7-XylosyltaxolTaxol (Paclitaxel) derivative CAS# 90332-66-4 |
- Mc-MMAD
Catalog No.:BCC1735
CAS No.:1401963-15-2
- Docetaxel Trihydrate
Catalog No.:BCC1535
CAS No.:148408-66-6
- MMAD
Catalog No.:BCC1774
CAS No.:203849-91-6
- Colchicine
Catalog No.:BCN6271
CAS No.:64-86-8
- D-64131
Catalog No.:BCC1510
CAS No.:74588-78-6
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

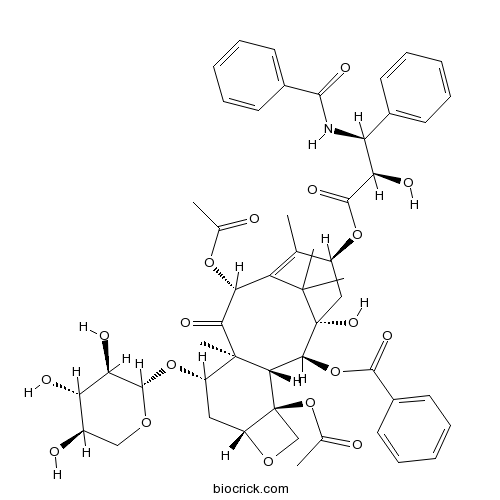
| Cas No. | 90332-66-4 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 11094265 | Appearance | Yellow powder |
| Formula | C52H59NO18 | M.Wt | 986.0 |
| Type of Compound | Diterpenoids | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Synonyms | 7-Xylosylpaclitaxel; Taxol-7-xyloside | ||
| Solubility | Soluble in Chloroform,Dichloromethane,Ethyl Acetate,DMSO,Acetone,etc. | ||
| Chemical Name | [(1S,2S,3R,4S,7R,9S,10S,12R,15S)-4,12-diacetyloxy-15-[(2R,3S)-3-benzamido-2-hydroxy-3-phenylpropanoyl]oxy-1-hydroxy-10,14,17,17-tetramethyl-11-oxo-9-[(2S,3R,4S,5R)-3,4,5-trihydroxyoxan-2-yl]oxy-6-oxatetracyclo[11.3.1.03,10.04,7]heptadec-13-en-2-yl] benzoate | ||
| SMILES | CC1=C2C(C(=O)C3(C(CC4C(C3C(C(C2(C)C)(CC1OC(=O)C(C(C5=CC=CC=C5)NC(=O)C6=CC=CC=C6)O)O)OC(=O)C7=CC=CC=C7)(CO4)OC(=O)C)OC8C(C(C(CO8)O)O)O)C)OC(=O)C | ||
| Standard InChIKey | ZVEGOBHUZTXSFK-TZIKQHFSSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C52H59NO18/c1-26-33(68-47(63)39(58)37(29-16-10-7-11-17-29)53-45(61)30-18-12-8-13-19-30)23-52(64)44(70-46(62)31-20-14-9-15-21-31)42-50(6,43(60)41(67-27(2)54)36(26)49(52,4)5)34(22-35-51(42,25-66-35)71-28(3)55)69-48-40(59)38(57)32(56)24-65-48/h7-21,32-35,37-42,44,48,56-59,64H,22-25H2,1-6H3,(H,53,61)/t32-,33+,34+,35-,37+,38+,39-,40-,41-,42+,44+,48+,50-,51+,52-/m1/s1 | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | 7-xylosyltaxol is a taxol (Paclitaxel) derivative, has antineoplastic activity. |
| In vitro | Development of an indirect competitive enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (icELISA) using highly specific monoclonal antibody against paclitaxel.[Pubmed: 23007175]J Nat Med. 2013 Jul;67(3):512-8.Paclitaxel, the major active component of the yew tree, is used as an important anti-cancer agent. |
| Structure Identification | Ying Yong Sheng Tai Xue Bao. 2012 Oct;23(10):2641-7.Content and distribution of active components in cultivated and wild Taxus chinensis var. mairei plants.[Pubmed: 23359921]Taxus chinensis var. mairei is an endemic and endangered plant species in China. The resources of T. chinensis var. mairei have been excessively exploited due to its anti-cancer potential, accordingly, the extant T. chinensis var. mairei population is decreasing. |

7-Xylosyltaxol Dilution Calculator

7-Xylosyltaxol Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 1.0142 mL | 5.071 mL | 10.142 mL | 20.284 mL | 25.355 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.2028 mL | 1.0142 mL | 2.0284 mL | 4.0568 mL | 5.071 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.1014 mL | 0.5071 mL | 1.0142 mL | 2.0284 mL | 2.5355 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0203 mL | 0.1014 mL | 0.2028 mL | 0.4057 mL | 0.5071 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0101 mL | 0.0507 mL | 0.1014 mL | 0.2028 mL | 0.2535 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
7-xylosyltaxol is a taxol (Paclitaxel) derivative. Paclitaxel is a compound extracted from the Pacific yew tree with antineoplastic activity. Paclitaxel binds to tubulin and inhibits the disassembly of microtubules, thereby resulting in the inhibition of cell division. Paclitaxel also induces apoptosis by binding to and blocking the function of the apoptosis inhibitor protein Bcl-2 (B-cell Leukemia 2). Paclitaxel inhibits DNA synthesis and stimulates the release of tumor necrosis factor-α. Paclitaxel induces apoptosis in murine mammary carcinoma MCA-4 and ovarian carcinoma OCA-1 tumors.
- 7-Xylosyl-10-deacetyltaxol C
Catalog No.:BCN7663
CAS No.:90332-65-3
- 7-Xylosyl-10-deacetyltaxol B
Catalog No.:BCN7667
CAS No.:90332-64-2
- 10-Deacetyl-7-xylosyl paclitaxel
Catalog No.:BCN2947
CAS No.:90332-63-1
- FPA 124
Catalog No.:BCC7518
CAS No.:902779-59-3
- UBP 310
Catalog No.:BCC6052
CAS No.:902464-46-4
- NVP-LCQ195
Catalog No.:BCC1816
CAS No.:902156-99-4
- AT7519 Hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC1376
CAS No.:902135-91-5
- Gossypolone
Catalog No.:BCC1375
CAS No.:4547-72-2
- GSK 5959
Catalog No.:BCC5597
CAS No.:901245-65-6
- Fostamatinib (R788)
Catalog No.:BCC5082
CAS No.:901119-35-5
- TAME
Catalog No.:BCC4367
CAS No.:901-47-3
- Rebamipide
Catalog No.:BCC4836
CAS No.:90098-04-7
- Shizukolidol
Catalog No.:BCN4444
CAS No.:90332-92-6
- Seneciphyllinine
Catalog No.:BCN2132
CAS No.:90341-45-0
- 10-O-Coumaroyl-10-O-deacetylasperuloside
Catalog No.:BCN7614
CAS No.:903519-82-4
- 7-Xylosyltaxol B
Catalog No.:BCN7675
CAS No.:90352-19-5
- Bicalutamide
Catalog No.:BCC2481
CAS No.:90357-06-5
- Pitolisant hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC1863
CAS No.:903576-44-3
- Ligularinine
Catalog No.:BCN2117
CAS No.:90364-90-2
- Neoligularidine
Catalog No.:BCN2137
CAS No.:90364-91-3
- Ligularizine
Catalog No.:BCN2091
CAS No.:90364-92-4
- (-)-Indolactam V
Catalog No.:BCC7735
CAS No.:90365-57-4
- Bleomycin Sulfate
Catalog No.:BCC3694
CAS No.:9041-93-4
- Neochamaejasmine B
Catalog No.:BCN3130
CAS No.:90411-12-4
Development of an indirect competitive enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (icELISA) using highly specific monoclonal antibody against paclitaxel.[Pubmed:23007175]
J Nat Med. 2013 Jul;67(3):512-8.
Paclitaxel, the major active component of the yew tree, is used as an important anti-cancer agent. To obtain the monoclonal antibody (MAb) against paclitaxel for paclitaxel determination using immunoassay, 7-Xylosyltaxol was conjugated to the carrier protein bovine serum albumin (BSA) to construct the immunogen, and the ratio of hapten in XylTax-BSA conjugate was determined by matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization time-of-flight mass spectrometry. After immunization of mice with this conjugate, hybridomas secreting MAbs against paclitaxel were obtained by fusing the splenocytes with the mouse myeloma cell line SP2/0. After hybridoma screening, the anti-paclitaxel MAb 3A3 was obtained, which showed a relatively high specificity to paclitaxel (cross-reactivities against other naturally occurred taxanes: 7-Xylosyltaxol, 31.8%; cephalomannine, 6.17%; baccatin III, 10-deacetyl-baccatin III, 1-hydroxybaccatin I, 13-acetyl-9-dihydrobaccatin III and 1-acetoxyl-5-deacetyl-baccatin I, <0.11%). Using the MAb 3A3, we established an indirect competitive enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (icELISA) for paclitaxel determination with a detection range of 0.098-312.5 mug ml(-1). Determination of paclitaxel contents in various yew tree samples with this icELISA resulted in recovery rates ranging from 92 to 94.8%, and intra- and inter-assay variations of 3.6 and 4.7%, respectively. This icELISA provides a valuable method of paclitaxel determination for various purposes.
[Content and distribution of active components in cultivated and wild Taxus chinensis var. mairei plants].[Pubmed:23359921]
Ying Yong Sheng Tai Xue Bao. 2012 Oct;23(10):2641-7.
Taxus chinensis var. mairei is an endemic and endangered plant species in China. The resources of T. chinensis var. mairei have been excessively exploited due to its anti-cancer potential, accordingly, the extant T. chinensis var. mairei population is decreasing. In this paper, ultrasonic extraction and HPLC were adopted to determine the contents of active components paclitaxel, 7-Xylosyltaxol and cephalomannine in cultivated and wild T. chinensis var. mairei plants, with the content distribution of these components in different parts of the plants having grown for different years and at different slope aspects investigated. There existed obvious differences in the contents of these active components between cultivated and wild T. chinensis var. mairei plants. The paclitaxel content in the wild plants was about 0.78 times more than that in the cultivated plants, whereas the 7-Xylosyltaxol and cephalomannine contents were slishtly higher in the cultivated plants. The differences in the three active components contents between different parts and tree canopies of the plants were notable, being higher in barks and upper tree canopies. Four-year old plants had comparatively higher contents of paclitaxel, 7-Xylosyltaxol and cephalomannine (0.08, 0.91 and 0.32 mg x g(-1), respectively), and the plants growing at sunny slope had higher contents of the three active components, with significant differences in the paclitaxel and 7-Xylosyltaxol contents and unapparent difference in the cephalomannine content of the plants at shady slope. It was suggested that the accumulation of the three active components in T. chinensis var. mairei plants were closely related to the sunshine conditions. To appropriately increase the sunshine during the artificial cultivation of T. chinensis var. mairei would be beneficial to the accumulation of the three active components in T. chinensis var. mairei plants.


