NodakeninCAS# 495-31-8 |
- Ammijin
Catalog No.:BCN3617
CAS No.:495-30-7
Quality Control & MSDS
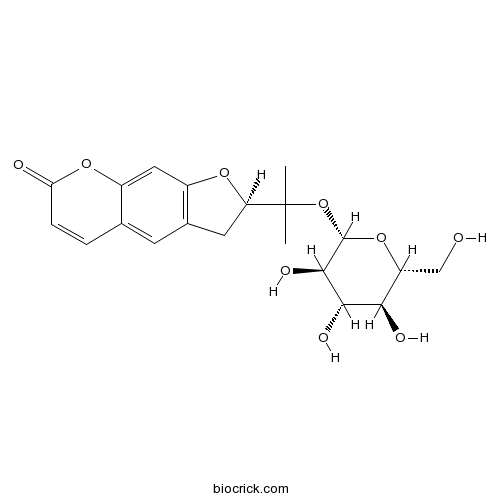
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 495-31-8 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 73191 | Appearance | White powder |
| Formula | C20H24O9 | M.Wt | 408.40 |
| Type of Compound | Coumarins | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Synonyms | (+)-Marmesinin; Nodakenetin β-D-glucopyranoside | ||
| Solubility | Soluble in methan | ||
| Chemical Name | (2R)-2-[2-[(2S,3R,4S,5S,6R)-3,4,5-trihydroxy-6-(hydroxymethyl)oxan-2-yl]oxypropan-2-yl]-2,3-dihydrofuro[3,2-g]chromen-7-one | ||
| SMILES | CC(C)(C1CC2=C(O1)C=C3C(=C2)C=CC(=O)O3)OC4C(C(C(C(O4)CO)O)O)O | ||
| Standard InChIKey | HXCGUCZXPFBNRD-DNLMCPORSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C20H24O9/c1-20(2,29-19-18(25)17(24)16(23)13(8-21)28-19)14-6-10-5-9-3-4-15(22)27-11(9)7-12(10)26-14/h3-5,7,13-14,16-19,21,23-25H,6,8H2,1-2H3/t13-,14-,16-,17+,18-,19+/m1/s1 | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | Nodakenin acts as an AChE inhibitor that inhibits AChE activity in a dosedependent manner with an IC50 value of 84.7 μM. Nodakenin possesses neuroprotective, anti-allergic, antiaggregatory, antibacterial, and memory -enhancing effects. Nodakenin down-regulates the expression of the proinflammatory iNOS, COX-2, TNF-α, IL-6, and IL-1β genes in macrophages by interfering with the activation of TRAF6, thus preventing NF-κB activation. |
| Targets | NOS | COX | TNF-α | IL Receptor | p65 | NF-kB | IkB | NO | PGE | Antifection | IKK | TRAF6 | AChE |
| In vitro | Nodakenin suppresses lipopolysaccharide-induced inflammatory responses in macrophage cells by inhibiting tumor necrosis factor receptor-associated factor 6 and nuclear factor-κB pathways and protects mice from lethal endotoxin shock.[Pubmed: 22637723]J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2012 Sep;342(3):654-64.Nodakenin, a coumarin isolated from the roots of Angelicae gigas, has been reported to possess neuroprotective, antiaggregatory, antibacterial, and memory-enhancing effects. |
| In vivo | The effects of nodakenin on airway inflammation, hyper-responsiveness and remodeling in a murine model of allergic asthma.[Pubmed: 25090633]Immunopharmacol Immunotoxicol. 2014 Oct;36(5):341-8.Nodakenin is a major coumarin glucoside in the root of Peucedanum decursivum Maxim, a commonly used traditional Chinese medicine for the treatment of asthma and chronic bronchitis for thousands of years.
In this work, the anti-asthma potential of Nodakenin was studied by investigation of its effect to suppress airway inflammation, hyper-responsiveness and remodeling in a murine model of chronic asthma.
Nodakenin, a coumarin compound, ameliorates scopolamine-induced memory disruption in mice.[Pubmed: 17382968 ]Life Sci. 2007 May 1;80(21):1944-50.Nodakenin is a coumarin compound initially isolated from the roots of Angelica gigas.
|
| Kinase Assay | Anti-Allergic Effects of Nodakenin in IgE/Ag-Induced Type I Hypersensitivity.[Reference: WebLink]Journal of Life Science,2011,21(12):1721-5.Mast cells are major effector cells associated with allergic responses. They are activated through the release of histamine, arachidonic acid, and proinflammatory cytokines. |
| Animal Research | Inhibitory effects of nodakenin on the airway inflammation and NF-κB signaling pathway in a murine asthmatic model.[Reference: WebLink]Effect of nodakenin on atopic dermatitis-like skin lesions.[Pubmed: 25209505]Biosci Biotechnol Biochem. 2014;78(9):1568-71.Nodakenin, derived from the roots of Angelica gigas Nakai, is an important natural resource and medicinal material with anti-allergic and anti- inflammatory activities.
We have previously shown that Nodakenin inhibits IgE/Ag-induced degranulation in mast cells.
Basic & Clinical Medicine, 2014 , 34 (5) :690-4.To observe the effects of Nodakenin on airway inflammation in a mouse model of allergic asthma. |

Nodakenin Dilution Calculator

Nodakenin Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 2.4486 mL | 12.2429 mL | 24.4858 mL | 48.9716 mL | 61.2145 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.4897 mL | 2.4486 mL | 4.8972 mL | 9.7943 mL | 12.2429 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.2449 mL | 1.2243 mL | 2.4486 mL | 4.8972 mL | 6.1214 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.049 mL | 0.2449 mL | 0.4897 mL | 0.9794 mL | 1.2243 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0245 mL | 0.1224 mL | 0.2449 mL | 0.4897 mL | 0.6121 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
- Ammijin
Catalog No.:BCN3617
CAS No.:495-30-7
- Auraptene
Catalog No.:BCN5603
CAS No.:495-02-3
- Ginsenoside Rk1
Catalog No.:BCN3552
CAS No.:494753-69-4
- TC-G 1001
Catalog No.:BCC6316
CAS No.:494191-73-0
- Nornicotine
Catalog No.:BCN8176
CAS No.:494-97-3
- Isoammodendrine
Catalog No.:BCN2146
CAS No.:494-15-5
- Nifuratel
Catalog No.:BCC1800
CAS No.:4936-47-4
- Methyl L-pyroglutamate
Catalog No.:BCN7060
CAS No.:4931-66-2
- Savinin
Catalog No.:BCN5602
CAS No.:493-95-8
- α-D-Glucose
Catalog No.:BCC9197
CAS No.:492-62-6
- Kynurenic acid
Catalog No.:BCN2228
CAS No.:492-27-3
- Butin
Catalog No.:BCN4630
CAS No.:492-14-8
- Nodakenetin
Catalog No.:BCN5604
CAS No.:495-32-9
- Desoxypeganine
Catalog No.:BCN8032
CAS No.:495-59-0
- Tropine isobutyrate
Catalog No.:BCN1923
CAS No.:495-80-7
- Valtropine
Catalog No.:BCN1926
CAS No.:495-82-9
- Tigloyltropeine
Catalog No.:BCN1944
CAS No.:495-83-0
- (+)-Methysticin
Catalog No.:BCN8429
CAS No.:495-85-2
- Org 25543 hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC6288
CAS No.:495076-64-7
- 11alpha,12alpha-Oxidotaraxerol palmitate
Catalog No.:BCN7129
CAS No.:495389-95-2
- Estradiol heptanoate
Catalog No.:BCC8961
CAS No.:4956-37-0
- Fenofibrate
Catalog No.:BCC4781
CAS No.:49562-28-9
- Benzofuran-2-carboxylic acid
Catalog No.:BCC8851
CAS No.:496-41-3
- Pyromeconic acid
Catalog No.:BCN7177
CAS No.:496-63-9
Nodakenin, a coumarin compound, ameliorates scopolamine-induced memory disruption in mice.[Pubmed:17382968]
Life Sci. 2007 May 1;80(21):1944-50.
Nodakenin is a coumarin compound initially isolated from the roots of Angelica gigas. In the present study, we investigated the effects of Nodakenin on learning and memory impairments induced by scopolamine (1 mg/kg, i.p.) using the passive avoidance test, the Y-maze test, and the Morris water maze test in mice. Nodakenin (10 mg/kg, p.o.) administration significantly reversed scopolamine-induced cognitive impairments in the passive avoidance test and the Y-maze test (P<0.05), and also reduced escape latency during training in the Morris water maze test (P<0.05). Moreover, swimming times and distances within the target zone of the Morris water maze were greater in the Nodakenin-treated group than in the scopolamine-treated group (P<0.05). In an in vitro study, Nodakenin was found to inhibit acetylcholinesterase activity in a dose-dependent manner (IC(50)=84.7 microM). In addition, Nodakenin was also found to inhibit acetylcholinesterase activity for 6 h in an ex-vivo study. These results suggest that Nodakenin may be a useful for the treatment of cognitive impairment, and that its beneficial effects are mediated, in part, via the enhancement of cholinergic signaling.
Effect of nodakenin on atopic dermatitis-like skin lesions.[Pubmed:25209505]
Biosci Biotechnol Biochem. 2014;78(9):1568-71.
Nodakenin, derived from the roots of Angelica gigas Nakai, is an important natural resource and medicinal material with anti-allergic and anti- inflammatory activities. We have previously shown that Nodakenin inhibits IgE/Ag-induced degranulation in mast cells. In this study, we investigated the inhibitory effect of Nodakenin on 2,4-dinitrochlorobenzene (DNCB)-induced atopic dermatitis (AD)- like skin lesions in ICR mice. Scratching behavior, skin severity score, blood IgE level, and skin thickness were improved in DNCB-induced AD-like ICR mice. Our results showed that Nodakenin suppressed the increase of AD-like skin lesions in ICR mice. These results suggest that Nodakenin may be a potential therapeutic resource for AD as well as an adjunctive agent to control itching associated with AD.
Nodakenin suppresses lipopolysaccharide-induced inflammatory responses in macrophage cells by inhibiting tumor necrosis factor receptor-associated factor 6 and nuclear factor-kappaB pathways and protects mice from lethal endotoxin shock.[Pubmed:22637723]
J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2012 Sep;342(3):654-64.
Nodakenin, a coumarin isolated from the roots of Angelicae gigas, has been reported to possess neuroprotective, antiaggregatory, antibacterial, and memory-enhancing effects. In the present study, we investigated the anti-inflammatory effects of Nodakenin by examining its in vitro inhibitory effects on inducible nitric-oxide synthase (iNOS), cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2), and proinflammatory cytokines in lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-induced RAW 264.7 macrophages and mouse peritoneal macrophages and its in vivo effects on LPS-induced septic shock in mice. Our results indicate that Nodakenin concentration-dependently inhibits iNOS and COX-2 at the protein, mRNA, and promoter binding levels, and these inhibitions cause attendant decreases in the production of nitric oxide (NO) and prostaglandin E(2) (PGE(2)). Furthermore, we found that Nodakenin inhibits the production and mRNA expression of tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-alpha), interleukin (IL)-6, and IL-1beta induced by LPS. Molecular data revealed that Nodakenin suppressed the transcriptional activity and translocation of nuclear factor-kappaB (NF-kappaB) by inhibiting inhibitory kappaB-alpha degradation and IkappaB kinase-alpha/beta phosphorylation. In addition, Nodakenin was found to significantly inhibit the LPS-induced binding of transforming growth factor-beta-activated kinase 1 to tumor necrosis factor receptor-associated factor 6 (TRAF6) by reducing TRAF6 ubiquitination. Pretreatment with Nodakenin reduced the serum levels of NO, PGE(2), and proinflammatory cytokines and increased the survival rate of mice with LPS-induced endotoxemia. Taken together, our data suggest that Nodakenin down-regulates the expression of the proinflammatory iNOS, COX-2, TNF-alpha, IL-6, and IL-1beta genes in macrophages by interfering with the activation of TRAF6, thus preventing NF-kappaB activation.
The effects of nodakenin on airway inflammation, hyper-responsiveness and remodeling in a murine model of allergic asthma.[Pubmed:25090633]
Immunopharmacol Immunotoxicol. 2014 Oct;36(5):341-8.
CONTEXT: Nodakenin is a major coumarin glucoside in the root of Peucedanum decursivum Maxim, a commonly used traditional Chinese medicine for the treatment of asthma and chronic bronchitis for thousands of years. OBJECTIVE: In this work, the anti-asthma potential of Nodakenin was studied by investigation of its effect to suppress airway inflammation, hyper-responsiveness and remodeling in a murine model of chronic asthma. MATERIALS AND METHODS: BALB/c mice sensitized to ovalbumin (OVA) were challenged with aerosolized OVA for 8 weeks, orally administered with Nodakenin at doses of 5, 10 and 20 mg/kg before each OVA challenge. RESULTS: Compared with the model group, Nodakenin treatment markedly inhibited airway inflammation, hyper-responsiveness and remodeling, showing improvement in subepithelial fibrosis, smooth muscle hypertrophy, and goblet cell hyperplasia, and decreased levels of interleukin (IL)-4, IL-5, IL-13 and matrix metalloproteinase-2/-9 in bronchoalveolar lavage fluid, and the level of OVA-specific IgE in serum. In addition, the NF-kappaB DNA-binding activity in lung tissues was also reduced by Nodakenin treatment. CONCLUSIONS: These data indicated that Nodakenin might mitigate the development of chronic experimental allergic asthma.


