VorapaxarPAR-1 antagonist,potent and orally active CAS# 618385-01-6 |
- Verteporfin
Catalog No.:BCC3690
CAS No.:129497-78-5
- TPT-260 Dihydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC5172
CAS No.:2076-91-7
- Miglustat hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC5186
CAS No.:210110-90-0
- Amifampridine
Catalog No.:BCC5185
CAS No.:54-96-6
- Miglustat
Catalog No.:BCC5187
CAS No.:72599-27-0
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 618385-01-6 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 10077130 | Appearance | Powder |
| Formula | C29H33FN2O4 | M.Wt | 492.58 |
| Type of Compound | N/A | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Synonyms | SCH 530348 | ||
| Solubility | DMSO : ≥ 150 mg/mL (304.52 mM) *"≥" means soluble, but saturation unknown. | ||
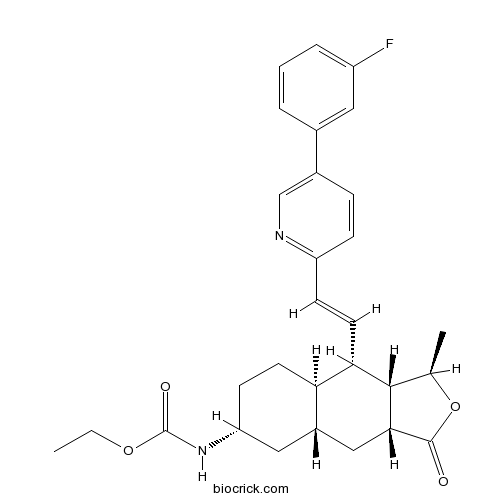
| Chemical Name | ethyl N-[(1R,3aR,4aR,6R,8aR,9S,9aS)-9-[(E)-2-[5-(3-fluorophenyl)pyridin-2-yl]ethenyl]-1-methyl-3-oxo-3a,4,4a,5,6,7,8,8a,9,9a-decahydro-1H-benzo[f][2]benzofuran-6-yl]carbamate | ||
| SMILES | CCOC(=O)NC1CCC2C(C1)CC3C(C2C=CC4=NC=C(C=C4)C5=CC(=CC=C5)F)C(OC3=O)C | ||
| Standard InChIKey | ZBGXUVOIWDMMJE-QHNZEKIYSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C29H33FN2O4/c1-3-35-29(34)32-23-10-11-24-20(14-23)15-26-27(17(2)36-28(26)33)25(24)12-9-22-8-7-19(16-31-22)18-5-4-6-21(30)13-18/h4-9,12-13,16-17,20,23-27H,3,10-11,14-15H2,1-2H3,(H,32,34)/b12-9+/t17-,20+,23-,24-,25+,26-,27+/m1/s1 | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | Vorapaxar (SCH 530348) is a potent and orally active antagonist of thrombin receptor (PAR-1) with a Ki value of 8.1 nM. | |||||
| Targets | PAR-1 | |||||
| IC50 | 8.1 nM (Ki) | |||||

Vorapaxar Dilution Calculator

Vorapaxar Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 2.0301 mL | 10.1506 mL | 20.3013 mL | 40.6025 mL | 50.7532 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.406 mL | 2.0301 mL | 4.0603 mL | 8.1205 mL | 10.1506 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.203 mL | 1.0151 mL | 2.0301 mL | 4.0603 mL | 5.0753 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0406 mL | 0.203 mL | 0.406 mL | 0.8121 mL | 1.0151 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0203 mL | 0.1015 mL | 0.203 mL | 0.406 mL | 0.5075 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
Vorapaxar is a potent PAR1 inhibitor and antiplatelet that was completed in phase III clinical trial[1].
PAR1 is one of the 4 thrombin receptor types that belong to G-protein coupled receptors super family[1]. By binding to thrombin, the N-terminal at the arginine 41 and serine 42 bond of PAR1 on platelet surface can be enzymatically cleaved, resulting in the activation of platelet and subsequent hemostasis process[1].
Vorapaxar is an ethyl-carbamate molecule that derived from natural himbacine and has been determined to be a selective PAR 1 inhibitor through direct binding[2]. In human plasma enriched with platelets, Vorapaxar was able to inhibit the aggregation of platelet with an IC50 value of 47 nM[2]. In addition, vorapaxar is able to inhibitthe platelet aggregation that triggered by the addition of thrombin receptor activating peptide with an IC50 value of 25 nM[2]. At the same time, however, vorapaxar does not interfere thrombin’s enzymatic activity on fibrin formation or thromboxane A2 receptors-induced platelet aggregation, as was demonstrated by its inability to inhibit platelet aggregation that induced by the addition of 9,11-dideoxy-11R,9R-epoxymethanoprostaglandin F2R (a thromboxane mimetic) [1].
In vivo, oral administration of 0.1 mg/kg of Vorapaxar completely inhibited the platelet aggregation monkey model for 24 hrs. In phase III clinical trial that involved 26,449 patients [1], administration of vorapaxar (2.5 mg/day) reduced the occurrence of cardiovascular death or ischemic events compared with placebo group by a statistically significant 1.2%[1].
References:
[1]. Chackalamannil S & XIA, Y. Thrombin receptor (PAR-1) antagonists as novel antithrombotic agents. Expert Opinion on Therapeutic Patents, 2006.16:493-505.
[2]. Chackalamannil S, Wang Y, Greenlee W J et al. 2008. Discovery of a novel, orally active himbacine-based thrombin receptor antagonist (SCH 530348) with potent antiplatelet activity. J Med Chem, 2008,51: 3061-3064.
- Sipeimine
Catalog No.:BCN1201
CAS No.:61825-98-7
- Oxaliplatin
Catalog No.:BCC3932
CAS No.:61825-94-3
- Trans-Melilotoside
Catalog No.:BCC8364
CAS No.:618-67-7
- Ethyl 3,4,5-trimethoxybenzoate
Catalog No.:BCN3973
CAS No.:6178-44-5
- 5-O-Methylnaringenin
Catalog No.:BCN4144
CAS No.:61775-19-7
- Methyl 2-(6-acetyl-5-hydroxy-2,3-dihydrobenzofuran-2-yl)propenoate
Catalog No.:BCN1395
CAS No.:617722-56-2
- Methyl 2-(5-acetyl-2,3-dihydrobenzofuran-2-yl)propenoate
Catalog No.:BCN1396
CAS No.:617722-55-1
- Fluvoxamine maleate
Catalog No.:BCC1215
CAS No.:61718-82-9
- W-7 hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC6622
CAS No.:61714-27-0
- W-5 hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC6621
CAS No.:61714-25-8
- 2-Chloro-1,4-phenylenediamine sulfate
Catalog No.:BCN8435
CAS No.:61702-44-1
- 2-Hydroxy-1-methoxyanthraquinone
Catalog No.:BCN3091
CAS No.:6170-06-5
- Benzyl p-coumarate
Catalog No.:BCN7717
CAS No.:61844-62-0
- Epoprostenol
Catalog No.:BCC7534
CAS No.:61849-14-7
- Demethoxycapillarisin
Catalog No.:BCN4611
CAS No.:61854-36-2
- Demethoxy-7-O-methylcapillarisin
Catalog No.:BCN6469
CAS No.:61854-37-3
- H-β-homo-Gln-OH.HCl
Catalog No.:BCC2648
CAS No.:61884-74-0
- Vernolide B
Catalog No.:BCN6749
CAS No.:618860-58-5
- 3-(1,1-Dimethylallyl)-8-hydroxy-7-methoxycoumarin
Catalog No.:BCN7570
CAS No.:61899-42-1
- 4-Hydroxybenzamide
Catalog No.:BCN4147
CAS No.:619-57-8
- p-Ethoxybenzoic acid
Catalog No.:BCN3378
CAS No.:619-86-3
- 4-Nitrocinnamic acid
Catalog No.:BCN5033
CAS No.:619-89-6
- Sceleratine
Catalog No.:BCN2126
CAS No.:6190-25-6
- Dihydroergotamine mesylate
Catalog No.:BCC5224
CAS No.:6190-39-2
Vorapaxar: The Current Role and Future Directions of a Novel Protease-Activated Receptor Antagonist for Risk Reduction in Atherosclerotic Disease.[Pubmed:28063023]
Drugs R D. 2017 Mar;17(1):65-72.
INTRODUCTION: Despite the current standard of care, patients with cardiovascular disease remain at a high risk for recurrent events. Inhibition of thrombin-mediated platelet activation through protease-activated receptor-1 antagonism may provide reductions in atherosclerotic disease beyond those achievable with the current standard of care. OBJECTIVE: Our primary objective is to evaluate the clinical literature regarding the role of Vorapaxar (Zontivity) in the reduction of cardiovascular events in patients with a history of myocardial infarction and peripheral artery disease. In particular, we focus on the potential future directions for protease-activating receptor antagonists in the treatment of a broad range of atherosclerotic diseases. DATA SOURCES: A literature search of PubMed and EBSCO was conducted to identify randomized clinical trials from August 2005 to June 2016 using the search terms: 'Vorapaxar', 'SCH 530348', 'protease-activated receptor-1 antagonist', and 'Zontivity'. Bibliographies were searched and additional resources were obtained. RESULTS: Vorapaxar is a first-in-class, protease-activated receptor-1 antagonist. The Thrombin Receptor Antagonist for Clinical Event Reduction (TRACER) trial did not demonstrate a significant reduction in a broad primary composite endpoint. However, the Thrombin-Receptor Antagonist in Secondary Prevention of Atherothrombotic Ischemic Events (TRA 2 degrees P-TIMI 50) trial examined a more traditional composite endpoint and found a significant benefit with Vorapaxar. Vorapaxar significantly increased bleeding compared with standard care. Ongoing trials will help define the role of Vorapaxar in patients with peripheral arterial disease, patients with diabetes mellitus, and other important subgroups. The use of multivariate modeling may enable the identification of subgroups with maximal benefit and minimal harm from Vorapaxar. CONCLUSION: Vorapaxar provides clinicians with a novel mechanism of action to further reduce the burden of ischemic heart disease. Identification of patients with a high ischemic risk and low bleeding risk would enable clinicians to maximize the utility of this unique agent.
Vorapaxar and Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis: Coincidence or Adverse Association?[Pubmed:28267691]
Am J Ther. 2017 Mar/Apr;24(2):e139-e143.
BACKGROUND: Vorapaxar, a novel antiplatelet thrombin PAR-1 inhibitor, is currently approved for post myocardial infarction and peripheral artery disease indications with concomitant use of clopidogrel and/or aspirin. The Vorapaxar safety profile was acceptable. However, aside from heightened bleeding risks, excesses of solid cancers and diplopia, there were more amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS) diagnoses after Vorapaxar. STUDY QUESTION: To assess the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) reviews on the potential association of Vorapaxar with ALS. STUDY DESIGN: The review the public FDA records on reported adverse events after Vorapaxar. MEASURES AND OUTCOMES: Incidence of ALS after Vorapaxar and placebo. RESULTS: The ALS risk appears very small, about 1 case per 10,000 treated subjects, but quite probable. Indeed, there were overall 2 placebo and 4 Vorapaxar ALS incidences in the Phase III clinical trials. CONCLUSIONS: Potential adverse association of Vorapaxar with ALS risks may be related to off-target neuronal PAR receptor(s) blockade beyond platelet inhibition.
State transition model: vorapaxar added to standard antiplatelet therapy to prevent thrombosis post myocardial infarction or peripheral artery disease.[Pubmed:28277861]
Curr Med Res Opin. 2017 Sep;33(9):1535-1543.
OBJECTIVE: To evaluate long-term health benefits and risks of adding Vorapaxar (VOR) to the standard care antiplatelet therapy (SC) of aspirin and/or clopidogrel, among a population with a recent myocardial infarction (MI) and/or peripheral artery disease (PAD). RESEARCH DESIGN AND METHODS: In a state-transition model, patients transition between health states (event-free, recurrent MI, stroke, death), while at risk of experiencing non-transition-related revascularization and non-fatal bleeding events. Risk equations developed from the TRA 2 degrees P-TIMI 50 trial's patient-level data were used to predict cardiovascular (CV) outcomes over longer time horizons. Additional sources, including trials and US-based observational studies, informed the inputs for short-term CV risk, non-CV death, and health-related quality of life. Survival and quality-adjusted life-years (QALYs) were estimated over a lifetime horizon, discounted at 3% per year. RESULTS: Within a cohort of 7361 patients with recent MI and/or PAD, VOR + SC relative to SC alone yielded 176 fewer CV events (MIs, strokes, or CV deaths), but 27 more major bleeding events. VOR + SC was associated with increased life expectancy and health benefits (19.93 undiscounted life-years [LYs], 9.57 discounted QALYs vs. 19.61 undiscounted LYs, 9.41 discounted QALYs). The results were most sensitive to scenarios varying time of Vorapaxar initiation, and the assumptions in the 90 day period post-MI. Additional analyses showed that add-on Vorapaxar provides consistent incremental benefits in high-risk subgroups. CONCLUSION: This study contributes to the growing literature on secondary prevention add-on therapy, as results from these modeling analyses suggest that adding Vorapaxar to SC for patients at high atherothrombotic risk can provide long-term health benefits.
Pharmacokinetic drug evaluation of vorapaxar for secondary prevention after acute coronary syndrome.[Pubmed:28135897]
Expert Opin Drug Metab Toxicol. 2017 Mar;13(3):339-350.
INTRODUCTION: Vorapaxar is the first protease-activated receptor-1 inhibitor approved for clinical use. Its main indication is the reduction in thrombotic cardiovascular events in patients with previous myocardial infarction or symptomatic peripheral artery disease. Areas covered: This article reviews the pharmacokinetics of Vorapaxar and its potential use in secondary prevention after an acute coronary syndrome. Expert opinion: Vorapaxar inhibits platelet aggregation mediated by thrombin. This effect is carried out without affecting to coagulation parameters and bleeding times. This drug has showed a significant reduction of cardiovascular events in patients with chronic atherosclerosis but not during the admission for an acute coronary syndrome. The rate of major bleeding found in patients treated with Vorapaxar in randomized trials was consistently higher than placebo in most of the analyzed subgroups. For this reason, cautious evaluation of risk-benefit profiles should be required before prescribing this drug.


