Bleomycin SulfateChemotherapy agent, induces DNA strand break CAS# 9041-93-4 |
- CX-5461
Catalog No.:BCC3700
CAS No.:1138549-36-6
- Gemcitabine HCl
Catalog No.:BCC1076
CAS No.:122111-03-9
- Fludarabine
Catalog No.:BCC2518
CAS No.:21679-14-1
- Carboplatin
Catalog No.:BCC1170
CAS No.:41575-94-4
- Epirubicin HCl
Catalog No.:BCC1192
CAS No.:56390-09-1
- Fludarabine Phosphate (Fludara)
Catalog No.:BCC3681
CAS No.:75607-67-9
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 9041-93-4 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 72466 | Appearance | Powder |
| Formula | C55H85N17O25S4 | M.Wt | 1512.6 |
| Type of Compound | N/A | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Solubility | H2O : 255 mg/mL (168.58 mM; Need ultrasonic and warming) DMSO : 16.67 mg/mL (11.02 mM; Need ultrasonic) DMF : < 1 mg/mL (insoluble) | ||
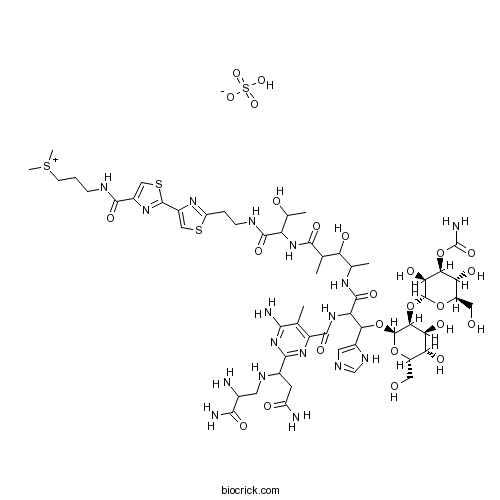
| Chemical Name | 3-[[2-[2-[2-[[2-[[4-[[2-[[6-amino-2-[3-amino-1-[(2,3-diamino-3-oxopropyl)amino]-3-oxopropyl]-5-methylpyrimidine-4-carbonyl]amino]-3-[(2R,3S,4S,5S,6S)-3-[(2R,3S,4S,5R,6R)-4-carbamoyloxy-3,5-dihydroxy-6-(hydroxymethyl)oxan-2-yl]oxy-4,5-dihydroxy-6-(hydroxymethyl)oxan-2-yl]oxy-3-(1H-imidazol-5-yl)propanoyl]amino]-3-hydroxy-2-methylpentanoyl]amino]-3-hydroxybutanoyl]amino]ethyl]-1,3-thiazol-4-yl]-1,3-thiazole-4-carbonyl]amino]propyl-dimethylsulfanium;hydrogen sulfate | ||
| SMILES | CC1=C(N=C(N=C1N)C(CC(=O)N)NCC(C(=O)N)N)C(=O)NC(C(C2=CN=CN2)OC3C(C(C(C(O3)CO)O)O)OC4C(C(C(C(O4)CO)O)OC(=O)N)O)C(=O)NC(C)C(C(C)C(=O)NC(C(C)O)C(=O)NCCC5=NC(=CS5)C6=NC(=CS6)C(=O)NCCC[S+](C)C)O.OS(=O)(=O)[O-] | ||
| Standard InChIKey | WUIABRMSWOKTOF-OCBSMOPSSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C55H83N17O21S3.H2O4S/c1-20-33(69-46(72-44(20)58)25(12-31(57)76)64-13-24(56)45(59)82)50(86)71-35(41(26-14-61-19-65-26)91-54-43(39(80)37(78)29(15-73)90-54)92-53-40(81)42(93-55(60)88)38(79)30(16-74)89-53)51(87)66-22(3)36(77)21(2)47(83)70-34(23(4)75)49(85)63-10-8-32-67-28(18-94-32)52-68-27(17-95-52)48(84)62-9-7-11-96(5)6;1-5(2,3)4/h14,17-19,21-25,29-30,34-43,53-54,64,73-75,77-81H,7-13,15-16,56H2,1-6H3,(H13-,57,58,59,60,61,62,63,65,66,69,70,71,72,76,82,83,84,85,86,87,88);(H2,1,2,3,4)/t21?,22?,23?,24?,25?,29-,30+,34?,35?,36?,37+,38+,39-,40-,41?,42-,43-,53+,54-;/m0./s1 | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | Bleomycin Sulfate is a glycopeptide antibiotic and an anticancer agent for squamous cell carcinomas (SCC) with IC50 of 4 nM in UT-SCC-19A cells. | |||||
| Targets | UT-SCC-129 cells | |||||
| IC50 | 4 nM | |||||

Bleomycin Sulfate Dilution Calculator

Bleomycin Sulfate Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 0.6611 mL | 3.3056 mL | 6.6111 mL | 13.2223 mL | 16.5278 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.1322 mL | 0.6611 mL | 1.3222 mL | 2.6445 mL | 3.3056 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.0661 mL | 0.3306 mL | 0.6611 mL | 1.3222 mL | 1.6528 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0132 mL | 0.0661 mL | 0.1322 mL | 0.2644 mL | 0.3306 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0066 mL | 0.0331 mL | 0.0661 mL | 0.1322 mL | 0.1653 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
Bleomycin sulfate (BLENOXANE®) is a mixture of cytotoxic glycopeptide antibiotics produced by a strain of streptomyces verticillus. This component is known to cause single and/ or double-stranded breaks in DNA through approximating metals and coordinate dioxygen to generate the active species.
Bleomycin sulfate treatment resulted in elongation of E. coli cells and enlargement of HeLa cells through inhibiting DNA and protein syntheses [1].
This component is widely used in the treatment of Hodgkin's lymphoma in combination with doxorubicin, testicular cancer, squamous cell carcinomas, pulmonary fiborosis as well as in the treatment of plantar warts. For instance, Bleomycin sulfate was also shown to have
moderate to marked effects upon Rous sarcoma virus induced mouse ascites sarcoma, particularly when F1 hybrid mice were employed as host animals [2]. In addition, recent studies support the role of the proinflammatory cytokines IL-18 and IL-1beta in the mechanism of bleomycin sulfate –induced human and mouse lung injury [3].
References:
1. Suzuki H, Nagai K, Yamaki H, Tanaka N, Umezawa H. Mechanism of action of bleomycin. Studies with the growing culture of bacterial and tumor cells. J Antibiot (Tokyo) 1968,21:379-386.
2. Takeuchi M, Yamamoto T. Effects of bleomycin on transplantable mouse tumors. J Antibiot (Tokyo) 1968,21:631-637.
3. Hoshino T, Okamoto M, Sakazaki Y, Kato S, Young HA, Aizawa H. Role of proinflammatory cytokines IL-18 and IL-1beta in bleomycin-induced lung injury in humans and mice. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol 2009,41:661-670.
- (-)-Indolactam V
Catalog No.:BCC7735
CAS No.:90365-57-4
- Ligularizine
Catalog No.:BCN2091
CAS No.:90364-92-4
- Neoligularidine
Catalog No.:BCN2137
CAS No.:90364-91-3
- Ligularinine
Catalog No.:BCN2117
CAS No.:90364-90-2
- Pitolisant hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC1863
CAS No.:903576-44-3
- Bicalutamide
Catalog No.:BCC2481
CAS No.:90357-06-5
- 7-Xylosyltaxol B
Catalog No.:BCN7675
CAS No.:90352-19-5
- 10-O-Coumaroyl-10-O-deacetylasperuloside
Catalog No.:BCN7614
CAS No.:903519-82-4
- Seneciphyllinine
Catalog No.:BCN2132
CAS No.:90341-45-0
- Shizukolidol
Catalog No.:BCN4444
CAS No.:90332-92-6
- 7-Xylosyltaxol
Catalog No.:BCN5341
CAS No.:90332-66-4
- 7-Xylosyl-10-deacetyltaxol C
Catalog No.:BCN7663
CAS No.:90332-65-3
- Neochamaejasmine B
Catalog No.:BCN3130
CAS No.:90411-12-4
- Neochamaejasmine A
Catalog No.:BCN3129
CAS No.:90411-13-5
- NU 1025
Catalog No.:BCC2454
CAS No.:90417-38-2
- Daturataturin A aglycone
Catalog No.:BCN4445
CAS No.:904665-71-0
- Daturametelin I
Catalog No.:BCN4446
CAS No.:904667-65-8
- Maoyerabdosin
Catalog No.:BCN3944
CAS No.:90468-72-7
- Valeriotetrate C
Catalog No.:BCN6753
CAS No.:904891-20-9
- Cryptochlorogenic acid
Catalog No.:BCN5907
CAS No.:905-99-7
- TMCB
Catalog No.:BCC7745
CAS No.:905105-89-7
- GDC-0879
Catalog No.:BCC2482
CAS No.:905281-76-7
- 2,5-dihydroxy-3-methoxy-Acetophenone
Catalog No.:BCN3780
CAS No.:90536-47-3
- Ethyl 2,4,6-trihydroxybenzoate
Catalog No.:BCN3997
CAS No.:90536-74-6
Effect of local bleomycin sulfate application on seroma formation in a rat mastectomy and axillary lymph node dissection model.[Pubmed:24231620]
Eur J Pharmacol. 2014 Jan 15;723:375-80.
Seroma formation is one of the most common complications following breast cancer surgery. It may lead to delay of adjuvant therapies and increasement of therapy costs. Bleomycin Sulfate is a sclerosing antibiotic with antineoplastic efficacy. It is locally used in the treatment of pleural effusion. The present study aimed to investigate seroma-reducing effect of local bleomycin application after mastectomy. Sixteen female Wistar Albino rats were used in this study. The rats were divided into two equal groups. Under general anesthesia all rats underwent unilateral mastectomy as definition by Harada. Serum physiologic was applied to animals in Group 1 (control group) and bleomycin to Group 2. Mastectomized localization was explored on the 10th day postoperatively. Seroma and tissue samples were obtained from axilla and thoracic wall for histopathological examination. The amount of seroma was significantly lower in the bleomycin group as compared to the control group (P=0.002). Fibrosis, PNL infiltration and the number of fibroblasts were significantly higher in the bleomycin group. No difference was identified between the groups in terms of angiogenesis, edema, congestion, and monocyte, lymphocyte and macrophage infiltration. Local Bleomycin Sulfate application might be a therapeutic option in patients with seroma formation, as well as in the patients with malignant pleural effusion. Nonetheless, further studies that compare the efficacy and adverse effects (benefit-to-harm ratio) of Bleomycin Sulfate are needed.
Comparative analysis of intralesional sclerotherapy with sodium tetradecyl sulfate versus bleomycin in the management of low flow craniofacial soft tissue vascular lesions.[Pubmed:23449774]
J Maxillofac Oral Surg. 2012 Mar;11(1):13-20.
OBJECTIVE: Comparison of the efficacy of bleomycin over sodium tetradecyl sulfate (STS) when given intralesionally in the treatment of oral and maxillofacial venous malformation. METHODS: 16 patients with venous malformation in craniofacial region were randomly divided into two groups of eight. Group 1 was given intralesional injection of bleomycin and group 2 was injected with STS. All the cases were evaluated for a minimum period of two and a maximum of 3 years. RESULTS: Efficacy of bleomycin was found to be superior to STS, when used as intralesional sclerotherapic agent. Most of the vascular lesions of group 1 resolved after first dose giving a cure rate of 87.5% and no recurrence was observed. Group 2 patients however, required 4-6, a mean of five repeated dosage of intralesional STS before their lesions started to resolve and three patients reported with recurrence within 2 years, giving an overall effective response rate of 62.5%. CONCLUSION: Bleomycin under selected conditions appears to be an excellent therapy for treating soft tissue vascular lesions of low flow nature in craniofacial region. Predictable results were obtained with a high success rate. No systemic or pulmonary complications occurred.
The effect of chemical therapy with bleomycin sulfate on the functional parameters of the endocrine pancreas.[Pubmed:19454822]
JOP. 2009 May 18;10(3):292-8.
OBJECTIVE: The objective of the present study was to evaluate the effect of Bleomycin Sulfate on parameters related to the functionality of pancreatic tissue, with emphasis on the glucose tolerance test, insulin tolerance test, insulinemia and static secretion of insulin as well as the insulin receptor, and PKA, PKC and GLUT2 concentrations in the pancreatic islets. DESIGN: Twenty-four male rats were divided into 2 groups: control and treated with bleomycin (2.5 mg/kg, intratracheal mode). After 7 days, the animals were euthanized and the analyses were carried out. STATISTICS: The normality and the homoscedasticity of the data distribution were tested and ANOVA was applied. The Tukey post hoc test followed ANOVA for the comparison of the static insulin secretion test at different glucose concentrations. RESULTS: In the glucose tolerance test, the bleomycin group showed a larger area (17,306+/-539 mg/dL x 60min) than that of the control group (9,151+/-517 mg/dL x 60 min) and in the insulin tolerance test, there was a greater percentage fall in glycemia (8.08+/-0.56%) in the bleomycin than in the control group (3.87+/-1.14%). The bleomycin group also presented a reduction in insulin secretion and an increase in plasmatic insulin concentration in the static insulin secretion test. With respect to the concentrations of the insulin receptor, GLUT2, PKC and PKA in the pancreatic islets of the bleomycin group, there was an increase in GLUT2 (48.4%) and PKC (70.8%) and a reduction in PKA (38.5%). CONCLUSION: During treatment with bleomycin, innumerable chemical-metabolic alterations were unleashed in the tissues which were not primary targets of the chemical therapy and which could compromise the homeostasis of the systems taking part in the glycemic adjustment, predisposing the organism to the development of a pre-diabetic pattern whose degree of incidence or reversibility is still unknown to the scientific community.
Mycobacterium tuberculosis Ku can bind to nuclear DNA damage and sensitize mammalian cells to bleomycin sulfate.[Pubmed:21811007]
Mutagenesis. 2011 Nov;26(6):795-803.
Radiotherapy and chemotherapy are effective cancer treatments due to their ability to generate DNA damage. The major lethal lesion is the DNA double-strand break (DSB). Human cells predominantly repair DSBs by non-homologous end joining (NHEJ), which requires Ku70, Ku80, DNA-PKcs, DNA ligase IV and accessory proteins. Repair is initiated by the binding of the Ku heterodimer at the ends of the DSB and this recruits DNA-PKcs, which initiates damage signaling and functions in repair. NHEJ also exists in certain types of bacteria that have dormant phases in their life cycle. The Mycobacterium tuberculosis Ku (Mt-Ku) resembles the DNA-binding domain of human Ku but does not have the N- and C-terminal domains of Ku70/80 that have been implicated in binding mammalian NHEJ repair proteins. The aim of this work was to determine whether Mt-Ku could be used as a tool to bind DSBs in mammalian cells and sensitize cells to DNA damage. We generated a fusion protein (KuEnls) of Mt-Ku, EGFP and a nuclear localization signal that is able to perform bacterial NHEJ and hence bind DSBs. Using transient transfection, we demonstrated that KuEnls is able to bind laser damage in the nucleus of Ku80-deficient cells within 10 sec and remains bound for up to 2 h. The Mt-Ku fusion protein was over-expressed in U2OS cells and this increased the sensitivity of the cells to Bleomycin Sulfate. Hydrogen peroxide and UV radiation do not predominantly produce DSBs and there was little or no change in sensitivity to these agents. Since in vitro studies were unable to detect binding of Mt-Ku to DNA-PKcs or human Ku70/80, this work suggests that KuEnls sensitizes cells by binding DSBs, preventing human NHEJ. This study indicates that blocking or decreasing the binding of human Ku to DSBs could be a method for enhancing existing cancer treatments.


