Artemisia sieversiana
Artemisia sieversiana
1. The products in our compound library are selected from thousands of unique natural products; 2. It has the characteristics of diverse structure, diverse sources and wide coverage of activities; 3. Provide information on the activity of products from major journals, patents and research reports around the world, providing theoretical direction and research basis for further research and screening; 4. Free combination according to the type, source, target and disease of natural product; 5. The compound powder is placed in a covered tube and then discharged into a 10 x 10 cryostat; 6. Transport in ice pack or dry ice pack. Please store it at -20 °C as soon as possible after receiving the product, and use it as soon as possible after opening.
Natural products/compounds from Artemisia sieversiana
- Cat.No. Product Name CAS Number COA
-
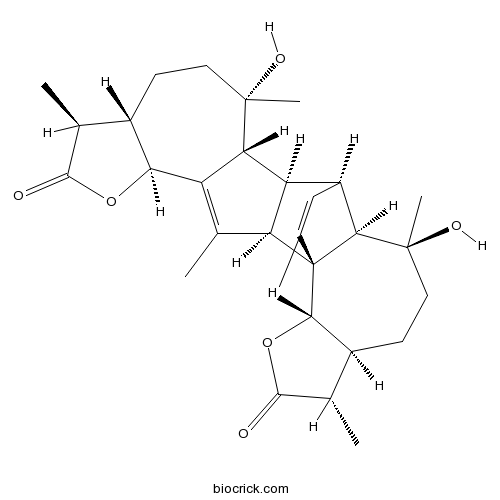
BCN2314
Absinthiin1362-42-1
Instructions
-
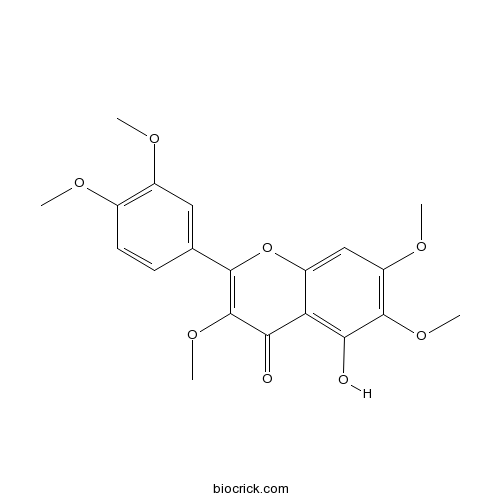
BCN5547
Artemetin479-90-3
Instructions
New terpenoids and thiophene derivatives from the aerial parts of Artemisia sieversiana.[Pubmed: 29122483]
None
DNA Barcode for Identifying Folium Artemisiae Argyi from Counterfeits.[Pubmed: 27582332]
Folium Artemisiae Argyi is an important herb in traditional Chinese medicine. It is commonly used in moxibustion, medicine, etc. However, identifying Artemisia argyi is difficult because this herb exhibits similar morphological characteristics to closely related species and counterfeits. To verify the applicability of DNA barcoding, ITS2 and psbA-trnH were used to identify A. argyi from 15 closely related species and counterfeits. Results indicated that total DNA was easily extracted from all the samples and that both ITS2 and psbA-trnH fragments can be easily amplified. ITS2 was a more ideal barcode than psbA-trnH and ITS2+psbA-trnH to identify A. argyi from closely related species and counterfeits on the basis of sequence character, genetic distance, and tree methods. The sequence length was 225 bp for the 56 ITS2 sequences of A. argyi, and no variable site was detected. For the ITS2 sequences, A. capillaris, A. anomala, A. annua, A. igniaria, A. maximowicziana, A. princeps, Dendranthema vestitum, and D. indicum had single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs). The intraspecific Kimura 2-Parameter distance was zero, which is lower than the minimum interspecific distance (0.005). A. argyi, the closely related species, and counterfeits, except for Artemisia maximowicziana and Artemisia sieversiana, were separated into pairs of divergent clusters by using the neighbor joining, maximum parsimony, and maximum likelihood tree methods. Thus, the ITS2 sequence was an ideal barcode to identify A. argyi from closely related species and counterfeits to ensure the safe use of this plant.
Two new sesquiterpenes from Artemisia sieversiana.[Pubmed: 24862063]
Two new sesquiterpenes, together with 32 known compounds(3-34), were isolated from Artemisia sieversiana Ehrhart ex willd. and the compounds 3-21 were isolated from this plant for the first time. The new compounds were elucidated as 2α,9α-dihydroxymuurol-3(4)-en-12-oic acid (1) and 13α-methyl-(5αH,6αH,7αH,8αH)-austricin 8-O-β-D-glucopyranoside (2), respectively. The structural identification of these compounds was mainly achieved by spectroscopic methods including 1D and 2D NMR techniques, and the structure of compound 1 was confirmed by a single crystal X-ray diffraction experiment. Compounds 1-2 were evaluated for cytotoxic activity in vitro against MCF-7, NCI-H460 and Hep-G2 cell lines, respectively.
Insecticidal activity and chemical composition of the essential oils of Artemisia lavandulaefolia and Artemisia sieversiana from China.[Pubmed: 20730967]
In our screening program for new agrochemicals from local wild plants, Artemisia lavandulaefolia and A. sieversiana were found to possess insecticidal activity against the maize weevil Sitophilus zeamais. The essential oils of the aerial parts of the two plants were obtained by hydrodistillation and analyzed by GC and GC/MS. The main components of A. lavandulaefolia oil were caryophyllene (15.5%), beta-thujone (13.8%), eucalyptol (13.1%), and beta-farnesene (12.3%), and the principal compounds identified in A. sieversiana oil were eucalyptol (9.2%), geranyl butyrate (9.2%), borneol (7.9%), and camphor (7.9%). The essential oils of A. lavandulaefolia and A. sieversiana possessed fumigant toxicity against S. zeamais adults with LC(50) values of 11.2 and 15.0 mg/l air, respectively. Both essential oils also showed contact toxicity against S. zeamais adults with LD(50) values of 55.2 and 112.7 microg/adult, respectively.


