CamstatinCalmodulin antagonist CAS# 1002295-95-5 |
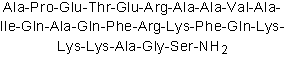
- Gatifloxacin
Catalog No.:BCC1064
CAS No.:112811-59-3
- Dexrazoxane HCl (ICRF-187, ADR-529)
Catalog No.:BCC1087
CAS No.:149003-01-0
- Doxorubicin (Adriamycin) HCl
Catalog No.:BCC1117
CAS No.:25316-40-9
- Etoposide
Catalog No.:BCC1151
CAS No.:33419-42-0
- Genistein
Catalog No.:BCN5499
CAS No.:446-72-0
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 1002295-95-5 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 90479747 | Appearance | Powder |
| Formula | C122H203N39O34 | M.Wt | 2760.19 |
| Type of Compound | N/A | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Solubility | Soluble to 1 mg/ml in water | ||
| Sequence | APETERAAVAIQAQFRKFQKKKAGS (Modifications: Ser-25 = C-terminal amide) | ||
| SMILES | CCC(C)C(C(=O)NC(CCC(=O)N)C(=O)NC(C)C(=O)NC(CCC(=O)N)C(=O)NC(CC1=CC=CC=C1)C(=O)NC(CCCNC(=N)N)C(=O)NC(CCCCN)C(=O)NC(CC2=CC=CC=C2)C(=O)NC(CCC(=O)N)C(=O)NC(CCCCN)C(=O)NC(CCCCN)C(=O)NC(CCCCN)C(=O)NC(C)C(=O)NCC(=O)NC(CO)C(=O)N)NC(=O)C(C)NC(=O)C(C(C)C)NC(=O)C(C)NC(=O)C(C)NC(=O)C(CCCNC(=N)N)NC(=O)C(CCC(=O)O)NC(=O)C(C(C)O)NC(=O)C(CCC(=O)O)NC(=O)C3CCCN3C(=O)C(C)N | ||
| Standard InChIKey | CZNWNBOOELGGSY-QCJADNLESA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C122H203N39O34/c1-12-63(4)95(159-102(177)69(10)143-117(192)94(62(2)3)158-101(176)68(9)139-99(174)66(7)141-104(179)77(38-27-55-136-121(132)133)150-111(186)82(44-49-92(168)169)155-119(194)96(70(11)163)160-113(188)83(45-50-93(170)171)153-116(191)87-40-29-57-161(87)120(195)64(5)127)118(193)154-79(41-46-88(128)164)105(180)142-67(8)100(175)145-80(42-47-89(129)165)112(187)157-84(58-71-30-15-13-16-31-71)114(189)151-78(39-28-56-137-122(134)135)108(183)148-76(37-22-26-54-126)109(184)156-85(59-72-32-17-14-18-33-72)115(190)152-81(43-48-90(130)166)110(185)149-75(36-21-25-53-125)107(182)147-74(35-20-24-52-124)106(181)146-73(34-19-23-51-123)103(178)140-65(6)98(173)138-60-91(167)144-86(61-162)97(131)172/h13-18,30-33,62-70,73-87,94-96,162-163H,12,19-29,34-61,123-127H2,1-11H3,(H2,128,164)(H2,129,165)(H2,130,166)(H2,131,172)(H,138,173)(H,139,174)(H,140,178)(H,141,179)(H,142,180)(H,143,192)(H,144,167)(H,145,175)(H,146,181)(H,147,182)(H,148,183)(H,149,185)(H,150,186)(H,151,189)(H,152,190)(H,153,191)(H,154,193)(H,155,194)(H,156,184)(H,157,187)(H,158,176)(H,159,177)(H,160,188)(H,168,169)(H,170,171)(H4,132,133,136)(H4,134,135,137)/t63-,64-,65-,66-,67-,68-,69-,70+,73-,74-,75-,76-,77-,78-,79-,80-,81-,82-,83-,84-,85-,86-,87-,94-,95-,96-/m0/s1 | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | An analog of PEP-19 with enhanced binding to and antagonism of calmodulin. |

Camstatin Dilution Calculator

Camstatin Molarity Calculator

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
- 5,5'-Dimethoxysecoisolariciresinol
Catalog No.:BCN7941
CAS No.:1002106-91-3
- 2,3-dihydroxy-3-(4-hydroxyphenyl)propanoic acid
Catalog No.:BCN1641
CAS No.:100201-57-8
- Piscidinol A
Catalog No.:BCN5818
CAS No.:100198-09-2
- MK-8033
Catalog No.:BCC1768
CAS No.:1001917-37-8
- INH6
Catalog No.:BCC5455
CAS No.:1001753-24-7
- SRT1720 HCl
Catalog No.:BCC2222
CAS No.:1001645-58-4
- BV6
Catalog No.:BCC5372
CAS No.:1001600-56-1
- 1,4,5,6-Tetrahydroxy-7-prenylxanthone
Catalog No.:BCN1642
CAS No.:1001424-68-5
- PDK1 inhibitor
Catalog No.:BCC1843
CAS No.:1001409-50-2
- VUF 8430 dihydrobromide
Catalog No.:BCC7384
CAS No.:100130-32-3
- GDC-0068 (RG7440)
Catalog No.:BCC1271
CAS No.:1001264-89-6
- GnRH Associated Peptide (GAP) (1-13), human
Catalog No.:BCC1013
CAS No.:100111-07-7
- AMG-208
Catalog No.:BCC1054
CAS No.:1002304-34-8
- Picrasidine I
Catalog No.:BCN5819
CAS No.:100234-59-1
- Picrasidine J
Catalog No.:BCN5820
CAS No.:100234-62-6
- TZ9
Catalog No.:BCC5547
CAS No.:1002789-86-7
- Irinotecan hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCN2949
CAS No.:100286-90-6
- Apiopaeonoside
Catalog No.:BCN2801
CAS No.:100291-86-9
- Pemirolast potassium
Catalog No.:BCC4532
CAS No.:100299-08-9
- L(+)-Rhamnose monohydrate
Catalog No.:BCN8368
CAS No.:10030-85-0
- Curcumenone
Catalog No.:BCN3008
CAS No.:100347-96-4
- Calcium chloride dihydrate
Catalog No.:BCC7582
CAS No.:10035-04-8
- GSK 1562590 hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC8010
CAS No.:1003878-07-6
- Sodium Picosulfate
Catalog No.:BCC4845
CAS No.:10040-45-6
A novel role for calmodulin: Ca2+-independent inhibition of type-1 inositol trisphosphate receptors.[Pubmed:9716504]
Biochem J. 1998 Sep 1;334 ( Pt 2):447-55.
Calmodulin inhibits both inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate (IP3) binding to, and IP3-evoked Ca2+ release by, cerebellar IP3 receptors [Patel, Morris, Adkins, O'Beirne and Taylor (1997) Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S.A. 94, 11627-11632]. In the present study, full-length rat type-1 and -3 IP3 receptors were expressed at high levels in insect Spodoptera frugiperda 9 cells and the effects of calmodulin were examined. In the absence of Ca2+, calmodulin caused a concentration-dependent and reversible inhibition of [3H]IP3 binding to type-1 IP3 receptors by decreasing their apparent affinity for IP3. The effect was not reproduced by high concentrations of troponin C, parvalbumin or S-100. Increasing the medium free [Ca2+] ([Ca2+]m) inhibited [3H]IP3 binding to type-1 receptors, but the further inhibition caused by a submaximal concentration of calmodulin was similar at each [Ca2+]m. In the absence of Ca2+, 125I-calmodulin bound to a single site on each type-1 receptor subunit and to an additional site in the presence of Ca2+. There was no detectable binding of 125I-calmodulin to type-3 receptors and binding of [3H]IP3 was insensitive to calmodulin at all [Ca2+]m. Both peptide and conventional Ca2+-calmodulin antagonists affected neither [3H]IP3 binding directly nor the inhibitory effect of calmodulin in the absence of Ca2+, but each caused a [Ca2+]m-dependent reversal of the inhibition of [3H]IP3 binding caused by calmodulin. Camstatin, a peptide that binds to calmodulin equally well in the presence or absence of Ca2+, reversed the inhibitory effects of calmodulin on [3H]IP3 binding at all [Ca2+]m. We conclude that calmodulin specifically inhibits [3H]IP3 binding to type-1 IP3 receptors: the first example of a protein regulated by calmodulin in an entirely Ca2+-independent manner. Inhibition of type-1 IP3 receptors by calmodulin may dynamically regulate their sensitivity to IP3 in response to the changes in cytosolic free calmodulin concentration thought to accompany stimulation of neurones.
Anti-calmodulins and tricyclic adjuvants in pain therapy block the TRPV1 channel.[Pubmed:17579717]
PLoS One. 2007 Jun 20;2(6):e545.
Ca(2+)-loaded calmodulin normally inhibits multiple Ca(2+)-channels upon dangerous elevation of intracellular Ca(2+) and protects cells from Ca(2+)-cytotoxicity, so blocking of calmodulin should theoretically lead to uncontrolled elevation of intracellular Ca(2+). Paradoxically, classical anti-psychotic, anti-calmodulin drugs were noted here to inhibit Ca(2+)-uptake via the vanilloid inducible Ca(2+)-channel/inflamatory pain receptor 1 (TRPV1), which suggests that calmodulin inhibitors may block pore formation and Ca(2+) entry. Functional assays on TRPV1 expressing cells support direct, dose-dependent inhibition of vanilloid-induced (45)Ca(2+)-uptake at microM concentrations: calmidazolium (broad range) > or = trifluoperazine (narrow range) chlorpromazine/amitriptyline>fluphenazine>>W-7 and W-13 (only partially). Most likely a short acidic domain at the pore loop of the channel orifice functions as binding site either for Ca(2+) or anti-calmodulin drugs. Camstatin, a selective peptide blocker of calmodulin, inhibits vanilloid-induced Ca(2+)-uptake in intact TRPV1(+) cells, and suggests an extracellular site of inhibition. TRPV1(+), inflammatory pain-conferring nociceptive neurons from sensory ganglia, were blocked by various anti-psychotic and anti-calmodulin drugs. Among them, calmidazolium, the most effective calmodulin agonist, blocked Ca(2+)-entry by a non-competitive kinetics, affecting the TRPV1 at a different site than the vanilloid binding pocket. Data suggest that various calmodulin antagonists dock to an extracellular site, not found in other Ca(2+)-channels. Calmodulin antagonist-evoked inhibition of TRPV1 and NMDA receptors/Ca(2+)-channels was validated by microiontophoresis of calmidazolium to laminectomised rat monitored with extracellular single unit recordings in vivo. These unexpected findings may explain empirically noted efficacy of clinical pain adjuvant therapy that justify efforts to develop hits into painkillers, selective to sensory Ca(2+)-channels but not affecting motoneurons.
The influence of phosphorylation on the activity and structure of the neuronal IQ motif protein, PEP-19.[Pubmed:16740252]
Brain Res. 2006 May 30;1092(1):16-27.
PEP-19 is a 7.6 kDa neuronally expressed polypeptide that contains a single calmodulin-binding IQ motif. The calmodulin-binding activity of several neuronal IQ motif proteins is regulated by phosphorylation of a conserved serine. We propose that the serine residue within the IQ motif of PEP-19 is phosphorylated, and that phosphorylation modifies the activity of PEP-19. Camstatin, a functionally active 25-residue fragment of PEP-19's IQ motif, binds calmodulin and inhibits neuronal nitric oxide synthase. A truncated Camstatin-in which the IQ motif serine is the only phosphorylatable residue-was screened against 42 different kinases. Truncated Camstatin is selectively phosphorylated by four isoforms of protein kinase C. Furthermore, treatment of full-length PEP-19 with PKCgamma catalyzes phosphorylation of the same serine residue. Fluorescent anisotropy shows that phosphorylation of Camstatin inhibits its binding to calmodulin. NMR solution structures indicate that both Camstatin and phospho-Camstatin exist in similar dynamic turn-like conformations. This suggests that Camstatin's greater affinity for calmodulin is due not to a change in the conformation of the phospho-peptide, but rather, to a disruption of hydrophobic interactions between phospho-Camstatin and calmodulin caused by the presence of the hydrophilic phosphate group. The H(alpha) chemical shifts and the circular dichroism spectra of the Camstatins are consistent with those of "nascent helices". We submit that PEP-19 is a PKC substrate, and that the phosphorylation state of PEP-19 may play a role in the modulation of calmodulin-dependent signaling.
Camstatins are peptide antagonists of calmodulin based upon a conserved structural motif in PEP-19, neurogranin, and neuromodulin.[Pubmed:8663125]
J Biol Chem. 1996 Jul 5;271(27):15911-7.
Unbridled increases in intracellular ionized calcium can result in neuronal damage and death. Since many of the deleterious effects of calcium are mediated by calmodulin, we have sought to identify neuronal proteins that inhibit activation of this ubiquitous protein. PEP-19 is a 7.6-kDa neuron-specific protein, which contains a motif similar to the calmodulin binding domains of neuromodulin (GAP-43) and neurogranin (RC3). Here we show that PEP-19 binds calmodulin in an analogous calcium-independent manner with an apparent Kd near 1.2 microM. Furthermore, using the calmodulin-dependent enzyme neuronal nitric oxide synthase, we demonstrate that native PEP-19 is also an antagonist of enzyme activity. Based on the PEP-19 sequence, a series of peptide calmodulin antagonists termed Camstatins were synthesized. These analogs define the minimally active domain of PEP-19 and provide a structure/activity relationship for calmodulin antagonism. There was a positive correlation between the binding affinities of the Camstatins for calmodulin and their potencies as neuronal nitric oxide synthase inhibitors. Despite the similar IQ motif in PEP-19 and neuromodulin or neurogranin, PEP-19 was not a substrate for protein kinase C. The properties of PEP-19 suggest that it could fulfill a role in neuroprotection.


