PitavastatinHMG-CoA reductase inhibitor CAS# 147511-69-1 |
- Atorvastatin Calcium
Catalog No.:BCC2319
CAS No.:134523-03-8
- Lovastatin
Catalog No.:BCN1060
CAS No.:75330-75-5
- Pravastatin sodium
Catalog No.:BCC2321
CAS No.:81131-70-6
- Fluvastatin
Catalog No.:BCC1579
CAS No.:93957-54-1
- Fluvastatin Sodium
Catalog No.:BCC2317
CAS No.:93957-55-2
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 147511-69-1 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 6366718 | Appearance | Powder |
| Formula | C25H24FNO4 | M.Wt | 421.46 |
| Type of Compound | N/A | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Synonyms | NK-104 | ||
| Solubility | >14.4mg/mL in DMSO | ||
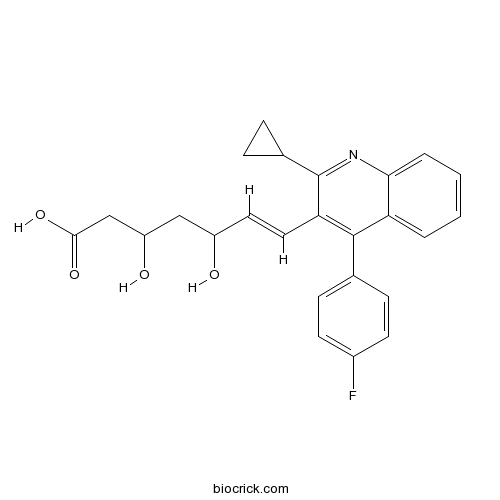
| Chemical Name | (E)-7-[2-cyclopropyl-4-(4-fluorophenyl)quinolin-3-yl]-3,5-dihydroxyhept-6-enoic acid | ||
| SMILES | C1CC1C2=NC3=CC=CC=C3C(=C2C=CC(CC(CC(=O)O)O)O)C4=CC=C(C=C4)F | ||
| Standard InChIKey | VGYFMXBACGZSIL-VAWYXSNFSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C25H24FNO4/c26-17-9-7-15(8-10-17)24-20-3-1-2-4-22(20)27-25(16-5-6-16)21(24)12-11-18(28)13-19(29)14-23(30)31/h1-4,7-12,16,18-19,28-29H,5-6,13-14H2,(H,30,31)/b12-11+ | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | Pitavastatin (NK-104) is a potent HMG-CoA reductase inhibitor, Pitavastatin inhibited cholesterol synthesis from acetic acid with an IC50 of 5.8 nM in a human liver cancer cell line (HepG2).
IC50 value: 5.8 nM(cholesterol synthesis from acetic
acid in HepG2) [1]
Target: HMG-CoA reductase
in vitro: Pitavastatin inhibited cholesterol synthesis from acetic
acid with an IC50 of 5.8 nM in a human liver cancer cell line (HepG2), which indicates that is 2.9 and 5.7 times as potent as simvastatin and atorvastatin, respectively. When the inhibitory activity interms of the ED50 was compared with that of simvastatin,
pitavastatin showed a 3-fold stronger activity in the rat and 15-fold stronger activity in a guinea pig model.22 The inhibitory effect of pitavastatin on sterol synthesis is thought to be liver-selective [1]. pitavastatin reduces total and phosphorylated tau levels in a cellular model of tauopathy, and in primary neuronal cultures. The decrease caused by pitavastatin is reversed by the addition of mevalonate, or geranylgeranyl pyrophosphate. The maturation of small G proteins, including RhoA was disrupted by pitavastatin, as was the activity of glycogen synthase kinase 3β (GSK3β), a major tau kinase [4].
in vivo: Intravenous treatment with pitavastatin-incorporated nanoparticles, but not with control nanoparticles or pitavastatin alone, inhibited plaque destabilization and rupture associated with decreased monocyte infiltration and gelatinase activity in the plaque[2].The EAM model was established in BALB/c mice by immunization with murine α-myosin heavy chain. Mice were fed pitavastatin (5 mg/kg) or vehicle once daily for 3 weeks from day 0 to day 21 after immunization [3]. References: | |||||

Pitavastatin Dilution Calculator

Pitavastatin Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 2.3727 mL | 11.8635 mL | 23.727 mL | 47.4541 mL | 59.3176 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.4745 mL | 2.3727 mL | 4.7454 mL | 9.4908 mL | 11.8635 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.2373 mL | 1.1864 mL | 2.3727 mL | 4.7454 mL | 5.9318 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0475 mL | 0.2373 mL | 0.4745 mL | 0.9491 mL | 1.1864 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0237 mL | 0.1186 mL | 0.2373 mL | 0.4745 mL | 0.5932 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
Pitavastatin (NK-104) is a potent HMG-CoA reductase inhibitor, Pitavastatin inhibited cholesterol synthesis from acetic acid with an IC50 of 5.8 nM in a human liver cancer cell line (HepG2).
- Ginsenoside Rg6
Catalog No.:BCN2706
CAS No.:147419-93-0
- Telenzepine dihydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC6946
CAS No.:147416-96-4
- Omaveloxolone (RTA-408)
Catalog No.:BCC5281
CAS No.:1474034-05-3
- Azilsartan
Catalog No.:BCC5014
CAS No.:147403-03-0
- Ligupurpuroside B
Catalog No.:BCC8199
CAS No.:147396-02-9
- Ligupurpuroside A
Catalog No.:BCC8198
CAS No.:147396-01-8
- MKT 077
Catalog No.:BCC6241
CAS No.:147366-41-4
- Cylindramide
Catalog No.:BCN1832
CAS No.:147362-39-8
- Antibiotic PF 1052
Catalog No.:BCN1828
CAS No.:147317-15-5
- KRCA 0008
Catalog No.:BCC8007
CAS No.:1472795-20-2
- 7ACC2
Catalog No.:BCC5554
CAS No.:1472624-85-3
- glatiramer acetate
Catalog No.:BCC5642
CAS No.:147245-92-9
- Thunberginol C
Catalog No.:BCN1654
CAS No.:147517-06-4
- LY 288513
Catalog No.:BCC5772
CAS No.:147523-65-7
- Pitavastatin Calcium
Catalog No.:BCC3842
CAS No.:147526-32-7
- Bosentan
Catalog No.:BCC4640
CAS No.:147536-97-8
- trans-3-Hydroxycinnamic acid
Catalog No.:BCN5029
CAS No.:14755-02-3
- Racemodine
Catalog No.:BCN2023
CAS No.:147554-28-7
- DiMNF
Catalog No.:BCC3900
CAS No.:14756-24-2
- ID-8
Catalog No.:BCC4787
CAS No.:147591-46-6
- Novobiocin Sodium
Catalog No.:BCC4812
CAS No.:1476-53-5
- 5-Chloro-4-methoxy-2-oxo-1,2-dihydropyridine-3-carbonitrile
Catalog No.:BCC8744
CAS No.:147619-40-7
- Calcipotriol monohydrate
Catalog No.:BCC1445
CAS No.:147657-22-5
- Magnolianin
Catalog No.:BCN3985
CAS No.:147663-91-0
Effects of pitavastatin and pravastatin on markers of immune activation and arterial inflammation in HIV.[Pubmed:28252528]
AIDS. 2017 Mar 27;31(6):797-806.
OBJECTIVE: Persistent immune activation is thought to contribute to increased cardiovascular disease risk in HIV and statins may help modulate systemic immune activation. We aimed to compare the effects of two key statins on markers of systemic immune activation and arterial inflammation in the HIV population. DESIGN: Double-blind, active-controlled, parallel-group comparative trial performed in 45 sites. METHODS: Two hundred and fifty-two antiretroviral therapy-treated HIV-infected participants with dyslipidemia were randomized (1 : 1) to Pitavastatin 4 mg daily vs. pravastatin 40 mg daily in the HIV-infected patieNts and TREatment with Pitavastatin vs. pravastatin for Dyslipidemia (INTREPID) trial. In this analysis of the INTREPID trial, we assessed markers of immune activation and arterial inflammation using a modified intent-to-treat population. This trial is registered with ClinicalTrials.gov (NCT01301066). RESULTS: One hundred and twenty-six participants were randomized to receive Pitavastatin and 126 to pravastatin. Ninety-nine participants in the Pitavastatin group and 91 participants in the pravastatin group completed the study. Median age was 50 (45, 56) years [median (interquartile range)]. Baseline, low-density lipoprotein-cholestrol (LDL-C) was 153 (135, 171) mg/dl, log HIV-1 viral load was 1.1 +/- 0.2 copies/ml, and CD4 cell count was 580 (439, 794) cells/mul. At week 52, the Pitavastatin group had a significantly greater reduction (% change) compared with pravastatin in soluble CD14 (sCD14), (-10.0 vs. 0.6%, P = 0.02), oxidized LDL (oxLDL) (-26.9 vs. -17.5%, P = 0.02), and lipoprotein-associated phospholipase 2 (Lp-PLA2) (-26.6 vs. -15.5%, P = 0.005) (Pitavastatin vs. pravastatin). CONCLUSION: Fifty-two weeks of Pitavastatin 4 mg daily (vs. pravastatin 40 mg daily) led to a greater reduction in select markers of immune activation and arterial inflammation (sCD14, oxLDL, and LpPLA2) among HIV-infected participants. Further work is needed to assess whether immune-modulatory effects of Pitavastatin reduce cardiovascular disease risk in HIV.
A validated LC-MS/MS method for the estimation of glimepiride and pitavastatin in rat plasma: Application to drug interaction studies.[Pubmed:28159531]
J Chromatogr B Analyt Technol Biomed Life Sci. 2017 Mar 1;1046:218-225.
Glimepiride (GLI) is prescribed for the management of type-2 diabetes where as Pitavastatin (PIT) for the treatment of diabetes associated dyslipidemia. Both the drugs are metabolized by CYP2C9 and have the potential of altering the enzyme through either inhibition or induction. In this respect, we present a simple, fast and validated bioanalytical LC-MS/MS method for the simultaneous estimation of GLI and PIT from rat plasma. Waters XTerra RP HPLC column (4.6x100mm, 5mum) with mobile phase consisting of acetonitrile and 10mM ammonium acetate (pH-6.0) in the ratio 85:15 (v/v) at a flow rate of 1mL/min was used for the chromatographic separation. The negative ionization mode with MRM transitions: m/z 420.17-->288.13 for PIT, m/z 489.59-->350.12 for GLI and m/z 380.08-->316.31for celecoxib as internal standard (IS). A total run time of 3min and LLOQ was found to be 5ng/mL for both PIT and GLI. The method was applied to study the drug interaction between GLI and PIT in rat liver microsomes. In vivo rat pharmacokinetics study showed there was a 1.29-fold increase in AUC0-infinity and 1.2-fold decrease in the clearance of PIT in presence of GLI. No notable difference in the pharmacokinetic profile of GLI was observed upon the intravenous co-administration of PIT.
Effects of Pitavastatin on Lipid-rich Carotid Plaques Studied Using High-resolution Magnetic Resonance Imaging.[Pubmed:28185713]
Clin Ther. 2017 Mar;39(3):620-629.
PURPOSE: This study evaluates the effectiveness of Pitavastatin in patients with atherosclerosis. METHODS: Sixty patients with atherosclerosis with lipid-rich carotid plaques were included and allocated into low-dose (2 mg/d) and high-dose (4 mg/d) Pitavastatin groups with 48 weeks of treatment. Total cholesterol, LDL-C, HDL-C, triglycerides, apolipoprotein A1, apolipoprotein B, lipoprotein (a), and the inflammation-related factors interleukin 6, high-sensitivity C-reactive protein, and homocysteine were determined. High-resolution (3.0-T) magnetic resonance imaging was used to evaluate the lipid core area, plaque thickness, total vessel area, lumen area, wall area, and normalized wall index. FINDINGS: After the treatment period, the blood serum values were improved in both groups, but the improvement was significantly better for total cholesterol (P < 0.009), HDL-C, LDL-C, triglycerides, apolipoprotein A1, apolipoprotein B, lipoprotein (a), and homocysteine (all P < 0.001) in the high-dose group. The high-resolution magnetic resonance images revealed great improvements in both groups, although significantly better for the lipid core area (P < 0.001), plaque thickness (P < 0.001), wall area (P < 0.05), normalized wall index (P < 0.001), and lumen area (P < 0.05) in the HD group. Further analyses revealed a close correlation between lipid-rich plaques and changes in blood lipid components. IMPLICATIONS: Pitavastatin had significant lipid-lowering and anti-inflammatory effects in patients with atherosclerosis. It also reduced the lipid components and plaques of lipid rich carotid plaques. The effect was obviously stronger in the high-dose than in the low-dose group.


