Arjunolic acidCAS# 465-00-9 |
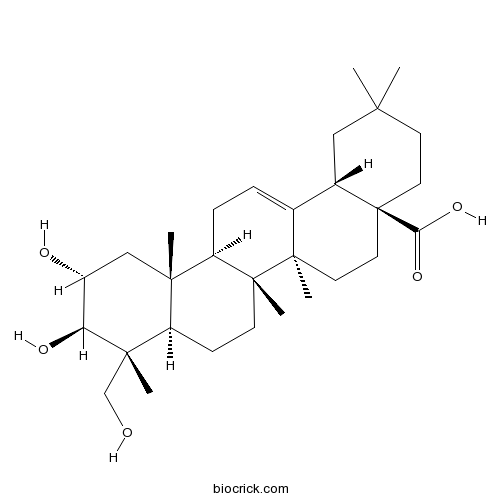
- 2,3,23-Trihydroxy-12-oleanen-28-oic acid
Catalog No.:BCN1638
CAS No.:102519-34-6
- 2,3,24-Trihydroxyolean-12-en-28-oic acid
Catalog No.:BCN1559
CAS No.:150821-16-2
- Bayogenin
Catalog No.:BCN2458
CAS No.:6989-24-8
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 465-00-9 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 73641 | Appearance | Powder |
| Formula | C30H48O5 | M.Wt | 488.7 |
| Type of Compound | Triterpenoids | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Solubility | Soluble in Chloroform,Dichloromethane,Ethyl Acetate,DMSO,Acetone,etc. | ||
| Chemical Name | (4aS,6aR,6aS,6bR,8aR,9R,10R,11R,12aR,14bS)-10,11-dihydroxy-9-(hydroxymethyl)-2,2,6a,6b,9,12a-hexamethyl-1,3,4,5,6,6a,7,8,8a,10,11,12,13,14b-tetradecahydropicene-4a-carboxylic acid | ||
| SMILES | CC1(CCC2(CCC3(C(=CCC4C3(CCC5C4(CC(C(C5(C)CO)O)O)C)C)C2C1)C)C(=O)O)C | ||
| Standard InChIKey | RWNHLTKFBKYDOJ-DDHMHSPCSA-N | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | Arjunolic acid has antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, antinociceptive and anticholinesterasic (AChE and BuChE) activities, it may as promising targets for the development of innovative multi-functional medicines for Alzheimer desease treatment.Arjunolic acid protects cardiac tissues from both extrinsic and intrinsic cell death pathways.Arjunolic acid exhibits better protection against histamine release than against acetylcholine release, anti-asthmatic and anaphylactic activity of it may be possibly due to membrane stabilizing potential and inhibition of antigen induced histamine and acetylcholine release. Arjunolic acid protects cardiac tissues from both extrinsic and intrinsic cell death pathways, it also has antitumor activity. |
| Targets | TNF-α | IL Receptor | JNK | Caspase | NOS | p38MAPK | ROS | TGF-β/Smad | AChR | Histamine Receptor | Antifection |
| In vitro | Arjunolic acid: a new multifunctional therapeutic promise of alternative medicine.[Pubmed: 23402784]Biochimie. 2013 Jun;95(6):1098-109.In recent years, a number of studies describing the effective therapeutic strategies of medicinal plants and their active constituents in traditional medicine have been reported. Indeed, tremendous demand for the development and implementation of these plant derived biomolecules in complementary and alternative medicine is increasing and appear to be promising candidates for pharmaceutical industrial research. These new molecules, especially those from natural resources, are considered as potential therapeutic targets, because they are derived from commonly consumed foodstuff and are considered to be safe for humans. Anti-tumor activity of arjunolic acid against Ehrlich Ascites Carcinoma cells in vivo and in vitro through blocking TGF-β type 1 receptor.[Pubmed: 27470335 ]Biomed Pharmacother. 2016 Aug;82:28-34.We aimed to evaluate therapeutic potential of Arjunolic acid (AA), in Terminalia Arjuna bark, on Ehrlich Ascites carcinoma (EAC) in-vivo and in-vitro. EAC was induced in fifty female Swiss albino mice. Antiallergic and anti-asthmatic activities of the alcoholic extract of Terminalia arjuna and arjunolic acid.[Reference: WebLink]Nat. Prod. Sci., 2004, 10(5):240-3.In the present study, the alcoholic extract of Terminalia arjuna (TA) and Arjunolic acid (AA) were studied for its anti-asthmatic and anaphylactic activity. |
| In vivo | Protective effects of arjunolic acid against cardiac toxicity induced by oral sodium nitrite: effects on cytokine balance and apoptosis.[Pubmed: 25064822]Life Sci. 2014 Aug 28;111(1-2):18-26.Sodium nitrite, a preservative used in meat products, helps in the production of free radicals, leading to increased lipid peroxidation, which plays a vital role in posing toxic effects in different body organs. On the other hand, Arjunolic acid possesses antioxidant properties and plays protective roles against chemically induced organ pathophysiology. We investigated the effect of sodium nitrite on cardiac tissue in rats on the inflammatory cytokine balance and the type of induced apoptosis, and we analyzed the protective role of Arjunolic acid.
Cisplatin-induced testicular toxicity in rats: the protective effect of arjunolic acid.[Pubmed: 25130312 ]J Biochem Mol Toxicol. 2014 Nov;28(11):515-21.
|
| Kinase Assay | Arjunolic acid in the ethanolic extract of Combretum leprosum root and its use as a potential multi-functional phytomedicine and drug for neurodegenerative disorders: Anti-inflammatory and anticholinesterasic activities.[Reference: WebLink]Protective effect of arjunolic acid against atorvastatin induced hepatic and renal pathophysiology via MAPK, mitochondria and ER dependent pathways.[Pubmed: 25736991]Biochimie. 2015 May;112:20-34.3-Hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl-CoA reductase inhibitor, atorvastatin (ATO), is a highly effective drug used for the treatment of hypercholesterolemia and hypertriglyceridemia. Its application is restricted now-a-days due to several acute and chronic side effects. ATO induced anti hypercholesterolemia and hepatic tissue toxicity has been reported to follow different mechanisms. J. Brazil. Chem. Soc., 2005, 16(6B):1309-12.Combretum leprosum Mart. & Eicher (Combretaceae) leaves and roots ethanolic extracts were investigated by HRGC-MS and showed mono- and oligosaccharides, fatty acids and triterpenes as major compounds after derivatization with BSTFA/ TMCS. Arjunolic acid (1) was quantified on dried roots ethanolic extract (65%) by external standard. Anti-inflammatory, antinociceptive and anticholinesterasic (AChE and BuChE) activities were observed for roots ethanolic extract of C. leprosum and Arjunolic acid, suggesting both as promising targets for the development of innovative multi-functional medicines for Alzheimer desease treatment. |
| Cell Research | Modes of action of arjunolic acid and derivatives on Trypanosoma cruzi cells.[Pubmed: 24660682]Curr Top Med Chem. 2014;14(8):1022-32.Chagas disease causes considerable morbimortality in the Americas, with circa 7 to 8 million infected people, causing at least 12,000 annual deaths and 100 million people at risk. Its chemotherapy is poorly selective and effective, associated to severe side effects and unresponsive cases. Thus, R&D on therapeutic alternatives is undoubtedly required. |

Arjunolic acid Dilution Calculator

Arjunolic acid Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 2.0462 mL | 10.2312 mL | 20.4625 mL | 40.9249 mL | 51.1561 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.4092 mL | 2.0462 mL | 4.0925 mL | 8.185 mL | 10.2312 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.2046 mL | 1.0231 mL | 2.0462 mL | 4.0925 mL | 5.1156 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0409 mL | 0.2046 mL | 0.4092 mL | 0.8185 mL | 1.0231 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0205 mL | 0.1023 mL | 0.2046 mL | 0.4092 mL | 0.5116 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
- Pseudotaraxasterol
Catalog No.:BCN5507
CAS No.:464-98-2
- Asiatic acid
Catalog No.:BCN5506
CAS No.:464-92-6
- Conquinamine
Catalog No.:BCN6622
CAS No.:464-86-8
- Quinamine
Catalog No.:BCN6590
CAS No.:464-85-7
- Arenobufagin
Catalog No.:BCN5401
CAS No.:464-74-4
- Benzopinacol
Catalog No.:BCC8860
CAS No.:464-72-2
- (+)-Camphor
Catalog No.:BCN7161
CAS No.:464-49-3
- (-)-Camphor
Catalog No.:BCN7160
CAS No.:464-48-2
- (-)-Borneol
Catalog No.:BCC8897
CAS No.:464-45-9
- (+)-Borneol
Catalog No.:BCC8376
CAS No.:464-43-7
- Bay 55-9837
Catalog No.:BCC5932
CAS No.:463930-25-8
- alpha-Linolenic acid
Catalog No.:BCN8319
CAS No.:463-40-1
- Germanicol
Catalog No.:BCN7507
CAS No.:465-02-1
- Gamabufotalin
Catalog No.:BCN2358
CAS No.:465-11-2
- Neritaloside
Catalog No.:BCN5509
CAS No.:465-13-4
- Oleandrin
Catalog No.:BCN5511
CAS No.:465-16-7
- Polyporenic acid C
Catalog No.:BCN3645
CAS No.:465-18-9
- Bufalin
Catalog No.:BCN1046
CAS No.:465-21-4
- Resibufogenin
Catalog No.:BCN5366
CAS No.:465-39-4
- Quinovic acid
Catalog No.:BCN5512
CAS No.:465-74-7
- Marrubiin
Catalog No.:BCC8208
CAS No.:465-92-9
- Hederagenin
Catalog No.:BCN5513
CAS No.:465-99-6
- alpha-Spinasterol acetate
Catalog No.:BCN5510
CAS No.:4651-46-1
- Cycloartanol
Catalog No.:BCN4860
CAS No.:4657-58-3
Modes of action of arjunolic acid and derivatives on Trypanosoma cruzi cells.[Pubmed:24660682]
Curr Top Med Chem. 2014;14(8):1022-32.
Chagas disease causes considerable morbimortality in the Americas, with circa 7 to 8 million infected people, causing at least 12,000 annual deaths and 100 million people at risk. Its chemotherapy is poorly selective and effective, associated to severe side effects and unresponsive cases. Thus, R&D on therapeutic alternatives is undoubtedly required. The Brazilian poorly studied biodiversity offers uncountable bioagents, which may be exploited for chemotherapy. The triterpene Arjunolic acid (AA), reduced the Trypanosoma cruzi epimastigote in vitro proliferation with an apparent IC(5)(0) of 171 microM. Electron microscopy analysis revealed remarkable effects on the parasite surface and architecture. AA-treated parasites displayed minutely corrugated plasma membranes devoid of subpellicular microtubules as well as biogenesis of multiple basal bodies. As the AA effects appeared mainly restricted or originated at the parasite peripheral cytoplasm, including the cytoskeleton membrane linkage, we inferred that the compound targeted primarily the lipid bilayer; therefore, we performed synthetic modification to increase the molecule lipophilicity and thus membrane permeability. The methyl ester (MeAA) and tri-acetylated derivatives (3AcAA) had potentiated trypanocidal activity, producing IC(5)(0) values of 21.9 and 15.8 microM, respectively. Both derivatives were able to produce remarkable ultrastructural alterations in the parasites, including inner compartments such as Golgi apparatus and the endocytic/autophagic pathway. Parasites cultured with both derivatives displayed numerous and large autophagic vacuoles, altered flagellar length and cell body connection. These data indicate that synthetically-modified natural products comprise valuable tools in antiparasitic chemotherapy and that electron microscopy may be useful not only in determining the mechanisms of action but also in directing such modifications for rational drug design.
Anti-tumor activity of arjunolic acid against Ehrlich Ascites Carcinoma cells in vivo and in vitro through blocking TGF-beta type 1 receptor.[Pubmed:27470335]
Biomed Pharmacother. 2016 Aug;82:28-34.
We aimed to evaluate therapeutic potential of Arjunolic acid (AA), in Terminalia Arjuna bark, on Ehrlich Ascites carcinoma (EAC) in-vivo and in-vitro. EAC was induced in fifty female Swiss albino mice. Two doses of AA was used 100 and 250mg/kg. Arjunulic acid reduced tumor volume and cells count. AA decreased EAC cells viability and increased cell toxicity. Moreover, AA reduced TNF-alpha, IL-1beta, TGF-beta, TGF-beta type I receptor and latency-associated peptide levels associated with elevated IL-10 in-vivo and in-vitro. In conclusion, AA produced antitumor activity against EAC by increasing cytotoxicity and apoptosis and partially blocking the TGF-betaR1 and affecting inflammatory cytokine levels.
Arjunolic acid: a new multifunctional therapeutic promise of alternative medicine.[Pubmed:23402784]
Biochimie. 2013 Jun;95(6):1098-109.
IMPORTANCE OF THE FIELD: In recent years, a number of studies describing the effective therapeutic strategies of medicinal plants and their active constituents in traditional medicine have been reported. Indeed, tremendous demand for the development and implementation of these plant derived biomolecules in complementary and alternative medicine is increasing and appear to be promising candidates for pharmaceutical industrial research. These new molecules, especially those from natural resources, are considered as potential therapeutic targets, because they are derived from commonly consumed foodstuff and are considered to be safe for humans. AREAS COVERED IN THIS REVIEW: This review highlights the beneficial role of Arjunolic acid, a naturally occurring chiral triterpenoid saponin, in various organ pathophysiology and the underlying mechanism of its protective action. Studies on the biochemistry and pharmacology suggest the potential use of Arjunolic acid as a novel promising therapeutic strategy. WHAT THE READERS WILL GAIN: The multifunctional therapeutic application of Arjunolic acid has already been documented by its various biological functions including antioxidant, anti-fungal, anti-bacterial, anticholinesterase, antitumor, antiasthmatic, wound healing and insect growth inhibitor activities. The scientific basis behind its therapeutic application as a cardioprotective agent in traditional medicine is justified by its ability to prevent myocardial necrosis and apoptosis, platelet aggregation, coagulation and lowering of blood pressure, heart rate, as well as cholesterol levels. Its antioxidant property coupled with metal chelating property (by its two hydroxyl groups) protects different organs from metal and drug-induced organ pathophysiology. Arjunolic acid also plays a beneficial role in the pathogenesis of diabetes and its associated complications. The mechanism of cytoprotection of Arjunolic acid, at least in part, results from the detoxification of reactive oxygen species (ROS) produced in the respective pathophysiology. In addition to its other biological functions, it also possesses vibrant insecticidal properties and it has the potential to be used as a structural molecular framework for the design of molecular receptors in the general area of supramolecular chemistry and nanochemistry. Esters of Arjunolic acid function as organogelators which has wide application in designing thermochromic switches and sensor devices. Arjunolic acid derived crown ether is an attractive candidate for the design of molecular receptors, biomimetics and supramolecular systems capable of performing some biological functions. HOME MESSAGE: This review would provide useful information about the recent progress of natural product research in the domain of clinical science. This review also aims to untie the multifunctional therapeutic application of Arjunolic acid, a nanometer-long naturally occurring chiral triterpenoid biomolecule.
Cisplatin-induced testicular toxicity in rats: the protective effect of arjunolic acid.[Pubmed:25130312]
J Biochem Mol Toxicol. 2014 Nov;28(11):515-21.
In the present study, the effect of Arjunolic acid on testicular damage induced by intraperitoneal injection of rats with 7 mg/kg cisplatin was studied. Cisplatin induced a significant reduction in testicular weights, plasma testosterone, and testicular reduced glutathione levels in addition to a significant elevation of testicular malondialdehyde levels and testicular gene expressions of inducible nitric oxide synthase (iNOS), tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-alpha), and p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) when compared with the control group (p < 0.05). Lower tubular diameters and depletion of germ cells and irregular small seminiferous tubules with Sertoli cells only were observed in the cisplatin group. Arjunolic acid administration significantly corrected the changes in both biochemical and histopathological parameters. Arjunolic acid plays a significant protective role against cisplatin-induced testicular injury by attenuating oxidative stress parameters along with downregulation of iNOS, TNF-alpha, and p38-MAPK testicular expressions.
Protective effects of arjunolic acid against cardiac toxicity induced by oral sodium nitrite: effects on cytokine balance and apoptosis.[Pubmed:25064822]
Life Sci. 2014 Aug 28;111(1-2):18-26.
AIMS: Sodium nitrite, a preservative used in meat products, helps in the production of free radicals, leading to increased lipid peroxidation, which plays a vital role in posing toxic effects in different body organs. On the other hand, Arjunolic acid possesses antioxidant properties and plays protective roles against chemically induced organ pathophysiology. We investigated the effect of sodium nitrite on cardiac tissue in rats on the inflammatory cytokine balance and the type of induced apoptosis, and we analyzed the protective role of Arjunolic acid. MAIN METHODS: Sixty adult male Sprague-Dawley rats were injected with 80mg/kg sodium nitrite in the presence/absence of Arjunolic acid (100 and 200mg/kg). Cardiac pro-inflammatory cytokines (TNF-alpha and IL-1beta), c-reactive protein (CRP) and anti-inflammatory cytokines (IL-4 and IL-10) were measured by ELISA. Cardiac mitochondrial activity (cytochrome-C-oxidase), JNK activation and apoptosis (caspase-3, caspase-8 and caspase-9) were assessed. KEY FINDINGS: Sodium nitrite resulted in increased TNF-alpha (1.6-fold), IL-1beta (3.7-fold) and CRP (2.4-fold) levels accompanied by 52%, 59% and 40% reductions in IL-10, IL-4 and cytochrome-C-oxidase, respectively, as well as enhanced JNK, caspase-3, caspase-8 and caspase-9 activities. Arjunolic acid markedly ameliorated these effects. SIGNIFICANCE: Arjunolic acid attenuated sodium nitrite-induced cardiac damage in rats and restored the normal balance between pro- and anti-inflammatory cytokines. Moreover, Arjunolic acid protected cardiac tissues from both extrinsic and intrinsic cell death pathways.
Protective effect of arjunolic acid against atorvastatin induced hepatic and renal pathophysiology via MAPK, mitochondria and ER dependent pathways.[Pubmed:25736991]
Biochimie. 2015 May;112:20-34.
3-Hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl-CoA reductase inhibitor, atorvastatin (ATO), is a highly effective drug used for the treatment of hypercholesterolemia and hypertriglyceridemia. Its application is restricted now-a-days due to several acute and chronic side effects. ATO induced anti hypercholesterolemia and hepatic tissue toxicity has been reported to follow different mechanisms. The present study has been carried out to investigate the protective role of Arjunolic acid (AA) against ATO induced oxidative impairment and cell death in hepatic and renal tissue in mice. Administration of ATO (at a dose 30 mg/kg/day for 8 weeks) enhanced serum markers, increased reactive oxygen species (ROS) production and altered the pro oxidant-antioxidant status of liver and kidney tissues. Our experimental evidence suggests that ATO exposure induces apoptotic cell deathby the activation of caspase-3 and reciprocal regulation of Bcl-2/Bax with the concomitant reduction of mitochondrial membrane potential and increased level of cytosolic cytochrome c, Apaf1, caspase-9. Besides, ATO markedly increased the phosphorylation of MAPKs, enhanced caspase-12 and calpain level. Histological studies and DNA fragmentation analysis also support the toxic effect of ATO in these organs pathophysiology. Post treatment with AA (at a dose of 20 mg/kg body weight for 4 days), however, reduced ATO-induced oxidative stress and suppressed all these apoptotic events. Results suggest that AA could effectively and extensively counteract these adverse effects and might protect liver and kidney from ATO-induced severe tissue toxicity.


