl group. It is assumed that lipophilic interaction of ligand-enzyme would be in charge of inhibiting the enzyme activity. The selectivity of the synthetic esters in inhibiting of 15-HLOb was also compared with 15-HLOa by molecular modeling and multiple alignment techniques.
Characterization of pu-erh tea using chemical and metabolic profiling approaches.[Pubmed:19320437]
J Agric Food Chem. 2009 Apr 22;57(8):3046-54.
In this study, the chemical constituents of pu-erh tea, black tea, and green tea, as well as those of pu-erh tea products of different ages, were analyzed and compared using a chemical profiling approach. Differences in tea processing resulted in differences in the chemical constituents and the color of tea infusions. Human biological responses to pu-erh tea ingestion were also studied by using ultraperformance liquid chromatography-quadrupole time-of-flight mass spectrometry (UPLC-QTOFMS) in conjunction with multivariate statistical techniques. Metabolic alterations during and after pu-erh tea ingestion were characterized by increased urinary excretion of 5-hydroxytryptophan, inositol, and 4-Methoxyphenylacetic acid, along with reduced excretion of 3-chlorotyrosine and creatinine. This study highlights the potential for metabonomic technology to assess nutritional interventions and is an important step toward a full understanding of pu-erh tea and its influence on human metabolism.
Anticancer activity of dinuclear gallium(III) carboxylate complexes.[Pubmed:19926362]
Eur J Med Chem. 2010 Feb;45(2):519-25.
The reaction of 3-methoxyphenylacetic acid, 4-Methoxyphenylacetic acid, mesitylthioacetic acid, 2,5-dimethyl-3-furoic acid and 1,4-benzodioxane-6-carboxylic acid with trimethylgallium (1:1) yielded the dimeric complexes [Me(2)Ga(micro-O(2)CCH(2)C(6)H(4)-3-OMe)](2) (1), [Me(2)Ga(micro-O(2)CCH(2)C(6)H(4)-4-OMe)](2) (2), [Me(2)Ga(micro-O(2)CCH(2)SMes)](2) (3) (Mes=2,4,6-Me(3)C(6)H(2)), [Me(2)Ga{micro-O(2)C(Fur)}](2) (4) (Fur=2,5-dimethylfuran) and [Me(2)Ga{micro-O(2)C(Bdo)}](2) (5) (Bdo=1,4-benzodioxane) respectively. The molecular structure of 5 was determined by X-ray diffraction studies. The cytotoxic activity of the gallium(III) complexes (1-5) was tested against human tumor cell lines 8505C anaplastic thyroid cancer, A253 head and neck tumor, A549 lung carcinoma, A2780 ovarian cancer, DLD-1 colon carcinoma and compared with that of cisplatin. Taking into account the standard deviation, there is no significant difference in the activity for any of the compounds in any cell line. However, complex 5 presents the best IC(50) value against A253 head and neck tumor (6.6+/-0.2 microM), while complex 3 seems to be the most active against A2780 ovarian cancer (12.0+/-0.4 microM) and marginally on DLD-1 colon carcinoma (12.4+/-0.1 microM).
Coenzyme Q0 induces apoptosis and modulates the cell cycle in estrogen receptor negative breast cancer cells.[Pubmed:18830129]
Anticancer Drugs. 2009 Jan;20(1):33-40.
We postulated that methoxy-substituted cyclic compounds could inhibit estrogen receptor (ER) negative breast cancer growth in vitro. Therefore, this study assessed the cytotoxic potential of various methoxy-substituted cyclic compounds [7,8-dimethoxyflavone, 4-Methoxyphenylacetic acid, 2-methoxyphenylacetic acid, 4-methoxybenzophenone, 5-methoxy-1-indanone, and coenzyme Q0 (CoQ0)] toward ER-negative human breast cancer cells (MDA-MB-231 and SKBr3). Cytotoxicity was assessed using the sulforhodamine B assay. CoQ0 demonstrated the strongest cytotoxicity toward MDA-MB-231 and SKBr3 cells with IC50 values of 1.7 micromol/l and 3.1 micromol/l, respectively, whereas the other compounds were either much less potent or completely lacked cytotoxicity toward both breast cancer cell lines. Therefore, only CoQ0 was examined for its ability to modulate cell cycle progression and induce apoptosis. Cell cycle experiments, using propidium iodide staining and flow cytometry, demonstrated that CoQ0 at 7.5 micromol/l increased the proportion of MDA-MB-231 cells in G1/G0-phase by 16.6+/-0.6% of control (P<0.05), and increased in the proportion of S-phase SKBr3 cells by 37.8+/-5.8% over control (P<0.05). Induction of apoptosis was determined using propidium iodide/Annexin-V-FLUOS staining followed by flow cytometry. The results demonstrated that treatment with CoQ0 (7.5 micromol/l) increased the proportion of apoptotic MDA-MB-231 and SKBr3 cells by 12-fold and 4-fold over control (P<0.05), respectively. Thus, CoQ0 is a potent cytotoxic drug that induces apoptosis and modulates cell cycle progression in ER-negative breast cancer cells. Therefore, CoQ0 is an appropriate candidate for further study and development as a potential drug for ER-negative breast cancer.


