Dioscorea nipponica
Dioscorea nipponica
1. The products in our compound library are selected from thousands of unique natural products; 2. It has the characteristics of diverse structure, diverse sources and wide coverage of activities; 3. Provide information on the activity of products from major journals, patents and research reports around the world, providing theoretical direction and research basis for further research and screening; 4. Free combination according to the type, source, target and disease of natural product; 5. The compound powder is placed in a covered tube and then discharged into a 10 x 10 cryostat; 6. Transport in ice pack or dry ice pack. Please store it at -20 °C as soon as possible after receiving the product, and use it as soon as possible after opening.
Natural products/compounds from Dioscorea nipponica
- Cat.No. Product Name CAS Number COA
-
BCN2827
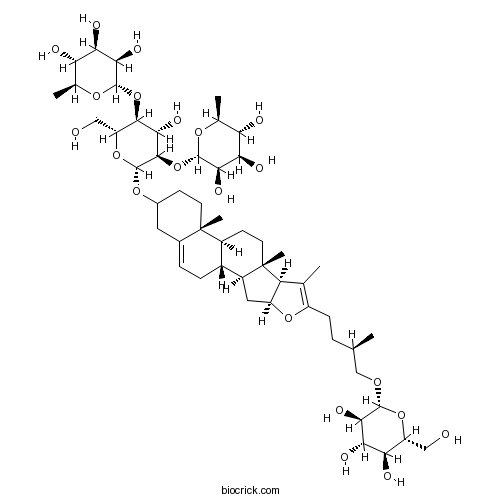
Pseudoprotodioscin102115-79-7
Instructions
-
BCN6105
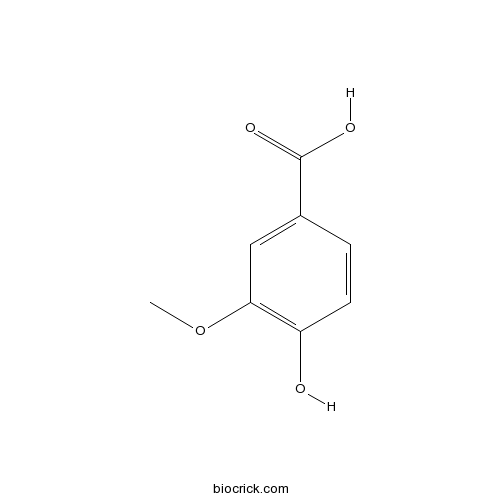
Vanillic acid121-34-6
Instructions
-
BCN5816
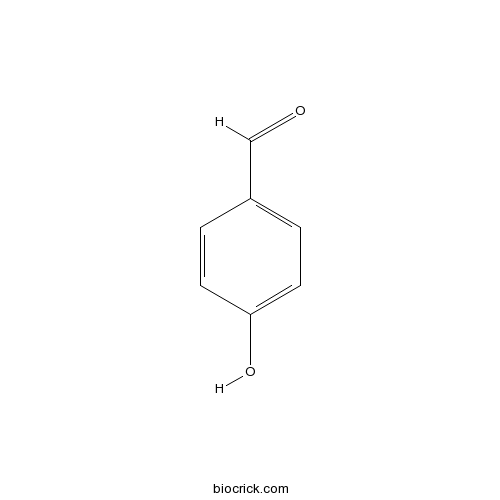
4-Hydroxybenzaldehyde123-08-0
Instructions
-
BCN1250
Diosgenin glucoside14144-06-0
Instructions
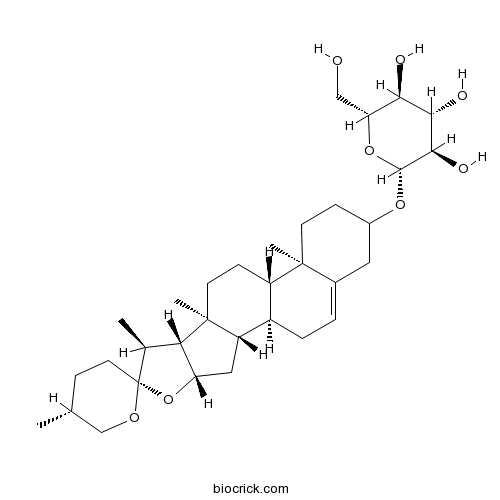
-
BCN6273
Dioscin19057-60-4
Instructions
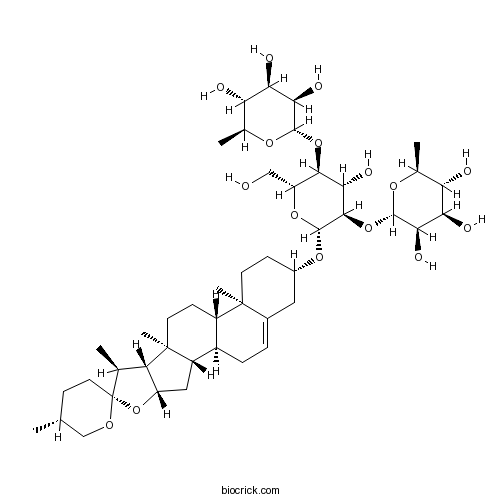
-
BCN2582
Prosapogenin A19057-67-1
Instructions
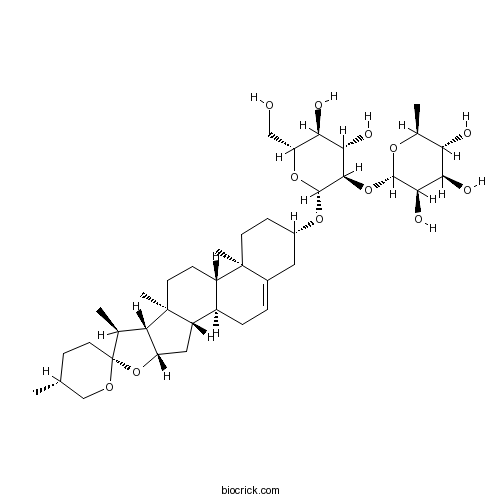
-
BCN5531
Daucosterol474-58-8
Instructions
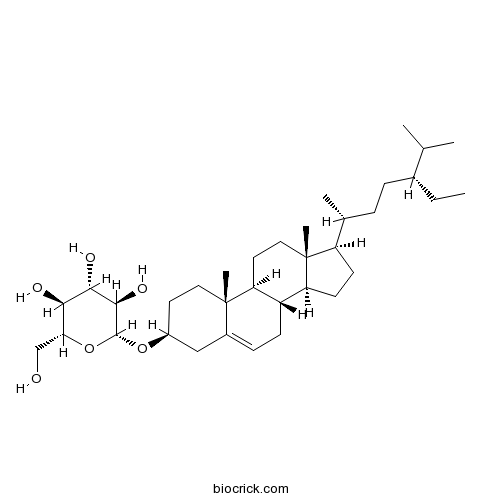
-
BCN6272
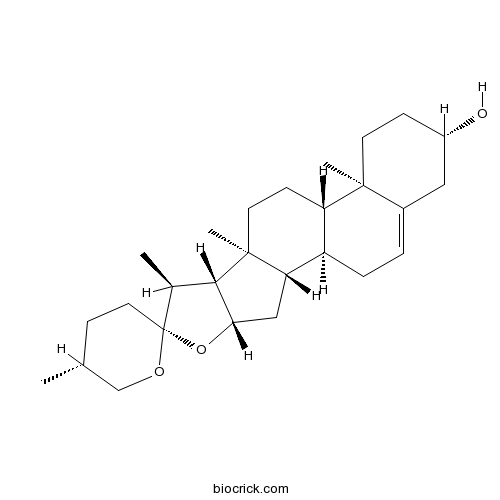
Diosgenin512-04-9
Instructions
-
BCN6342
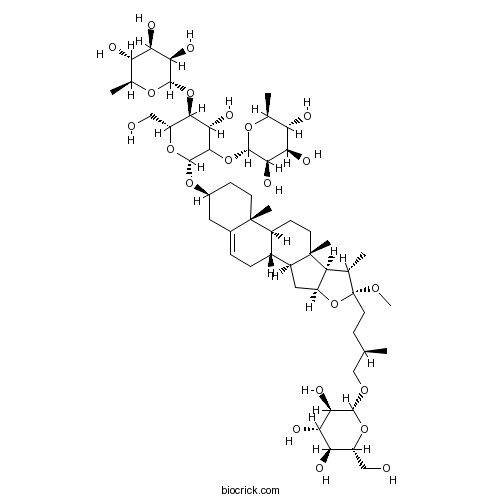
Methyl protodioscin54522-52-0
Instructions
-
BCN6274
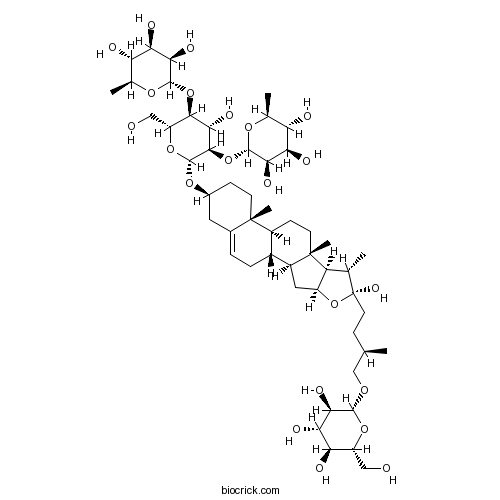
Protodioscin55056-80-9
Instructions
-
BCN5946
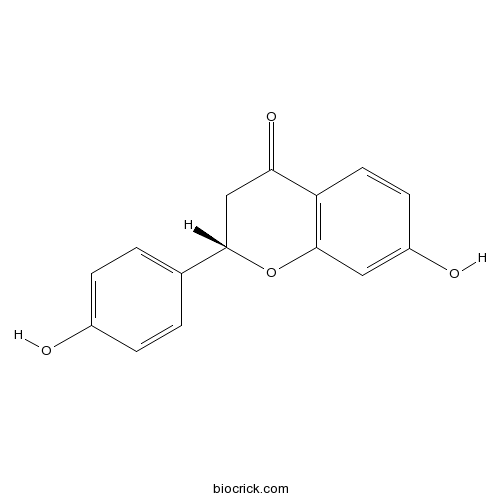
Liquiritigenin578-86-9
Instructions
-
BCN1015
Beta-Sitosterol83-46-5
Instructions
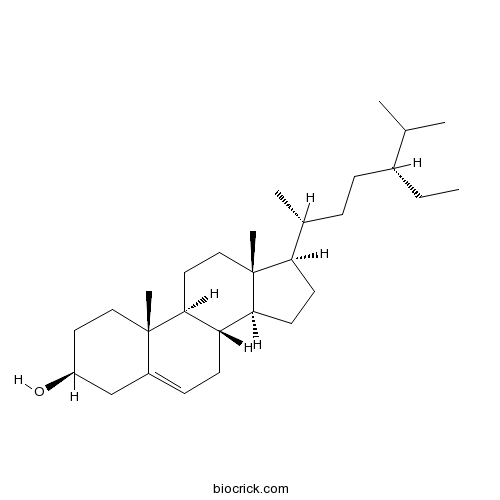
-
BCN4537
3,4-Dihydroxybenzoic acid99-50-3
Instructions
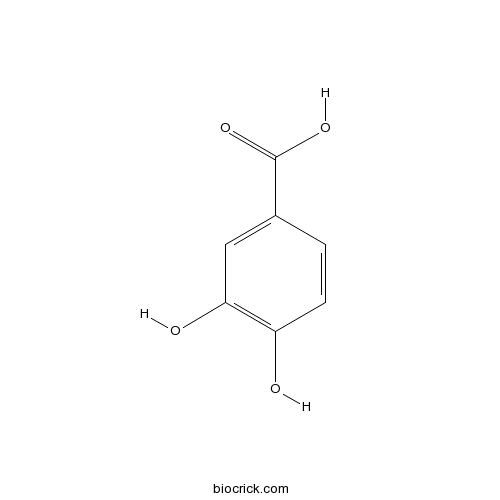
-
BCN4546
4-Hydroxybenzoic acid99-96-7
Instructions
Dioscorea nipponica Makino: a systematic review on its ethnobotany, phytochemical and pharmacological profiles.[Pubmed: 29748731]
Dioscorea nipponica Makino is a perennial twining herbs belonging to the family Dioscoreaceae, which is mainly distributed in the northeastern, northern, eastern and central regions of China. Traditionally, the rhizome of this herb has been commonly used by Miao and Meng ethnic groups of China to treat rheumatoid arthritis, pain in the legs and lumbar area, Kashin Beck disease, bruises, sprains, chronic bronchitis, cough and asthma. Modern pharmacological studies have discovered that this herb possesses anti-tumor, anti-inflammatory, anti-diuretic, analgesic, anti-tussive, panting-calming and phlegm-dispelling activities, along with enhancing immune function and improving cardiovascular health. In recent years, both fat-soluble and water-soluble steroidal saponins were isolated from the rhizomes of D. nipponica using silica gel column chromatography, thin layer chromatography and high performance liquid chromatography methods. Saponin and sapogenins are mainly responsible for most of the pharmacological effects of this plant. Further, the chemical components of the aboveground parts contain more than 10 kinds of phenanthrene derivatives. The present review summarizes the knowledge concerning the geographical distribution, chemical composition, pharmacological effects, toxicology studies and clinical applications of D. nipponica.
[Pharmacological actions and mechanism of saponins from Dioscorea nipponica].[Pubmed: 29493133]
Dioscorea nipponica, a famous traditional Chinese medicine, belongs to the Dioscoreaceae family and has been widely distributed in the north, northeast and Qinghai regions of China. With its root and rhizome as an important herb material, it has been applied in China for several thousand years. Traditional Chinese medicine reported that this plant had been used for relieving cough and asthma, eliminating rheumatic aches, alleviating pain and improving blood circulation. Modern pharmacology studies have confirmed that saponins, the major active compounds in this herb, have shown various pharmacological actions including anti-tumor, anti-inflammatory,lipid-lowering, anti-fungal and anti-virus activities. Therefore, the studies on saponins from D. nipponica are valuable and promising. In this present research, the pharmacological actions, therapeutic effects and mechanism of saponins from D. nipponica were summarized in order to provide the theoretical basis for the further research.
[Regionalization study of Dioscorea nipponica in Jilin province based on MaxEnt and ArcGIS].[Pubmed: 29318838]
At the urgent practical issue of resource protection and artificial cultivation area selection of Dioscorea nipponica, the dominant environmental factors affecting the distribution of D. nipponicain Jilin province were selected by field investigation and using the maximum information entropy model and geographic information technology. MaxEnt model study found that the standard deviation of seasonal variation of temperature, precipitation in October and other six environmental factors on the growth of D. nipponica are the greatest impacting factors. The range of suitability for the growth of D. nipponica was 4.612 08×10-6-0.544 31, and the regionalization study was divided into four parts: high fitness area, middle fitness area, low fitness area and unfavorable area. The high fitness area is concentrated in the central and southern areas of Jilin Province, using ArcGIS statistical environment factors in the appropriate area of the numerical situation. The results showed that the regionalization study of D. nipponica was basically the same as the actual situation. It is clear that the natural environment suitable for the growth of D. nipponica is also the basis for the protection of the resources and the selection of cultivated area.
Combination of cheminformatics and bioinformatics to explore the chemical basis of the rhizomes and aerial parts of Dioscorea nipponica Makino.[Pubmed: 28940203]
This study was aimed to explore the chemical basis of the rhizomes and aerial parts of Dioscorea nipponica Makino (DN).
Novel phenanthrene and isocoumarin from the rhizomes of Dioscorea nipponica Makino subsp. rosthornii (Prain et Burkill) C. T. Ting (Dioscoreaceae).[Pubmed: 28606759]
The investigation of the constituents in the rhizomes of Dioscorea nipponica Makino subsp. rosthornii (Prain et Burkill) C. T. Ting afforded one new phenanthrene 2,2',7,7'-tetramethoxy-[1,1'-biphenanthrene]-4,4',6,6'-tetrol (7) and one new isocoumarin diorosthornoumarin (8), together with 16 known compounds (1-6 and 9-18). Their structures were established on the basis of extensive spectroscopic evidences (IR, HR-ESI-MS, NMR and optical rotation), as well as comparison with literature values. All the compounds 1-18 were firstly isolated from Dioscorea nipponica Makino subsp. Rosthornii (Prain et Burkill) C. T. Ting, and compound 9 was firstly obtained as a natural product from plants, while the compounds 11 and 14 were obtained from both the genus Dioscorea and the family Dioscoreaceae for the first time. Moreover, the antitumor activities of the compounds were tested against lung carcinoma NCI-H460 cell line. Compound 12, 13, 15 and 16 showed significant cytotoxic activities, whereas 7 displayed moderate cytotoxicity.


