Z-LigustilideCAS# 81944-09-4 |
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 81944-09-4 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 158018 | Appearance | Light yellow liquid |
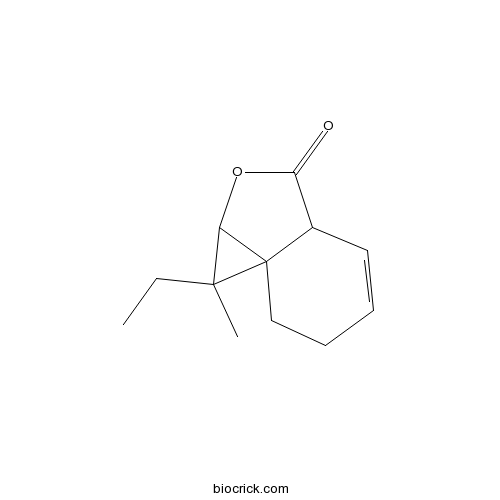
| Formula | C12H14O2 | M.Wt | 190 |
| Type of Compound | Organic acids & Esters | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Synonyms | cis-Ligustilide | ||
| Solubility | Soluble in diethyl ether, ethanol and methan | ||
| Chemical Name | 1-ethyl-1-methyl-1a,3a,6,7-tetrahydrocyclopropa[c][2]benzofuran-3-one | ||
| SMILES | CCC1(C2C13CCC=CC3C(=O)O2)C | ||
| Standard InChIKey | WHNUXUAEXHHXPK-UHFFFAOYSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C12H16O2/c1-3-11(2)10-12(11)7-5-4-6-8(12)9(13)14-10/h4,6,8,10H,3,5,7H2,1-2H3 | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||

Z-Ligustilide Dilution Calculator

Z-Ligustilide Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 5.2632 mL | 26.3158 mL | 52.6316 mL | 105.2632 mL | 131.5789 mL |
| 5 mM | 1.0526 mL | 5.2632 mL | 10.5263 mL | 21.0526 mL | 26.3158 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.5263 mL | 2.6316 mL | 5.2632 mL | 10.5263 mL | 13.1579 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.1053 mL | 0.5263 mL | 1.0526 mL | 2.1053 mL | 2.6316 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0526 mL | 0.2632 mL | 0.5263 mL | 1.0526 mL | 1.3158 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
- Zofenopril calcium
Catalog No.:BCC5229
CAS No.:81938-43-4
- Polyphyllin H
Catalog No.:BCN2834
CAS No.:81917-50-2
- Momordicoside I aglycone
Catalog No.:BCN4353
CAS No.:81910-41-0
- 5,19-Epoxy-25-methoxycucurbita-6,23-dien-3-ol
Catalog No.:BCN1341
CAS No.:81910-39-6
- Ganoderic acid A
Catalog No.:BCN3033
CAS No.:81907-62-2
- Ganoderic acid B
Catalog No.:BCN3034
CAS No.:81907-61-1
- Forskolin J
Catalog No.:BCN4352
CAS No.:81873-08-7
- Seneciocannabine
Catalog No.:BCN2128
CAS No.:81855-31-4
- Neotriptophenolide
Catalog No.:BCN8059
CAS No.:81827-74-9
- Quinocetone
Catalog No.:BCC9133
CAS No.:81810-66-4
- Methimepip dihydrobromide
Catalog No.:BCC7524
CAS No.:817636-54-7
- Praeruptorin B
Catalog No.:BCN4988
CAS No.:81740-07-0
- 4(15),5,10(14)-Germacratrien-1-ol
Catalog No.:BCN4354
CAS No.:81968-62-9
- Splendoside
Catalog No.:BCN6647
CAS No.:81969-41-7
- Clovin
Catalog No.:BCN7817
CAS No.:81970-00-5
- KW-2478
Catalog No.:BCC2127
CAS No.:819812-04-9
- Hyperxanthone E
Catalog No.:BCN8072
CAS No.:819860-76-9
- Vitedoin A
Catalog No.:BCN6741
CAS No.:819861-40-0
- Lancerin
Catalog No.:BCN2803
CAS No.:81991-99-3
- Khellin
Catalog No.:BCN4356
CAS No.:82-02-0
- Benzanthrone
Catalog No.:BCC8845
CAS No.:82-05-3
- Rottlerin
Catalog No.:BCC7127
CAS No.:82-08-6
- Alpha-Toxicarol
Catalog No.:BCN6467
CAS No.:82-09-7
- 1-Amino-2-methylanthraquinone
Catalog No.:BCC8451
CAS No.:82-28-0
Z-Ligustilide protects vascular endothelial cells from oxidative stress and rescues high fat diet-induced atherosclerosis by activating multiple NRF2 downstream genes.[Pubmed:30897380]
Atherosclerosis. 2019 Feb 25;284:110-120.
BACKGROUND AND AIMS: Oxidative stress-induced endothelial dysfunction is considered to exert a vital role in the development of atherosclerotic coronary heart disease (CHD). NRF2 is a key transcriptional factor against oxidative stress through activation of multiple ARE-mediated genes. Z-Lig is derived from the Ligusticum species with antitumor, anti-inflammation and neuroprotection activities. However, the antioxidant potentials of Z-Lig on endothelial dysfunction and atherosclerosis have not been well elucidated. Therefore, in the present work, we appraise the cytoprotective property and anti-atherosclerosis effect of Z-Lig. METHODS: Potential NRF2 activators were screened and verified by luciferase reporter gene assay. The protein and mRNA levels of NRF2 and ARE-mediated genes, and GSH/GSSG level in EA.hy926cells treated with Z-Lig were detected. The cytoprotective property of Z-Lig was assessed in the tert-butyl hydroperoxide (t-BHP)-evoked oxidative stress model. Cell viability and reactive oxygen species (ROS) levels in EA.hy926cells were determined. An atherosclerosis model induced by HFD was used to determine the anti-atherosclerosis effect of Z-Lig in HFD-fed Ldlr-deficient mice. RESULTS: In vitro, 100muM Z-Lig upregulated expressions of NRF2 and ARE-driven genes, promoted accumulation of nuclear NRF2 and unbound NRF2- KEAP1 complex in EA.hy926cells. Furthermore, Z-Lig alleviated oxidative stress and cell injury caused by t-BHP via stimulation of the NRF2/ARE pathway. In vivo, intervention with 20mg/kg Z-Lig markedly restrained atherosclerosis progression, including attenuation of HFD-induced atherosclerotic plaque formation, alleviation of lipid peroxidation and increase in antioxidant enzyme activity in aortas of HFD-fed Ldlr(-/-) mice. The chemopreventive effects of Z-Lig might be associated with the activation of NRF2 and ARE-driven genes. CONCLUSIONS: The present study suggested that Z-Lig is an effective NRF2 activator, which can protect vascular endothelial cells from oxidative stress and rescue HFD-induced atherosclerosis.
Cytoprotective Effects of Mangiferin and Z-Ligustilide in PAH-Exposed Human Airway Epithelium in Vitro.[Pubmed:30678167]
Nutrients. 2019 Jan 22;11(2). pii: nu11020218.
According to World Health Organisation (WHO) air pollution increases the risk of cardiovascular disorders, respiratory diseases, including COPD, lung cancer and acute respiratory infections, neuro-degenerative and other diseases. It is also known that various phytochemicals may mitigate such risks. This study tested if phytochemicals mangiferin (MNG) and Z-Ligustilide (Z-LG) may protect PAH-exposed human lung bronchial epithelial cells (BEAS-2B). Organic PAH extract was obtained from the urban fine PM with high benzo(a)pyrene content collected in Eastern European mid-sized city during winter heating season. Cell proliferation traits and levels of intracellular oxidative stress were examined. Effect of MNG (0.5 microg/mL) alone or in combination with PAH on bronchial epithelium wound healing was evaluated. Both phytochemicals were also evaluated for their antioxidant properties in acellular system. Treatment with MNG produced strong cytoprotective effect on PAH-exposed cells (p < 0.01) while Z-LG (0.5 microg/mL) exhibited strong negative effect on cell proliferation in untreated and PAH-exposed cells (p < 0.001). MNG, being many times stronger antioxidant than Z-LG in chemical in vitro assays (p < 0.0001), was also able to decrease PAH-induced oxidative stress in the cell cultures (p < 0.05). Consequently MNG ameliorates oxidative stress, speeds up wound healing process and restores proliferation rate in PAH-exposed bronchial epithelium. Such protective effects of MNG in air pollution affected airway epithelium stimulate further research on this promising phytochemical.
Apoptotic cell death induced by Z-Ligustilidein human ovarian cancer cells and role of NRF2.[Pubmed:30243965]
Food Chem Toxicol. 2018 Nov;121:631-638.
Z-Ligustilide is the most potent bioactive component of Angelica sinensis, which is widely used in Chinese traditional medicine. Z-Ligustilide selectively affected ovarian cancer cell survival in a dose dependent manner. Z-Ligustilide induced apoptotic cell death was determined by flow cytometry. We also demonstrated that apoptotic cell death was triggered by Z-Ligustilideinduced oxidative stress and mitochondria played an active role. Mitochondrial polarization was reduced by Z-Ligustilidewhereas mitochondrial superoxide formation was increased. NRF2 was induced by Z-Ligustilide in OVCAR-3cells at epigenetic level and its downstream antioxidant defense genesHeme oxygenase-1,NAD(P)H Quinone Dehydrogenase 1, UDP Glucuronosyltransferase Family 1 Member A1and Glutamate-Cysteine Ligase. NRF2 knockdown by siRNA resulted increased cell death by Z-Ligustilide in ovarian cancer cells. Our result demonstrated the pro-survival role of NRF2 in Z-Ligustilide induced ovarian cancer cell death.


