XanthoangelolCAS# 62949-76-2 |
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 62949-76-2 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 643007 | Appearance | Powder |
| Formula | C25H28O4 | M.Wt | 392.49 |
| Type of Compound | Chalcones | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Solubility | Soluble in Chloroform,Dichloromethane,Ethyl Acetate,DMSO,Acetone,etc. | ||
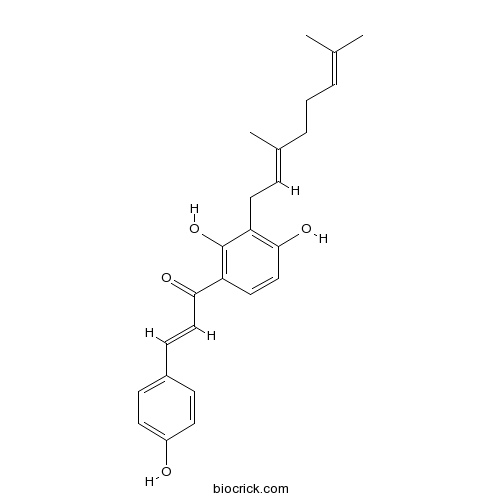
| Chemical Name | (~{E})-1-[3-[(2~{E})-3,7-dimethylocta-2,6-dienyl]-2,4-dihydroxyphenyl]-3-(4-hydroxyphenyl)prop-2-en-1-one | ||
| SMILES | CC(=CCCC(=CCC1=C(C=CC(=C1O)C(=O)C=CC2=CC=C(C=C2)O)O)C)C | ||
| Standard InChIKey | LRSMBOSQWGHYCW-MDGZPELGSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C25H28O4/c1-17(2)5-4-6-18(3)7-13-21-24(28)16-14-22(25(21)29)23(27)15-10-19-8-11-20(26)12-9-19/h5,7-12,14-16,26,28-29H,4,6,13H2,1-3H3/b15-10+,18-7+ | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | Xanthoangelol has anti-inflammatory,anti-platelet and antibacterial activities. It also shows antitumor and/or antimetastatic activities, which may be due to inhibition of DNA synthesis in LLC cells and of tumor-induced neovascularization through inhibition of the formation of capillary-like tubes by vascular endothelial cells and inhibition of the binding of VEGF to vascular endothelial cells. Xanthoangelol may be applicable as an effective drug for treatment of neuroblastoma and leukemia. |
| Targets | DNA synthesis | VEGF | Antifection |
| In vitro | Antibacterial activity of two chalcones, xanthoangelol and 4-hydroxyderricin, isolated from the root of Angelica keiskei KOIDZUMI.[Pubmed: 1934181 ]Chem Pharm Bull (Tokyo). 1991 Jun;39(6):1604-5.Two chalcones, Xanthoangelol (I) and 4-hydroxyderricin (II), isolated from the root of Angelica keiskei KOIDZUMI (Umbelliferae) showed antibacterial activity against gram-positive pathogenic bacteria.
Anti-platelet effects of chalcones from Angelica keiskei Koidzumi (Ashitaba) in vivo.[Pubmed: 29441970 ]Pharmazie. 2016 Nov 2;71(11):651-654.Angelica keiskei Koidzumi (Ashitaba) is a traditional folk medicine that is also regarded in Japan as a health food with potential antithrombotic properties. The ability of the major chalcones, Xanthoangelol (XA) and 4-hydroxyderricin (4-HD) extracted from Ashitaba roots to inhibit platelet aggregation activity in vitro was recently determined. However, the anti-platelet activities of Ashitaba chalcones in vivo have remained unclear. |
| In vivo | Antitumor and antimetastatic activities of Angelica keiskei roots, part 1: Isolation of an active substance, xanthoangelol.[Pubmed: 12845685 ]Int J Cancer. 2003 Sep 1;106(3):429-37.The roots of Angelica keiskei Koizumi have traditionally been used as a health food, with diuretic, laxative, analeptic and galactagogic effects. It has been thought that the roots and leaves of A. keiskei have preventive effects against coronary heart disease, hypertension and cancer. In the present study, we examined the antitumor and antimetastatic activities of various fractions isolated from a 50% ethanol extract of A. keiskei roots. |
| Kinase Assay | Inhibitory effects of 4-hydroxyderricin and xanthoangelol on lipopolysaccharide-induced inflammatory responses in RAW264 macrophages.[Pubmed: 24369884 ]Xanthoangelol, a major chalcone constituent of Angelica keiskei, induces apoptosis in neuroblastoma and leukemia cells.[Pubmed: 16079483]Biol Pharm Bull. 2005 Aug;28(8):1404-7.Xanthoangelol, a major chalcone constituent of the stem exudates of Angelica keiskei, was evaluated for cell toxicity and apoptosis-inducing activity in human neuroblastoma (IMR-32) and leukemia (Jurkat) cells.
J Agric Food Chem. 2014 Jan 15;62(2):462-7.The Japanese herb, Ashitaba (Angelica keiskei Koidzumi), contains two prenylated chalcones, 4-hydroxyderricin and Xanthoangelol, which are considered to be the major active compounds of Ashitaba. However, their effects on inflammatory responses are poorly understood.
|

Xanthoangelol Dilution Calculator

Xanthoangelol Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 2.5478 mL | 12.7392 mL | 25.4784 mL | 50.9567 mL | 63.6959 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.5096 mL | 2.5478 mL | 5.0957 mL | 10.1913 mL | 12.7392 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.2548 mL | 1.2739 mL | 2.5478 mL | 5.0957 mL | 6.3696 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.051 mL | 0.2548 mL | 0.5096 mL | 1.0191 mL | 1.2739 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0255 mL | 0.1274 mL | 0.2548 mL | 0.5096 mL | 0.637 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
- Trillikamtoside Q
Catalog No.:BCN8195
CAS No.:2098642-70-5
- 2''-O-acetylsaikosaponin A
Catalog No.:BCN8736
CAS No.:102934-42-9
- (R)-alpha-methyltryptamine
Catalog No.:BCN8160
CAS No.:7795-52-0
- Quercetin 3-O-(6''-galloyl)-beta-D-glucopyranoside
Catalog No.:BCN8742
CAS No.:56316-75-7
- Scutellarein-7-O-glucoside
Catalog No.:BCN8099
CAS No.:26046-94-6
- Steviol-19-O-Glucoside
Catalog No.:BCN6373
CAS No.:1185737-16-9
- (-)-Epiafzelechin 3-O-gallate
Catalog No.:BCN8740
CAS No.:108907-43-3
- 8-Hydroxypinoresinol diglucoside
Catalog No.:BCN6368
CAS No.:112747-99-6
- Caraganaphenol A
Catalog No.:BCN8731
CAS No.:174916-31-5
- Cyclocurcumin
Catalog No.:BCN6379
CAS No.:153127-42-5
- Daidzein-4',7-diglucoside
Catalog No.:BCN8135
CAS No.:53681-67-7
- Quercetagetin
Catalog No.:BCN8729
CAS No.:90-18-6
- Arecaidine
Catalog No.:BCN8282
CAS No.:499-04-7
- Isosilybin B
Catalog No.:BCN6764
CAS No.:142796-22-3
- Luteolin-3',7-di-O-glucoside
Catalog No.:BCN6380
CAS No.:257-724-7
- Isosilybin A
Catalog No.:BCN6369
CAS No.:142796-21-2
- Cistantubuloside C1
Catalog No.:BCN6362
CAS No.:620632-36-2
- Niga-ichigoside F1
Catalog No.:BCN8356
CAS No.:95262-48-9
- 1,3,6-Trihydroxy-2-methylanthraquinone 3-O-alpha-L-rhamnosyl-(1->2)-beta-D-glucoside
Catalog No.:BCN8732
CAS No.:87686-88-2
- L-Fucitol
Catalog No.:BCN8464
CAS No.:13074-06-1
- Ganoderic acid R
Catalog No.:BCN8489
CAS No.:103963-39-9
- Tessaric acid
Catalog No.:BCN8743
CAS No.:58142-10-2
- Quercetin 3-Caffeylrobinobioside
Catalog No.:BCN8744
CAS No.:957110-26-8
- Momordicine II
Catalog No.:BCN8745
CAS No.:91590-75-9
Autophagy induction by xanthoangelol exhibits anti-metastatic activities in hepatocellular carcinoma.[Pubmed:30883849]
Cell Biochem Funct. 2019 Mar 18.
Xanthoangelol (XAG), a prenylated chalcone isolated from the Japanese herb Angelica keiskei Koidzumi, has been reported to exhibit antineoplastic properties. However, the specific anti-tumor activity of XAG in human hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC), and the relevant mechanisms are not known. Herein, we evaluated the effect of XAG against HCC in vitro and in vivo. Although XAG treatment did not significantly reduce the viability of the Hep3B and Huh7 cell lines, it suppressed cell migration, invasion, and EMT. This anti-metastatic effect of XAG was due to induction of autophagy, because treatment with the autophagy inhibitor 3-methyadenine (3-MA) or knockdown of the pro-autophagy Beclin-1 effectively abrogated the XAG-induced suppression of metastasis. Mechanistically, XAG induced autophagy via activation of the AMPK/mTOR signaling pathway, and XAG treatment dramatically increased the expression of p-AMPK while decreasing p-mTOR expression. In addition, blocking AMPK/mTOR axis with compound C abrogated the autophagy-mediated inhibition of metastasis. The murine model of HCC metastasis also showed that XAG effectively reduced the number of metastatic pulmonary nodules. Taken together, our results revealed that autophagy via the activation of AMPK/mTOR pathway is essential for the anti-metastatic effect of XAG against HCC. These findings not only contribute to our understanding of the anti-tumor activity of XAG but also provide a basis for its clinical application in HCC. Before this study, evidence of XAG on HCC was purely anecdotal; present study provides the first comprehensive assessments of XAG on HCC metastasis and investigates its underlying mechanism. Results suggest that XAG exerts anti-metastatic properties against HCC through inducing autophagy which is mediated by the activation of AMPK/mTOR signaling pathway. This research extends our knowledge about the antineoplastic properties of XAG and suggests that induction autophagy may represent future treatment strategies for metastatic HCC.
Angelica keiskei (Ashitaba) powder and its functional compound xanthoangelol prevent heat stress-induced impairment in sperm density and quality in mouse testes.[Pubmed:30686791]
J Reprod Dev. 2019 Jan 26.
Recently, gradual decline in human sperm production has become a serious worldwide concern because it leads to increased rates of infertility. Endocrine disrupters, lifestyle changes, and varicocele, all of which elevate testicular temperature, are thought to be the main causes of this decline. The present study aimed to determine whether the dietary phytochemicals Angelica keiskei (Ashitaba) powder (57.5 mg/kg) and its functional component, Xanthoangelol (3 mg/kg), can prevent heat stress-induced impairment in sperm density and quality in mice. Sperm parameters were analyzed 28 days after mice exposure to heat. Supplementation with Ashitaba powder completely prevented heat-induced impairment in sperm parameters, including densities of motile sperms and progressive sperms (> 25 mum/sec), and amplitude of lateral head displacement. Xanthoangelol did not exert a complete protective effect; nevertheless, it significantly prevented heat stress-induced reduction in most parameters. Both Ashitaba powder and Xanthoangelol elevated the expression of the widely expressed heat shock proteins (HSPs) Hspa1a and Hsp40 and the antioxidant enzyme glutathione synthase in non-stressed testes. Ashitaba powder significantly prevented heat stress-induced reduction in the expression of Hspa1l and Hspa2, which are highly expressed in the testes and critical for fertility. Our results showed that Ashitaba powder and Xanthoangelol protected testicular cells from heat stress, probably by elevating the levels of antioxidant enzymes and HSPs. Supplementation with dietary functional phytochemicals may help prevent heat stress-induced male infertility.
Endoplasmic reticulum stress triggers Xanthoangelol-induced protective autophagy via activation of JNK/c-Jun Axis in hepatocellular carcinoma.[Pubmed:30621754]
J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2019 Jan 8;38(1):8.
BACKGROUND: Xanthoangelol (XAG) was reported to exhibit antitumor properties in several cancer. However, the specific anti-tumor activity of XAG in human hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) and the relevant mechanisms are not known. METHODS: The effects of XAG on HCC cell proliferation and apoptosis were respectively examined by CCK-8 assay and Annexin V-FITC/PI apoptosis kit. Western blotting was conducted to detect the expression of proteins. The effect of XAG on the development of acidic vesicle organelles was assessed using acridine orange staining. mRFP-GFP-LC3 adenovirus was used to transfect HCC cells and the formation of autolysosome was detected using a confocal microscope. RESULTS: Mechanistically, XAG promotes HCC cell death through triggering intrinsic apoptosis pathway, not extrinsic apoptotic pathway. Furthermore, XAG treatment induced autophagy in Bel 7402 and SMMC 7721 cells, as evidenced by an increase in autophagy-associated proteins, including LC3B-II, Beclin-1, and Atg5. Interestingly, inhibition of autophagy with 3-MA, Bafilomycin A1 (Baf A1), or siRNA targeting Atg5 effectively enhanced the apoptotic cell ratio in XAG-treated cells, indicating that protective effect of autophagy induced by XAG in HCC. Moreover, autophagy induced by XAG was mediated by activating endoplasmic reticulum stress (ERS), along with administration of XAG, the expression levels of ERS-associated proteins, including CHOP, GRP78, ATF6, p-eIF2alpha, IRE1alpha, and cleaved caspase-12 were significantly increased in HCC cells. Meanwhile, suppressing ERS with chemical chaperones (TUDCA) or CHOP shRNA could effectively abrogate the autophagy-inducing effect of XAG, and increase the apoptotic cell death. Further mechanistic studies showed that ERS-induced autophagy in XAG-treated cells was mediated by activation of JNK/c-jun pathway. XAG treatment resulted in the increase of p-JNK and p-c-jun, while suppressing ERS with TUDCA or CHOP shRNA could effectively reverse it. Meanwhile, SP600125, a JNK inhibitor, effectively reversed XAG-induced protective autophagy and enhanced cell apoptosis in XAG-treated HCC cells. In vivo results demonstrated that XAG exerts potent antitumor properties with low toxicity. CONCLUSIONS: Collectively, these results suggested that XAG could be served as a promising candidate for the treatment and prevention of HCC.
Total Synthesis of Xanthoangelol B and Its Various Fragments: Toward Inhibition of Virulence Factor Production of Staphylococcus aureus.[Pubmed:30388007]
J Med Chem. 2018 Nov 14.
As an alternative strategy to fight antibiotic resistance, two-component systems (TCSs) have emerged as novel targets. Among TCSs, master virulence regulators that control the expression of multiple virulence factors are considered as excellent antivirulence targets. In Staphylococcus aureus, virulence factor expression is tightly regulated by a few master regulators, including the SaeRS TCS. In this study, we used a SaeRS GFP-reporter system to screen natural compound inhibitors of SaeRS, and identified Xanthoangelol B 1, a prenylated chalcone from Angelica keiskei as a hit. We have synthesized 1 and its derivative PM-56 and shown that 1 and PM-56 both had excellent inhibitory potency against the SaeRS TCS, as demonstrated by various in vitro and in vivo experiments. As a mode of action, 1 and PM-56 were shown to bind directly to SaeS and inhibit its histidine kinase activity, which suggests a possibility of a broad spectrum inhibitor of histidine kinases.
The Ashitaba (Angelica keiskei) Chalcones 4-hydroxyderricin and Xanthoangelol Suppress Melanomagenesis By Targeting BRAF and PI3K.[Pubmed:29980517]
Cancer Prev Res (Phila). 2018 Oct;11(10):607-620.
Malignant melanoma is an aggressive tumor of the skin and still lacks effective preventive and therapeutic treatments. In melanoma, both the BRAF/MEK/ERK and PI3-K/AKT signaling pathways are constitutively activated through multiple mechanisms, which result in cell-cycle progression and prevention of apoptosis. Therefore, the development of novel strategies for targeting BRAF and PI3K are of utmost importance. In this study, we found that Ashitaba (Angelica keiskei) chalcones, 4-hydroxyderricin (4HD) and Xanthoangelol (XAG), suppressed melanoma development by directly targeting both BRAFV600E and PI3K, which blocked the activation of downstream signaling. This led to the induction of G1 phase cell-cycle arrest and apoptosis in melanoma cells. Importantly, 4HD or XAG dramatically attenuated tumor incidence and volume in the BRAF-activated Pten-deficient melanoma mouse model. Our findings suggest that 4HD and XAG are promising chemopreventive or potential therapeutic agents against melanomagenesis that act by targeting both BRAF and PI3K, providing hope for rapid clinical translation. Cancer Prev Res; 11(10); 607-20. (c)2018 AACR.
3'-Geranyl-mono-substituted chalcone Xanthoangelovl induces apoptosis in human leukemia K562 cells via activation of mitochondrial pathway.[Pubmed:27908776]
Chem Biol Interact. 2017 Jan 5;261:103-107.
3'-Geranyl-mono-substituted chalcone Xanthoangelol (1b), a chalcone derivative, was previously reported to show selective cytotoxicity against human chronic myelogenous leukemia K562 cells with a half-maximal inhibitory concentration (IC50) of 3.98 muM. In the present study, we investigated the molecular mechanism underlying the cytotoxicity of 1b in K562 cells. Treatment with compound 1b caused K562 cells to adopt a typical apoptotic morphology. Flow cytometric analysis also confirmed the presence of an apoptotic cell population following treatment of Annexin-V-FITC and propidium iodide (PI) double-labeled K562 cells with 1b. Furthermore, we observed dissipation of the mitochondrial membrane potential, caspase-3 activation, and a reduction of the Bcl-2/Bax ratio in these cells, which suggest that the mitochondrial apoptotic pathway is induced by 1b in K562 cells. Collectively, our findings demonstrate that compound 1b notably induces mitochondrial-mediated apoptosis in K562 cells, which might have a potential anticancer activity.
Xanthoangelol and 4-hydroxyderrcin suppress obesity-induced inflammatory responses.[Pubmed:27619735]
Obesity (Silver Spring). 2016 Nov;24(11):2351-2360.
OBJECTIVE: Obesity-induced inflammation plays a pivotal role in the pathogenesis of insulin resistance and type 2 diabetes. Xanthoangelol (XA) and 4-hydroxyderrcin (4-HD), phytochemicals extracted from Angelica keiskei, have been reported to possess various biological properties. Whether XA and 4-HD alleviate obesity-induced inflammation and inflammation-induced adipocyte dysfunction was investigated. METHODS: For the in vitro study, a co-culture system composed of macrophages and adipocytes and macrophages stimulated with conditioned medium derived from fully differentiated adipocytes was conducted. For the in vivo study, mice were fed a high-fat diet supplemented with XA for 14 weeks. RESULTS: XA and 4-HD suppressed inflammatory factors in co-culture system. Moreover, treatment of RAW macrophages with XA and 4-HD moderated the suppression of uncoupling protein 1 promoter activity and gene expression in C3H10T1/2 adipocytes, which was induced by conditioned medium derived from LPS-stimulated RAW macrophages. Also, XA and 4-HD inhibited c-Jun N-terminal kinase phosphorylation, nuclear factor-kappaB, and activator protein 1, the last two being transcription activators in activated macrophages. Furthermore, in mice fed the high-fat diet, XA reduced inflammatory factors within the white adipose tissue. CONCLUSIONS: These results suggest that XA and 4-HD might be promising phytochemicals to suppress obesity-induced inflammation and inflammation-induced adipocyte dysfunction.
Antitumor and antimetastatic actions of xanthoangelol and 4-hydroxyderricin isolated from Angelica keiskei roots through the inhibited activation and differentiation of M2 macrophages.[Pubmed:26141763]
Phytomedicine. 2015 Jul 15;22(7-8):759-67.
BACKGROUND: Tumor growth and metastasis have been closely associated with the M2 macrophage-induced activation of tumor-associated macrophages (TAMs). PURPOSE: The antitumor and antimetastatic actions of xanthangelol and 4-hydroxyderricin on the role of M2 macrophages in the TAMs of highly metastatic osteosarcoma LM8-bearing mice have not yet been fully elucidated. In order to clarify the mechanisms underlying the antitumor and antimetastatic actions of the above chalcones, we performed in vivo and in vitro studies. STUDY DESIGN: The antitumor and antimetastatic actions of Xanthoangelol and 4-hydroxyderricin were examined in vivo and the effects on M2 macrophage differentiation and activation were examined in vitro. METHODS: We examined the antitumor and antimetastatic effects of Xanthoangelol and 4-hydroxyderricin on highly metastatic osteosarcoma LM8-bearing mice (in vivo). Further, we examined their effects on the differentiation of interleukin (IL)-4 plus IL-13-induced M2 macrophages and activation of IL-4 plus IL13-induced M2 macrophages (in vitro). We also investigated the expression and phosphorylation of signal transducer and activator of transcript 3 (Stat 3) in the differentiation process of M2-polarized macrophages (in vitro). RESULTS: Xanthoangelol or 4-hydroxyderricin (25 or 50 mg/kg, twice daily) inhibited tumor growth, metastasis to the lung and liver, and TAM expression in tumors. In addition, Xanthoangelol (10, 25 or 50 muM) and 4-hydroxyderricin (5, 10, 25 or 50 muM) inhibited the production of IL-10 and monocyte chemoattractant protein (MCP)-1 in M2-polarized macrophages. This result indicated that Xanthoangelol and 4-hydroxyderricin inhibited the activation of M2 macrophages. Furthermore, Xanthoangelol (5-50 muM) inhibited the phosphorylation of Stat 3 without affecting the expression of the Stat 3 protein in the differentiation process of M2 macrophages, which indicated that these chalcones inhibited the differentiation of M2 macrophages. CONCLUSION: These findings suggested that the antitumor and antimetastatic actions of Xanthoangelol and 4-hydroxyderrcin might be attributed to the regulated activated TAMs through the inhibition of activation and differentiation of M2 macrophages in the tumor microenvironment.


