NF 449purinergic receptor antagonist CAS# 627034-85-9 |
- Tubastatin A HCl
Catalog No.:BCC3877
CAS No.:1310693-92-5
- Entinostat (MS-275,SNDX-275)
Catalog No.:BCC3595
CAS No.:209783-80-2
- M344
Catalog No.:BCC2162
CAS No.:251456-60-7
- Panobinostat (LBH589)
Catalog No.:BCC3601
CAS No.:404950-80-7
Quality Control & MSDS
Number of papers citing our products

Chemical structure

3D structure
| Cas No. | 627034-85-9 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 91895233 | Appearance | Powder |
| Formula | C41H24N6Na8O29S8 | M.Wt | 1505.06 |
| Type of Compound | N/A | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Solubility | Soluble to 50 mM in water with gentle warming | ||
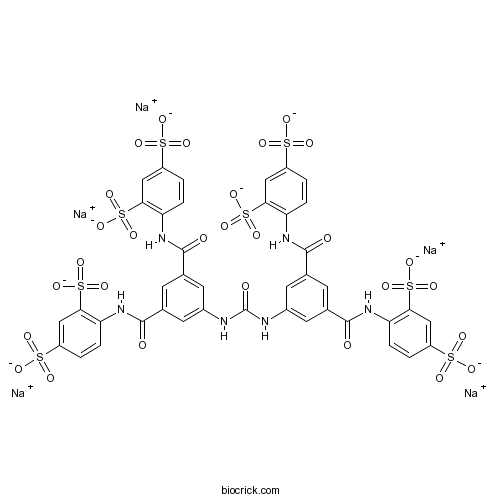
| Chemical Name | pentasodium;4-[[3-[[3,5-bis[(2,4-disulfonatophenyl)carbamoyl]phenyl]carbamoylamino]-5-[(2,4-disulfonatophenyl)carbamoyl]benzoyl]amino]benzene-1,3-disulfonate | ||
| SMILES | C1=CC(=C(C=C1S(=O)(=O)[O-])S(=O)(=O)[O-])NC(=O)C2=CC(=CC(=C2)NC(=O)NC3=CC(=CC(=C3)C(=O)NC4=C(C=C(C=C4)S(=O)(=O)[O-])S(=O)(=O)[O-])C(=O)NC5=C(C=C(C=C5)S(=O)(=O)[O-])S(=O)(=O)[O-])C(=O)NC6=C(C=C(C=C6)S(=O)(=O)[O-])S(=O)(=O)[O-].[Na+].[Na+].[Na+].[Na+].[Na+] | ||
| Standard InChIKey | PHCBPKWKKHYRSA-UHFFFAOYSA-F | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C41H32N6O29S8.5Na/c48-37(44-29-5-1-25(77(53,54)55)15-33(29)81(65,66)67)19-9-20(38(49)45-30-6-2-26(78(56,57)58)16-34(30)82(68,69)70)12-23(11-19)42-41(52)43-24-13-21(39(50)46-31-7-3-27(79(59,60)61)17-35(31)83(71,72)73)10-22(14-24)40(51)47-32-8-4-28(80(62,63)64)18-36(32)84(74,75)76;;;;;/h1-18H,(H,44,48)(H,45,49)(H,46,50)(H,47,51)(H2,42,43,52)(H,53,54,55)(H,56,57,58)(H,59,60,61)(H,62,63,64)(H,65,66,67)(H,68,69,70)(H,71,72,73)(H,74,75,76);;;;;/q;5*+1/p-8 | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | Potent purinergic receptor antagonist that displays high selectivity for P2X1 (IC50 values are 0.28, 0.69, 120, 1820, 47000 and > 300000 nM for rP2X1, rP2X1+5, rP2X2+3, rP2X3, rP2X2 and P2X4 receptors respectively). Provides antithrombotic protection in vivo. Also acts as a Gsα-selective antagonist. |

NF 449 Dilution Calculator

NF 449 Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 0.6644 mL | 3.3221 mL | 6.6443 mL | 13.2885 mL | 16.6106 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.1329 mL | 0.6644 mL | 1.3289 mL | 2.6577 mL | 3.3221 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.0664 mL | 0.3322 mL | 0.6644 mL | 1.3289 mL | 1.6611 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0133 mL | 0.0664 mL | 0.1329 mL | 0.2658 mL | 0.3322 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0066 mL | 0.0332 mL | 0.0664 mL | 0.1329 mL | 0.1661 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
IC50: 0.28 nm for rP2X1
NF 449 is a potent purinergic receptor antagonist that displays high selectivity for P2X1. The P2X1 ion channel is activated by ATP among the three P2 receptor subtypes present on blood platelets.
In vitro: The interaction of the A1-adenosine receptor with its cognate G proteins (Gi/Go) disrupted by NF503 and NF449 at concentrations that are >30- fold higher than those required for uncoupling of b-adrenergic receptor/Gs tandems; similarly, the compounds barely affected the angiotensin II type-1 receptor . Thus, NF503 and NF449 achieve essential criteria for Gsa-selective antagonists. The observations demonstrate that subtype-selective G protein inhibition is feasible[1]. inhibited 5-triphosphate-induced shape change in treatment of washed human platelets with apyrase to abolish desensitization of the P2X1 receptor. The calcium rise mediated by the P2Y1 receptor was also antagonized by NF449, but with lower potency. In contrast, NF449 was a very weak antagonist of inhibiting adenylyl cyclase activity mediated by P2Y12. Selective blockade of the P2X1 receptor with NF449 led to decreased collagen-induced aggregation. Therefore, a role of this receptor in platelet activation induced by collagen was confirmed [2]. So far, characterize NF449 as the most potent and selective antagonist of receptors (the P2X1 subunit such as the P2X1 homomer and the P2X1C5 heteromer) [3].
In vivo: Intravenous injection of 10 mg/kg NF449 into mice exhibited selective inhibition of the P2X1 receptor and reduced intravascular platelet aggregation in a model of systemic thromboembolism without prolongation of the bleeding time. At a higher dose (50 mg/kg), NF449 blocked the three platelet P2 receptors. This, compared with mice injected with saline, led to a further reduction in platelet consumption. NF449 also decreased dose-dependently the size of thrombi formed after laser-induced injury of mesenteric arterioles. Overall, our results indicate that NF449 constitutes a new agent to investigate the functions of the P2X1 receptor and could be a starting compound in the investigation for new antithrombotic drugs targeting the platelet tP2 receptors [2].
Clinical trial: So far, no clinical study has been conducted.
References:
[1] Hohenegger M, Waldhoer M, Beindl W, Bing B, Kreimeyer A, Nickel P, Nanoff C, Freissmuth M. Gsalpha-selective G protein antagonists. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1998 Jan 6;95(1):346-51.
[2] Hechler B, Magnenat S, Zighetti ML, Kassack MU, Ullmann H, Cazenave JP, Evans R, Cattaneo M, Gachet C. Inhibition of platelet functions and thrombosis through selective or nonselective inhibition of the platelet P2 receptors with increasing doses of NF449 [4,4',4'',4'''-(carbonylbis(imino-5,1,3-benzenetriylbis-(carbonylimino)))tetrakis-benzene-1,3-disulfonic acid octasodium salt]. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2005 Jul;314(1):232-43. Epub 2005 Mar 25.
[3]. Rettinger J, Braun K, Hochmann H, Kassack MU, Ullmann H, Nickel P, Schmalzing G, Lambrecht G. Profiling at recombinant homomeric and heteromeric rat P2X receptors identifies the suramin analogue NF449 as a highly potent P2X1 receptor antagonist. Neuropharmacology. 2005 Mar;48 (3):461-8.
- Dioctanoylglycol
Catalog No.:BCC6662
CAS No.:627-86-1
- H-D-Arg-OH.HCl
Catalog No.:BCC2869
CAS No.:627-75-8
- Saikosaponin F
Catalog No.:BCN2776
CAS No.:62687-63-2
- Handelin
Catalog No.:BCN2953
CAS No.:62687-22-3
- 1-Hydroxy-2-methylanthraquinone
Catalog No.:BCN3478
CAS No.:6268-09-3
- SIB 1893
Catalog No.:BCC6970
CAS No.:6266-99-5
- Ro 106-9920
Catalog No.:BCC7175
CAS No.:62645-28-7
- 11S,12-Dihydroxyspirovetiv-1(10)-en-2-one
Catalog No.:BCN1391
CAS No.:62623-86-3
- (+)-Mellein
Catalog No.:BCN7220
CAS No.:62623-84-1
- 4,6,7-Trimethoxy-5-methylcoumarin
Catalog No.:BCN4166
CAS No.:62615-63-8
- 2',4'-Dihydroxy-3'-methoxyacetophenone
Catalog No.:BCN7535
CAS No.:62615-26-3
- Oxiracetam
Catalog No.:BCC5447
CAS No.:62613-82-5
- Dihydrolycorine
Catalog No.:BCN2475
CAS No.:6271-21-2
- SKF38393 HCl
Catalog No.:BCC6526
CAS No.:62717-42-4
- 4-Amino-N-methylbenzamide
Catalog No.:BCC8685
CAS No.:6274-22-2
- BMS-564929
Catalog No.:BCC1425
CAS No.:627530-84-1
- SD-208
Catalog No.:BCC1938
CAS No.:627536-09-8
- Epitrametol
Catalog No.:BCN7073
CAS No.:627538-65-2
- Pterophorine
Catalog No.:BCN2118
CAS No.:62786-99-6
- Senampeline A
Catalog No.:BCN2030
CAS No.:62787-00-2
- Senampeline D
Catalog No.:BCN2033
CAS No.:62787-01-3
- SU14813
Catalog No.:BCC1971
CAS No.:627908-92-3
- Palmitic acid ethyl ester
Catalog No.:BCN8298
CAS No.:628-97-7
- Jolkinol A
Catalog No.:BCN3778
CAS No.:62820-11-5
The shrimp NF-kappaB pathway is activated by white spot syndrome virus (WSSV) 449 to facilitate the expression of WSSV069 (ie1), WSSV303 and WSSV371.[Pubmed:21931849]
PLoS One. 2011;6(9):e24773.
The Toll-like receptor (TLR)-mediated NF-kappaB pathway is essential for defending against viruses in insects and mammals. Viruses also develop strategies to utilize this pathway to benefit their infection and replication in mammal hosts. In invertebrates, the TLR-mediated NF-kappaB pathway has only been well-studied in insects and has been demonstrated to be important in antiviral responses. However, there are few reports of interactions between viruses and the TLR-mediated NF-kappaB pathway in invertebrate hosts. Here, we studied Litopenaeus vannamei Pelle, which is the central regulator of the Toll pathway, and proposed that a similar TLR/MyD88/Tube/Pelle/TRAF6/NF-kappaB cascade may exist in shrimp for immune gene regulation. After performing genome-wild analysis of white spot syndrome virus (WSSV) encoded proteins, we found that WSSV449 shows 15.7-19.4% identity to Tube, which is an important component of the insect Toll pathway. We further found that WSSV449 activated promoters of Toll pathway-controlled antimicrobial peptide genes, indicating WSSV449 has a similar function to host Tube in activating the NF-kappaB pathway. We suspected that WSSV449 activated the Toll-mediated NF-kappaB pathway for regulating viral gene expression. To test this hypothesis, we analyzed the promoters of viral genes and found 40 promoters that possess NF-kappaB binding sites. A promoter screen showed that the promoter activities of WSSV069 (ie1), WSSV303 and WSSV371 can be highly induced by the shrimp NF-kappaB family protein LvDorsal. WSSV449 also induced these three viral promoter activities by activating the NF-kappaB pathway. To our knowledge, this is the first report of a virus that encodes a protein similar to the Toll pathway component Tube to upregulate gene expression in the invertebrate host.
Chemical modulators of autophagy as biological probes and potential therapeutics.[Pubmed:21164513]
Nat Chem Biol. 2011 Jan;7(1):9-17.
Autophagy is an evolutionarily conserved mechanism for protein degradation that is critical for the maintenance of homeostasis in man. Autophagy has unexpected pleiotropic functions that favor survival of the cell, including nutrient supply under starvation, cleaning of the cellular interior, defense against infection and antigen presentation. Moreover, defective autophagy is associated with a diverse range of disease states, including neurodegeneration, cancer and Crohn's disease. Here we discuss the roles of mammalian autophagy in health and disease and highlight recent advances in pharmacological manipulation of autophagic pathways as a therapeutic strategy for a variety of pathological conditions.
Inhibition of platelet functions and thrombosis through selective or nonselective inhibition of the platelet P2 receptors with increasing doses of NF449 [4,4',4'',4'''-(carbonylbis(imino-5,1,3-benzenetriylbis-(carbonylimino)))tetrakis -benzene-1,3-disulfonic acid octasodium salt].[Pubmed:15792995]
J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2005 Jul;314(1):232-43.
Our aim was to determine whether the newly described P2X1 antagonist NF449 [4,4',4'',4'''-(carbonylbis(imino-5,1,3-benzenetriylbis(carbonylimino)))tetrakis- benzene-1,3-disulfonic acid octasodium salt] could selectively antagonize the platelet P2X1 receptor and how it affected platelet function. NF449 inhibited alpha,beta-methyleneadenosine 5'-triphosphate-induced shape change (IC50 = 83 +/- 13 nM; n = 3) and calcium influx (pA2 = 7.2 +/- 0.1; n = 3) (pIC50 = 6.95) in washed human platelets treated with apyrase to prevent desensitization of the P2X1 receptor. NF449 also antagonized the calcium rise mediated by the P2Y1 receptor, but with lower potency (IC50 = 5.8 +/- 2.2 microM; n = 3). In contrast, it was a very weak antagonist of the P2Y12-mediated inhibition of adenylyl cyclase activity. Selective blockade of the P2X1 receptor with NF449 led to reduced collagen-induced aggregation, confirming a role of this receptor in platelet activation induced by collagen. Intravenous injection of 10 mg/kg NF449 into mice resulted in selective inhibition of the P2X1 receptor and decreased intravascular platelet aggregation in a model of systemic thromboembolism (35 +/- 4 versus 51 +/- 3%) (P = 0.0061; n = 10) but without prolongation of the bleeding time (106 +/- 16 versus 78 +/- 7 s; n = 10) (N.S.; P = 0.1209). At a higher dose (50 mg/kg), NF449 inhibited the three platelet P2 receptors. This led to a further reduction in platelet consumption compared with mice injected with saline (13 +/- 4 versus 42 +/- 3%) (P = 0.0002; n = 5). NF449 also reduced dose-dependently the size of thrombi formed after laser-induced injury of mesenteric arterioles. Overall, our results indicate that NF449 constitutes a new tool to investigate the functions of the P2X1 receptor and could be a starting compound in the search for new antithrombotic drugs targeting the platelet P2 receptors.
Profiling at recombinant homomeric and heteromeric rat P2X receptors identifies the suramin analogue NF449 as a highly potent P2X1 receptor antagonist.[Pubmed:15721178]
Neuropharmacology. 2005 Mar;48(3):461-8.
P2X receptors are cation channels gated by extracellular ATP and related nucleotides. Because of the widespread distribution of P2X receptors and the high subtype diversity, potent and selective antagonists are needed to dissect their roles in intact tissues. Based on suramin as a lead compound, several derivates have been described that block recombinant P2X receptors with orders of magnitude higher potency than suramin. Here we characterized the suramin analogue 4,4',4'',4'''-(carbonylbis(imino-5,1,3-benzenetriylbis(carbonylimino)))tetrakis-b enzene-1,3-disulfonic acid (NF449) with respect to its potency to antagonize ATP or alphabeta-methyleneadenosine 5'-trisphosphate-induced inward currents of homomeric rat P2X(1)-P2X(4) receptors or heteromeric P2X(1 + 5) and P2X(2+3) receptors, respectively. NF449 most potently blocked P2X(1) and P2X(1 + 5) receptors with IC(50) values of 0.3 nM and 0.7 nM, respectively. Three to four orders of magnitude higher NF449 concentrations were required to block homomeric P2X(3) or heteromeric P2X(2 + 3) receptors (IC(50) 1.8 and 0.3 microM, respectively). NF449 was least potent at homomeric P2X(2) receptors (IC(50) 47 microM) and homomeric P2X(4) receptors (IC(50) > 300 microM). Altogether, these results characterize NF449 as the so far most potent and selective antagonist of receptors incorporating the P2X(1) subunit such as the P2X(1) homomer and the P2X(1 + 5) heteromer.
Gsalpha-selective G protein antagonists.[Pubmed:9419378]
Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1998 Jan 6;95(1):346-51.
Suramin acts as a G protein inhibitor because it inhibits the rate-limiting step in activation of the Galpha subunit, i.e., the exchange of GDP for GTP. Here, we have searched for analogues that are selective for Gsalpha. Two compounds have been identified: NF449 (4,4',4",4'"-[carbonyl-bis[imino-5,1,3-benzenetriyl bis-(carbonylimino)]]tetrakis-(benzene-1,3-disulfonate) and NF503 (4, 4'-[carbonylbis[imino-3,1-phenylene-(2, 5-benzimidazolylene)carbonylimino]]bis-benzenesulfonate). These compounds (i) suppress the association rate of guanosine 5'-[gamma-thio]triphosphate ([35S]GTP[gammaS]) binding to Gsalpha-s but not to Gialpha-1, (ii) inhibit stimulation of adenylyl cyclase activity in S49 cyc- membranes (deficient in endogenous Gsalpha) by exogenously added Gsalpha-s, and (iii) block the coupling of beta-adrenergic receptors to Gs with half-maximum effects in the low micromolar range. In contrast to suramin, which is not selective, NF503 and NF449 disrupt the interaction of the A1-adenosine receptor with its cognate G proteins (Gi/Go) at concentrations that are >30-fold higher than those required for uncoupling of beta-adrenergic receptor/Gs tandems; similarly, the angiotensin II type-1 receptor (a prototypical Gq-coupled receptor) is barely affected by the compounds. Thus, NF503 and NF449 fulfill essential criteria for Gsalpha-selective antagonists. The observations demonstrate the feasibility of subtype-selective G protein inhibition.


