DCEBIOActivates Cl- conductance and hKCa3.1 channels CAS# 60563-36-2 |
- Imatinib Mesylate (STI571)
Catalog No.:BCC1115
CAS No.:220127-57-1
- Sunitinib malate
Catalog No.:BCC3664
CAS No.:341031-54-7
- Pazopanib (GW-786034)
Catalog No.:BCC1286
CAS No.:444731-52-6
- Nintedanib (BIBF 1120)
Catalog No.:BCC3661
CAS No.:656247-17-5
- Regorafenib
Catalog No.:BCC3646
CAS No.:755037-03-7
- Amuvatinib (MP-470, HPK 56)
Catalog No.:BCC2258
CAS No.:850879-09-3
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 60563-36-2 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 656765 | Appearance | Powder |
| Formula | C9H8Cl2N2O | M.Wt | 231.08 |
| Type of Compound | N/A | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Solubility | Soluble to 100 mM in DMSO and to 100 mM in ethanol | ||
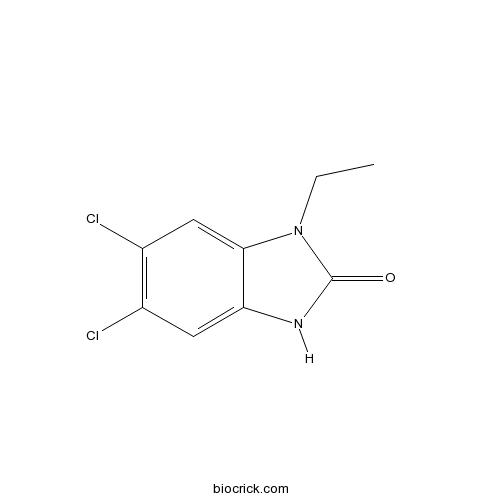
| Chemical Name | 5,6-dichloro-3-ethyl-1H-benzimidazol-2-one | ||
| SMILES | CCN1C2=CC(=C(C=C2NC1=O)Cl)Cl | ||
| Standard InChIKey | LKHRMULASXZCLG-UHFFFAOYSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C9H8Cl2N2O/c1-2-13-8-4-6(11)5(10)3-7(8)12-9(13)14/h3-4H,2H2,1H3,(H,12,14) | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | Stimulates Cl- secretion via the activation of hKCa3.1 (IK1) potassium channels and an apical Cl- conductance carried by the CFTR channel. More potent than its analog 1-EBIO. |

DCEBIO Dilution Calculator

DCEBIO Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 4.3275 mL | 21.6375 mL | 43.2751 mL | 86.5501 mL | 108.1876 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.8655 mL | 4.3275 mL | 8.655 mL | 17.31 mL | 21.6375 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.4328 mL | 2.1638 mL | 4.3275 mL | 8.655 mL | 10.8188 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0866 mL | 0.4328 mL | 0.8655 mL | 1.731 mL | 2.1638 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0433 mL | 0.2164 mL | 0.4328 mL | 0.8655 mL | 1.0819 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
- P1075
Catalog No.:BCC7027
CAS No.:60559-98-0
- 1-Acetyltagitinin A
Catalog No.:BCN4119
CAS No.:60547-63-9
- Gomisin D
Catalog No.:BCN2268
CAS No.:60546-10-3
- Olsalazine Sodium
Catalog No.:BCC3829
CAS No.:6054-98-4
- Braylin
Catalog No.:BCN4118
CAS No.:6054-10-0
- Methyloleoside
Catalog No.:BCN8079
CAS No.:60539-23-3
- H-D-Thr-OMe.HCl
Catalog No.:BCC2675
CAS No.:60538-15-0
- Zimelidine dihydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC7173
CAS No.:60525-15-7
- 5,6-Dihydropyridin-2(1H)-one
Catalog No.:BCN4013
CAS No.:6052-73-9
- Serpentinic acid
Catalog No.:BCN4616
CAS No.:605-14-1
- Pifithrin-β
Catalog No.:BCC5503
CAS No.:60477-34-1
- Cytisine Hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCN8133
CAS No.:6047-01-4
- Tirandamycin B
Catalog No.:BCN1862
CAS No.:60587-14-6
- Pamabrom
Catalog No.:BCC1835
CAS No.:606-04-2
- 2,4'-Dihydroxybenzophenone
Catalog No.:BCN3358
CAS No.:606-12-2
- Toyocamycin
Catalog No.:BCC8047
CAS No.:606-58-6
- Cinnabarinic acid
Catalog No.:BCC7865
CAS No.:606-59-7
- Homopterocarpin
Catalog No.:BCN4615
CAS No.:606-91-7
- MK-0773
Catalog No.:BCC1754
CAS No.:606101-58-0
- Momor-cerebroside I
Catalog No.:BCN4120
CAS No.:606125-07-9
- AZD6244 (Selumetinib)
Catalog No.:BCC3624
CAS No.:606143-52-6
- MEK162 (ARRY-162, ARRY-438162)
Catalog No.:BCC1148
CAS No.:606143-89-9
- Bifonazole
Catalog No.:BCC4766
CAS No.:60628-96-8
- Danaidone
Catalog No.:BCN1966
CAS No.:6064-85-3
DCEBIO-mediated dilations are attenuated in the female rat middle cerebral artery.[Pubmed:17308435]
J Vasc Res. 2007;44(3):169-74.
BACKGROUND: Unlike in peripheral vessels, the endothelium-derived hyperpolarizing factor (EDHF)-mediated component to P2Y(2) receptor-mediated dilations is significantly attenuated in the middle cerebral artery (MCA) of female rats compared to male rats. One aspect to the EDHF phenomenon is activation of the intermediate calcium-sensitive potassium (IK(Ca)) channels located on the endothelium. In an attempt to pinpoint the site along the EDHF pathway that is compromised in females, we tested the hypothesis that direct activation of IK(Ca) channels with DCEBIO would elicit attenuated hyperpolarization in the endothelium and smooth muscle of females compared to males. METHODS: Inhibitors of nitric oxide synthase and cyclooxygenase were present throughout all experiments. Vessel diameter changes were assessed in pressurized and luminally perfused MCAs. Membrane potential changes in the endothelium and smooth muscle were measured using the perforated patch clamp method and sharp electrodes, respectively. RESULTS AND CONCLUSIONS: The maximum vasodilation to 3 x 10(-4)M DCEBIO was significantly reduced in females (37 +/- 9%) compared to intact males (70 +/- 4%). Endothelial cell hyperpolarization to DCEBIO was similar in both males and females. Smooth muscle cell hyperpolarization was attenuated in females (2 +/- 1 mV) compared to males (15 +/- 3 mV). Taken together, our data suggest that the transfer of hyperpolarization from the endothelium to the smooth muscle is impeded in the female rat MCA.
DCEBIO facilitates myogenic differentiation via intermediate conductance Ca(2+) activated K(+) channel activation in C2C12 myoblasts.[Pubmed:28302447]
J Pharmacol Sci. 2017 Apr;133(4):276-279.
Membrane hyperpolarization is suggested to be a trigger for skeletal muscle differentiation. We investigated whether DCEBIO, an opener of the small/intermediate conductance Ca(2+) activated K(+) (SKCa/IKCa) channels, increase myogenic differentiation in C2C12 skeletal myoblasts. DCEBIO significantly increased myotube formation, protein expression level of myosin heavy chain II, and mRNA expression level of myogenin in C2C12 myoblasts cultured in differentiation medium. DCEBIO induced myotube formation and hyperpolarization were reduced by the IKCa channel blocker TRAM-34, but not by the SKCa channel blocker apamin. These findings show that DCEBIO increases myogenic differentiation by activating IKCa channels.
DCEBIO stimulates Cl- secretion in the mouse jejunum.[Pubmed:16135545]
Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2006 Jan;290(1):C152-64.
We investigated the effects of 5,6-dichloro-1-ethyl-1,3-dihydro-2H-benzimidazol-2-one(DCEBIO) on the Cl- secretory response of the mouse jejunum using the Ussing short-circuit current (Isc) technique. DCEBIO stimulated a concentration-dependent, sustained increase in Isc (EC50 41 +/- 1 microM). Pretreating tissues with 0.25 microM forskolin reduced the concentration-dependent increase in Isc by DCEBIO and increased the EC50 (53 +/- 5 microM). Bumetanide blocked (82 +/- 5%) the DCEBIO-stimulated Isc consistent with Cl- secretion. DCEBIO was a more potent stimulator of Cl- secretion than its parent molecule, 1-ethyl-2-benzimidazolinone. Glibenclamide or NPPB reduced the DCEBIO-stimulated Isc by >80% indicating the participation of CFTR in the DCEBIO-stimulated Isc response. Clotrimazole reduced DCEBIO-stimulated Isc by 67 +/- 15%, suggesting the participation of the intermediate conductance Ca2+-activated K+ channel (IKCa) in the DCEBIO-activated Isc response. In the presence of maximum forskolin (10 microM), the DCEBIO response was reduced and biphasic, reaching a peak response of the change in Isc of 43 +/- 5 microA/cm2 and then falling to a steady-state response of 17 +/- 10 microA/cm2 compared with DCEBIO control tissues (61 +/- 6 microA/cm2). The forskolin-stimulated Isc in the presence of DCEBIO was reduced compared with forskolin control tissues. Similar results were observed with DCEBIO and 8-BrcAMP where adenylate cyclase was bypassed. H89, a PKA inhibitor, reduced the DCEBIO-activated Isc, providing evidence that DCEBIO increased Cl- secretion via a cAMP/PKA-dependent manner. These data suggest that DCEBIO stimulates Cl- secretion of the mouse jejunum and that DCEBIO targets components of the Cl- secretory mechanism.
Benzimidazolone activators of chloride secretion: potential therapeutics for cystic fibrosis and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease.[Pubmed:11160649]
J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2001 Feb;296(2):600-11.
The diseases of cystic fibrosis (CF) and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) are characterized by mucus-congested airways. Agents that stimulate the secretion of Cl- are anticipated to facilitate mucociliary clearance and thus be of benefit in the treatment of CF and COPD. Recently 1-EBIO (1-ethyl-2-benzimidazolinone or 1-ethyl-1,3-dihydro-2H-benzimidazol-2-one) was shown to stimulate chloride secretion albeit at relatively high concentrations (0.6-1 mM). The studies reported here were undertaken to develop a more potent benzimidazolone. Structure activity studies with 30 benzimidazolone derivatives revealed that ethyl and hydrogen groups at the 1 and 3 nitrogen positions, respectively, were critical for the activation of hIK1 K+ channels and that other alkyl groups were not tolerated at these positions without some loss in potency. Substitutions at the 5 and 6 positions improved the potency of 1-EBIO. Compared with 1-EBIO, the most potent of these derivatives, DCEBIO (5,6-dichloro-1-ethyl-1,3-dihydro-2H-benzimidazol-2-one) was severalfold better in a 86Rb+ uptake assay, 20-fold better in short circuit current measurements on T84 monolayers, and 100-fold better in patch-clamp assays of hIK1 activity. Short circuit current studies revealed DCEBIO stimulates Cl- secretion via the activation of hIK1 K+ channels and the activation of an apical membrane Cl- conductance. The improved potency of DCEBIO strengthens the possibility that compounds in this class may be of therapeutic benefit in the treatment of CF and COPD.


