Crassicauline ACAS# 79592-91-9 |
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 79592-91-9 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 157539 | Appearance | Cryst. |
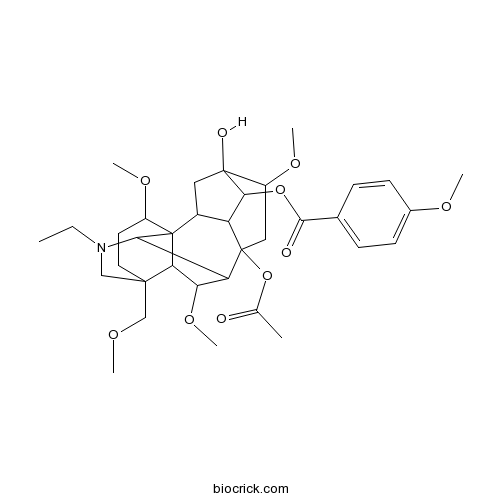
| Formula | C35H49NO10 | M.Wt | 643.77 |
| Type of Compound | Alkaloids | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Solubility | Soluble in Chloroform,Dichloromethane,Ethyl Acetate,DMSO,Acetone,etc. | ||
| SMILES | CCN1CC2(CCC(C34C2C(C(C31)C5(CC(C6(CC4C5C6OC(=O)C7=CC=C(C=C7)OC)O)OC)OC(=O)C)OC)OC)COC | ||
| Standard InChIKey | GAZDXIGXYWVWQX-UHFFFAOYSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C35H49NO10/c1-8-36-17-32(18-40-3)14-13-23(42-5)35-22-15-33(39)24(43-6)16-34(46-19(2)37,26(29(35)36)27(44-7)28(32)35)25(22)30(33)45-31(38)20-9-11-21(41-4)12-10-20/h9-12,22-30,39H,8,13-18H2,1-7H3 | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | Crassicauline A, a diterpenoid alkaloid in Aconitum herbs, is an analgesic drug clinically used in China. Crassicauline A possesses feeding deterrent activity against T. castaneum adults, with the EC(50) value of 1134.5 ppm. |
| In vitro | Measurement of yunaconitine and crassicauline A in small-volume blood serum samples by LC-MS/MS: tracing of aconite poisoning in clinical diagnosis.[Pubmed: 22841113]Talanta. 2012 Aug 15;97:491-8.Aconite poisoning is one of the most serious types of herb-related medical emergencies. In Hong Kong, many if not most of these poisoning cases are due to confusion in herbal species; that is, the wrong herbs are used in prescriptions. Such human errors, while inevitable perhaps, can be serious, and sometimes fatal. The chemical components responsible for aconite poisoning are yunaconitine and Crassicauline A. |
| In vivo | Feeding deterrents from Aconitum episcopale roots against the red flour beetle, Tribolium castaneum.[Pubmed: 21417277]J Agric Food Chem. 2011 Apr 27;59(8):3701-6.The screening for insecticidal principles from several Chinese medicinal herbs showed that the ethanol extract of Aconitum episcopale roots possessed significant feeding deterrence against the red flour beetle, Tribolium castaneum . |
| Structure Identification | Chem Pharm Bull (Tokyo). 2009 Aug;57(8):801-7.Structure-analgesic activity relationship studies on the C(18)- and C(19)-diterpenoid alkaloids.[Pubmed: 19652403]For evaluation of C(18)- and C(19)-diterpenoid alkaloids as analgesics, three C(19)-diterpenoid alkaloids were isolated from the roots of Aconitum hemsleyanum var. circinatum and A. transsecutum; and twenty-five semisynthetic C(18)- or C(19)-diterpenoid alkaloids were prepared from lappaconitine, Crassicauline A or yunaconitine. |

Crassicauline A Dilution Calculator

Crassicauline A Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 1.5533 mL | 7.7667 mL | 15.5335 mL | 31.067 mL | 38.8337 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.3107 mL | 1.5533 mL | 3.1067 mL | 6.2134 mL | 7.7667 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.1553 mL | 0.7767 mL | 1.5533 mL | 3.1067 mL | 3.8834 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0311 mL | 0.1553 mL | 0.3107 mL | 0.6213 mL | 0.7767 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0155 mL | 0.0777 mL | 0.1553 mL | 0.3107 mL | 0.3883 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
- Alarelin Acetate
Catalog No.:BCC1336
CAS No.:79561-22-1
- Sertraline HCl
Catalog No.:BCC5059
CAS No.:79559-97-0
- 1,7-Diphenyl-4-hepten-3-one
Catalog No.:BCN3592
CAS No.:79559-59-4
- 5-Ethoxychelerthrine
Catalog No.:BCC8105
CAS No.:79559-55-0
- L-165041
Catalog No.:BCC1687
CAS No.:79558-09-1
- 20-HETE
Catalog No.:BCC1301
CAS No.:79551-86-3
- Stelleranol
Catalog No.:BCN8014
CAS No.:795308-62-2
- Norketamine hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC5859
CAS No.:79499-59-5
- Glaucocalyxin A
Catalog No.:BCN2353
CAS No.:79498-31-0
- 9-Oxo-10,11-dehydroageraphorone
Catalog No.:BCN4333
CAS No.:79491-71-7
- Eleutheroside D
Catalog No.:BCN5336
CAS No.:79484-75-6
- Nicaraven
Catalog No.:BCC4684
CAS No.:79455-30-4
- Linifanib (ABT-869)
Catalog No.:BCC1261
CAS No.:796967-16-3
- Levonorgestrel
Catalog No.:BCC4792
CAS No.:797-63-7
- H-Hyp(tBu)-OH
Catalog No.:BCC3249
CAS No.:79775-07-8
- Loratadine
Catalog No.:BCC1262
CAS No.:79794-75-5
- Castanospermine
Catalog No.:BCC6783
CAS No.:79831-76-8
- 1,2,3,6-Tetragalloylglucose
Catalog No.:BCN2159
CAS No.:79886-50-3
- Simvastatin
Catalog No.:BCN2569
CAS No.:79902-63-9
- Forsythoside A
Catalog No.:BCN1195
CAS No.:79916-77-1
- ML130 (Nodinitib-1)
Catalog No.:BCC4611
CAS No.:799264-47-4
- Idazoxan hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC6798
CAS No.:79944-56-2
- Boc-His(Bom)-OH
Catalog No.:BCC3400
CAS No.:79950-65-5
- Quinovic acid 3-O-beta-D-glucoside
Catalog No.:BCN4334
CAS No.:79955-41-2
Measurement of yunaconitine and crassicauline A in small-volume blood serum samples by LC-MS/MS: tracing of aconite poisoning in clinical diagnosis.[Pubmed:22841113]
Talanta. 2012 Aug 15;97:491-8.
Aconite poisoning is one of the most serious types of herb-related medical emergencies. In Hong Kong, many if not most of these poisoning cases are due to confusion in herbal species; that is, the wrong herbs are used in prescriptions. Such human errors, while inevitable perhaps, can be serious, and sometimes fatal. The chemical components responsible for aconite poisoning are yunaconitine and Crassicauline A. In the present study, a rapid and sensitive method for the screening and quantification of yunaconitine and Crassicauline A in human serum, using LC-MS/MS, was developed and validated. Methyllycaconitine was chosen as the internal standard. The limit of detection (LOD) of yunaconitine and Crassicauline A were found to be 0.022 and 0.021 ng/mL, respectively. The limit of quantification (LOQ) was 0.1 ng/mL for both yunaconitine and Crassicauline A. The recovery of yunaconitine and Crassicauline A ranged from 78.6% to 84.9% and 78.3% to 87.2%, respectively. The matrix effect of yunaconitine and Crassicauline A ranged from 110.0% to 130.4% and 121.2 to 130.0%, respectively. Both yunaconitine and Crassicauline A were stable in serum for at least 3 months at -20 degrees C, and the extracts were stable for at least 7 days. For clinical applications, serum samples of two patients confirmed to have had aconite herbs poisoning in 2008 were quantified using the developed method. The result showed that this method can be utilized in clinical routine applications. This screening method expedites the diagnosis in cases of suspected aconite poisoning, thus enabling doctors to treat the condition more quickly and effectively.
Feeding deterrents from Aconitum episcopale roots against the red flour beetle, Tribolium castaneum.[Pubmed:21417277]
J Agric Food Chem. 2011 Apr 27;59(8):3701-6.
The screening for insecticidal principles from several Chinese medicinal herbs showed that the ethanol extract of Aconitum episcopale roots possessed significant feeding deterrence against the red flour beetle, Tribolium castaneum . From the ethanol extract, six feeding deterrents were isolated by bioassay-guided fractionation. The compounds were identified as chasmanine, Crassicauline A, karacoline, sachaconitine, talatisamine, and yunaconitine from their spectroscopic data. Chasmanine, talatisamine, karacoline, and sachaconitine exhibited feeding deterrent activity against T. castaneum adults, with EC(50) values of 297.0, 342.8, 395.3, and 427.8 ppm, respectively. Yunaconitine and Crassicauline A also possessed feeding deterrent activity against T. castaneum adults, with EC(50) values of 653.4 and 1134.5 ppm, respectively.
Structure-analgesic activity relationship studies on the C(18)- and C(19)-diterpenoid alkaloids.[Pubmed:19652403]
Chem Pharm Bull (Tokyo). 2009 Aug;57(8):801-7.
For evaluation of C(18)- and C(19)-diterpenoid alkaloids as analgesics, three C(19)-diterpenoid alkaloids were isolated from the roots of Aconitum hemsleyanum var. circinatum and A. transsecutum; and twenty-five semisynthetic C(18)- or C(19)-diterpenoid alkaloids were prepared from lappaconitine, Crassicauline A or yunaconitine. In a mice acetic acid-induced abdominal constriction assay, four Crassicauline A analogs and three yunaconitine analogs exhibited good analgesic activities with 77.8-94.1% inhibition range in 0.1-10 mg/kg subcutaneous (s.c.) dose range at the point of 20 min after drug administration. Among them, 8-O-deacetyl-8-O-ethylCrassicauline A (ED(50)=0.0972 mg/kg) and 8-O-ethylyunaconitine (ED(50)=0.0591 mg/kg) were the most potent analgesics relative to the reference drugs lappaconitine (ED(50)=3.50 mg/kg) and Crassicauline A (ED(50)=0.0480 mg/kg). Analgesic activity data of these C(18)- and C(19)-diterpenoid alkaloids indicate that a tertiary amine in ring A, an acetoxyl or an ethoxyl group at C-8, an aromatic ester at C-14, and the saturation state of the ring D are important structural features necessary to the analgesic activity of the C(19)-diterpenoid alkaloids.


