Hygromycin BSuitable for mammalian cell selection CAS# 31282-04-9 |
- chroman 1
Catalog No.:BCC1480
CAS No.:1273579-40-0
- Y-27632 dihydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC1273
CAS No.:129830-38-2
- Hydroxyfasudil hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC1636
CAS No.:155558-32-0
- H-1152
Catalog No.:BCC1615
CAS No.:451462-58-1
- H-1152 dihydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC1616
CAS No.:871543-07-6
Quality Control & MSDS
Number of papers citing our products

Chemical structure

3D structure
| Cas No. | 31282-04-9 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 35766 | Appearance | Powder |
| Formula | C20H37N3O13 | M.Wt | 527.5 |
| Type of Compound | N/A | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Synonyms | Hygrovetine | ||
| Solubility | DMSO : 250 mg/mL (473.92 mM; Need ultrasonic) H2O : 16.67 mg/mL (31.60 mM; Need ultrasonic) | ||
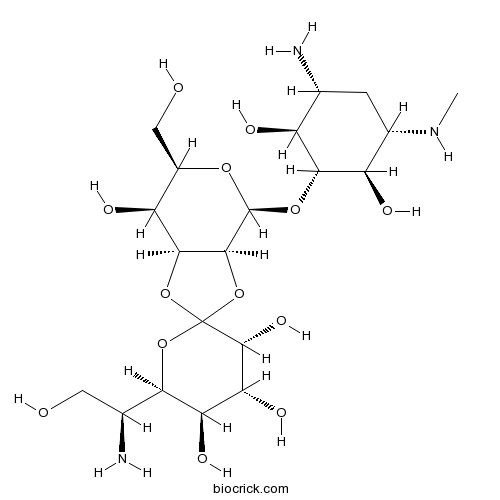
| Chemical Name | (3'R,3aS,4S,4'R,5'R,6R,6'R,7S,7aS)-4-[(1R,2S,3R,5S,6R)-3-amino-2,6-dihydroxy-5-(methylamino)cyclohexyl]oxy-6'-[(1S)-1-amino-2-hydroxyethyl]-6-(hydroxymethyl)spiro[4,6,7,7a-tetrahydro-3aH-[1,3]dioxolo[4,5-c]pyran-2,2'-oxane]-3',4',5',7-tetrol | ||
| SMILES | CNC1CC(C(C(C1O)OC2C3C(C(C(O2)CO)O)OC4(O3)C(C(C(C(O4)C(CO)N)O)O)O)O)N | ||
| Standard InChIKey | GRRNUXAQVGOGFE-KPBUCVLVSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C20H37N3O13/c1-23-7-2-5(21)9(26)15(10(7)27)33-19-17-16(11(28)8(4-25)32-19)35-20(36-17)18(31)13(30)12(29)14(34-20)6(22)3-24/h5-19,23-31H,2-4,21-22H2,1H3/t5-,6+,7+,8-,9+,10-,11+,12-,13-,14-,15-,16+,17+,18-,19+,20?/m1/s1 | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | Aminoglycoside antibiotic. Active against both prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells. Inhibits protein synthesis by binding to the 30S subunit and inhibiting the ribosomal translocation step of elongation. |

Hygromycin B Dilution Calculator

Hygromycin B Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 1.8957 mL | 9.4787 mL | 18.9573 mL | 37.9147 mL | 47.3934 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.3791 mL | 1.8957 mL | 3.7915 mL | 7.5829 mL | 9.4787 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.1896 mL | 0.9479 mL | 1.8957 mL | 3.7915 mL | 4.7393 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0379 mL | 0.1896 mL | 0.3791 mL | 0.7583 mL | 0.9479 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.019 mL | 0.0948 mL | 0.1896 mL | 0.3791 mL | 0.4739 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
Hygromycin B is a selective antibiotic.
Antibiotics are a type of antimicrobial used in the treatment and prevention of bacterial infection.
Hygromycin B is an antibiotic that is effective on most bacteria, fungi and higher eukaryotes. Hygromycin B has a single binding site within the 30S subunit, which is in consistent with its monophasic effect. The binding site is located in the major groove of the helix with a highly sequence-specific way. Hygromycin B inhibits protein synthesis by inhibiting the translocation step of elongation and causing mistranslation of mRNA in the 70S ribosome [1]. Hygromycin B selectively inhibited activity of the ribosomal ATPase (RbbA) on 70S ribosomes and releases RbbA from 70S ribosomes at physiological concentrations. RbbA enhances the reactivity of A889 and G890 of the 16S rRNA switch helix region. Also, Hygromycin B protects G1494 and A1408 in the decoding region.
References:
[1]. Brodersen DE, Clemons WM Jr, Carter AP, et al. The structural basis for the action of the antibiotics tetracycline, pactamycin, and hygromycin B on the 30S ribosomal subunit. Cell, 2000, 103(7): 1143-1154.
[2]. Ganoza MC, Kiel MC. A ribosomal ATPase is a target for hygromycin B inhibition on Escherichia coli ribosomes. Antimicrob Agents Chemother, 2001, 45(10): 2813-2819.
- Indacaterol
Catalog No.:BCC1650
CAS No.:312753-06-3
- gamma-Mangostin
Catalog No.:BCN5228
CAS No.:31271-07-5
- THIQ
Catalog No.:BCC7539
CAS No.:312637-48-2
- SKI II
Catalog No.:BCC5029
CAS No.:312636-16-1
- Tetrahydrocannabivarin
Catalog No.:BCN6935
CAS No.:31262-37-0
- IQ 3
Catalog No.:BCC8093
CAS No.:312538-03-7
- Cimigenol-3-one
Catalog No.:BCN7430
CAS No.:31222-32-9
- Eucalyptin
Catalog No.:BCN5227
CAS No.:3122-88-1
- Sideroxylin
Catalog No.:BCN5226
CAS No.:3122-87-0
- H-D-Ser-OH
Catalog No.:BCC2676
CAS No.:312-84-5
- Methylionene
Catalog No.:BCN7120
CAS No.:31197-54-3
- Sudan II
Catalog No.:BCN8383
CAS No.:3118-97-6
- Raucaffricine
Catalog No.:BCN4653
CAS No.:31282-07-2
- TCS JNK 5a
Catalog No.:BCC5148
CAS No.:312917-14-9
- LDN-27219
Catalog No.:BCC6236
CAS No.:312946-37-5
- Arjunic acid
Catalog No.:BCN5229
CAS No.:31298-06-3
- Estradiol Cypionate
Catalog No.:BCC4477
CAS No.:313-06-4
- Aristolochic acid A
Catalog No.:BCN6262
CAS No.:313-67-7
- ICA 121431
Catalog No.:BCC6358
CAS No.:313254-51-2
- Regadenoson
Catalog No.:BCC6438
CAS No.:313348-27-5
- Reversan
Catalog No.:BCC7764
CAS No.:313397-13-6
- VU 590 dihydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC7803
CAS No.:313505-85-0
- T0070907
Catalog No.:BCC2261
CAS No.:313516-66-4
- INH1
Catalog No.:BCC6040
CAS No.:313553-47-8
Hygromycin B hypersensitive (hhy) mutants implicate an intact trans-Golgi and late endosome interface in efficient Tor1 vacuolar localization and TORC1 function.[Pubmed:27812735]
Curr Genet. 2017 Jun;63(3):531-551.
Saccharomyces cerevisiae vacuoles are functionally analogous to mammalian lysosomes. Both also serve as physical platforms for Tor Complex 1 (TORC1) signal transduction, the master regulator of cellular growth and proliferation. Hygromycin B is a eukaryotic translation inhibitor. We recently reported on Hygromycin B hypersensitive (hhy) mutants that fail to grow at subtranslation inhibitory concentrations of the drug and exhibit vacuolar defects (Banuelos et al. in Curr Genet 56:121-137, 2010). Here, we show that hhy phenotype is not due to increased sensitivity to translation inhibition and establish a super HHY (s-HHY) subgroup of genes comprised of ARF1, CHC1, DRS2, SAC1, VPS1, VPS34, VPS45, VPS52, and VPS54 that function exclusively or inclusively at trans-Golgi and late endosome interface. Live cell imaging of s-hhy mutants revealed that Hygromycin B treatment disrupts vacuolar morphology and the localization of late endosome marker Pep12, but not that of late endosome-independent vacuolar SNARE Vam3. This, along with normal post-late endosome trafficking of the vital dye FM4-64, establishes that severe hypersensitivity to Hygromycin B correlates specifically with compromised trans-Golgi and late endosome interface. We also show that Tor1p vacuolar localization and TORC1 anabolic functions, including growth promotion and phosphorylation of its direct substrate Sch9, are compromised in s-hhy mutants. Thus, an intact trans-Golgi and late endosome interface is a requisite for efficient Tor1 vacuolar localization and TORC1 function.
Hygromycin B-induced cell death is partly mediated by reactive oxygen species in rice (Oryza sativa L.).[Pubmed:26415870]
Plant Mol Biol. 2015 Dec;89(6):577-88.
The aminoglycoside antibiotic Hygromycin B (Hyg) inhibits prokaryotic, chloroplast and mitochondrial protein synthesis. Because of the toxic effect of Hyg on plant cells, the HPT gene, encoding hygromycin phosphotransferase, has become one of the most widely used selectable markers in plant transformation. Yet the mechanism behind Hyg-induced cell lethality in plants is not clearly understood. In this study, we aimed to decipher this mechanism. With Hyg treatment, rice calli exhibited cell death, and rice seedlings showed severe growth defects, leaf chlorosis and leaf shrinkage. Rice seedlings also exhibited severe lipid peroxidation and protein carbonylation, for oxidative stress damage at the cellular level. The production of reactive oxygen species such as O2(.-), H2O2 and OH(.) was greatly induced in rice seedlings under Hyg stress, and pre-treatment with ascorbate increased resistance to Hyg-induced toxicity indicating the existence of oxidative stress. Overexpression of mitochondrial Alternative oxidase1a gene without HPT selection marker in rice enhanced tolerance to Hyg and attenuated the degradation of protein content, whereas the rice plastidial glutathione reductase 3 mutant showed increased sensitivity to Hyg. These results demonstrate that Hyg-induced cell lethality in rice is not only due to the inhibition of protein synthesis but also mediated by oxidative stress.
[Construction of an integration vector carrying hygromycin B resistance gene and its genetic transformation in Rhizopus oryzae].[Pubmed:26762042]
Sheng Wu Gong Cheng Xue Bao. 2015 Aug;31(8):1203-18.
To construct a system of genetic transformation suitable for Rhizopus oryzae, we constructed a single-exchange vector pBS-hygro carrying Hygromycin B resistance gene (hph) as its selective marker using gene splicing by overlap extension PCR (SOE PCR) technique. We introduced this recombinant vector into Rhizopus oryzae AS 3.819 by PEG/CaCl2-mediated transformation of protoplast, electroporation of protoplast and germinated spores; and we studied the effects of hydrolysis time, field strength and spore germination time on transformation frequency. We conducted quantitative real-time PCR (qPCR) assay to determine the gene copy number of ldhA integrated in the genome of R. oryzae transformants and its effect on the stability of transformants. We successfully achieved R. oryzae transformants integrated with pBS-hygro-ldhA vector. The optimal hydrolysis time for protoplast production was 140 min, and the optimal field strength of electroporation pulse for protoplast was 13 kV/cm. The optimal germination time of spores for electroporation was 2.5 h, and the optimal field strength of electroporation pulse was 14 kV/cm. The transformation frequency of method based on germinated spores was generally higher than the methods based on protoplast. The qPCR test results suggested that transformants with high copy number of integration in a certain range were relatively stable. Our results provided basis and support for metabolic regulation and genetic engineering breeding of R. oryzae.
DNA Damage Responses Are Induced by tRNA Anticodon Nucleases and Hygromycin B.[Pubmed:27472060]
PLoS One. 2016 Jul 29;11(7):e0157611.
Previous studies revealed DNA damage to occur during the toxic action of PaT, a fungal anticodon ribonuclease (ACNase) targeting the translation machinery via tRNA cleavage. Here, we demonstrate that other translational stressors induce DNA damage-like responses in yeast as well: not only zymocin, another ACNase from the dairy yeast Kluyveromyces lactis, but also translational antibiotics, most pronouncedly Hygromycin B (HygB). Specifically, DNA repair mechanisms BER (base excision repair), HR (homologous recombination) and PRR (post replication repair) provided protection, whereas NHEJ (non-homologous end-joining) aggravated toxicity of all translational inhibitors. Analysis of specific BER mutants disclosed a strong HygB, zymocin and PaT protective effect of the endonucleases acting on apurinic sites. In cells defective in AP endonucleases, inactivation of the DNA glycosylase Ung1 increased tolerance to ACNases and HygB. In addition, Mag1 specifically contributes to the repair of DNA lesions caused by HygB. Consistent with DNA damage provoked by translation inhibitors, mutation frequencies were elevated upon exposure to both fungal ACNases and HygB. Since polymerase zeta contributed to toxicity in all instances, error-prone lesion-bypass probably accounts for the mutagenic effects. The finding that differently acting inhibitors of protein biosynthesis induce alike cellular responses in DNA repair mutants is novel and suggests the dependency of genome stability on translational fidelity.
A ribosomal ATPase is a target for hygromycin B inhibition on Escherichia coli ribosomes.[Pubmed:11557474]
Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2001 Oct;45(10):2813-9.
We demonstrate that the transfer of fully charged aminoacyl-tRNAs into peptides directed by the MS2 RNA template requires both ATP and GTP, initiation factors (IF1, IF2, and IF3), elongation factors (EF-Tu, EF-Ts, and EF-G), and the ribosomal ATPase (RbbA). The nonhydrolyzable analogue AMPPCP inhibits the reactions, suggesting that hydrolysis of ATP is required for synthesis. The RbbA protein occurs bound to ribosomes and stimulates the ATPase activity of Escherichia coli 70S and 30S particles. The gene encoding RbbA harbors four ATP binding domains; the C-terminal half of the protein bears extensive sequence similarity to EF-3, a ribosome-dependent ATPase. Here, we show that the antibiotic Hygromycin B selectively inhibits the ATPase activity of RbbA. Other antibiotics with similar effects on miscoding, streptomycin and neomycin, as well as antibiotics that impair peptide bond synthesis and translocation, had little effect on the ATPase activity of RbbA on 70S ribosomes. Immunoblot analysis indicates that at physiological concentrations, Hygromycin B selectively releases RbbA from 70S ribosomes. Hygromycin B protects G1494 and A1408 in the decoding region, and RbbA enhances the reactivity of A889 and G890 of the 16S rRNA switch helix region. Cross-linking and X-ray diffraction data have revealed that this helix switch and the decoding region are in close proximity. Mutations in the switch helix (889-890) region affect translational fidelity and translocation. The binding site of Hygromycin B and its known dual effect on the fidelity of decoding and translocation suggest a model for the action of this drug on ribosomes.
The structural basis for the action of the antibiotics tetracycline, pactamycin, and hygromycin B on the 30S ribosomal subunit.[Pubmed:11163189]
Cell. 2000 Dec 22;103(7):1143-54.
We have used the recently determined atomic structure of the 30S ribosomal subunit to determine the structures of its complexes with the antibiotics tetracycline, pactamycin, and Hygromycin B. The antibiotics bind to discrete sites on the 30S subunit in a manner consistent with much but not all biochemical data. For each of these antibiotics, interactions with the 30S subunit suggest a mechanism for its effects on ribosome function.
Hygromycin B phosphotransferase as a selectable marker for DNA transfer experiments with higher eucaryotic cells.[Pubmed:6098829]
Mol Cell Biol. 1984 Dec;4(12):2929-31.
The DNA coding sequence for the Hygromycin B phosphotransferase gene was placed under the control of the regulatory sequences of a cloned long terminal repeat of Moloney sarcoma virus. This construction allowed direct selection for Hygromycin B resistance after transfection of eucaryotic cell lines not naturally resistant to this antibiotic, thus providing another dominant marker for DNA transfer in eucaryotic cells.


