H-7 dihydrochlorideProtein kinase inhibitor CAS# 108930-17-2 |
- Hydroxyfasudil
Catalog No.:BCC1635
CAS No.:105628-72-6
- chroman 1
Catalog No.:BCC1480
CAS No.:1273579-40-0
- Y-27632 dihydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC1273
CAS No.:129830-38-2
- Hydroxyfasudil hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC1636
CAS No.:155558-32-0
- H-1152 dihydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC1616
CAS No.:871543-07-6
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

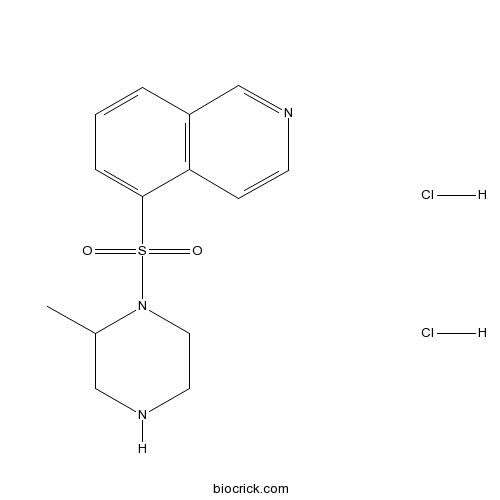
| Cas No. | 108930-17-2 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 73332 | Appearance | Powder |
| Formula | C14H19Cl2N3O2S | M.Wt | 364.29 |
| Type of Compound | N/A | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Solubility | Soluble to 100 mM in water and to 20 mM in DMSO | ||
| Chemical Name | 5-(2-methylpiperazin-1-yl)sulfonylisoquinoline;dihydrochloride | ||
| SMILES | CC1CNCCN1S(=O)(=O)C2=CC=CC3=C2C=CN=C3.Cl.Cl | ||
| Standard InChIKey | OARGPFMFRLLKPF-UHFFFAOYSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C14H17N3O2S.2ClH/c1-11-9-16-7-8-17(11)20(18,19)14-4-2-3-12-10-15-6-5-13(12)14;;/h2-6,10-11,16H,7-9H2,1H3;2*1H | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | Protein kinase inhibitor. IC50 values for inhibition of PKC, PKG, PKA and myosin light chain kinase are 6.0, 5.8, 3.0 and 97.0 μM respectively. |

H-7 dihydrochloride Dilution Calculator

H-7 dihydrochloride Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 2.7451 mL | 13.7253 mL | 27.4507 mL | 54.9013 mL | 68.6266 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.549 mL | 2.7451 mL | 5.4901 mL | 10.9803 mL | 13.7253 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.2745 mL | 1.3725 mL | 2.7451 mL | 5.4901 mL | 6.8627 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0549 mL | 0.2745 mL | 0.549 mL | 1.098 mL | 1.3725 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0275 mL | 0.1373 mL | 0.2745 mL | 0.549 mL | 0.6863 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
- GSK1904529A
Catalog No.:BCC1062
CAS No.:1089283-49-7
- U0124
Catalog No.:BCC7200
CAS No.:108923-79-1
- Soyasaponin IV
Catalog No.:BCN1627
CAS No.:108906-97-4
- MK 6096
Catalog No.:BCC4020
CAS No.:1088991-73-4
- GSK-923295
Catalog No.:BCC1608
CAS No.:1088965-37-0
- 13-O-Acetylcorianin
Catalog No.:BCN5883
CAS No.:108887-44-1
- Taccalonolide B
Catalog No.:BCN2743
CAS No.:108885-69-4
- Taccalonolide A
Catalog No.:BCN2737
CAS No.:108885-68-3
- Lupeol 3-hydroxyoctadecanoate
Catalog No.:BCN6686
CAS No.:108885-61-6
- Gardenolic acid B
Catalog No.:BCN7140
CAS No.:108864-53-5
- Dendrophenol
Catalog No.:BCC8165
CAS No.:108853-14-1
- Nemorubicin
Catalog No.:BCC4151
CAS No.:108852-90-0
- Neocurdione
Catalog No.:BCC9242
CAS No.:108944-67-8
- FURA-2AM
Catalog No.:BCC7296
CAS No.:108964-32-5
- N-Valeric acid
Catalog No.:BCC8220
CAS No.:109-52-4
- Allylthiourea
Catalog No.:BCC4759
CAS No.:109-57-9
- Butylamine
Catalog No.:BCC8304
CAS No.:109-73-9
- 2-Methylaminoethanol
Catalog No.:BCN1758
CAS No.:109-83-1
- Ilexoside K
Catalog No.:BCN7866
CAS No.:109008-26-6
- Ilexoside D
Catalog No.:BCN7865
CAS No.:109008-27-7
- Mauritianin
Catalog No.:BCN2932
CAS No.:109008-28-8
- CGS 12066B dimaleate
Catalog No.:BCC6732
CAS No.:109028-10-6
- Schizanthine E
Catalog No.:BCN1937
CAS No.:109031-04-1
- Icariside B1
Catalog No.:BCN7271
CAS No.:109062-00-2
The protein kinase C inhibitor 1-(5-isoquinolinesulfonyl)-2-methylpiperazine dihydrochloride (H-7) inhibits PMA-induced promiscuous cytolytic activity but not specific cytolytic activity by a cloned cytolytic T lymphocyte.[Pubmed:1898396]
Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1991 Sep 16;179(2):720-5.
Phorbol 12-myristate 13-acetate (PMA) induces the cytolytic T lymphocyte (CTL) clone 4D (H-2b anti-H-2d) to promiscuously kill the inappropriate target EL-4 (H-2b). The protein kinase C (PKC) inhibitor 1-(5-isoquinolinesulfonyl)-2-methylpiperazine dihydrochloride (H-7) inhibited the PMA-induced promiscuous lympholysis. The concentration of H-7 that inhibited PMA-induced lympholysis by 50% (IC50) was calculated to be 4 microM, which closely approximates the reported IC50 of H-7 of 6 microM for PKC activity in vitro. In striking contrast, specific cytolysis of appropriate P815 (H-2d) target cell by CTL clone 4D was not inhibited by concentrations of H-7 which inhibited PMA-induced promiscuous lympholysis. These results indicate that PMA-induced promiscuous lympholysis of inappropriate target cell is triggered via activation of PKC, whereas PKC activation is not obligatory in triggering CTL clone 4D to specifically kill appropriate target cells. Thus, these data suggest that cloned CTL have two or more triggering mechanisms than may initiate one or more cytolytic pathways.
Preincubation of thymocytes with 1-(5-isoquinolinesulfonyl)-2-methylpiperazine dihydrochloride (H-7) induces apoptosis in non-stimulated thymocytes.[Pubmed:9247701]
Biochem Mol Biol Int. 1997 Jul;42(3):433-41.
1-(5-Isoquinolinesulfonyl1)-2-methylpiperazine hydrochloride (H-7), an inhibitor of protein kinases, has been shown to inhibit the thymocyte apoptosis induced by various apoptogenic agents. In the present study, when mouse thymocytes were pretreated with H-7, washed, and cultured for an additional time, apoptosis was induced depending on the preincubation time and the dose of H-7. The protein kinase C activity in the H-7-pretreated and -washed cells was not altered, suggesting that an alteration of a certain PKC isoform is related to both the triggering and the progression of apoptosis.
Effects of protein kinase inhibitors 1(5-isoquinolinesulfonyl)-2-methylpiperazine dihydrochloride (H-7) and N-[2-guanidinoethyl]-5-isoquinolinesulfonamide hydrochloride (HA1004) on calcitriol-induced differentiation of HL-60 cells.[Pubmed:3422561]
Biochem Pharmacol. 1988 Feb 15;37(4):635-40.
HL-60 promyelocytic leukemia cells were induced to differentiate by 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3 (calcitriol) into mature monocytes. Differentiation was assessed by nitro blue tetrazolium dye reduction, nonspecific esterase activity, and DNA synthesis. Terminal differentiation of cultures induced by calcitriol (10 nM) was inhibited by 80% when cells were treated simultaneously with protein kinase inhibitors 1-(5-isoquinolinesulfonyl)-2-methylpiperazine dihydrochloride (H-7) (32 microM) and N-[2-guanidinoethyl]-5-isoquinolinesulfonamide hydrochloride (HA1004) (320 microM). The IC50 for inhibition of calcitriol-induced differentiation was approximately 15 microM for H-7 and 170 microM for HA1004. The IC50 values for H-7 and HA1004 antagonism of calcitriol-induced differentiation are quantitatively and relatively correlated to their known action to inhibit protein kinase C activity. Treatment of cells with concentrations of 0-32 microM H-7 or 0-320 microM HA1004 alone did not affect cell growth, differentiation, or trypan blue exclusion. However, higher concentrations of H7 (greater than 32 microM) and HA1004 (greater than 320 microM) were found to be cytotoxic. The data presented suggest that calcitriol-induced differentiation is antagonized by inhibitors of protein kinase and are consistent with the hypothesis that kinase C activity is required for HL-60 cell differentiation.
Modulation of inhibitory efficiency of rat skeletal muscle calpastatin by phosphorylation.[Pubmed:1530632]
Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1992 Sep 16;187(2):751-9.
Rat skeletal muscle calpastatin form is markedly modified in its inhibitory properties by means of a reverse reaction which involves both phosphorylation and dephosphorylation. Dephospho-calpastatin shows greater inhibitory efficiency versus mu-calpain, whereas phospho-calpastatin shows maximal inhibition versus m-calpain. Both forms are present in fresh rat muscle. Phosphorylation has been reproduced "in vitro" using a homologous Ca2+ independent protein kinase and found to result in the incorporation of approximately one mole of 32P per mole of protein. Dephosphorylation was induced by treatment with alkaline phosphatase and 32P release shown found to correlate with modifications of the inhibitory properties. This reversible covalent modification of calpastatin is considered an important advancement in the understanding of how different calpain isoforms can be more efficiently controlled by a single inhibitor isozyme form.
Effect of the kinase inhibitor, H-7, on stress, crossbridge phosphorylation, muscle shortening and inositol phosphate production in rabbit arteries.[Pubmed:2299593]
J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1990 Jan;252(1):253-9.
Smooth muscle contractile agents cause large increases in crossbridge phosphorylation (Mp) and cycling rates resulting in the rapid development of stress (force/muscle cross-sectional area). Despite temporal declines in Mp and cycling during continued activation, stress is maintained at high levels. This observation led to several different hypotheses describing the regulation of steady-state stress. One proposal is that protein kinase C regulates stress maintenance, whereas another invokes a steady-state dependence on Ca+(+)-calmodulin-dependent myosin light chain kinase. The aim of this study was to investigate the mechanism of stress-maintenance by analyzing the inhibitory efficacy of a protein kinase C inhibitor, H-7 [1-(5-isoquinolinesulfonyl)-2-methylpiperizine], on steady-state values of stress, Mp and crossbridge cycling in rabbit renal and femoral arteries. H-7 effectively inhibited steady-state stress produced by KCl (IC50 = 3.7-4.4 microM) and phenylephrine (PhE) (IC50 = 10.6-15.2 microM). Likewise, increases in the level of Mp and the rate of crossbridge cycling induced by both KCl and PhE were significantly reduced by 10 microM H-7. H-7 did not reduce inositol phosphate production stimulated by PhE, but did reduce early stress development thought to be mediated by inositol phosphate-induced mobilization of intracellular calcium. Calcium-induced increases in stress and Mp produced in saponin-skinned artery strips were reduced by less than 50% by 320 microM H-7.(ABSTRACT TRUNCATED AT 250 WORDS)
Isoquinolinesulfonamides, novel and potent inhibitors of cyclic nucleotide dependent protein kinase and protein kinase C.[Pubmed:6238627]
Biochemistry. 1984 Oct 9;23(21):5036-41.
Naphthalenesulfonamides such as N-(6-amino-hexyl)-5-chloro-1-naphthalenesulfonamide (W-7) are potent calmodulin (CaM) antagonists and act upon several protein kinases at higher concentration. When the naphthalene ring was replaced by isoquinoline, the derivatives were no longer CaM antagonists but retained the ability to inhibit protein kinases, and some of the derivatives exhibited selective inhibition toward a certain protein kinase. cAMP-dependent, cGMP-dependent, and Ca2+-phospholipid-dependent (protein kinase C) protein kinases were inhibited significantly by addition of 10(-6) M N-[2-(methylamino)ethyl]-5-isoquinoline-sulfonamide (H-8) and 1-(5-isoquinolinylsulfonyl)-2-methylpiperazine (H-7). H-8 was the most active of the inhibitors in this series and inhibited more markedly cyclic nucleotide dependent protein kinases, than other kinases, while the derivative with the sulfonylpiperazine residue (H-7) was the most potent in inhibiting protein kinase C. Apparent Ki values of H-8 were 0.48 and 1.2 microM for cGMP-dependent and cAMP-dependent protein kinases, respectively, and the Ki value of H-7 for protein kinase C was 6 microM. Both the holoenzyme and the catalytic subunit (or fragment), which is active without an enzyme activator, are susceptible to these compounds with a similar concentration dependency, thereby indicating that the inhibitory effect is attributed to the direct interaction of the compound with the active center of the enzyme but not with the enzyme activator. The inhibitions were freely reversible and of the competitive type with respect to ATP and of the noncompetitive type with respect to the phosphate acceptor.(ABSTRACT TRUNCATED AT 250 WORDS)


