NFPSCAS# 405225-21-0 |
- Calyculin A
Catalog No.:BCC2457
CAS No.:101932-71-2
- Calcineurin Autoinhibitory Peptide
Catalog No.:BCC2456
CAS No.:148067-21-4
- DL-AP3
Catalog No.:BCC2459
CAS No.:20263-06-3
- Ceramide
Catalog No.:BCC2458
CAS No.:3102-57-6
- Fostriecin sodium salt
Catalog No.:BCC2460
CAS No.:87860-39-7
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 405225-21-0 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 5311283 | Appearance | Powder |
| Formula | C24H24FNO3 | M.Wt | 393.45 |
| Type of Compound | N/A | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Solubility | Soluble in DMSO > 10 mM | ||
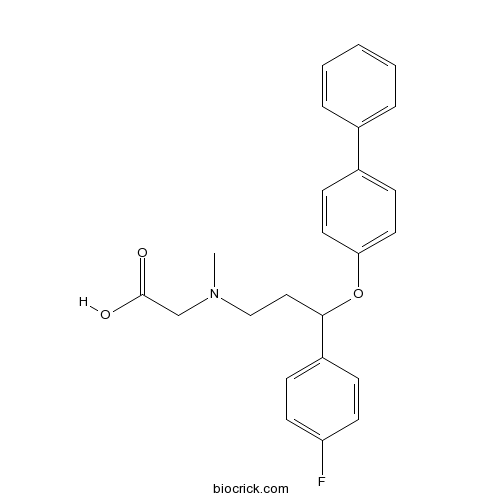
| Chemical Name | 2-[[3-(4-fluorophenyl)-3-(4-phenylphenoxy)propyl]-methylamino]acetic acid | ||
| SMILES | CN(CCC(C1=CC=C(C=C1)F)OC2=CC=C(C=C2)C3=CC=CC=C3)CC(=O)O | ||
| Standard InChIKey | FDORQEIHOKEJNX-UHFFFAOYSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C24H24FNO3/c1-26(17-24(27)28)16-15-23(20-7-11-21(25)12-8-20)29-22-13-9-19(10-14-22)18-5-3-2-4-6-18/h2-14,23H,15-17H2,1H3,(H,27,28) | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | Selective, non-transportable inhibitor of GlyT1 which displays no activity at GABA or glutamate receptors (IC50 values are 2.8, 9.8 and 56000 nM for hGlyT1, rGlyT1 and rGlyT2 respectively). Enhances the amplitude of the NMDA component of glutamatergic EPSCs. |

NFPS Dilution Calculator

NFPS Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 2.5416 mL | 12.7081 mL | 25.4162 mL | 50.8324 mL | 63.5405 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.5083 mL | 2.5416 mL | 5.0832 mL | 10.1665 mL | 12.7081 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.2542 mL | 1.2708 mL | 2.5416 mL | 5.0832 mL | 6.354 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0508 mL | 0.2542 mL | 0.5083 mL | 1.0166 mL | 1.2708 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0254 mL | 0.1271 mL | 0.2542 mL | 0.5083 mL | 0.6354 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
- Dovitinib (TKI-258, CHIR-258)
Catalog No.:BCC1169
CAS No.:405169-16-6
- CHIR-124
Catalog No.:BCC3750
CAS No.:405168-58-3
- Besifloxacin HCl
Catalog No.:BCC4764
CAS No.:405165-61-9
- Drechslerine D
Catalog No.:BCN7502
CAS No.:405157-88-2
- Drechslerine A
Catalog No.:BCN7561
CAS No.:405157-84-8
- Salubrinal
Catalog No.:BCC4843
CAS No.:405060-95-9
- 4'-Demethylpodophyllotoxin
Catalog No.:BCN2625
CAS No.:40505-27-9
- Z-Lys(Z)-OH
Catalog No.:BCC2762
CAS No.:405-39-0
- LAQ824 (NVP-LAQ824,Dacinostat)
Catalog No.:BCC2160
CAS No.:404951-53-7
- Panobinostat (LBH589)
Catalog No.:BCC3601
CAS No.:404950-80-7
- Ethyl ferulate
Catalog No.:BCN1257
CAS No.:4046-02-0
- Bursehernin
Catalog No.:BCN3040
CAS No.:40456-51-7
- Dadahol A
Catalog No.:BCN5457
CAS No.:405281-76-7
- Cyclapolin 9
Catalog No.:BCC7571
CAS No.:40533-25-3
- SB590885
Catalog No.:BCC4392
CAS No.:405554-55-4
- GW3965
Catalog No.:BCC1612
CAS No.:405911-09-3
- GW3965 HCl
Catalog No.:BCC3790
CAS No.:405911-17-3
- C34
Catalog No.:BCC5603
CAS No.:40592-88-9
- Cirazoline hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC6833
CAS No.:40600-13-3
- DMT-Cl
Catalog No.:BCC2799
CAS No.:40615-36-9
- DMT-T
Catalog No.:BCC2843
CAS No.:40615-39-2
- DSP-4
Catalog No.:BCC7527
CAS No.:40616-75-9
- ACHP
Catalog No.:BCC6223
CAS No.:406208-42-2
- IKK-2 inhibitor VIII
Catalog No.:BCC1642
CAS No.:406209-26-5
Temporal alteration of spreading depression by the glycine transporter type-1 inhibitors NFPS and Org-24461 in chicken retina.[Pubmed:23178696]
Brain Res. 2013 Jan 25;1492:1-6.
We used isolated chicken retina to induce spreading depression by the glutamate receptor agonist N-methyl-d-aspartate. The N-methyl-d-aspartate-induced latency time of spreading depression was extended by the glycine(B) binding site competitive antagonist 7-chlorokynurenic acid. Addition of the glycine transporter type-1 inhibitors NFPS and Org-24461 reversed the inhibitory effect of 7-chlorokynurenic acid on N-methyl-d-aspartate-evoked spreading depression. The glycine uptake inhibitory activity of Org-24461, NFPS, and some newly synthesized analogs of NFPS was determined in CHO cells stably expressing human glycine transporter type-1b isoform. Compounds, which failed to inhibit glycine transporter type-1, also did not have effect on retinal spreading depression. These experiments indicate that the spreading depression model in chicken retina is a useful in vitro test to determine activity of glycine transporter type-1 inhibitors. In addition, our data serve further evidence for the role of glycine transporter type-1 in retinal neurotransmission and light processing.
GlyT1 Inhibitor NFPS Exerts Neuroprotection via GlyR Alpha1 Subunit in the Rat Model of Transient Focal Cerebral Ischaemia and Reperfusion.[Pubmed:27161043]
Cell Physiol Biochem. 2016;38(5):1952-62.
BACKGROUND/AIMS: Glycine is a strychnine-sensitive inhibitory neurotransmitter in the central nervous system (CNS), especially in the spinal cord, brainstem, and retina. The objective of the present study was to investigate the potential neuroprotective effects of GlyT1 inhibitor N [3-(4'-fluorophenyl)-3-(4'-phenylphenoxy) propyl] sarcosine (NFPS) in the rat model of experimental stroke. METHODS: In vivo ischaemia was induced by transient middle cerebral artery occlusion (tMCAO). The methods of Western Blotting, Nissl Staining and Morris water maze methods were applied to analyze the anti-ischaemia mechanism. RESULTS: The results showed that high dose of NFPS (H-NFPS) significantly reduced infarct volume, neuronal injury and the expression of cleaved caspase-3, enhanced Bcl-2/Bax, and improved spatial learning deficits which were administered three hours after transient middle cerebral artery occlusion (tMCAO) induction in rats, while, low dose of NFPS (L-NFPS) exacerbated the injury of ischaemia. These findings suggested that low and high dose of NFPS produced opposite effects. Importantly, it was demonstrated that H-NFPS-dependent neuronal protection was inverted by salicylate (Sal), a specific GlyR x0251;1 antagonist. Such effects could probably be attributed to the enhanced glycine level in both synaptic and extrasynaptic clefts and the subsequently altered extrasynaptic GlyRs and their subtypes. CONCLUSIONS: These data imply that GlyT1 inhibitor NFPS may be a novel target for clinical treatment of transient focal cerebral ischaemia and reperfusion which are associated with altered GlyR alpha 1 subunits.
Inhibition of hypoxia-induced [(3)H]glycine release from chicken retina by the glycine transporter type-1 (GlyT-1) inhibitors NFPS and Org-24461.[Pubmed:22079563]
Exp Eye Res. 2012 Jan;94(1):6-12.
Chicken posterior eyecup lined by the retina were prepared, loaded with [(3)H]glycine and superfused in order to determine its release in various experimental conditions. Electrical field stimulation of the retina evoked [(3)H]glycine release with a voltage- and frequency-dependent manner and this release may be originated from glycinergic amacrine cell processes of the inner plexiform layer of the retina. Glycine released from an abundance of different amacrine cells may modulate retinal circuitry by activation of inhibitory glycine receptors and by acting as a coagonist on N-methyl-d-aspartate receptors on AII amacrine cells and retinal ganglion cells. The latter effect of glycine may be modulated by glycine transporter type-1. Cells with glycine transporter type-1 immunopositive staining were visualized in the inner nuclear layer and dens immunolabeling was also detected throughout the inner plexiform layer of chicken retina. Glycine and the substrate-type glycine transporter type-1 inhibitor sarcosine increased [(3)H]glycine release from glycinergic amacrine cells and/or glial cells by extrusion of glycine from cytoplasmic pools by homo- and heteroexchange mechanisms. Deprivation of oxygen and glucose from the buffer used for superfusion evoked a marked increase in [(3)H]glycine efflux, an effect probably due to reverse mode operation of glycine transporter type-1. The non-transportable glycine transporter type-1 inhibitors NFPS and Org-24461, which did not alter [(3)H]glycine efflux from isolated chicken retina by themselves in normoxic condition, inhibited oxygen and glucose deprivation-induced [(3)H]glycine release. It is concluded that reduction of the N-methyl-d-aspartate receptor coagonist glycine concentrations in hypoxic conditions by glycine transporter type-1 inhibitors may decrease N-methyl-d-aspartate receptor-mediated neuronal toxicity and cell death in retinal tissue.
Evaluation of nucleosome forming potentials (NFPs) of forensically important STRs.[Pubmed:20541991]
Forensic Sci Int Genet. 2011 Aug;5(4):285-90.
Degraded forensic samples have proved difficult to analyze and interpret. New analysis techniques are constantly being discovered and improved but researchers have overlooked the structural properties that could prevent or slow the process of degradation. In theory, DNA that are bound to histones as nucleosomes are less prone to degradation, because nucleosomes prevent DNA from being exposed to degradative enzymes. In this study we determined the probability of 60 forensic DNA markers to be bound to histones based on their base sequence composition. Two web-based tools - NXSensor and nuScore - were used to analyze four hundred base pairs surrounding each DNA marker for properties that inhibit or promote the binding of DNA to histones. Our results showed that the majority of markers analyzed were likely to be bound as nucleosomes. Selection of the markers that are more protected to form a multiplex could increase the chance of obtaining a better balanced, easier to interpret DNA profile from degraded samples.


