alpha-Linolenic acidCAS# 463-40-1 |
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 463-40-1 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 5280934 | Appearance | Colorless liquid |
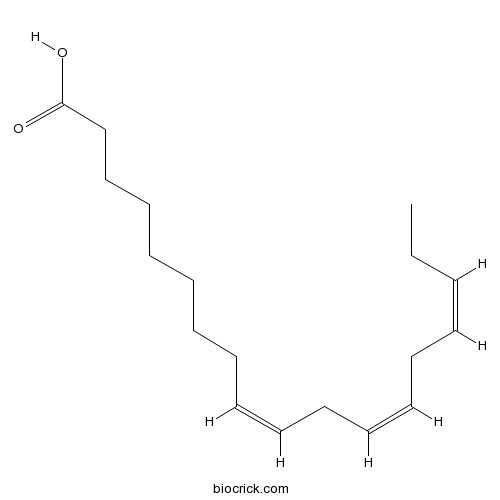
| Formula | C18H30O2 | M.Wt | 278.43 |
| Type of Compound | N/A | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Solubility | Soluble in Chloroform,Dichloromethane,Ethyl Acetate,DMSO,Acetone,etc. | ||
| Chemical Name | (9Z,12Z,15Z)-octadeca-9,12,15-trienoic acid | ||
| SMILES | CCC=CCC=CCC=CCCCCCCCC(=O)O | ||
| Standard InChIKey | DTOSIQBPPRVQHS-PDBXOOCHSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C18H30O2/c1-2-3-4-5-6-7-8-9-10-11-12-13-14-15-16-17-18(19)20/h3-4,6-7,9-10H,2,5,8,11-17H2,1H3,(H,19,20)/b4-3-,7-6-,10-9- | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||

alpha-Linolenic acid Dilution Calculator

alpha-Linolenic acid Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 3.5916 mL | 17.9578 mL | 35.9157 mL | 71.8313 mL | 89.7892 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.7183 mL | 3.5916 mL | 7.1831 mL | 14.3663 mL | 17.9578 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.3592 mL | 1.7958 mL | 3.5916 mL | 7.1831 mL | 8.9789 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0718 mL | 0.3592 mL | 0.7183 mL | 1.4366 mL | 1.7958 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0359 mL | 0.1796 mL | 0.3592 mL | 0.7183 mL | 0.8979 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
- Gnemonol B
Catalog No.:BCN3399
CAS No.:462636-74-4
- Lactulose
Catalog No.:BCC4669
CAS No.:4618-18-2
- 4beta,12-dihydroxyguaian-6,10-diene
Catalog No.:BCN7829
CAS No.:461644-90-6
- Dapagliflozin
Catalog No.:BCC2552
CAS No.:461432-26-8
- Ko 143
Catalog No.:BCC1684
CAS No.:461054-93-3
- Eact
Catalog No.:BCC6313
CAS No.:461000-66-8
- Larixyl acetate
Catalog No.:BCC8195
CAS No.:4608-49-5
- Interiotherin C
Catalog No.:BCN3636
CAS No.:460090-65-7
- Rucaparib (AG-014699,PF-01367338)
Catalog No.:BCC2207
CAS No.:459868-92-9
- 5-[(2R)-2-Aminopropyl]-2,3-dihydro-1-[3-(phenylmethoxy)propyl]-1H-indole-7-carbonitrile
Catalog No.:BCN1438
CAS No.:459868-73-6
- PEAQX
Catalog No.:BCC5495
CAS No.:459836-30-7
- Obeticholic Acid
Catalog No.:BCC5572
CAS No.:459789-99-2
- Bay 55-9837
Catalog No.:BCC5932
CAS No.:463930-25-8
- (+)-Borneol
Catalog No.:BCC8376
CAS No.:464-43-7
- (-)-Borneol
Catalog No.:BCC8897
CAS No.:464-45-9
- (-)-Camphor
Catalog No.:BCN7160
CAS No.:464-48-2
- (+)-Camphor
Catalog No.:BCN7161
CAS No.:464-49-3
- Benzopinacol
Catalog No.:BCC8860
CAS No.:464-72-2
- Arenobufagin
Catalog No.:BCN5401
CAS No.:464-74-4
- Quinamine
Catalog No.:BCN6590
CAS No.:464-85-7
- Conquinamine
Catalog No.:BCN6622
CAS No.:464-86-8
- Asiatic acid
Catalog No.:BCN5506
CAS No.:464-92-6
- Pseudotaraxasterol
Catalog No.:BCN5507
CAS No.:464-98-2
- Arjunolic acid
Catalog No.:BCN5508
CAS No.:465-00-9
Biofortification of safflower: an oil seed crop engineered for ALA-targeting better sustainability and plant based omega-3 fatty acids.[Pubmed:29752697]
Transgenic Res. 2018 Jun;27(3):253-263.
alpha-Linolenic acid (ALA) deficiency and a skewed n6:n3 fatty acid ratio in the diet is a major explanation for the prevalence of cardiovascular diseases and inflammatory/autoimmune diseases. There is mounting evidence of the health benefits associated with omega-3 long chain polyunsaturated fatty acids (LC PUFA's). Although present in abundance in fish, a number of factors limit our consumption of fish based omega-3 PUFA's. To name a few, overexploitation of wild fish stocks has reduced their sustainability due to increased demand of aquaculture for fish oil and meal; the pollution of marine food webs has raised concerns over the ingestion of toxic substances such as heavy metals and dioxins; vegetarians do not consider fish-based sources for supplemental nutrition. Thus alternative sources are being sought and one approach to the sustainable supply of LC-PUFAs is the metabolic engineering of transgenic plants with the capacity to synthesize n3 LC-PUFAs. The present investigation was carried out with the goal of developing transgenic safflower capable of producing pharmaceutically important alpha-Linolenic acid (ALA, C18:3, n3). This crop was selected as the seeds accumulate ~ 78% of the total fatty acids as linoleic acid (LA, C18:2, n6), the immediate precursor of ALA. In the present work, ALA production was achieved successfully in safflower seeds by transforming safflower hypocotyls with Arabidopsis specific delta 15 desaturase (FAD3) driven by truncated seed specific promoter. Transgenic safflower fortified with ALA is not only potentially valuable nutritional superior novel oil but also has reduced ratio of LA to ALA which is required for good health.
DHA upregulates FADS2 expression in primary cortical astrocytes exposed to vitamin A.[Pubmed:29750879]
Physiol Res. 2018 Aug 16;67(4):663-668. Epub 2018 May 10.
The fads2 gene encoding delta6-desaturase, the rate-limiting enzyme of the LCPUFA biosynthesis is expressed in astrocytes. Dietary fatty acids, which cross the blood-brain barrier, may regulate the transcription of lipogenic enzymes through activation of transcription factors such as peroxisome proliferator-activated receptors (PPARs). The PPARs form the transcription complex with retinoid X receptors (RXRs) that are activated by 9-cis retinoic acid, a metabolite of vitamin A (VA). The study examines whether challenge of astrocytes with VA, prior 24-h treatment with palmitic acid (PA), alpha-Linolenic acid (ALA) or docosahexaenoic acid (DHA) has the effect on the FADS2 expression. RT-qPCR showed that in astrocytes not challenged with VA, PA increased fads2 gene expression and DHA decreased it. However, in VA-primed astrocytes, PA doubled the FADS2 mRNA levels, while DHA increased fads2 gene expression, oppositely to non-primed cells. Furthermore, similar changes were seen in VA-primed astrocytes with regard to delta6-desaturase protein levels following PA and DHA treatment. ALA did not have any effect on the FADS2 mRNA and protein levels in either VA-primed or non-primed astrocytes. These findings indicate that in the presence of vitamin A, DHA upregulates fads2 gene expression in astrocytes.
Dietary Intake of alpha-Linolenic Acid Is Not Appreciably Associated with Risk of Ischemic Stroke among Middle-Aged Danish Men and Women.[Pubmed:29767732]
J Nutr. 2018 Jun 1;148(6):952-958.
Background: Intake of the plant-derived omega-3 (n-3) fatty acid alpha-Linolenic acid (ALA) may reduce the risk of ischemic stroke. Objective: We have investigated the associations between dietary intake of ALA and the risk of ischemic stroke and ischemic stroke subtypes. Methods: This was a follow-up study. A total of 57,053 participants aged 50-64 y were enrolled into the Danish Diet, Cancer and Health cohort between 1993 and 1997. Intake of ALA was assessed by a validated semiquantitative food frequency questionnaire. Potential incident cases of ischemic stroke were identified in the Danish National Patient Register, validated, and classified into subtypes based on assumed etiology. Statistical analyses were performed via Cox proportional hazard regression with adjustment for established ischemic stroke risk factors. Results: A total of 1859 ischemic stroke cases were identified during a median of 13.5 y of follow-up. In multivariable analyses using restricted cubic splines adjusting for traditional risk factors for ischemic stroke, we observed no clear associations between dietary intake of ALA and the risk of total ischemic stroke or any of its subtypes including ischemic stroke due to large artery atherosclerosis, ischemic stroke due to small-vessel occlusion, and ischemic stroke due to cardio-embolism. Conclusion: Dietary intake of ALA was neither consistently nor appreciably associated with the risk of ischemic stroke or ischemic stroke subtypes among middle-aged Danish men and women. This study was registered at clinicaltrials.gov as NCT03258983.


