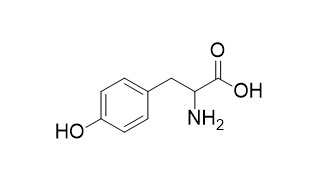
DL-TyrosineCAS# 556-03-6 |
Quality Control & MSDS
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 556-03-6 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | N/A | Appearance | Powder |
| Formula | C9H11NO3 | M.Wt | 181.1 |
| Type of Compound | Alkaloids | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Solubility | Soluble in Chloroform,Dichloromethane,Ethyl Acetate,DMSO,Acetone,etc. | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | Reference standards. | |||||

DL-Tyrosine Dilution Calculator

DL-Tyrosine Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 5.5218 mL | 27.6091 mL | 55.2181 mL | 110.4362 mL | 138.0453 mL |
| 5 mM | 1.1044 mL | 5.5218 mL | 11.0436 mL | 22.0872 mL | 27.6091 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.5522 mL | 2.7609 mL | 5.5218 mL | 11.0436 mL | 13.8045 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.1104 mL | 0.5522 mL | 1.1044 mL | 2.2087 mL | 2.7609 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0552 mL | 0.2761 mL | 0.5522 mL | 1.1044 mL | 1.3805 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
- 4'-Methoxychalcone
Catalog No.:BCN9772
CAS No.:959-23-9
- (-)-Eburnamonine
Catalog No.:BCN9771
CAS No.:4880-88-0
- Comanthosid A
Catalog No.:BCN9770
CAS No.:70938-59-9
- 2'-Methoxyflavone
Catalog No.:BCN9769
CAS No.:19725-47-4
- N-trans-caffeoyloctopamine
Catalog No.:BCN9768
CAS No.:1378868-10-0
- Rebaudioside M
Catalog No.:BCN9767
CAS No.:1220616-44-3
- (S)-(-)-Limonene
Catalog No.:BCN9766
CAS No.:5989-54-8
- L-(-)-Malic acid
Catalog No.:BCN9765
CAS No.:97-67-6
- Glucofrangulin B
Catalog No.:BCN9764
CAS No.:14062-59-0
- Dodeca 2E,4E,8Z,10E,Z-tetraenoic acid isobutylamide
Catalog No.:BCN9763
CAS No.:866602-52-0
- 2,3-Dihydro-2-phenyl-4H-benzopyran-4-one
Catalog No.:BCN9762
CAS No.:487-26-3
- Quinine sulfate dihydrate
Catalog No.:BCN9761
CAS No.:6119-70-6
- Glucofrangulin A
Catalog No.:BCN9774
CAS No.:21133-53-9
- Nortrachelogenin-5'-C-beta-glucoside
Catalog No.:BCN9775
CAS No.:858127-39-6
- 3,5-Dihydroxy-4-methoxybenzoic acid
Catalog No.:BCN9776
CAS No.:4319-02-2
- 3,4-Dimethoxyacetophenone
Catalog No.:BCN9777
CAS No.:1131-62-0
- Calvatic acid
Catalog No.:BCN9778
CAS No.:54723-08-9
- alpha-Hexylcinnamaldehyde
Catalog No.:BCN9779
CAS No.:101-86-0
- (+/-)-Anabasine
Catalog No.:BCN9780
CAS No.:13078-04-1
- Cannabisin B
Catalog No.:BCN9781
CAS No.:144506-17-2
- Deacylgymnemic acid
Catalog No.:BCN9782
CAS No.:121686-42-8
- Cinobufotenine
Catalog No.:BCN9783
CAS No.:60657-23-0
- Indole
Catalog No.:BCN9784
CAS No.:120-72-9
- 5,6,7-Trimethoxyflavone
Catalog No.:BCN9785
CAS No.:973-67-1
Procedure to build a signal transfer set, independent of the target analytes, between a portable fluorimeter based on light-emitting diodes and a master fluorimeter.[Pubmed:32145853]
Anal Chim Acta. 2020 Apr 15;1106:33-41.
The need of performing "in situ" analytical determinations together with the availability of high-power deep UV-LEDs have led to the use of fluorescence spectroscopy. However, it is necessary to register excitation-emission matrices (EEM) to obtain three-way data which can be decomposed using parallel factor analysis for enabling the unequivocal identification of the analytes. In this context, the feasibility of transferring EEM between a portable fluorimeter based on LEDs and a master fluorimeter based on a xenon source has been recently reported without losing analytical quality. To build the transfer function, the signals of the same N samples must be recorded in the portable and in the master fluorimeter. In literature, these samples always contained the target analytes so the EEM signal transfer methodology is very limited in practice. Therefore, the challenge is to search for a set of samples whose EEM enable to perform the signal transfer without previously knowing the target analytes. The aim of this work is the design of a procedure to build N mixtures of P fluorophores so the N EEM would be optimal for the signal transfer. Five criteria have been defined a priori to identify the quality of a transfer set made up of N EEM. Then, a procedure has been designed to obtain the n mixtures of the P fluorophores "in silico" using the Pareto front of the optimal solutions and a desirability function to choose the desired N EEM. The procedure has been used to find five mixtures of the three chosen fluorophores for the signal transfer (coumarin 120, DL-Tyrosine and DL-Tryptophan) which are chemically different from the analytes of interest (enrofloxacin and flumequine) and are contained in a different matrix. These two analytes are antibiotics which have maximum residue limits set in the EU legislation in force. The correlation coefficients between the experimental reference spectra and the PARAFAC spectral loadings of the data registered with the master fluorimeter were greater than or equal to 0.999 in all cases. On the other hand, the correlation coefficients obtained with the portable fluorimeter ranged from 0.900 to 0.950 once the procedure was applied to the two antibiotics. Therefore, the unequivocal identification of the analytes was ensured.
Behavioral effects of Bj-PRO-7a, a proline-rich oligopeptide from Bothrops jararaca venom.[Pubmed:31721904]
Braz J Med Biol Res. 2019 Nov 7;52(11):e8441.
The heptapeptide Bj-PRO-7a, isolated and identified from Bothrops jararaca (Bj) venom, produces antihypertensive and other cardiovascular effects that are independent on angiotensin converting enzyme inhibition, possibly relying on cholinergic muscarinic receptors subtype 1 (M1R). However, whether Bj-PRO-7a acts upon the central nervous system and modifies behavior is yet to be determined. Therefore, the aims of this study were: i) to assess the effects of acute administration of Bj-PRO-7a upon behavior; ii) to reveal mechanisms involved in the effects of Bj-PRO-7a upon locomotion/exploration, anxiety, and depression-like behaviors. For this purpose, adult male Wistar (WT, wild type) and spontaneous hypertensive rats (SHR) received intraperitoneal injections of vehicle (0.9% NaCl), diazepam (2 mg/kg), imipramine (15 mg/kg), Bj-PRO-7a (71, 213 or 426 nmol/kg), pirenzepine (852 nmol/kg), alpha-methyl-DL-Tyrosine (200 mg/kg), or chlorpromazine (2 mg/kg), and underwent elevated plus maze, open field, and forced swimming tests. The heptapeptide promoted anxiolytic and antidepressant-like effects and increased locomotion/exploration. These effects of Bj-PRO-7a seem to be dependent on M1R activation and dopaminergic receptors and rely on catecholaminergic pathways.
Monoaminergic system is implicated in the antidepressant-like effect of hyperoside and protocatechuic acid isolated from Impatiens glandulifera Royle in mice.[Pubmed:31077758]
Neurochem Int. 2019 Sep;128:206-214.
We have recently demonstrated that the hydroethanolic extracts of Impatiens glandulifera Royle (Balsaminaceae) have antianxiety effect in mice. The present study was aimed to investigate an antidepressant activity of hyperoside (HYP) and protocatechuic acid (PCA), two polyphenols isolated from the aerial parts of this plant, using the forced swimming test (FST) and tail suspension test (TST) in mice. The implication of the monoaminergic system in this effect was assessed and brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) expression was measured. At doses 1.875, 3.75 and 7.5mg/kg, HYP and PCA significantly reduced immobility in the FST and TST, without affecting locomotor activity of mice. Pretreatment with p-chlorophenylalanine (PCPA 100mg/kg, a serotonin synthesis inhibitor) or alpha-methyl-DL-Tyrosine (AMPT 100mg/kg, a catecholamine synthesis inhibitor) was able to prevent antidepressant-like effect of HYP and PCA (3.75mg/kg). Sub-effective doses of fluoxetine (5mg/kg) or reboxetine (2mg/kg) were capable of potentiating the effect of a sub-effective dose of HYP (0.94mg/kg) in the FST. Co-administration of sub-effective dose of PCA (0.94mg/kg) and reboxetine (2mg/kg) resulted in reducing immobility in the FST. The antidepressant-like effect of HYP and PCA was also prevented by the administration of sulpiride (50mg/kg), a D2 antagonist. In addition, HYP (3.75 and 7.5mg/kg) and PCA (7.5mg/kg) improved the expression of hippocampal BDNF of mice subjected to TST. Altogether, our findings suggest that HYP and PCA exert antidepressant-like effects in mice, which was possibly mediated by monoaminergic system and the upregulation of BDNF level.
Low-cost LED-based Photo-CIDNP Enables Biocompatible Hyperpolarization of (19) F for NMR and MRI at 7 T and 4.7 T.[Pubmed:29944199]
Chemphyschem. 2018 Oct 5;19(19):2453-2456.
Substrates containing (19) F can serve as background-free reporter molecules for NMR and MRI. However, in vivo applications are still limited due to the lower signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) when compared with (1) H NMR. Although hyperpolarization can increase the SNR, to date, only photo-chemically induced dynamic nuclear polarization (photo-CIDNP) allows for hyperpolarization without harmful metal catalysts. Photo-CIDNP was shown to significantly enhance (19) F NMR signals of 3-fluoro-DL-Tyrosine in aqueous solution using flavins as photosensitizers. However, lasers were used for photoexcitation, which is expensive and requires appropriate protection procedures in a medical or lab environment. Herein, we report (19) F MR hyperpolarization at 4.7 T and 7 T with a biocompatible system using a low-cost and easy-to-handle LED-based set-up. First hyperpolarized (19) F MR images could be acquired, because photo-CIDNP enabled repetitive hyperpolarization without adding new substrates.
Anxiolytic- and antidepressant-like activities of a methanolic extract of Morinda citrifolia Linn. (noni) fruit in mice: Involvement of benzodiazepine-GABAAergic, serotonergic and adrenergic systems.[Pubmed:29217165]
Biomed Pharmacother. 2017 Dec;96:944-952.
This study presents anxiolytic- and antidepressant-like effects of a methanolic extract of Morinda citrifolia Linn. (noni) fruit (MMC) in well-established mouse models of anxiety and depression. The administration of MMC (1 g/kg, p.o.) and diazepam (1 mg/kg, i.p.) significantly attenuated anxiety-like behaviour in mice by increasing the percentage of time spent and number of entries in the open arms in the elevated plus maze (EPM), and significantly enhanced the exploration in the light box in the light/dark test (LDT). The pre-treatment with flumazenil (6 mg/kg, i.p.) or bicuculline (3 mg/kg, i.p.) or WAY 100635 (1 mg/kg, i.p.) antagonized the anxiolytic-like effect elicited by MMC (1 g/kg, p.o.). These results suggest the possible involvement of benzodiazepine-GABAAergic and serotonergic mechanisms in the anxiolytic-like effect of noni fruit. Meanwhile, in the antidepressant study, the administration of MMC (0.5 and 0.75 g/kg, p.o.) and desipramine (30 mg/kg, i.p.) significantly reduced the duration of immobility in the tail suspension test (TST). Furthermore, pre-treatment of mice with 4-chloro-DL-phenylalanine methyl ester hydrochloride (PCPA; 100 mg/kg, i.p., an inhibitor of serotonin synthesis) for four consecutive days or a single dose of WAY 100635 (1 mg/kg, i.p., 5HT1A receptor antagonist) or alpha-methyl-DL-Tyrosine (AMPT; 100 mg/kg, i.p., an inhibitor of noradrenaline synthesis) significantly reversed the anti-immobility effect of MMC (0.5 g/kg, p.o.) in TST by indicating the specific involvement of the serotonergic and noradrenergic systems in the antidepressant-like effect of noni fruit. Taken together, these findings suggest that MMC has both anxiolytic- and antidepressant-like activities to be resorted as a valuable alternative therapy for comorbid anxiety and depressive conditions.
Monitoring In Vivo Changes in Tonic Extracellular Dopamine Level by Charge-Balancing Multiple Waveform Fast-Scan Cyclic Voltammetry.[Pubmed:27774784]
Anal Chem. 2016 Nov 15;88(22):10962-10970.
Dopamine (DA) modulates central neuronal activity through both phasic (second to second) and tonic (minutes to hours) terminal release. Conventional fast-scan cyclic voltammetry (FSCV), in combination with carbon fiber microelectrodes, has been used to measure phasic DA release in vivo by adopting a background subtraction procedure to remove background capacitive currents. However, measuring tonic changes in DA concentrations using conventional FSCV has been difficult because background capacitive currents are inherently unstable over long recording periods. To measure tonic changes in DA concentrations over several hours, we applied a novel charge-balancing multiple waveform FSCV (CBM-FSCV), combined with a dual background subtraction technique, to minimize temporal variations in background capacitive currents. Using this method, in vitro, charge variations from a reference time point were nearly zero for 48 h, whereas with conventional background subtraction, charge variations progressively increased. CBM-FSCV also demonstrated a high selectivity against 3,4-dihydroxyphenylacetic acid and ascorbic acid, two major chemical interferents in the brain, yielding a sensitivity of 85.40 +/- 14.30 nA/muM and limit of detection of 5.8 +/- 0.9 nM for DA while maintaining selectivity. Recorded in vivo by CBM-FSCV, pharmacological inhibition of DA reuptake (nomifensine) resulted in a 235 +/- 60 nM increase in tonic extracellular DA concentrations, while inhibition of DA synthesis (alpha-methyl-DL-Tyrosine) resulted in a 72.5 +/- 4.8 nM decrease in DA concentrations over a 2 h period. This study showed that CBM-FSCV may serve as a unique voltammetric technique to monitor relatively slow changes in tonic extracellular DA concentrations in vivo over a prolonged time period.
[Catalytic properties of aminoacylase of strain Rhodococcus armeniensis AM6.1].[Pubmed:29509381]
Prikl Biokhim Mikrobiol. 2016 May-Jun;52(3):272-8.
Studies of substrate specificity revealed that the D-aminoacylase of Rhodococcus armeniensis AM6.1 strain exhibits absolute stereospecificity to the D-stereoisomers of N-acetyl-amino acids. The enzyme is the most active reacted with N-acetyl-D-methionine, as well as with aromatic and hydrophobic N-acetylamino acids and interacts weakly with the basic substrates. It is practically not reacted with acidic and hydrophilic N-acetyl-amino acids. Michaelis constants (K m) and maximum reaction velocities (V max) were calculated, using linear regression analysis, for the following substrates: N-acetyl-D-methionine, N-acetyl-D-alanine, N-acetyl-D-phenylalanine, N-acetyl-D-tyrosine, N-acetyl-D-valine, N-acetyl-D-oxyvaline, N-acetyl- D-leucine. Substrate inhibition of D-aminoacylase was displayed with N-acetyl-D-leucine (K s = 35.5 +/- 28.3 mM) and N-acetyl-DL-Tyrosine (K s = 15.8 +/- 4.5 mM). Competitive inhibition of the enzyme with product-acetic acid (K i = 104.7 +/- 21.7 mM, K m = 2.5 +/- 0.5 mM, V max = 25.1 +/- 1.5 U/mg) was observed.
Silica-based polypeptide-monolithic stationary phase for hydrophilic chromatography and chiral separation.[Pubmed:27083263]
J Chromatogr A. 2016 May 13;1446:125-33.
Glutathione (GSH)-, somatostatin acetate (ST)- and ovomucoid (OV)-functionalized silica-monolithic stationary phases were designed and synthesized for HILIC and chiral separation using capillary electrochromatography (CEC). GSH, ST and OV were covalently incorporated into the silica skeleton via the epoxy ring-opening reaction between their amino groups and the glycidyl moiety in gamma-glycidoxypropyltrimethoxysilane (GPTMS) together with polycondensation and copolymerization of tetramethyloxysilane and GPTMS. Not only could the direction and electroosmotic flow magnitude on the prepared GSH-, ST- and OV-silica hybrid monolithic stationary phases be controlled by the pH of the mobile phase, but also a typical HILIC behavior was observed so that the nucleotides and HPLC peptide standard mixture could be baseline separated using an aqueous mobile phase without any acetonitrile during CEC. Moreover, the prepared monolithic columns had a chiral separation ability to separate dl-amino acids. The OV-silica hybrid monolithic column was most effective in chiral separation and could separate dl-glutamic acid (Glu) (the resolution R=1.07), DL-Tyrosine (Tyr) (1.57) and dl-histidine (His) (1.06). Importantly, the chiral separation ability of the GSH-silica hybrid monolithic column could be remarkably enhanced when using gold nanoparticles (AuNPs) to fabricate an AuNP-mediated GSH-AuNP-GSH-silica hybrid monolithic column. The R of dl-Glu, dl-Tyr and dl-His reached 1.19, 1.60 and 2.03. This monolithic column was thus applied to separate drug enantiomers, and quantitative separation of all four R/S drug enantiomers were achieved with R ranging from 4.36 to 5.64. These peptide- and protein-silica monolithic stationary phases with typical HILIC separation behavior and chiral separation ability implied their promise for the analysis of not only the future metabolic studies, but also drug enantiomers recognition.
Water-compatible molecularly imprinted polymers for selective solid phase extraction of dencichine from the aqueous extract of Panax notoginseng.[Pubmed:26680322]
J Chromatogr B Analyt Technol Biomed Life Sci. 2016 Jan 1;1008:225-233.
Specific molecularly imprinted polymers for dencichine were developed for the first time in this study by the bulk polymerization using phenylpyruvic acid and DL-Tyrosine as multi-templates. The photographs confirmed that molecularly imprinted polymers prepared using N,N'-methylene diacrylamide as cross-linker and glycol dimethyl ether as porogen displayed excellent hydrophilicity. Selectivity, adsorption isotherm and adsorption kinetics were investigated. The sample loading-washing-eluting solvent was optimized to evaluate the property of molecularly imprinted solid phase extract. Compared with LC/WCX-SPE, water-compatible molecularly imprinted solid phase extraction displayed more excellent specific adsorption performance. The extracted dencichine from Panax notoginseng with the purity of 98.5% and the average recovery of 85.6% (n=3) was obtained.
Dopamine modulates hemocyte phagocytosis via a D1-like receptor in the rice stem borer, Chilo suppressalis.[Pubmed:26179416]
Sci Rep. 2015 Jul 16;5:12247.
Dopamine (DA) is a signal moiety bridging the nervous and immune systems. DA dysregulation is linked to serious human diseases, including addiction, schizophrenia, and Parkinson's disease. However, DA actions in the immune system remain incompletely understood. In this study, we found that DA modulates insect hemocyte phagocytosis using hemocytes prepared from the rice stem borer (RSB), Chilo suppressalis. We investigated whether insect hemocytes are capable of de novo DA production. Here we show that exposing hemocytes to lipopolysaccharide (LPS) led to induction of DA-generating enzymes. Exogenous DA induced rapid phosphorylation of extracellular signal-regulated kinase (ERK) in naive hemocytes. Activation of ERK was inhibited by preincubating with a DOP1 receptor antagonist. Thus, DA signaling via the DOP1 receptor may contribute to early hemocyte activation. DA synthesized and released from hemocytes may act in an autocrine mechanism to stimulate or maintain phagocytic activity. Consistent with this hypothesis, we found that inhibition of DA synthesis with alpha-methyl-DL-Tyrosine methyl ester hydrochloride or blockage of DOP1 receptor with antagonist SCH23390 impaired hemocyte phagocytosis. Topical DA application also significantly decreased RSB mortality following challenge with the insect pathogenic fungus, Beauveria bassiana. We infer that a DA-dependent signaling system operates in hemocytes to mediate phagocytotic functions.
Validated chiral high performance liquid chromatography separation method and simulation studies of dipeptides on amylose chiral column.[Pubmed:26122854]
J Chromatogr A. 2015 Aug 7;1406:201-9.
Chiral resolution of dl-alanine-DL-Tyrosine and dl-leucine-dl-phenylalanine dipeptides was achieved on AmyCoat-RP column. The mobile phase used for dl-alanine-DL-Tyrosine was acetonitrile-ammonium acetate (10mM, pH 6.0) [50:50, v/v]. It was acetonitrile-methanol-ammonium acetate (10mM; pH adjusted to 4.5 with glacial acetic acid) [50:20:30, v/v] for dl-leucine-dl-phenylalanine. The flow rate of the mobile phases was 0.8mL/min with UV detection at 275nm. The values of retention factors for ll-, dd-, dl- and ld-stereomers of dl-alanine-DL-Tyrosine were 1.71, 2.86, 5.43 and 9.42, respectively. The values of separation and resolution factors were 1.67, 1.90 and 1.73 and 2.88, 6.43 and 7.90, respectively. Similarly, these values for dl-leucine-dl-phenylalanine stereomers were 1.50, 2.88, 3.50 and 4.07 (retention factors), 1.92, 1.22 and 1.62 (separation factors) and 2.67, 1.55 and 2.30 (resolution factors). The limits of detections and quantitation were ranged from 2.03 to 6.40 and 6.79 to 21.30mug/mL, respectively. The modeling studies were in agreement with the elution orders. The mechanism of chiral recognition was established by modeling and chromatographic studies. It was observed that hydrogen bondings and pi-pi interactions are the major forces for chiral separation.
Analgesic Effects of Toad Cake and Toad-cake-containing Herbal Drugs: Analgesic effects of toad cake.[Pubmed:25780693]
J Pharmacopuncture. 2014 Mar;17(1):74-9.
OBJECTIVES: This study was conducted to clarify the analgesic effect of toad cake and toad-cake-containing herbal drugs. METHODS: We counted the writhing response of mice after the intraperitoneal administration of acetic acid as a nociceptive pain model and the withdrawal response after the plantar surface stimulation of the hind paw induced by partial sciatic nerve ligation of the mice as a neuropathic pain model to investigate the analgesic effect of toad cake and toad-cake-containing herbal drugs. A co-treatment study with serotonin biosynthesis inhibitory drug 4-chloro- DL-phenylalanine methyl ester hydrochloride (PCPA), the catecholamine biosynthesis inhibitory drug alpha-methyl- DL-Tyrosine methyl ester hydrochloride (AMPT) or the opioid receptor antagonist naloxone hydrochloride was also conducted. RESULTS: Analgesic effects in a mouse model of nociceptive pain and neuropathic pain were shown by oral administration of toad cake and toad-cake-containing herbal drugs. The effects of toad cake and toad-cake-containing herbal drugs disappeared upon co-treatment with PCPA, but not with AMPT or naloxone in the nociceptive pain model; the analgesic effect of toad-cake-containing herbal drugs also disappeared upon co-treatment with PCPA in the neuropathic pain model. CONCLUSION: Toad cake and toad-cake-containing herbal drugs have potential for the treatments of nociceptive pain and of neuropathic pain, such as post-herpetic neuralgia, trigeminal neuralgia, diabetic neuralgia, and postoperative or posttraumatic pain, by activation of the central serotonin nervous system.
"Green" synthesis of unnatural poly(Amino Acid)s with Zwitterionic character and pH-responsive solution behavior, mediated by linear-dendritic laccase complexes.[Pubmed:25325886]
Biomacromolecules. 2014 Nov 10;15(11):4082-95.
This article describes the enzyme-catalyzed "green" synthesis of an unnatural poly(amino acid). DL-Tyrosine was polymerized under environmentally friendly conditions using linear-dendritic laccase complexes as initiators and water as solvent. The influence of the dendron generation in the linear-dendritic copolymers, the monomer concentration, and time and temperature on the polymer yields and molecular masses was investigated. Depending on the reaction conditions poly(tyrosine) with molecular mass (Mw) up to 82 kDa could be obtained in yields ranging between 45 and 69%. It was found that the linear-dendritic laccase complexes can induce further chain growth upon addition of fresh monomer to the preformed poly(tyrosine) in a fashion resembling the classic "living" polymerization. The structure of the poly(tyrosine) was investigated by NMR, FT-IR, and MALDI-TOF and it was discovered that the polymer chains consist of phenol repeating units linked together by C-C and C-O bonds randomly distributed along the backbone of the polymers. The materials formed are completely water-soluble and behave as typical poly(zwitterions) changing charge and size with the medium pH. DLS measurements reveal that the zeta potential of the polymers can vary between +15 mV at pH 1.2 with hydrodynamic diameter (Dh) = 6.7 nm to -35 mV at pH 11.8 and Dh = 10 nm. The isoelectric point was found at pH = 2.3-2.6, where Dh of the polymer is at the minimum (2.4 nm).
Fine refinement of solid state structure of racemic form of phospho-tyrosine employing NMR Crystallography approach.[Pubmed:25240460]
Solid State Nucl Magn Reson. 2015 Feb;65:2-11.
We present step by step facets important in NMR Crystallography strategy employing O-phospho-DL-Tyrosine as model sample. The significance of three major techniques being components of this approach: solid state NMR (SS NMR), X-ray diffraction of powdered sample (PXRD) and theoretical calculations (Gauge Invariant Projector Augmented Wave; GIPAW) is discussed. Each experimental technique provides different set of structural constraints. From the PXRD measurement the size of the unit cell, space group and roughly refined molecular structure are established. SS NMR provides information about content of crystallographic asymmetric unit, local geometry, molecular motion in the crystal lattice and hydrogen bonding pattern. GIPAW calculations are employed for validation of quality of elucidation and fine refinement of structure. Crystal and molecular structure of O-phospho-DL-Tyrosine solved by NMR Crystallography is deposited at Cambridge Crystallographic Data Center under number CCDC 1005924.
Preparation and characterization of a polystyrene/bovine serum albumin nanoparticle-coated capillary for chiral separation using open-tubular capillary electrochromatography.[Pubmed:23463447]
Electrophoresis. 2013 May;34(9-10):1339-42.
Polystyrene (PS) nanoparticles coated by BSA, hereafter denoted as PS/BSA, were prepared and chemically immobilized for the first time onto a capillary inner wall for open-tubular CEC (OTCEC). EOF and scanning electron micrography were used to characterize the prepared nanoparticle-coated capillaries. To investigate the performance of the prepared columns in OTCEC, chiral separation of d,l-tryptophan (dl-Trp) was performed in monolayer BSA-modified capillary and PS/BSA nanoparticle-coated columns. The results indicated that the nanoparticle-modified column afforded a higher resolution compared with the monolayer type. Rapid enantioseparation of dl-Trp (within 3 min) was achieved with the PS/BSA-immobilized column using an electroosmotic pump-assisted CEC. Enantiomer separations of other compounds like DL-Tyrosine and warfarin were also achieved with the column. Besides, run-to-run and column-to-column repeatabilities of the PS/BSA-coated column in the chiral separation were systematically introduced.


