MethoxyresorufinFluorometric CYP450 substrate CAS# 5725-89-3 |
- Pemetrexed
Catalog No.:BCC9115
CAS No.:137281-23-3
- Pralatrexate
Catalog No.:BCC2304
CAS No.:146464-95-1
- Pemetrexed disodium hemipenta hydrate
Catalog No.:BCC1844
CAS No.:357166-30-4
- Pyrimethamine
Catalog No.:BCC2307
CAS No.:58-14-0
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 5725-89-3 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 119220 | Appearance | Powder |
| Formula | C13H9NO3 | M.Wt | 227.22 |
| Type of Compound | N/A | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Solubility | Soluble to 1 mM in DMSO with gentle warming | ||
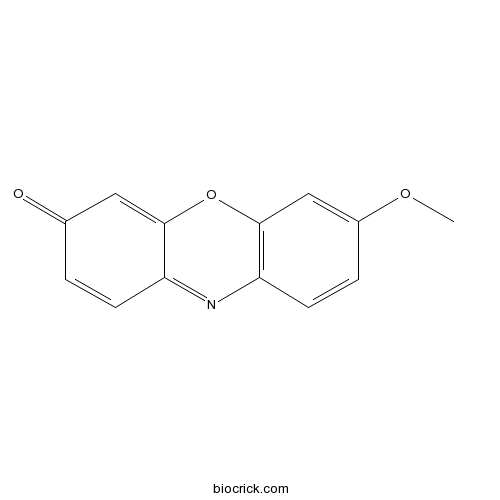
| Chemical Name | 7-methoxyphenoxazin-3-one | ||
| SMILES | COC1=CC2=C(C=C1)N=C3C=CC(=O)C=C3O2 | ||
| Standard InChIKey | KNYYMGDYROYBRE-UHFFFAOYSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C13H9NO3/c1-16-9-3-5-11-13(7-9)17-12-6-8(15)2-4-10(12)14-11/h2-7H,1H3 | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | Fluorometric substrate of cytochrome P450; displays preferential metabolism by rodent cytochrome P4501A2 (CYP1A2). |

Methoxyresorufin Dilution Calculator

Methoxyresorufin Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 4.401 mL | 22.0051 mL | 44.0102 mL | 88.0204 mL | 110.0255 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.8802 mL | 4.401 mL | 8.802 mL | 17.6041 mL | 22.0051 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.4401 mL | 2.2005 mL | 4.401 mL | 8.802 mL | 11.0026 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.088 mL | 0.4401 mL | 0.8802 mL | 1.7604 mL | 2.2005 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.044 mL | 0.2201 mL | 0.4401 mL | 0.8802 mL | 1.1003 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
- Pamidronate Disodium
Catalog No.:BCC1193
CAS No.:57248-88-1
- H-Phe(3-CN)-OH
Catalog No.:BCC3182
CAS No.:57213-48-6
- Testosterone decanoate
Catalog No.:BCC9168
CAS No.:5721-91-5
- Ayanin
Catalog No.:BCN4056
CAS No.:572-32-7
- Engeletin
Catalog No.:BCN5772
CAS No.:572-31-6
- Avicularin
Catalog No.:BCN5771
CAS No.:572-30-5
- Neosenkirkine
Catalog No.:BCN2138
CAS No.:57194-70-4
- Paxilline
Catalog No.:BCC7235
CAS No.:57186-25-1
- Naftopidil DiHCl
Catalog No.:BCC4355
CAS No.:57149-08-3
- Naftopidil
Catalog No.:BCC4352
CAS No.:57149-07-2
- 16,17-Dihydroapovincamine
Catalog No.:BCN8049
CAS No.:57130-30-0
- Erastin
Catalog No.:BCC4497
CAS No.:571203-78-6
- 7-Ethoxyresorufin
Catalog No.:BCC6476
CAS No.:5725-91-7
- Salsolinol-1-carboxylic acid
Catalog No.:BCC6731
CAS No.:57256-34-5
- Setiptiline
Catalog No.:BCC1945
CAS No.:57262-94-9
- Calmidazolium chloride
Catalog No.:BCC7410
CAS No.:57265-65-3
- Boc-D-Phe(4-Cl)-OH
Catalog No.:BCC3176
CAS No.:57292-44-1
- Boc-D-Phe(4-F)-OH
Catalog No.:BCC3218
CAS No.:57292-45-2
- Ridaforolimus (Deforolimus, MK-8669)
Catalog No.:BCC4605
CAS No.:572924-54-0
- Boehmenan
Catalog No.:BCN5773
CAS No.:57296-22-7
- Liriodendrin
Catalog No.:BCN5774
CAS No.:573-44-4
- Congo Red
Catalog No.:BCC8023
CAS No.:573-58-0
- Tacalcitol
Catalog No.:BCC1975
CAS No.:57333-96-7
- Dihydroepistephamiersine 6-acetate
Catalog No.:BCN5775
CAS No.:57361-74-7
Enhancement of 7-methoxyresorufin O-demethylation activity of human cytochrome P450 1A2 by molecular breeding.[Pubmed:15519301]
Arch Biochem Biophys. 2004 Dec 1;432(1):102-8.
Alkylresorufins are model substrates for cytochrome P450 (P450) 1A2. The ability of human P450 1A2 to catalyze 7-Methoxyresorufin O-demethylation was improved by screening of random mutant libraries (expressed in Escherichia coli) on the basis of 7-Methoxyresorufin O-demethylation. After three rounds of mutagenesis and screening, the triple mutant E163K/V193M/K170Q yielded a kcat > five times faster than wild type P450 1A2 in steady-state kinetic analysis using either isolated membrane fractions or purified, reconstituted enzymes. The enhanced catalytic activity was not attributed to changes in substrate affinity. The kinetic hydrogen isotope effect of the triple mutant did not change from wild type enzyme and suggests that C-H bond cleavage is rate-limiting in both enzymes. Homology modeling, based on an X-ray structure of rabbit P450 2C5, suggests that the locations of mutated residues are not close to the substrate binding site and therefore that structural elements outside of this site play roles in changing the catalytic activity. This approach has potential value in understanding P450 1A2 and generating engineered enzymes with enhanced catalytic activity.
Inhibition of methoxyresorufin demethylase activity by flavonoids in human liver microsomes.[Pubmed:9718089]
Life Sci. 1998;63(8):PL119-23.
Flavonoids are a class of dietary phytochemicals with anticarcinogenic properties. A series of ten structurally related flavonoids were evaluated for their effect on Methoxyresorufin O-demethylase (MROD) activity in human liver microsomes. All compounds inhibited this cytochrome P450 1A2 (CYP1A2) mediated activity. 3,5,7-Trihydoxyflavone (galangin) was the most potent inhibitor, followed by 3-hydroxyflavone and flavone. The relative inhibitory potency of flavonoids is related to their structures. The results suggest that flavonoids may modulate pharmacological and toxicological effects mediated by CYP1A2.
Arginine to lysine 108 substitution in recombinant CYP1A2 abolishes methoxyresorufin metabolism in lymphoblastoid cells.[Pubmed:12023936]
Br J Pharmacol. 2002 Jun;136(3):347-52.
1. Cytochrome P4501A2 (CYP1A2) activates a large number of procarcinogens to carcinogens. Phytochemicals such as flavones can inhibit CYP1A2 activity competitively, and hydroxylated derivatives of flavone (galangin) may be potent, selective inhibitors of CYP1A2 activity relative to CYP1A1 activity. Molecular modelling of the CYP1A2 interaction with hydroxylated derivatives of flavone suggests that a number of hydrophobic residues of the substrate-binding domain engage in hydrogen bonding with such inhibitors. 2. We have tested this model using site-directed mutagenesis of these residues in expression plasmids transfected into the human B-lymphoblastoid cell line, AHH-1 TK+/-. 3. Consistent with the molecular model's predicted placement in the active site, amino acid substitutions at the predicted residues abolished CYP1A2 enzymatic activity. 4. Transfected cell lines contained equal amounts of immunoreactive CYP1A2. 5. Our results support the molecular model's prediction of the critical amino acid residues present in the hydrophobic active site, residues that can hydrogen bond with CYP1A2 inhibitors and modify substrate binding and/or turnover.
Methoxyresorufin: an inappropriate substrate for CYP1A2 in the mouse.[Pubmed:9973187]
Biochem Pharmacol. 1998 Dec 15;56(12):1657-60.
Hepatic microsomes derived from Cypla2(-/-) knockout (KO) and parental strains of mice, C57BL/6N and 129Sv, were used to examine the specificity of Methoxyresorufin and acetanilide as substrates for CYP1A2 activity. In addition, animals from each group were exposed to CYP1-inducing compounds. As expected, microsomes from untreated 1a2 KO mice did not have immunodetectable CYP1A2 protein; however, Methoxyresorufin-O-demethylase (MROD, 25.5+/-6.1 pmol/min/mg protein) and acetanilide-4-hydroxylation (ACOH, 0.64+/-0.04 nmol/min/mg protein) activities were still present. Furthermore, induction of ethoxyresorufin-O-deethylase (EROD) by 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin (TCDD) in 1a2 KO mice was accompanied by a greater than 70-fold increase in MROD activity. In contrast, ACOH was only induced 2-fold by TCDD. As with 1a2 KO mice, the parental strains exposed to TCDD or 2,3,4,7,8-pentachlorodibenzofuran (4-PeCDF) showed substantial EROD and MROD induction, whereas ACOH activity was induced to a lesser degree. PCB153 (2,2',4,4',5,5'-hexachlorobiphenyl) resulted in low levels of both EROD and MROD induction. Results indicate that both substrates are subject to metabolism by non-CYP1A2 sources, and the apparent contribution of CYP1A1 activity to Methoxyresorufin metabolism makes MROD unsuitable for differentiating CYP1A1 and CYP1A2 activities in the mouse.
Methoxyresorufin and benzyloxyresorufin: substrates preferentially metabolized by cytochromes P4501A2 and 2B, respectively, in the rat and mouse.[Pubmed:8373445]
Biochem Pharmacol. 1993 Sep 1;46(5):933-43.
The cytochrome P450 isozyme specificity for the O-dealkylation of Methoxyresorufin (MTR) and benzyloxyresorufin (BZR) in the rat and mouse was investigated. The induction of various alkoxyresorufin O-dealkylation activities was measured in male F344/NCr rats exposed to 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin or 3,4,5,3',4',5'-hexachlorobiphenyl. MTR and ethoxyresorufin (ETR) O-dealkylation activities were induced 30- and 80-fold, respectively, in the liver. ETR O-dealkylation activity was induced > 250-fold in the kidney, whereas the metabolism of MTR was induced only 30-fold in this extrahepatic tissue. Phenacetin, a fairly specific CYP1A2 inhibitor, caused concentration-dependent competitive inhibition of MTR O-dealkylation (ki approximately 20 microM at 0.5 microM substrate) in hepatic microsomes from 3,4,5,3',4',5'-hexachlorobiphenyl-treated rats. The corresponding ki for inhibition of ETR O-dealkylation by phenacetin was > or = 333 microM at a 0.5 microM substrate concentration. A monoclonal antibody displaying inhibitory activity against rat CYP1A1 inhibited ETR O-dealkylation activity, whereas it failed to inhibit MTR O-dealkylation activity. In contrast, a monoclonal antibody reactive with both CYP1A1 and CYP1A2 inhibited both O-dealkylation activities to an equal extent. Similar experiments, employing phenacetin or specific monoclonal antibodies, yielded comparable results when performed with mouse microsomes. The maximal induction of MTR O-dealkylation activity in mice was > 100-fold. The P450 isozyme specificity of BZR O-dealkylation was also examined in both rats and mice. Pregnenolone-alpha-carbonitrile, a strong inducer of CYP3A, only weakly induced BZR O-dealkylation activity. In addition, a monoclonal antibody that specifically inhibits CYP2B caused inhibition of BZR metabolism in microsomes from phenobarbital- or dexamethasone-pretreated rats. In B6C3F1 mice exposed to dietary Aroclor 1254, significant induction of hepatic MTR O-dealkylation activity was observed at concentrations lower than those required for the induction of ETR or BZR O-dealkylation. In summary, it would appear that MTR is a relatively specific substrate for CYP1A2 activity in rodents, while BZR appears to be relatively specific for CYP2B.


