Crategolic acidCAS# 4373-41-5 |
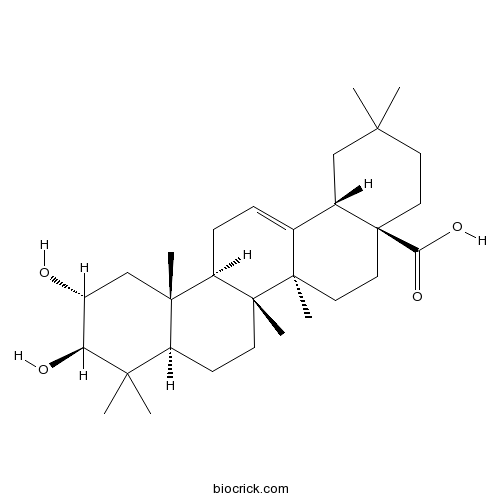
- 2,3-Dihydroxy-12-oleanen-28-oic acid
Catalog No.:BCN5145
CAS No.:26563-68-8
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 4373-41-5 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 73659 | Appearance | White powder |
| Formula | C30H48O4 | M.Wt | 472.7 |
| Type of Compound | Triterpenoids | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Synonyms | Crategolic acid; 2α-Hydroxyoleanolic acid | ||
| Solubility | DMSO : 100 mg/mL (211.55 mM; Need ultrasonic) H2O : < 0.1 mg/mL (insoluble) | ||
| Chemical Name | (4aS,6aR,6aS,6bR,8aR,10R,11R,12aR,14bS)-10,11-dihydroxy-2,2,6a,6b,9,9,12a-heptamethyl-1,3,4,5,6,6a,7,8,8a,10,11,12,13,14b-tetradecahydropicene-4a-carboxylic acid | ||
| SMILES | CC1(CCC2(CCC3(C(=CCC4C3(CCC5C4(CC(C(C5(C)C)O)O)C)C)C2C1)C)C(=O)O)C | ||
| Standard InChIKey | MDZKJHQSJHYOHJ-LLICELPBSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C30H48O4/c1-25(2)12-14-30(24(33)34)15-13-28(6)18(19(30)16-25)8-9-22-27(5)17-20(31)23(32)26(3,4)21(27)10-11-29(22,28)7/h8,19-23,31-32H,9-17H2,1-7H3,(H,33,34)/t19-,20+,21-,22+,23-,27-,28+,29+,30-/m0/s1 | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | Crategolic acid(Maslinic acid) has neuroprotective, anti-inflammatory, anti- osteoporosis, cytotoxic and antiviral activities, it suppresses RANKL-induced osteoclastogenesis through NF-κB and MAPK/AP-1 signaling pathways , and has beneficial effects on hypoxic neurons by suppressing iNOS activation.Crategolic acid as a feed additive to stimulate growth and hepatic protein-turnover rates in rainbow trout ( Onchorhynchus mykiss ). |
| Targets | TNF-α | NF-kB | p65 | COX | c-Myc | Survivin | Bcl-2/Bax | MMP(e.g.TIMP) | VEGFR | HIV | AP-1 | Src | Caspase | NOS | NO |
| In vitro | Studies on differentiation-inducing activities of triterpenes.[Pubmed: 1606636]Chem Pharm Bull (Tokyo). 1992 Feb;40(2):401-5.Differentiation-inducing activity of over 180 extracts of crude drugs and plants was tested using mouse myeloid leukemia cell line (M1). Solution- and solid-phase synthesis and anti-HIV activity of maslinic acid derivatives containing amino acids and peptides.[Pubmed: 19135380 ]Bioorg Med Chem. 2009 Feb 1;17(3):1139-45.
Maslinic acid suppresses osteoclastogenesis and prevents ovariectomy-induced bone loss by regulating RANKL-mediated NF-κB and MAPK signaling pathways.[Pubmed: 20814972 ]J Bone Miner Res. 2011 Mar;26(3):644-56.Activation of NF-κB and MAPK/activator protein 1 (AP-1) signaling pathways by receptor activator NF-κB ligand (RANKL) is essential for osteoclast activity. Targeting NF-κB and MAPK/AP-1 signaling to modulate osteoclast activity has been a promising strategy for osteoclast-related diseases. |
| Kinase Assay | Maslinic acid potentiates the anti-tumor activity of tumor necrosis factor α by inhibiting NF-κB signaling pathway[Pubmed: 20367887]Mol. Cancer, 2010, 9(1):1-13.Tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNFalpha) has been used to treat certain tumors in clinic trials. However, the curative effect of TNFalpha has been undermined by the induced-NF-kappaB activation in many types of tumor. Maslinic acid (Crategolic acid,MA),a pharmacological safe natural product, has been known for its important effects as anti-oxidant, anti-inflammatory, and anti-viral activities. The aim of this study was to determine whether MA potentiates the anti-tumor activity of TNFalpha though the regulation of NF-kappaB activation.
|
| Cell Research | Anti-inflammatory effects of maslinic acid, a natural triterpene, in cultured cortical astrocytes via suppression of nuclear factor-kappa B.[Pubmed: 21970807 ]Maslinic acid, a natural triterpenoid compound from Olea europaea, protects cortical neurons against oxygen-glucose deprivation-induced injury.[Pubmed: 21839077]Eur J Pharmacol. 2011 Nov 16;670(1):148-53.Maslinic acid(Crategolic acid) is a triterpenoid compound present in plants of Olea europaea. This compound has been reported to have potent antioxidant, anti-cancer, anti-HIV and anti-inflammatory activities. Eur J Pharmacol. 2011 Dec 15;672(1-3):169-74.Maslinic acid (Crategolic acid,2-α, 3-β-dihydroxyolean-12-en-28-oic acid) is a natural triterpenoid compound from Olea europaea. This compound prevents oxidative stress and pro-inflammatory cytokine generation in vitro. |
| Animal Research | Maslinic acid as a feed additive to stimulate growth and hepatic protein-turnover rates in rainbow trout (Onchorhynchus mykiss).[Pubmed: 16934535 ]Comp Biochem Physiol C Toxicol Pharmacol. 2006 Oct;144(2):130-40.Maslinic acid (Crategolic acid) is a triterpene present in a considerable proportion in solid residues from olive-oil production. |

Crategolic acid Dilution Calculator

Crategolic acid Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 2.1155 mL | 10.5775 mL | 21.1551 mL | 42.3101 mL | 52.8877 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.4231 mL | 2.1155 mL | 4.231 mL | 8.462 mL | 10.5775 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.2116 mL | 1.0578 mL | 2.1155 mL | 4.231 mL | 5.2888 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0423 mL | 0.2116 mL | 0.4231 mL | 0.8462 mL | 1.0578 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0212 mL | 0.1058 mL | 0.2116 mL | 0.4231 mL | 0.5289 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
Maslinic acid can inhibit the DNA-binding activity of NF-κB p65 and abolish the phosphorylation of IκB-α, which is required for p65 activation
In Vitro:Maslinic acid (MA) inhibits LPS-induced NF-κB translocation to nucleus and phosphorylation of IκB-α. Maslinic acid has also been reported to suppress NF-κB regulated osteoclastogenesis in bone marrow monocytes and inhibit TNF-α-induced NF-κB activity and its downstream genes’ expression in pancreatic cancer cells. To confirm if the anti-inflammatory effects of olive pomace extracts (OPEs) inRAW264.7 cells can be attributed to Maslinic acid, dose-dependence experiments determined the effective concentration of Maslinic acid to be 10-20 μM. 20 μM Maslinic acid significantly suppresses TNF-α production and inhibits IL-1, IL-6, and COX-2 mRNA expression in RAW 264.7 cell. Maslinic acid (at 10 and 20 μM) significantly suppresses the DNA-binding activity of NF-κB p65 in LPS-induced RAW 264.7 cells. Pretreatment with Maslinic acid significantly reduces the LPS-induced phosphorylation of IκB-α[1].
In Vivo:Paw swelling is alleviated when mice are administered with 200 mg/kg Maslinic acid (MA), significantly suppressing inflammation, compared to the carrageenan induced control group, 4 h after λ-carrageenan injection (0.91±0.51 mm and 1.79±0.4 mm, respectively)[1].
References:
[1]. Fukumitsu S, et al. Anti-inflammatory and anti-arthritic effects of pentacyclic triterpenoids maslinic acid through NF-κB inactivation. Mol Nutr Food Res. 2016 Feb;60(2):399-409.
- Xanthinol nicotinate
Catalog No.:BCC9191
CAS No.:437-74-1
- Genkwanin
Catalog No.:BCN5488
CAS No.:437-64-9
- Gentisin
Catalog No.:BCN7518
CAS No.:437-50-3
- MRS 2365
Catalog No.:BCC5879
CAS No.:436847-09-5
- Tetrodotoxin
Catalog No.:BCN1035
CAS No.:4368-28-9
- Kobe0065
Catalog No.:BCC5290
CAS No.:436133-68-5
- JKC 363
Catalog No.:BCC6022
CAS No.:436083-30-6
- Ajmaline
Catalog No.:BCN3867
CAS No.:4360-12-7
- Fangchinoline
Catalog No.:BCN5956
CAS No.:436-77-1
- Diffractic Acid
Catalog No.:BCN8506
CAS No.:436-32-8
- (-)-Curine
Catalog No.:BCN2673
CAS No.:436-05-5
- 5-Hydroxy-9-(3,4,5-trimethoxyphenyl)-5a,6,8a,9-tetrahydro-5H-[2]benzofuro[5,6-f][1,3]benzodioxol-8-one
Catalog No.:BCC8350
CAS No.:4354-76-1
- Salinosporamide A (NPI-0052, Marizomib)
Catalog No.:BCC2094
CAS No.:437742-34-2
- H-Thr(tBu)-OH
Catalog No.:BCC3106
CAS No.:4378-13-6
- 4-(4-Aminophenyl)morpholin-3-one
Catalog No.:BCC8650
CAS No.:438056-69-0
- SMI-4a
Catalog No.:BCC2233
CAS No.:438190-29-5
- Quercetin 3,3'-dimethyl ether
Catalog No.:BCN7781
CAS No.:4382-17-6
- Dihydrorobinetin
Catalog No.:BCN5489
CAS No.:4382-33-6
- Robtin
Catalog No.:BCN5490
CAS No.:4382-34-7
- Perakine
Catalog No.:BCN5491
CAS No.:4382-56-3
- PFK-015
Catalog No.:BCC5280
CAS No.:4382-63-2
- 3(20)-Phytene-1,2-diol
Catalog No.:BCN6589
CAS No.:438536-34-6
- JIP-1 (153-163)
Catalog No.:BCC5777
CAS No.:438567-88-5
- 2-Amino-3-methylbenzoic acid
Catalog No.:BCC8528
CAS No.:4389-45-1
Maslinic acid suppresses osteoclastogenesis and prevents ovariectomy-induced bone loss by regulating RANKL-mediated NF-kappaB and MAPK signaling pathways.[Pubmed:20814972]
J Bone Miner Res. 2011 Mar;26(3):644-56.
Activation of NF-kappaB and MAPK/activator protein 1 (AP-1) signaling pathways by receptor activator NF-kappaB ligand (RANKL) is essential for osteoclast activity. Targeting NF-kappaB and MAPK/AP-1 signaling to modulate osteoclast activity has been a promising strategy for osteoclast-related diseases. In this study we examined the effects of maslinic acid (MA), a pentacyclic triterpene acid that is widely present in dietary plants, on RANKL-induced osteoclastogenesis, osteoclast function, and signaling pathways by in vitro and in vivo assay systems. In mouse bone marrow monocytes (BMMs) and RAW264.7 cells, MA inhibited RANKL-induced osteoclastogenesis in a dose-dependent manner within nongrowth inhibitory concentration, and MA decreased osteoclastogenesis-related marker gene expression, including TRACP, MMP9, c-Src, CTR, and cathepsin K. Specifically, MA suppressed osteoclastogenesis and actin ring formation at early stage. In ovariectomized mice, administration of MA prevented ovariectomy-induced bone loss by inhibiting osteoclast activity. At molecular levels, MA abrogated the phosphorylation of MAPKs and AP-1 activity, inhibited the IkappaBalpha phosphorylation and degradation, blocked NF-kappaB/p65 phosphorylation, nuclear translocation, and DNA-binding activity by downregulating RANK expression and blocking RANK interaction with TRAF6. Together our data demonstrate that MA suppresses RANKL-induced osteoclastogenesis through NF-kappaB and MAPK/AP-1 signaling pathways and that MA is a promising agent in the treatment of osteoclast-related diseases such as osteoporosis.
A New HPLC-MS Method for Measuring Maslinic Acid and Oleanolic Acid in HT29 and HepG2 Human Cancer Cells.[Pubmed:26370984]
Int J Mol Sci. 2015 Sep 9;16(9):21681-94.
Maslinic acid (MA) and oleanolic acid (OA), the main triterpenic acids present in olive, have important properties for health and disease prevention. MA selectively inhibits cell proliferation of the HT29 human colon-cancer cell line by inducing selective apoptosis. For measuring the MA and OA concentration inside the cell and in the culture medium, a new HPLC-MS procedure has been developed. With this method, a determination of the amount of MA and OA incorporated into HT29 and HepG2 human cancer-cell lines incubated with different concentrations of MA corresponding to 50% growth inhibitory concentration (IC50), IC50/2, IC50/4, and IC50/8 has been made. The results demonstrate that this method is appropriate for determining the MA and OA concentration in different types of cultured cells and reveals the specific dynamics of entry of MA into HT29 and HepG2 cells.
Maslinic acid potentiates the anti-tumor activity of tumor necrosis factor alpha by inhibiting NF-kappaB signaling pathway.[Pubmed:20367887]
Mol Cancer. 2010 Apr 6;9:73.
BACKGROUND: Tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNFalpha) has been used to treat certain tumors in clinic trials. However, the curative effect of TNFalpha has been undermined by the induced-NF-kappaB activation in many types of tumor. Maslinic acid (MA), a pharmacological safe natural product, has been known for its important effects as anti-oxidant, anti-inflammatory, and anti-viral activities. The aim of this study was to determine whether MA potentiates the anti-tumor activity of TNFalpha though the regulation of NF-kappaB activation. RESULTS: In this study, we demonstrate that MA significantly enhanced TNFalpha-induced inhibition of pancreatic cancer cell proliferation, invasion, and potentiated TNFalpha-induced cell apoptosis by suppressing TNFalpha-induced NF-kappaB activation in a dose- and time-dependent manner. Addition of MA inhibited TNFalpha-induced IkappaBalpha degradation, p65 phosphorylation, and nuclear translocation. Furthermore, MA decreased the expression levels of NF-kappaB-regulated genes, including genes involved in tumor cell proliferation (Cyclin D1, COX-2 and c-Myc), apoptosis (Survivin, Bcl-2, Bcl-xl, XIAP, IAP-1), invasion (MMP-9 and ICAM-1), and angiogenesis (VEGF). In athymic nu/nu mouse model, we further demonstrated that MA significantly suppressed pancreatic tumor growth, induced tumor apoptosis, and inhibited NF-kappaB-regulated anti-apoptotic gene expression, such as Survivin and Bcl-xl. CONCLUSIONS: Our data demonstrate that MA can potentiate the anti-tumor activities of TNFalpha and inhibit pancreatic tumor growth and invasion by activating caspase-dependent apoptotic pathway and by suppressing NF-kappaB activation and its downstream gene expression. Therefore, MA together with TNFalpha could be new promising agents in the treatment of pancreatic cancer.
Maslinic acid, a natural triterpenoid compound from Olea europaea, protects cortical neurons against oxygen-glucose deprivation-induced injury.[Pubmed:21839077]
Eur J Pharmacol. 2011 Nov 16;670(1):148-53.
Maslinic acid is a triterpenoid compound present in plants of Olea europaea. This compound has been reported to have potent antioxidant, anti-cancer, anti-HIV and anti-inflammatory activities. In this study, we investigated the neuroprotective effect of maslinic acid and its mechanism of action. With presence or absence of maslinic acid, cortical neurons were subjected to 1h of oxygen-glucose deprivation and 24h of reoxygenation. Cell injury was determined by lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) measurement and 3-(4,5-dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2, 5-diphenyl-tetrazolium bromide (MTT) assay. Neuronal apoptosis was evaluated by flow cytometry assay, caspase-3 expression/activity, caspase-9 activity and Bcl-2/Bax ratio. Nitric Oxide (NO) production and inducible nitric oxide synthase (iNOS) expression were also detected. Results showed that maslinic acid dose-dependently ameliorated neuron injury and apoptosis. Maslinic acid treatment normalized the caspase expression/activation and increased the Bcl-2/Bax ratio. In addition, maslinic acid inhibited oxygen-glucose deprivation-induced NO production and iNOS expression. These results indicated that maslinic acid has beneficial effects on hypoxic neurons by suppressing iNOS activation, which may, in turn, provide neuroprotection.
Maslinic acid as a feed additive to stimulate growth and hepatic protein-turnover rates in rainbow trout (Onchorhynchus mykiss).[Pubmed:16934535]
Comp Biochem Physiol C Toxicol Pharmacol. 2006 Oct;144(2):130-40.
Maslinic acid is a triterpene present in a considerable proportion in solid residues from olive-oil production. In the present work the effects of maslinic acid on growth, protein-turnover rates and nucleic-acid concentration on liver were investigated in the rainbow trout. Five groups of 120 fish of a mean body mass of 20 g were fed for 225 days with diets containing 0, 1, 5, 25 and 250 mg of maslinic acid per kg diet. At the end of the experiment, whole-body and liver weight and growth rate of trout fed with maslinic acid were higher than controls. The highest weight increase was registered for the group fed 250 mg kg(-1), representing a 29% increase over controls. The total hepatic DNA or liver cell hyperplasia levels in trout fed with 25 and 250 mg of maslinic acid kg(-1) were 37% and 68% higher than controls. Also in these same groups of trout, fractional and absolute hepatic protein-synthesis rates were significantly higher than in control, and significant increments in hepatic protein-synthesis efficiency and protein-synthesis capacity were reported. In close agreement with these results, microscopy studies showed that trout fed on 25 and 250 mg kg(-1) hepatocytes appeared to be more compact, with a larger rough-endoplasmic reticulum and larger glycogen stores than controls. These results suggest that maslinic acid can act as a growth factor when added to trout diet.
Anti-inflammatory effects of maslinic acid, a natural triterpene, in cultured cortical astrocytes via suppression of nuclear factor-kappa B.[Pubmed:21970807]
Eur J Pharmacol. 2011 Dec 15;672(1-3):169-74.
Maslinic acid (2-alpha, 3-beta-dihydroxyolean-12-en-28-oic acid) is a natural triterpenoid compound from Olea europaea. This compound prevents oxidative stress and pro-inflammatory cytokine generation in vitro. This study was planned to investigate the anti-inflammatory effects of maslinic acid in central nervous system by using rat astrocyte cultures stimulated with lipopolysaccharide (LPS). We evaluated different proteins implicated in the nuclear factor kappa B (NF-kappaB) signal transducer pathway employing Western blot and quantitative real time PCR techniques. Results demonstrated that maslinic acid treatment exerted potent anti-inflammatory action by inhibiting the production of Nitric Oxide and tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNF-alpha). Western blot analysis showed that maslinic acid treatment attenuated LPS-induced translocation of NF-kappaB p65 subunit to the nucleus and prevented LPS-induced IkappaBalpha phosphorylation in a concentration-dependent manner, Moreover, maslinic acid significantly suppressed the expression of cyclooxygenase 2 (COX-2) and inducible nitric oxide synthase (iNOS) at protein and mRNA levels. These results suggest that maslinic acid can potentially reduce neuroinflammation by inhibiting NF-kappaB signal transducer pathway in cultured cortical astrocytes.
Studies on differentiation-inducing activities of triterpenes.[Pubmed:1606636]
Chem Pharm Bull (Tokyo). 1992 Feb;40(2):401-5.
Differentiation-inducing activity of over 180 extracts of crude drugs and plants was tested using mouse myeloid leukemia cell line (M1). The methanol extracts of clove (Syzygium aromaticum Merrill et Perry, Myrtaceae) showed remarkable induction of differentiation of M1 cells into macrophage-like cells. From the extract, oleanolic acid (1) and Crategolic acid (2) were isolated as the active components. We also tested other triterpenes, such as oleananes, ursanes and dammaranes, to investigate the structure-activity relationship. Some triterpene aglycones showed differentiation-inducing activity, but triterpene glycosides showed little activity. Furthermore, the differentiation-inducing activity of these triterpene compounds was tested against human acute promyelocytic leukemia cell line (HL-60).
Solution- and solid-phase synthesis and anti-HIV activity of maslinic acid derivatives containing amino acids and peptides.[Pubmed:19135380]
Bioorg Med Chem. 2009 Feb 1;17(3):1139-45.
Maslinic acid (1) has been coupled at C-28 with several alpha- and omega-amino acids by using solution- and solid-phase synthetic procedures. Twelve derivatives (2-13) with a single amino acid residue were prepared in solution phase, whereas a dipeptide (14), a tripeptide (15), and a series of conjugate dipeptides (16-24) were synthesized in solid phase. The anti-HIV activity of these compounds was assessed on MT-2 cells infected with viral clones carrying the luciferase gene as a reporter. While in maslinic acid (1) were present both cytotoxic and antiviral activities, only the derivatives 13 and 24 showed anti-HIV-1 activity and therefore represent a novel class of anti-HIV-1 compounds.


