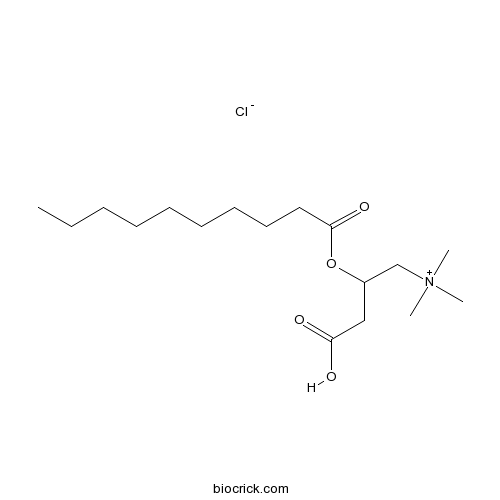
(±)-Decanoylcarnitine chloridecholinergic agonist CAS# 14919-36-9 |
- Alvespimycin
Catalog No.:BCC1346
CAS No.:467214-20-6
- 17-AAG (KOS953)
Catalog No.:BCC2121
CAS No.:75747-14-7
- Retaspimycin
Catalog No.:BCC1889
CAS No.:857402-23-4
- PU-H71
Catalog No.:BCC1872
CAS No.:873436-91-0
- 17-AAG Hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC1297
CAS No.:911710-03-7
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 14919-36-9 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 24802062 | Appearance | Powder |
| Formula | C17H34ClNO4 | M.Wt | 351.91 |
| Type of Compound | N/A | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Solubility | Soluble to 100 mM in water | ||
| Chemical Name | (3-carboxy-2-decanoyloxypropyl)-trimethylazanium;chloride | ||
| SMILES | CCCCCCCCCC(=O)OC(CC(=O)O)C[N+](C)(C)C.[Cl-] | ||
| Standard InChIKey | KETNUEKCBCWXCU-UHFFFAOYSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C17H33NO4.ClH/c1-5-6-7-8-9-10-11-12-17(21)22-15(13-16(19)20)14-18(2,3)4;/h15H,5-14H2,1-4H3;1H | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | Homolog of acetylcarnitine chloride. |

(±)-Decanoylcarnitine chloride Dilution Calculator

(±)-Decanoylcarnitine chloride Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 2.8416 mL | 14.2082 mL | 28.4164 mL | 56.8327 mL | 71.0409 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.5683 mL | 2.8416 mL | 5.6833 mL | 11.3665 mL | 14.2082 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.2842 mL | 1.4208 mL | 2.8416 mL | 5.6833 mL | 7.1041 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0568 mL | 0.2842 mL | 0.5683 mL | 1.1367 mL | 1.4208 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0284 mL | 0.1421 mL | 0.2842 mL | 0.5683 mL | 0.7104 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
(±)-Decanoylcarnitine chloride is an agonist for cholinergic and a homolog of acetylcarnitine chloride (Cat No. B6273).
Acetylcholine receptor (AChR) is an integral membrane protein receptor for acetylcholine. There are two kinds of AChRs: nicotinic acetylcholine receptors and muscarinic acetylcholine receptors.
(±)-Decanoylcarnitine chloride is a cholinergic agonist and an intermediate in lipid metabolism [1]. In retinal ganglion cells, acetylcarnitine and acetylcholine inhibited GABAergic responses to exogenous GABA and GABAergic inhibitory postsynaptic currents [2].
In dogs with coronary ligation, (-)-carnitine chloride (LCC) (300 mg/kg) and acetyl (-)-carnitine chloride (ALCC) (300 mg/kg) inhibited the ventricular arrhythmia. Also, LCC and ALCC improved oxidative phosphorylation rate and the mitochondrial function [1]. In the mouse hot plate test, acetyl-l-carnitine (ALCAR) (100 mg/kg) exhibited analgesia. While, U-73122 and neomycin (the phospholipase C (PLC) inhibitors) blocked the increase of the pain threshold induced by ALCAR. LiCl that impairing phosphatidylinositol synthesis antagonized the antinociception in a dose-dependent way. PMA and PDBu (PKC activators) blocked the increase of the pain threshold in a dose-dependent way. These results suggested that ALCAR analgesia required the participation of the PLC-IP3 pathway [3].
References:
[1]. Imai S, Matsui K, Nakazawa M, et al. Anti-arrhythmic effects of (-)-carnitine chloride and its acetyl analogue on canine late ventricular arrhythmia induced by ligation of the coronary artery as related to improvement of mitochondrial function. Br J Pharmacol, 1984, 82(2): 533-542.
[2]. B?hring R, Standhardt H, Martelli EA, et al. GABA-activated chloride currents of postnatal mouse retinal ganglion cells are blocked by acetylcholine and acetylcarnitine: how specific are ion channels in immature neurons? Eur J Neurosci, 1994, 6(7): 1089-1099.
[3]. Galeotti N, Bartolini A, Calvani M, et al. Acetyl-L-carnitine requires phospholipase C-IP3 pathway activation to induce antinociception. Neuropharmacology, 2004, 47(2): 286-294.
- CGP 55845 hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC5737
CAS No.:149184-22-5
- CGP 54626 hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC6934
CAS No.:149184-21-4
- Irenolone
Catalog No.:BCN7146
CAS No.:149184-19-0
- 3-(2,4-Dihydroxybenzyl)-5-hydroxy-7,8-dimethoxy-6-methylchroman-4-one
Catalog No.:BCN6634
CAS No.:149180-48-3
- Eriodictyol chalcone
Catalog No.:BCN8276
CAS No.:14917-41-0
- Homaloside D
Catalog No.:BCN1661
CAS No.:149155-19-1
- Cratoxylone
Catalog No.:BCN3875
CAS No.:149155-01-1
- Brugine
Catalog No.:BCN1899
CAS No.:14912-30-2
- AG 825
Catalog No.:BCC7113
CAS No.:149092-50-2
- Brusatol
Catalog No.:BCN8278
CAS No.:14907-98-3
- H-D-Trp-OMe.HCl
Catalog No.:BCC3118
CAS No.:14907-27-8
- (S)-WAY 100135 dihydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC6993
CAS No.:149007-54-5
- (±)-Myristoylcarnitine chloride
Catalog No.:BCC6698
CAS No.:14919-38-1
- Benserazide HCl
Catalog No.:BCC4468
CAS No.:14919-77-8
- H-Abu-OH
Catalog No.:BCC3198
CAS No.:1492-24-6
- Z-Ser(Tos)-OMe
Catalog No.:BCC2741
CAS No.:1492-52-0
- Arcaine sulfate
Catalog No.:BCC6631
CAS No.:14923-17-2
- Neotripterifordin
Catalog No.:BCN7477
CAS No.:149249-32-1
- De-4'-O-methylyangambin
Catalog No.:BCN1662
CAS No.:149250-48-6
- 1-Dehydroxy-23-deoxojessic acid
Catalog No.:BCN1663
CAS No.:149252-87-9
- pp60 c-src (521-533) (phosphorylated)
Catalog No.:BCC5851
CAS No.:149299-77-4
- Cytochalasin B
Catalog No.:BCN7084
CAS No.:14930-96-2
- AACOCF3
Catalog No.:BCC7075
CAS No.:149301-79-1
- UNC2250
Catalog No.:BCC4876
CAS No.:1493694-70-4
Determination of acylcarnitines in urine of patients with inborn errors of metabolism using high-performance liquid chromatography after derivatization with 4'-bromophenacylbromide.[Pubmed:8222273]
Clin Chim Acta. 1993 Jul 16;216(1-2):53-61.
A high-performance liquid chromatographic method is presented for the determination of urinary acylcarnitines. After solid phase extraction on silica columns the acylcarnitines are converted to 4'-bromophenacyl esters with 4'-bromophenacylbromide in the presence of N,N-diisopropylethylamine. Complete derivatization was achieved at 37 degrees C within 30 min. The 4'-bromophenacyl esters were separated by high-performance liquid chromatography on a Hypersil BDS C8 reversed-phase column with a binary gradient containing varying proportions of acetonitrile, water and 0.1 M triethylamine phosphate buffer. Essentially baseline separation was obtained with a standard mixture containing 4'-bromophenacyl esters of carnitine and synthetic acylcarnitines of increasing chain length ranging from acetyl- to palmitoylcarnitine. The method was used to obtain urinary acylcarnitine profiles from patients with propionic, methylmalonic and isovaleric acidemia and with medium-chain and multiple acyl-CoA dehydrogenase deficiency. Quantification of the acylcarnitines was achieved using undecanoylcarnitine as internal standard.
Molecular basis of mitochondrial fatty acid oxidation defects.[Pubmed:1431593]
J Lipid Res. 1992 Aug;33(8):1099-110.
A dozen separate inherited disorders of mitochondrial fatty acid beta-oxidation have been described in humans. This represents about half of the potential sites for genetic error that can affect this important pathway of energy metabolism. As the characterization of these disorders at the clinical and biochemical levels has progressed rapidly, so has the delineation of the molecular defects that underlie them. The most commonly recognized disorder of beta-oxidation is medium-chain acyl-CoA dehydrogenase deficiency; a striking feature of this disorder is that there is a single point mutation that accounts for 90% of the variant alleles among patients with medium-chain acyl-CoA dehydrogenase deficiency. Molecular defects of other enzymes in the pathway have been identified, and it seems likely that a complete description of these defects at the molecular level is a realistic goal. In basic biological terms, such studies will lead to a better understanding of the genetic control exerted on this pathway. In clinical terms, they will lead to improved understanding of the molecular pathophysiology of these diseases and may well provide the necessary techniques to proceed with the screening of these disorders.
Urinary excretion of l-carnitine and acylcarnitines by patients with disorders of organic acid metabolism: evidence for secondary insufficiency of l-carnitine.[Pubmed:6441143]
Pediatr Res. 1984 Dec;18(12):1325-8.
Concentrations of l-carnitine and acylcarnitines have been determined in urine from patients with disorders of organic acid metabolism associated with an intramitochondrial accumulation of acyl-CoA intermediates. These included propionic acidemia, methylmalonic aciduria, isovaleric acidemia, multicarboxylase deficiency, 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaric aciduria, methylacetoacetyl-CoA thiolase deficiency, and various dicarboxylic acidurias including glutaric aciduria, medium-chain acyl-CoA dehydrogenase deficiency, and multiple acyl-CoA dehydrogenase deficiency. In all cases, concentrations of acylcarnitines were greatly increased above normal with free carnitine concentrations ranging from undetectable to supranormal values. The ratios of acylcarnitine/carnitine were elevated above the normal value of 2.0 +/- 1.1. l-Carnitine was given to three of these patients; in each case, concentrations of plasma and urine carnitines increased accompanied by a marked increase in concentrations of short-chain acylcarnitines. These acylcarnitines have been examined using fast atom bombardment mass spectrometry in some of these diseases and have been shown to be propionylcarnitine in methylmalonic aciduria and propionic acidemia, isovalerylcarnitine in isovaleric acidemia, and hexanoylcarnitine and octanoylcarnitine in medium-chain acyl-CoA dehydrogenase deficiency. The excretion of these acylcarnitines is compatible with the known accumulation of the corresponding acyl-CoA esters in these diseases. In this group of disorders, the increased acylcarnitine/carnitine ratio in urine and plasma indicates an imbalance of mitochondrial mass action homeostasis and, hence, of acyl-CoA/CoA ratios. Despite naturally occurring attempts to increase endogeneous l-carnitine biosynthesis, there is insufficient carnitine available to restore the mass action ratio as demonstrated by the further increase in acylcarnitine excretion when patients were given oral l-carnitine.(ABSTRACT TRUNCATED AT 250 WORDS)


