PoliumosideCAS# 94079-81-9 |
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 94079-81-9 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 6442411 | Appearance | White powder |
| Formula | C35H46O19 | M.Wt | 770.73 |
| Type of Compound | Phenylpropanoids | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Solubility | DMSO : 100 mg/mL (129.75 mM; Need ultrasonic) Ethanol : 50 mg/mL (64.87 mM; Need ultrasonic) | ||
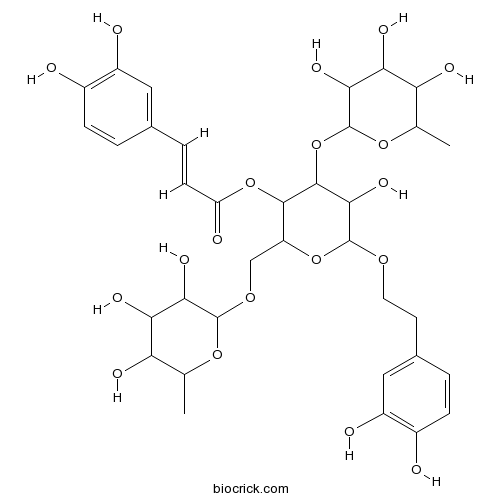
| Chemical Name | [6-[2-(3,4-dihydroxyphenyl)ethoxy]-5-hydroxy-4-(3,4,5-trihydroxy-6-methyloxan-2-yl)oxy-2-[(3,4,5-trihydroxy-6-methyloxan-2-yl)oxymethyl]oxan-3-yl] (E)-3-(3,4-dihydroxyphenyl)prop-2-enoate | ||
| SMILES | CC1C(C(C(C(O1)OCC2C(C(C(C(O2)OCCC3=CC(=C(C=C3)O)O)O)OC4C(C(C(C(O4)C)O)O)O)OC(=O)C=CC5=CC(=C(C=C5)O)O)O)O)O | ||
| Standard InChIKey | YMWRMAOPKNYHMZ-VMPITWQZSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C35H46O19/c1-14-24(41)26(43)28(45)33(50-14)49-13-22-31(53-23(40)8-5-16-3-6-18(36)20(38)11-16)32(54-35-29(46)27(44)25(42)15(2)51-35)30(47)34(52-22)48-10-9-17-4-7-19(37)21(39)12-17/h3-8,11-12,14-15,22,24-39,41-47H,9-10,13H2,1-2H3/b8-5+ | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | Poliumoside is a natural compound which exhibits significant inhibition of advanced glycation end product formation with IC50 value of 4.6-25.7 μM, it also exhibits great inhibitory effects on rat lens aldose reductase with IC50 values of 0.85 μM.Poliumoside has oxidant scavenging, antibacterial and hemostasis capacities, it can inhibit Biofilm-forming Staphylococcus aureus in mice. |
| Targets | Antifection | Lens aldose reductase |
| In vitro | Total peroxynitrite scavenging capacity of phenylethanoid and flavonoid glycosides from the flowers of Buddleja officinalis.[Pubmed: 19952410]Biol Pharm Bull. 2009 Dec;32(12):1952-6.
Caffeoylated phenylpropanoid glycosides from Brandisia hancei inhibit advanced glycation end product formation and aldose reductase in vitro and vessel dilation in larval zebrafish in vivo.[Pubmed: 24288293]Planta Med. 2013 Dec;79(18):1705-9.In our continuing efforts to identify effective naturally sourced agents for diabetic complications, five caffeoylated phenylpropanoid glycosides, acteoside (1), isoacteoside (2), Poliumoside (3), brandioside (4), and pheliposide (5) were isolated from the 80% EtOH extract of Brandisia hancei stems and leaves. These isolates (1-5) were subjected to an in vitro bioassay evaluating their inhibitory activity on advanced glycation end product formation and rat lens aldose reductase activity.
|
| In vivo | Poliumoside from Teucrium polium Inhibit Biofilm-forming Staphylococcus aureus in Mice.[Reference: WebLink]International Eurasia Pharmacy Congress. 2015, 9.Previous studies have demonstrated the therapeutic efficacy of Teucrium species, family Lamiaceae, as antibacterial. T. polium has been used for wound healing and the extract has shown a marked antibacterial activity against both Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria.
|
| Structure Identification | J Chromatogr B Analyt Technol Biomed Life Sci. 2014 Oct 15;969:285-96.Identification of poliumoside metabolites in rat feces by high performance liquid chromatography coupled with quadrupole time-of-flight tandem mass spectrometry.[Pubmed: 25215644]Poliumoside is one of the major phenylethanoid glycosides (PhGs) isolated from Callicarpae Caulis et Folium (CCF) which is a traditional Chinese medicine used for hemostasis in clinic.
|

Poliumoside Dilution Calculator

Poliumoside Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 1.2975 mL | 6.4874 mL | 12.9747 mL | 25.9494 mL | 32.4368 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.2595 mL | 1.2975 mL | 2.5949 mL | 5.1899 mL | 6.4874 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.1297 mL | 0.6487 mL | 1.2975 mL | 2.5949 mL | 3.2437 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0259 mL | 0.1297 mL | 0.2595 mL | 0.519 mL | 0.6487 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.013 mL | 0.0649 mL | 0.1297 mL | 0.2595 mL | 0.3244 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
Poliumoside is a natural compound which exhibit significant inhibition of advanced glycation end product formation with IC50 value of 4.6-25.7 μM. IC50 value: Target: Poliumoside exhibited greater inhibitory effects on rat lens aldose reductase with IC50 values of 0.85 μM, than those of the positive controls, 3,3-tetramethyleneglutaric acid (IC50=4.03 μM) and quercetin (IC50=7.2 μM).
References:
[1]. Yu SY, et al. Caffeoylated phenylpropanoid glycosides from Brandisia hancei inhibit advanced glycation end product formation and aldose reductase in vitro and vessel dilation in larval zebrafish in vivo. Planta Med. 2013 Dec;79(18):1705-9.
- Suplatast Tosylate
Catalog No.:BCC4961
CAS No.:94055-76-2
- NVP-BHG712
Catalog No.:BCC3963
CAS No.:940310-85-0
- N,N'-Bis(salicylidene)ethylenediamine
Catalog No.:BCC9064
CAS No.:94-93-9
- Piperine
Catalog No.:BCN1018
CAS No.:94-62-2
- 2-Amino-6-ethoxybenzothiazole
Catalog No.:BCC8541
CAS No.:94-45-1
- Benzyl nicotinate
Catalog No.:BCC8874
CAS No.:94-44-0
- Butylparaben
Catalog No.:BCN8418
CAS No.:94-26-8
- Tetracaine
Catalog No.:BCC9175
CAS No.:94-24-6
- Chlorpropamide
Catalog No.:BCC4647
CAS No.:94-20-2
- Benzyl 4-hydroxybenzoate
Catalog No.:BCC8869
CAS No.:94-18-8
- Sodium 4-amiropparaty Hyalrate
Catalog No.:BCC3855
CAS No.:94-16-6
- Propylparaben
Catalog No.:BCN8416
CAS No.:94-13-3
- R-7128
Catalog No.:BCC1880
CAS No.:940908-79-2
- SB743921
Catalog No.:BCC4559
CAS No.:940929-33-9
- KD 5170
Catalog No.:BCC2420
CAS No.:940943-37-3
- 1'-Acetonaphthone
Catalog No.:BCC8446
CAS No.:941-98-0
- 1,3,5-Cadinatriene-3,8-diol
Catalog No.:BCN4486
CAS No.:941227-27-6
- Selaginellin
Catalog No.:BCN8215
CAS No.:941269-84-7
- Ruxolitinib (INCB018424)
Catalog No.:BCC1276
CAS No.:941678-49-5
- INCB032304
Catalog No.:BCC6455
CAS No.:941685-27-4
- S-Ruxolitinib (INCB018424)
Catalog No.:BCC2201
CAS No.:941685-37-6
- 8beta-(4'-Hydroxytigloyloxy)costunolide
Catalog No.:BCN7885
CAS No.:94190-32-6
- Methyl 3-indolecarboxylate
Catalog No.:BCN4487
CAS No.:942-24-5
- VTP-27999
Catalog No.:BCC2048
CAS No.:942142-51-0
Identification of poliumoside metabolites in rat feces by high performance liquid chromatography coupled with quadrupole time-of-flight tandem mass spectrometry.[Pubmed:25215644]
J Chromatogr B Analyt Technol Biomed Life Sci. 2014 Oct 15;969:285-96.
Poliumoside is one of the major phenylethanoid glycosides (PhGs) isolated from Callicarpae Caulis et Folium (CCF) which is a traditional Chinese medicine used for hemostasis in clinic. In this study, high performance liquid chromatography coupled with quadrupole time-of-flight tandem mass spectrometry (HPLC/Q-TOF-MS) was applied to investigate the metabolites of Poliumoside in rat feces after oral administration. A total of 66 metabolites were confirmed or tentatively identified. Poliumoside could be partly transformed into its positional isomer isoPoliumoside in vivo, and Poliumoside was easily hydrolyzed and metabolized into degradation products. The parent compound and its degradation products could further undergo extensive phase I and phase II metabolism. The results indicated that hydrolysis, hydroxylation, acetylation, sulfation, hydration, reduction, dehydrogenation and dimethylation were the major metabolic pathways of Poliumoside. The major metabolic soft spots of Poliumoside and the fragmentation patterns of the metabolites were also proposed. This study provided valuable information regarding the metabolites of Poliumoside in rats.
Caffeoylated phenylpropanoid glycosides from Brandisia hancei inhibit advanced glycation end product formation and aldose reductase in vitro and vessel dilation in larval zebrafish in vivo.[Pubmed:24288293]
Planta Med. 2013 Dec;79(18):1705-9.
In our continuing efforts to identify effective naturally sourced agents for diabetic complications, five caffeoylated phenylpropanoid glycosides, acteoside (1), isoacteoside (2), Poliumoside (3), brandioside (4), and pheliposide (5) were isolated from the 80% EtOH extract of Brandisia hancei stems and leaves. These isolates (1-5) were subjected to an in vitro bioassay evaluating their inhibitory activity on advanced glycation end product formation and rat lens aldose reductase activity. All tested compounds exhibited significant inhibition of advanced glycation end product formation with IC50 values of 4.6-25.7 microM, compared with those of aminoguanidine (IC50=1,056 microM) and quercetin (IC50=28.4 microM) as positive controls. In the rat lens aldose reductase assay, acteoside, isoacteoside, and Poliumoside exhibited greater inhibitory effects on rat lens aldose reductase with IC50 values of 0.83, 0.83, and 0.85 microM, respectively, than those of the positive controls, 3,3-tetramethyleneglutaric acid (IC50=4.03 microM) and quercetin (IC50=7.2 microM). In addition, the effect of acteoside on the dilation of hyaloid-retinal vessels induced by high glucose in larval zebrafish was investigated. Acteoside reduced the diameters of high glucose-induced hyaloid-retinal vessels by 69% at 10 microM and 81% at 20 microM, compared to the high glucose-treated control group. These results suggest that B. hancei and its active components might be beneficial in the treatment and prevention of diabetic vascular complications.
Total peroxynitrite scavenging capacity of phenylethanoid and flavonoid glycosides from the flowers of Buddleja officinalis.[Pubmed:19952410]
Biol Pharm Bull. 2009 Dec;32(12):1952-6.
Nine compounds, including six phenylethanoid glycosides: acteoside (1); bioside (2); echinacoside (3); Poliumoside (4); phenylethyl glycoside (5); salidroside (6) and three flavonoids; linarin (7); apigenin (8); isorhoifolin (9), were isolated from the flowers of Buddleja officinalis MAXIM. (Buddlejaceae). Chemical structures were confirmed by (1)H-, and (13)C-NMR, and MS spectral methods and compared with those reported in the literature. Antioxidant activities of the methanol and water extracts, and all isolated compounds were evaluated using the total oxidant scavenging capacity (TOSC) assay against peroxynitrite. Results of the assay showed that the phenylethanoid glycosides, a major class of compounds of the flowers of B. officinalis, possess strong antioxidant activity. Of these, acteoside, echinacoside and Poliumoside have 9.9-, 9.8- and 9.5-fold TOSC value, respectively, compared with the positive control, Trolox.


