BufotenineCAS# 487-93-4 |
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 487-93-4 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 10257 | Appearance | Powder |
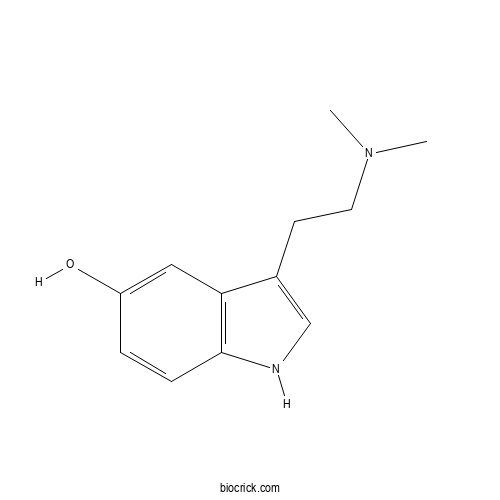
| Formula | C12H16N2O | M.Wt | 204.3 |
| Type of Compound | Alkaloids | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Solubility | Soluble in Chloroform,Dichloromethane,Ethyl Acetate,DMSO,Acetone,etc. | ||
| Chemical Name | 3-[2-(dimethylamino)ethyl]-1H-indol-5-ol | ||
| SMILES | CN(C)CCC1=CNC2=C1C=C(C=C2)O | ||
| Standard InChIKey | VTTONGPRPXSUTJ-UHFFFAOYSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C12H16N2O/c1-14(2)6-5-9-8-13-12-4-3-10(15)7-11(9)12/h3-4,7-8,13,15H,5-6H2,1-2H3 | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | Bufotenine may have hallucinogenic potential, the presence and levels of bufotenine might be useful and important markers of some psychiatric disorders. Bufotenine is able to block rabies virus infection in BHK-21 cells. | |||||

Bufotenine Dilution Calculator

Bufotenine Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 4.8948 mL | 24.4738 mL | 48.9476 mL | 97.8953 mL | 122.3691 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.979 mL | 4.8948 mL | 9.7895 mL | 19.5791 mL | 24.4738 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.4895 mL | 2.4474 mL | 4.8948 mL | 9.7895 mL | 12.2369 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0979 mL | 0.4895 mL | 0.979 mL | 1.9579 mL | 2.4474 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0489 mL | 0.2447 mL | 0.4895 mL | 0.979 mL | 1.2237 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
- Methyl benzoate
Catalog No.:BCN9900
CAS No.:93-58-3
- cis-Jasmone
Catalog No.:BCN9899
CAS No.:488-10-8
- Dihydroisoferulic acid
Catalog No.:BCN9898
CAS No.:1135-15-5
- 3',4'-Dimethoxyflavone
Catalog No.:BCN9897
CAS No.:4143-62-8
- Decanoic acid
Catalog No.:BCN9896
CAS No.:334-48-5
- 3-Octanone
Catalog No.:BCN9895
CAS No.:106-68-3
- Methyl anthranilate
Catalog No.:BCN9894
CAS No.:134-20-3
- (-)-Linalool
Catalog No.:BCN9893
CAS No.:126-91-0
- 5-Geranoxy-7-methoxycoumarin
Catalog No.:BCN9892
CAS No.:7380-39-4
- Caffeoyl alcohol
Catalog No.:BCN9891
CAS No.:3598-26-3
- Tryptamine hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCN9890
CAS No.:343-94-2
- Cinnamtannin A2
Catalog No.:BCN9889
CAS No.:86631-38-1
- 3-Methyl ellagic acid
Catalog No.:BCN9902
CAS No.:51768-38-8
- 5-Methyl-3-heptanone
Catalog No.:BCN9903
CAS No.:541-85-5
- 3-O-Acetyl 9,11-dehydro beta-boswellic acid
Catalog No.:BCN9904
CAS No.:122651-20-1
- Eupalitin
Catalog No.:BCN9905
CAS No.:29536-41-2
- Eupalitin 3-galactoside
Catalog No.:BCN9906
CAS No.:35399-32-7
- Calycopterin
Catalog No.:BCN9907
CAS No.:481-52-7
- Epoxybergamottin
Catalog No.:BCN9729
CAS No.:206978-14-5
- Corynanthine
Catalog No.:BCN9910
CAS No.:483-10-3
- 5-Methoxypiperonal
Catalog No.:BCN9911
CAS No.:5780-07-4
- (R)-O-isobutyroyllomatin
Catalog No.:BCN9912
CAS No.:440094-38-2
- Daucoidin A
Catalog No.:BCN9913
CAS No.:103629-87-4
- (-)-Sparteine
Catalog No.:BCN9914
CAS No.:90-39-1
The Psilocin (4-hydroxy-N,N-dimethyltryptamine) and Bufotenine (5-hydroxy-N,N-dimethyltryptamine) Case: Ensuring the Correct Isomer has Been Identified.[Pubmed:32374425]
J Forensic Sci. 2020 Sep;65(5):1450-1457.
Psilocin (4-hydroxy-N,N-dimethyltryptamine, 4-HO-DMT) and Bufotenine (5-hydroxy-N,N-dimethyltryptamine, 5-HO-DMT), which are both naturally occurring compounds, are classified as controlled substances in numerous countries due to their pharmacological activities and recreational usage. There are two other benzene ring regioisomers, 6-hydroxy-N,N-dimethyltryptamine (6-HO-DMT) and 7-hydroxy-N,N-dimethyltryptamine (7-HO-DMT), which are not classified by name as controlled substances, and which were synthesized for this current work. The four isomers were analyzed using routine methodologies employed by the Israel's Police Division of Identification and Forensic Science (DIFS) Laboratory, namely thin layer chromatography (TLC), Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR), and gas chromatography mass spectroscopy (GC-MS). It was found possible to differentiate the four isomers. Forensic specimens that were suspected to be psilocybe mushrooms were examined, confirming that it is now possible to unequivocally identify the presence of psilocin and rule out the presence of its other isomers.
Development and application of a strategy for analyzing eight biomarkers in human urine to verify toxic mushroom or ricinus communis ingestions by means of hydrophilic interaction LC coupled to HRMS/MS.[Pubmed:32200933]
Talanta. 2020 Jun 1;213:120847.
The analytical proof of a toxic mushroom and/or plant ingestion at an early stage of a suspected intoxication can be crucial for fast therapeutic decision making. Therefore, comprehensive analytical procedures need to be available. This study aimed to develop a strategy for the qualitative analysis of alpha- and beta-amanitin, psilocin, Bufotenine, muscarine, muscimol, ibotenic acid, and ricinine in human urine by means of hydrophilic interaction liquid chromatography-high resolution MS/MS (HILIC-HRMS/MS). Urine samples were prepared by hydrophilic-phase liquid-liquid extraction using dichloromethane and subsequent solid-phase extraction and precipitation, performed in parallel. Separation and identification of the biomarkers were achieved by HILIC using acetonitrile and methanol as main eluents and Orbitrap-based mass spectrometry, respectively. The method was validated as recommended for qualitative procedures and tests for selectivity, carryover, and extraction recoveries were included to also estimate the robustness and reproducibility of the sample preparation. Limits of identification were 1 ng/mL for alpha- and beta-amanitin, 5 ng/mL for psilocin, Bufotenine, muscarine, and ricinine, and 1500 ng/mL and 2000 ng/mL for ibotenic acid and muscimol, respectively. Using gamma-amanitin, l-tryptophan-d5, and psilocin-d10 as internal standards, compensation for variations of matrix effects was shown to be acceptable for most of the toxins. In eight urine samples obtained from intoxicated individuals, alpha- and beta-amanitin, psilocin, psilocin-O-glucuronide, muscimol, ibotenic acid, and muscarine could be identified. Moreover, psilocin-O-glucuronide and Bufotenine-O-glucuronide were found to be suitable additional targets. The analytical strategy developed was thus well suited for analyzing several biomarkers of toxic mushrooms and plants in human urine to support therapeutic decision making in a clinical toxicology setting. To our knowledge, the presented method is by far the most comprehensive approach for identification of the included biomarkers in a human matrix.
Bioactive Azepine-Indole Alkaloids from Psychotria nemorosa.[Pubmed:32150413]
J Nat Prod. 2020 Apr 24;83(4):852-863.
Phytochemical investigation of the alkaloid extract of the aerial parts of Psychotria nemorosa led to the isolation and characterization of 10 azepine-indole alkaloids, i.e., cimitrypazepine (1), fargesine (2), nemorosines A (3), and B (12), nemorosinosides A-F (4-9), as well as two beta-carboline derivatives, 10-hydroxyisodolichantoside (10) and 10-hydroxydolichantoside (11), an isoxazole alkaloid, nemorosinoside G (13), serotonin (14), Bufotenine (15), and (S)-gentianol (16). Compounds 3-13 have not yet been described. These compounds were isolated by semipreparative HPLC, and their structures were determined by means of HRMS, NMR, and ECD measurements. In addition, the monoamine oxidase-A (MAO-A), MAO-B, acetylcholinesterase (AChE), and butyrylcholinesterase (BChE) inhibitory activities were evaluated. Alkaloids 1-3 inhibited the MAO-A activity with IC50 values of 1.4, 1.4, and 0.9 muM, respectively.
Bufotenine, a tryptophan-derived alkaloid, suppresses the symptoms and increases the survival rate of rabies-infected mice: the development of a pharmacological approach for rabies treatment.[Pubmed:32071597]
J Venom Anim Toxins Incl Trop Dis. 2020 Feb 3;26:e20190050.
Background: Between 40,000-70,000 people die yearly of rabies, an incurable disease. Besides post-bite vaccination, no treatment is available for it. Methods: First, virus dilution for antiviral effects in mice was determined. Then, animals were treated as follows: control (NaCl 250 microL/animal/day); Bufotenine (0.63, 1.05 and 2.1 mg in 250 microL of NaCl/animal/day); rabies (10(-6,82)CVS dilution); and test (10(-6,82) CVS dilution and Bufotenine, in the above-mentioned doses). Animals were observed daily for 21 days or until the 3(rd) stage of rabies infection. Twitch-tension and liposome studies were applied to understand the possible interaction of Bufotenine with receptors, particularly acetylcholine. Results: Bufotenine was able to increase the survival rate of intracerebrally virus-infected mice from 15 to 40%. Bufotenine did not seem to interfere with the acetylcholine response in the skeletal muscle, indicating that its mechanism of action is not blocking the virus entrance due to nAChR antagonism. By analyzing liposomes, we could observe that Bufotenine did not passively penetrates cell membranes, indicating the necessity of complementary structures to cell penetration. Conclusions: Bufotenine is a promising candidate for drug development. After further chemical modification, it might be possible to dissociate minor side effects, increase efficiency, efficacy and pharmacokinetics, yielding a true anti-rabies drug.
The protection of indolealkylamines from LPS-induced inflammation in zebrafish.[Pubmed:31356965]
J Ethnopharmacol. 2019 Oct 28;243:112122.
ETHNOPHARMACOLOGICAL RELEVANCE: Toad skin came from Bufo bufo gargarizans Cantor and Bufo melanostictus Schneider. As the traditional Chinese medicine, it had the effect of clearing away heat and detoxification. In traditional applications, toad skin was often used for the treatment of cancer and inflammation. Total indolealkylamines (IAAs) from this medicine were proved the main compounds exert anti-inflammatory activity in our previous research. AIM OF THE STUDY: In the present study, we aimed to investigate the potential mechanism of anti-inflammatory activity of IAAs on LPS induced zebrafish. MATERIALS AND METHODS: LPS induced zebrafish was applicated as an in vivo inflammation model to clarify the structure-activity relationship of 4 major IAAs (N-methyl serotonin, Bufotenine, dehydroBufotenine and bufothionine) from toad skin. Quantitative RT-PCR was applied to detect key cytokines and members of the MyD88-dependent signaling pathway. In addition, the targeted lipidomics was conducted to find out the potential biomarkers in the inflammatory zebrafish. Network pharmacology was used to unveil the main enzymes closely related to the target lipids. RESULTS: Our results showed that the anti-inflammatory activity of free IAAs (N-methyl serotonin, Bufotenine and dehydroBufotenine) was more potent than that of combined IAAs (bufothionine). RT-PCR demonstrated that 4 IAAs exerted antiendotoxin inflammatory effect via suppressing the TLR4/MyD88/NF-kappaB and TLR4/MyD88/MAPKs signaling pathway. A total of 33 possible inflammatory biomarkers, including 14 SM, 6 Cer, 11PC and 2 GlcCer, triggered by LPS were screened out. The levels of most of candidates could be regulated toward a normal level by IAAs, especially in N-methyl serotonin and dehydroBufotenine groups. Enzymes especially LBP, PLA2, CERK, SMPD and SGMS were found closely associated with the regulation of most lipid markers. CONCLUSIONS: Overall, the mechanism underlying the anti-inflammatory activity of IAAs probably attributed to their capability to suppress NF-kappaB and MAPKs inflammatory pathway. Meanwhile, IAAs could also interfere the metabolism of SM, Cer and PC probably by regulating LBP, PLA2, CERK, SMPD and SGMS.
Chemical evidence for the use of multiple psychotropic plants in a 1,000-year-old ritual bundle from South America.[Pubmed:31061128]
Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2019 Jun 4;116(23):11207-11212.
Over several millennia, various native plant species in South America have been used for their healing and psychoactive properties. Chemical analysis of archaeological artifacts provides an opportunity to study the use of psychoactive plants in the past and to better understand ancient botanical knowledge systems. Liquid chromatography tandem mass spectrometry (LC-MS/MS) was used to analyze organic residues from a ritual bundle, radiocarbon dated to approximately 1,000 C.E., recovered from archaeological excavations in a rock shelter located in the Lipez Altiplano of southwestern Bolivia. The site is located at an elevation of approximately 3,900 m above sea level and contains evidence of intermittent human occupations during the last 4,000 years. Chemical traces of Bufotenine, dimethyltryptamine, harmine, and cocaine, including its degradation product benzoylecgonine, were identified, suggesting that at least three plants containing these compounds were part of the shamanic paraphernalia dating back 1,000 years ago, the largest number of compounds recovered from a single artifact from this area of the world, to date. This is also a documented case of a ritual bundle containing both harmine and dimethyltryptamine, the two primary ingredients of ayahuasca. The presence of multiple plants that come from disparate and distant ecological areas in South America suggests that hallucinogenic plants moved across significant distances and that an intricate botanical knowledge was intrinsic to pre-Columbian ritual practices.
Comparing the Detection of Endogenous Psychedelics in Individuals With and Without Alleged Mediumistic Experiences.[Pubmed:30241696]
Explore (NY). 2018 Nov;14(6):448-452.
CONTEXT: Mediumship is the alleged ability to communicate with deceased personalities. Previous studies have suggested that the endogenous psychotomimetic molecules Bufotenine (BT) and dimethyltryptamine (DMT) may play a role in the pathogenesis of psychotic disorders. Distortion of perceptions observed during spiritual experiences could supposedly relate to these substances. OBJECTIVE: To compare the presence of BT and DMT in human urine samples between individuals with and without mediumistic experiences. METHODS: All participants (5 from medium's group - MG and 5 from non-medium's group - CG) undertook a single night continuous 6-h urine pool collection (6:00-11:59 PM). Mediums collected urine samples in nights when they reported having experienced mediumistic communication. A sensitive high-performance liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry (HPLC-MS) assay was used. Questionnaires were used to detect common mental disorders symptoms, and to screen and quantify anomalous experiences. RESULTS: DMT was not detected in any urine specimen tested. The presence of BT detection in urine samples was greater in CG (2/5) than in MG (1/5), with no significant differences (p > 0.99). MG reported more anomalous experiences than CG (6.6+/-0.8 vs. 2.2+/-1.5, p=0.03), but there was no difference concerning their mental health. CONCLUSION: There were no differences between individuals with and without alleged mediumistic experiences concerning endogenous psychedelics. Both BT and DMT are highly sensitive to metabolism by monoamine oxidase and to N-oxidation, and do not survive in the periphery for long. Alternative strategies should be considered to further investigate the putative role of the endogenous psychedelics pathway for the spiritual experiences.
Biological Effects and Biodistribution of Bufotenine on Mice.[Pubmed:29955598]
Biomed Res Int. 2018 May 31;2018:1032638.
Bufotenine is an alkaloid derived from serotonin, structurally similar to LSD and psilocin. This molecule is able to inhibit the rabies virus infection in in vitro and in vivo models, increasing the survival rate of infected animals. Being a very promising molecule for an incurable disease and because of the fact that there is no consensus regarding its neurological effects, this study aimed to evaluate chronic treatment of Bufotenine on behavior, pathophysiology, and pharmacokinetics of mice. Animals were daily treated for 21 consecutive days with 0.63, 1.05, and 2.1 mg/animal/day Bufotenine and evaluated by open field test and physiological parameters during all the experiment. After this period, organs were collected for histopathological and biodistribution analysis. Animals treated with Bufotenine had mild behavioral alterations compared to the control group, being dose-response relationship. On the other hand, animals showed normal physiological functions and no histological alterations in the organs. With high doses, an inflammatory reaction was observed in the site of injection, but with no cellular damage. The alkaloid could be found in the heart and kidney with all doses and in the lungs and brain with higher doses. These results show that the effective dose, 0.63 mg/day, is safe to be administered in mice, since it did not cause significant effects on the animals' physiology and on the CNS. Higher doses were well tolerated, causing only mild behavioral effects. Thus, Bufotenine might be a drug prototype for rabies treatment, an incurable disease.
PH-zone-refining counter-current chromatography with a hydrophilic organic/salt-containing two-phase solvent system for preparative separation of polar alkaloids from natural products.[Pubmed:29680742]
J Chromatogr A. 2018 Jun 8;1553:1-6.
This study presents an efficient strategy based on pH-zone-refining counter-current chromatography with a hydrophilic organic/salt-containing two-phase system composed of acetonitrile, sodium chloride and water for preparative separation of polar alkaloids from natural products. Acetonitrile-sodium chloride-water system provides a wider range of polarity for polar alkaloids than classical aqueous two-phase systems. It gets rid of the effect of free hydrogen ion, strong ionic strength, hold low viscosity and the sharp retainer border could be formed easily. So acetonitrile-sodium chloride-water system showed great advantages to pH-zone-refining counter-current chromatography for polar alkaloids. The separation of polar indole alkaloids from toad venom was selected as an example to show the advantage and practicability of this strategy. An optimized acetonitrile-sodium chloride-water (54%:5%:41%, w%) system was applied in this study, where 10mM triethylamine (TEA) as the retainer and 15mM hydrochloric acid (HCl) as the eluter were added. As a result, three polar indole alkaloids, including 19mg of serotonin, 45mg of 5-Hydroxy-N'-methyl tryptamine, 33mg of Bufotenine were simultaneously separated from 500mg of 5% ethanol elution fraction of toad venom on macroporous resin chromatography, with the purity of 91.3%, 97.5% and 89.4%, respectively. Their structures were identified by spectroscopic analysis.


