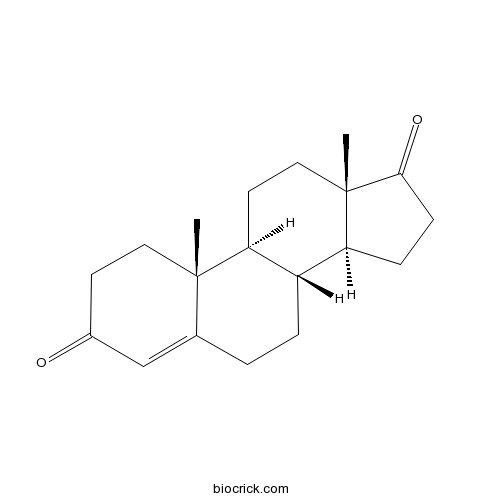
AndrostenedioneCAS# 63-05-8 |
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 63-05-8 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 6128 | Appearance | White-pale yellow powder |
| Formula | C19H26O2 | M.Wt | 286.4 |
| Type of Compound | Isoprenoids | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Synonyms | Δ4-Androstene 3,17-dione; 3,17-Dioxoandrost 4-ene; Fecundin; 17-Ketosterone | ||
| Solubility | Soluble in chloroform, ethanol and methanol; insoluble in water | ||
| Chemical Name | (8R,9S,10R,13S,14S)-10,13-dimethyl-2,6,7,8,9,11,12,14,15,16-decahydro-1H-cyclopenta[a]phenanthrene-3,17-dione | ||
| SMILES | CC12CCC(=O)C=C1CCC3C2CCC4(C3CCC4=O)C | ||
| Standard InChIKey | AEMFNILZOJDQLW-QAGGRKNESA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C19H26O2/c1-18-9-7-13(20)11-12(18)3-4-14-15-5-6-17(21)19(15,2)10-8-16(14)18/h11,14-16H,3-10H2,1-2H3/t14-,15-,16-,18-,19-/m0/s1 | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||

Androstenedione Dilution Calculator

Androstenedione Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 3.4916 mL | 17.4581 mL | 34.9162 mL | 69.8324 mL | 87.2905 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.6983 mL | 3.4916 mL | 6.9832 mL | 13.9665 mL | 17.4581 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.3492 mL | 1.7458 mL | 3.4916 mL | 6.9832 mL | 8.7291 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0698 mL | 0.3492 mL | 0.6983 mL | 1.3966 mL | 1.7458 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0349 mL | 0.1746 mL | 0.3492 mL | 0.6983 mL | 0.8729 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
- Staurosporine
Catalog No.:BCC3612
CAS No.:62996-74-1
- 6-Aminoquinoxaline
Catalog No.:BCC8767
CAS No.:6298-37-9
- XL335
Catalog No.:BCC4501
CAS No.:629664-81-9
- Boc-Tle-OH
Catalog No.:BCC3343
CAS No.:62965-35-9
- Gnetucleistol D
Catalog No.:BCN3400
CAS No.:629643-26-1
- Gomisin G
Catalog No.:BCN2269
CAS No.:62956-48-3
- Gomisin F
Catalog No.:BCN3625
CAS No.:62956-47-2
- (2-Benzothiazolylthio)acetic acid
Catalog No.:BCC8387
CAS No.:6295-57-4
- 6-Methoxy-4-methylcoumarin
Catalog No.:BCN6537
CAS No.:6295-35-8
- Morusinol
Catalog No.:BCN4168
CAS No.:62949-93-3
- Mulberrin
Catalog No.:BCN4167
CAS No.:62949-79-5
- Kuwanon A
Catalog No.:BCN2944
CAS No.:62949-77-3
- Primaquine Diphosphate
Catalog No.:BCC4706
CAS No.:63-45-6
- H-Met-OH
Catalog No.:BCC2993
CAS No.:63-68-3
- Sulfanilamide
Catalog No.:BCC4858
CAS No.:63-74-1
- L-Phenylalanine
Catalog No.:BCN3818
CAS No.:63-91-2
- Phenoxybenzamine HCl
Catalog No.:BCC4334
CAS No.:63-92-3
- Nonacosane
Catalog No.:BCC9102
CAS No.:630-03-5
- Ouabain
Catalog No.:BCC5069
CAS No.:630-60-4
- Phenytoin sodium
Catalog No.:BCC5071
CAS No.:630-93-3
- Corynoxeine
Catalog No.:BCN5002
CAS No.:630-94-4
- Neoprzewaquinone A
Catalog No.:BCN4169
CAS No.:630057-39-5
- MRS 2500 tetraammonium salt
Catalog No.:BCC5881
CAS No.:630103-23-0
- PD 168077 maleate
Catalog No.:BCC6919
CAS No.:630117-19-0
Quantitative-Profiling Method of Serum Steroid Hormones by Hydroxylamine-Derivatization HPLC-MS.[Pubmed:30968349]
Nat Prod Bioprospect. 2019 Apr 9. pii: 10.1007/s13659-019-0204-3.
A sensitive and rapid high performance liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry (HPLC-MS) method was developed and validated for simultaneous quantification of ten steroid hormones, including estrogens, androgens, progesterones, and corticosteroids four classes of steroids. The following ten steroid hormones were analyzed: progesterone, 21-deoxycortisol, estrone, 4-Androstenedione, testosterone, dihydro-testosterone, androstenone, dehydroepiandrosterone, corticosterone and cortisone. Stable deuterated isotopes were used as internal standards for quantification. Sample preparation with and without derivatization were performed after liquid-liquid extraction, and the corresponding results were compared according to sensitivity and selectivity. Hydroxylamine derivatization was found to improve the ionization efficiency of the analytes for electrospray ionization MS analysis. The gradient of mobile phase and experimental parameters for HPLC separation were optimized. The lower limits of quantification were in the range of 0.05-5 ng mL(-1) with wide linear range for the ten steroid hormones. The intra-day precision < 11.1% and recovery of 84.5-120% with negligible matrix effect were achieved, where within the acceptance limits of the FDA guideline. Total HPLC-MS analysis time was 6 min. This method enables simultaneous quantification of steroids in human serum. It will be helpful for the serum steroid profiling in order to understand various endocrinology diseases.
Elucidation of the biosynthetic pathways of boldenone in the equine testis.[Pubmed:30951760]
Steroids. 2019 Apr 2;146:79-91.
Boldenone is an anabolic-androgenic steroid that is prohibited in equine sports. Urine from the uncastrated male horse contains boldenone that is thought to be of endogenous origin and thus a threshold ('cut-off') concentration has been adopted internationally for free and conjugated boldenone to help distinguish cases of doping from its natural production. The testis is likely to be a source of boldenone. Qualitative analysis was performed on extracts of equine testicular homogenates (n=3 horses) incubated non-spiked and in the presence of its potential precursors using liquid chromatography tandem mass spectrometry (LC-MS/MS) and LC high resolution mass spectrometry (LC-HRMS). Samples were analysed both underivatised and derivatised to increase the certainty of identification. In addition to previously reported endogenous steroids, analysis of non-spiked testicular tissue samples demonstrated the presence of boldenone and boldienone at trace levels in the equine testis. Incubation of homogenates with deuterium or carbon isotope labelled testosterone and Androstenedione resulted in the matching stable isotope analogues of boldenone and boldienone being formed. Additionally, deuterium and carbon labelled 2-hydroxyAndrostenedione was detected, raising the possibility that this steroid is a biosynthetic intermediate. In conclusion, boldenone and boldienone are naturally present in the equine testis, with the biosynthesis of these steroids arising from the conversion of testosterone and Androstenedione. However, additional work employing larger numbers of animals, further enzyme kinetic experiments and pure reference standards for 2-OH Androstenedione isomers would be required to better characterize the pathways involved in these transformations.
The lncRNA MIR2052HG regulates ERalpha levels and aromatase inhibitor resistance through LMTK3 by recruiting EGR1.[Pubmed:30944027]
Breast Cancer Res. 2019 Apr 3;21(1):47.
BACKGROUND: Our previous genome-wide association study using the MA.27 aromatase inhibitors adjuvant trial identified SNPs in the long noncoding RNA MIR2052HG associated with breast cancer-free interval. MIR2052HG maintained ERalpha both by promoting AKT/FOXO3-mediated ESR1 transcription and by limiting ubiquitin-mediated ERalpha degradation. Our goal was to further elucidate MIR2052HG's mechanism of action. METHODS: RNA-binding protein immunoprecipitation assays were performed to demonstrate that the transcription factor, early growth response protein 1 (EGR1), worked together with MIR2052HG to regulate that lemur tyrosine kinase-3 (LMTK3) transcription in MCF7/AC1 and CAMA-1 cells. The location of EGR1 on the LMTK3 gene locus was mapped using chromatin immunoprecipitation assays. The co-localization of MIR2052HG RNA and the LMTK3 gene locus was determined using RNA-DNA dual fluorescent in situ hybridization. Single-nucleotide polymorphisms (SNP) effects were evaluated using a panel of human lymphoblastoid cell lines. RESULTS: MIR2052HG depletion in breast cancer cells results in a decrease in LMTK3 expression and cell growth. Mechanistically, MIR2052HG interacts with EGR1 and facilitates its recruitment to the LMTK3 promoter. LMTK3 sustains ERalpha levels by reducing protein kinase C (PKC) activity, resulting in increased ESR1 transcription mediated through AKT/FOXO3 and reduced ERalpha degradation mediated by the PKC/MEK/ERK/RSK1 pathway. MIR2052HG regulated LMTK3 in a SNP- and aromatase inhibitor-dependent fashion: the variant SNP increased EGR1 binding to LMTK3 promoter in response to Androstenedione, relative to wild-type genotype, a pattern that can be reversed by aromatase inhibitor treatment. Finally, LMTK3 overexpression abolished the effect of MIR2052HG on PKC activity and ERalpha levels. CONCLUSIONS: Our findings support a model in which the MIR2052HG regulates LMTK3 via EGR1, and LMTK3 regulates ERalpha stability via the PKC/MEK/ERK/RSK1 axis. These results reveal a direct role of MIR2052HG in LMTK3 regulation and raise the possibilities of targeting MIR2052HG or LMTK3 in ERalpha-positive breast cancer.
Effect of chlormadinone acetate versus drospirenone-containing oral contraceptives on the endocrinal features of women with polycystic ovary syndrome: Systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized clinical trials.[Pubmed:30940512]
J Gynecol Obstet Hum Reprod. 2019 Mar 30. pii: S2468-7847(18)30473-2.
BACKGROUND: Polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) is a serious endocrinal disorder in women of reproductive age. Hormonal treatment with oral contraceptives, containing estrogen (ethinyl-estradiol, EE) with progestogen (drospirenone, DRSP) or (chlormadinone acetate, CMA), has improved symptoms and biomarkers of PCOS. OBJECTIVE: The aim of the present meta-analysis is to compare the effects of EE/DRSP versus EE/CMA on the endocrinal features of women with PCOS. DATA SOURCES: Several electronic databases were searched for combinations of the following relevant MeSH terms were used: (ethinyl-estradiol OR EE) AND (drospirenone OR DRSP) AND (chlormadinone acetate OR CMA) AND (polycystic ovary syndrome). METHODS: Records were screened for eligible studies and data were extracted to an online data extraction form. Outcomes of Ferryman-Gallwey score (FGS), body mass index, dehydroepiandrosterone sulfate (DHEAS), free androgen index, sex hormone-binding globulin, delta-4-Androstenedione (A) and total testosterone levels (T) were pooled as weighted mean difference (WMD) and 95% confidence interval (CI) in a fixed effect meta-analysis model. RESULTS: Three RCTs (EE/DRSP: n = 98 and EE/CMA: n = 87) were pooled in the analysis. The overall effect favoured EE/DRSP over EE/CMA in reducing (A) levels after three months (WMD -0.63; 95% CI [-0.94, -0.32], P < 0.001), FGS after six months (WMD -0.44; 95% CI [-0.99, -0.19], P = 0.0006), and total (T) after three months (WMD -0.12; 95% CI [-0.23, -0.01], P = 0.03). CONCLUSIONS: EE/DRSP showed a more potent effect than EE/CMA in the reduction of FGS after six months, (A) levels and (T) levels after three months in patients with PCOS.
Evaluating the in-sewer stability of three potential population biomarkers for application in wastewater-based epidemiology.[Pubmed:30928753]
Sci Total Environ. 2019 Mar 16;671:248-253.
Endogenous chemicals specific to human metabolism have been suggested to be good candidates for markers of population size in wastewater-based epidemiology (WBE). So far, creatinine is the only endogenous chemical to be assessed against the criteria of in-sewer stability. This study thus aimed to evaluate the fate of three other endogenous compounds, 5-hydroxy indole acetic acid (5-HIAA), cortisol and Androstenedione, under different sewer conditions using laboratory-scale sewer reactors. The results showed that while all compounds were stable in wastewater only (i.e. without biofilm), cortisol and Androstenedione degraded quickly in sewers with the presence of sewer biofilms. The degradation followed first-order kinetics similar to that of creatinine. In contrast, 5-HIAA was relatively stable in sewer reactors. This study also recognised the impact of wastewater pH on the detectability of 5-HIAA using a LC-MS/MS direct injection method. In samples acidified to pH2, the method did not allow routine detection/quantification of 5-HIAA whereas in non-acidified samples the method was sufficiently sensitive for routine quantification of 5-HIAA. The stability of 5-HIAA in sewers and the possibility to measure it using a simple and rapid analytical method corroborate that 5-HIAA may be a suitable biomarker for estimation of population size in WBE.
Green Tea Catechin Extract Supplementation Does Not Influence Circulating Sex Hormones and Insulin-Like Growth Factor Axis Proteins in a Randomized Controlled Trial of Postmenopausal Women at High Risk of Breast Cancer.[Pubmed:30926986]
J Nutr. 2019 Mar 30. pii: 5423559.
BACKGROUND: Consumption of green tea has been associated with reduced risk of breast cancer. Hormonal modulation has been suggested as one of the potential underlying mechanisms; however, it has yet to be fully elucidated in large, long-term human clinical trials. OBJECTIVE: We investigated the effects of decaffeinated green tea extract (GTE) on circulating sex hormones and insulin-like growth factor (IGF) proteins. METHODS: We conducted a placebo-controlled double-blind randomized clinical trial recruiting from 8 clinical centers in Minnesota. Participants were 538 healthy postmenopausal women randomly assigned to the GTE group (463 completed the study; mean age = 60.0 y) and 537 to the placebo group (474 completed; mean age = 59.7 y). Women in the GTE group orally took 4 decaffeinated capsules containing 1315 mg total catechins including 843 mg epigallocatechin-3-gallate daily for 1 y, whereas women in the placebo group took similar capsules containing no tea catechins. Blood sex hormones (estrone, estradiol, Androstenedione, testosterone, and sex hormone-binding globulin) and IGF proteins (IGF-1 and IGF binding protein-3) were quantified at baseline and months 6 (for IGF proteins only) and 12, and were assessed as secondary outcomes of the study using a mixed-effect repeated-measures ANOVA model. RESULTS: Women in the GTE group had significantly higher blood total estradiol (16%; P = 0.02) and bioavailable estradiol (21%; P = 0.03) than in the placebo group at month 12. There was a statistically significant interaction between GTE supplementation and duration of treatment on estradiol and bioavailable estradiol (both Ps for interaction = 0.001). The catechol-O-methyltransferase genotype did not influence blood sex hormones before or after GTE supplementation. The circulating concentrations of IGF proteins were comparable between GTE and placebo groups at all 3 time points. CONCLUSION: These results suggest that a 12-mo GTE supplementation significantly increases circulating estradiol concentrations in healthy postmenopausal women. This trial was registered at clinicaltrials.gov as NCT00917735.
Identification of in vitro effect of 4-octylphenol on the basal and human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG) stimulated secretion of androgens and superoxide radicals in mouse Leydig cells.[Pubmed:30925854]
J Environ Sci Health A Tox Hazard Subst Environ Eng. 2019 Mar 29:1-9.
The aim of our in vitro study was to assess the potential effect of 4-octylphenol (4-OP) on the basal and human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG)-stimulated cholesterol levels and biosynthesis of steroid hormones in cultured mouse Leydig cells. In addition, we evaluated the intracellular superoxide production following 4-OP treatment. Isolated mouse Leydig cells were cultured in the presence or absence of 1 IU/mL (hCG) with the addition of 0.04; 0.2; 1.0; 2.5 and 5.0 microg/mL 4-OP during 44 h. The level of cholesterol was determined from the culture medium using photometry. Quantification of steroid hormones was performed by the enzyme linked immunosorbent assay and intracellular generation of superoxide radicals was assessed by the nitroblue-tetrazolium assay. Administered concentrations of 4-OP (0.04-5.0 microg/mL) did not affect basal and hCG-stimulated cholesterol level significantly. However, basal DHEA secretion was increased significantly (P < 0.001) in the highest experimental dose (5 microg/mL) of 4-OP. By hCG-stimulated DHEA secretion, a significant (P < 0.001) decrease was recorded at 5.0 microg/mL 4-OP in comparison to the control group. The stimulatory effect of 4-OP was also confirmed in Androstenedione secretion, when 2.5 and 5.0 microg/mL increased hormone secretion significantly (P<0.05; P<0.001). Exposure to experimental concentrations (0.04 to 5.0 microg/mL) of tested chemical reduced hCG-stimulated Androstenedione formation, but not significantly. Measurements of basal testosterone production have shown significant (P<0.01; P<0.001) increase at 1.0; 2.5 and 5.0 microg/mL of 4-OP. Furthermore, 44 h treatment by 4-OP (1.0-5.0 microg/mL) caused significant (P<0.01; P<0.001) intracellular accumulation of superoxide radicals in exposed cells. A considerably more detailed and systematic research is required for a better understanding of risks associated with male reproductive system in humans and wildlife.
LC-MS/MS assay for the quantification of testosterone, dihydrotestosterone, androstenedione, cortisol and prednisone in plasma from castrated prostate cancer patients treated with abiraterone acetate or enzalutamide.[Pubmed:30925273]
J Pharm Biomed Anal. 2019 Mar 20;170:161-168.
Prostate cancer is the most common malignancy among men in the Western world. Treatment of this patient population, e.g. by (chemical) castration, is primarily focused on depletion of tumor-stimulating androgens, with testosterone being the major androgenic hormone. After initial therapy, prostate cancer may progress to metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer. Anti-hormonal drugs abiraterone acetate and enzalutamide are commonly used to treat patients with this disease as both drugs reduce tumor growth and increase time to tumor progression. To evaluate the pharmacodynamic effects of anti-hormonal drugs in this patient population, we developed an LC-MS/MS method for the quantification of testosterone, dihydrotestosterone, Androstenedione, cortisol and prednisone in human plasma. The validated assay ranges from 10-10,000 pg/mL for testosterone and Androstenedione, 100-10,000 pg/mL for dihydrotestosterone, 50-5000 pg/mL for cortisol and 500-50,000 pg/mL for prednisone. Intra-assay and inter-assay variabilities were within +/-15% of the nominal concentrations for quality control (QC) samples at low, medium and high concentrations and within +/-20% at the lower limit of quantification (LLOQ), respectively. The applicability of the method was demonstrated in plasma from patients with metastatic castrated-resistant prostate cancer using either abiraterone acetate or enzalutamide.
Development and validation of a LC-MS/MS method for the establishment of reference intervals and biological variation for five plasma steroid hormones.[Pubmed:30922617]
Clin Biochem. 2019 Mar 25. pii: S0009-9120(19)30102-X.
BACKGROUND: With liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry (LC-MS/MS) increasingly being used for the quantification of steroid hormones, there is a need for studies that re-establish reference intervals and biological variation in well-defined cohorts. METHODS: A plasma steroid hormone profiling method using LC-MS/MS for quantification of progesterone, 17-hydroxyprogesterone, Androstenedione, testosterone and dihydrotestosterone was developed and validated. For reference interval assessment, 280 well-characterized healthy subjects from the LifeLines cohort were selected, including 40 women using oral contraceptive pills (OCP). The biological variation was examined in 30 healthy individuals. Samples were collected over a period of 4months with 4week intervals. RESULTS: The developed method proved to be robust and sensitive. The reference interval levels in men are higher, whereas in women the levels tend to decrease with increasing age. In addition, women using OCP had lower levels of 17-OH-progesterone and Androstenedione. The biological variation is generally higher in women compared to men, especially with regard to the inter-individual variation. CONCLUSIONS: The gender-specific determination of the reference intervals, together with the observation that the biological variation demonstrated a high degree of variation, allows interpretation of data on individual and group level for improved biochemical characterization of patients in clinical practice.
Environmental inhibitors of the expression of cytochrome P450 17A1 in mammals.[Pubmed:30921671]
Environ Toxicol Pharmacol. 2019 Mar 14;69:16-25.
Cytochrome P450 17A1 (CYP17A1; EC: 1.14.14.19) is a critically important bifunctional enzyme with nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate (NADPH) as its cofactor that catalyzes the formation of all endogenous androgens. Its hydroxylase activity catalyzes the 17alpha-hydroxylation of pregnenolone (PREG)/progesterone (P4) to 17alpha-OH-pregnenolone/17alpha-OH-progesterone, and its 17,20-lyase activity converts 17alpha-OH-pregnenolone/17alpha-OH-progesterone to dehydroepiandrosterone/Androstenedione. Androgens are required for male reproductive development, so androgen deficiency resulting from CYP17A1 inhibition may lead to reproductive disorders. There has been some advances on the study of environmental chemicals inhibiting mammalian CYP17A1 expression but no related review was available so we think it now necessary to review their characteristics and inhibiting properties.
Primary antiphospholipid syndrome during aromatase inhibitors therapy: A case report and review of the literature.[Pubmed:30921233]
Medicine (Baltimore). 2019 Mar;98(13):e15052.
RATIONALE: Aromatase inhibitors (AIs) are a class of drugs widely used in the treatment of estrogen sensitive breast and ovarian cancer which convert testosterone to estradiol and Androstenedione to estrogen. The AIs of third generation, including anastrazole, letrozole and exemestane, have actually become the standard of care of estrogen-receptor-positive breast cancer in menopausal women and are recommended as adjuvant treatment after surgery in place of/or following tamoxifen. Their main side-effects include reduction in bone mineral density, occurrence of menopausal manifestations and development of musculoskeletal symptoms which are, usually, transient, but sometimes evolve into a typical form of arthritis, such as rheumatoid arthritis (RA). Recently, a pathogenic linkage with other autoimmunity diseases, such as Sjogren syndrome (SjS), anti-synthetase antibody syndrome (ASAS), systemic sclerosis (SS) and subacute cutaneous lupus erythematosus (SCLE), was also described. PATIENT CONCERNS: Here, we report the first case of a patient with primary antiphospholipid syndrome (APS) developed during treatment with anastrazole. DIAGNOSIS: The patient developed a sudden onset of speech disturbance and disorientation, due to ischemic lesions, after 6 months of AIs therapy and the laboratory examination showed the positivity of anti-Cardiolipin antibodies, anti-beta2 Glycoprotein 1 antibodies and Lupus Anticoagulant, so a certain diagnosis of APS was achieved. INTERVENTIONS: The patient was treated with warfarin associated to hydroxychloroquine and monthly cycles of low doses intravenous immunoglobulins. OUTCOMES: A good control of the disease was obtained despite the continuation of anastrazole; the patient's clinical and laboratory situation remained not modified after AIs withdrawal. LESSONS: We discussed the possible role of anastrazole treatment in inducing APS in our patient, reporting the available literature data about the association between AIs treatment and autoimmune diseases. Furthermore, we analyzed the mechanism of action of estrogens in the pathophysiology of autoimmune rheumatic disorders.
[Adrenal androgen measurement for assessing the selectivity of adrenal venous sampling in primary aldosteronism].[Pubmed:30917442]
Zhonghua Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2019 Mar 26;99(12):923-928.
Objective: To investigate the usefulness of adrenal androgens for assessing the selectivity of adrenal venous sampling (AVS). Methods: Between January 2010 and December 2016, 37 consecutive patients [with an average age of (47+/-14) years, 16 males and 21 females] with primary aldosteronism (PA) who underwent AVS were enrolled. AVS procedures were performed with the bilateral simultaneous technique without cosyntropin stimulation. Cortisol, Androstenedione, dehydroepiandrosterone (DHEA), and DHEA sulfate (DHEAS) concentrations were measured in adrenal venous (AV) and peripheral venous (PV) samples, respectively. Results: The selectivity index (SI) based on Androstenedione and DHEA was higher than that of cortisol (SI-left: 13.9, 13.1 vs 6.05, P=0.006, 0.035; SI-right: 30.4, 18.5 vs 11.6, P=0.028, 0.051). However, the SI based on DHEAS was lower than that of cortisol (SI-left: 1.3 vs 6.0, P=0.002; SI-right: 1.5 vs 11.6, P=0.038). Plasma Androstenedione and DHEA concentrations were positively correlated with cortisol and aldosterone in AV samples (all P<0.001). Compared to cortisol, the variation ratio of AV Androstenedione and DHEA was lower from t(-15) to t(0) (0.23, 0.43 vs 0.52, both P<0.05). Using the receiver operating characteristic curve, a SI >/= 3.0 for Androstenedione or DHEA provided optimal sensitivity(97.7%, 91.9%) and specificity (93.8%, 93.8%) in AVS. Conclusion: Given the greater AV/PV ratios and reduced variability compared to cortisol, the adrenal androgens Androstenedione and DHEA are useful for assessing the selectivity of AVS without cosyntropin stimulation and may be superior analytes in conditions with marked variability of cortisol levels or with adrenocortical tumors co-secreting cortisol and aldosterone.
Metabolism of formestane in humans: Identification of urinary biomarkers for antidoping analysis.[Pubmed:30904502]
Steroids. 2019 Mar 20;146:34-42.
Formestane (4-hydroxyandrost-4-ene-3,17-dione, 4OH-AED) is an aromatase inhibitor prohibited in sports. In recent years, it has been demonstrated that it can also originate endogenously by the hydroxylation in C4 position of Androstenedione. Thus, the use of isotope ratio mass spectrometry (IRMS) is mandatory according to the World Antidoping Agency (WADA) to discriminate endogenous from synthetic origin. In a previous work and after oral administrations of formestane (4OH-AED), the ratio between the main formestane metabolite (4alpha-hydroxyepiandrosterone; 4OH-EA) and formestane parent compound could help to identify the endogenous origin, avoiding unnecessary and costly IRMS confirmations. In the present work, we investigated whether the same criteria could also be applied after transdermal applications. Six volunteers were transdermally treated once with formestane. Urine samples were collected for 120h postadministration and analyzed by gas chromatography coupled to mass spectrometry (GC-MS and GC-MS/MS). Formestane and its major metabolites were monitored. The kinetic profile of formestane and its main metabolites was found different between oral and transdermal application. A shift on the excretion of the metabolites compared to formestane itself that can be observed after the oral administration, is absent after the transdermal one. This makes that a simple criteria cannot be applied to differentiate the endogenous from the synthetic origin based on metabolic ratios. The ratio between 4-hydroxyepiandrosterone and 4-hydroxyandrosterone (4OH-A) can be used to differentiate the route of administration. Ratios higher than one (4OH-EA/4OH-A>1) are diagnostic of an oral administration. This allows to correctly interpret the 4OH-EA/4OH-AED ratio as proposed in our previous investigation. The results of this work demonstrate that the use of appropriate biomarkers (metabolic ratios) helps to reach correct conclusions without using complex and costly instrumentation approaches.
Adipose-derived stem cells promote survival, growth, and maturation of early-stage murine follicles.[Pubmed:30898159]
Stem Cell Res Ther. 2019 Mar 21;10(1):102.
BACKGROUND: Premature ovarian insufficiency is a common complication of anticancer treatments in young women and girls. The ovary is a complex, highly regulated reproductive organ, whose proper function is contingent upon the bidirectional endocrine, paracrine, and autocrine signaling. These factors facilitate the development of the follicles, the functional units of the ovary, to progress from the gonadotropin-independent, paracrine-controlled early stage to the gonadotropin-dependent, endocrine-controlled later stage. We hypothesized that the low survival rate of individually cultured early-stage follicles could be improved with co-culture of adipose-derived stem cells (ADSCs) that secrete survival- and growth-promoting factors. MATERIALS AND METHODS: Ovarian follicles ranging from 85 to 115 mum in diameter, from 10- to 12-day-old B6CBAF1 mice were mechanically isolated and co-encapsulated with ADSCs within alginate-based 3D culture system. The follicles were cultured for 14 days, imaged using light microscopy every 2 days, and matured at the end. Follicle media were changed every 2 days and collected for hormone measurements. Follicle diameter, morphology, number of transzonal projections, and survival and maturation rates were recorded. Statistical analyses using one- and two-way ANOVA were performed to compare hormone levels, survival of the follicles and ADSCs, oocyte maturation rates, and follicle growth. RESULTS: The co-encapsulation of the follicles with ADSCs increased follicle survival, ranging from 42.4% for the 86-95 mum to 86.2% for the 106-115-mum follicle size group. Co-culture also improved the follicle growth, the rate of antrum formation and oocyte maturation compared to the follicles cultured alone. The levels of Androstenedione, estradiol, and progesterone of co-encapsulated follicles increased progressively with time in culture. CONCLUSIONS: To our knowledge, this is the first report of an in vitro system utilizing mouse adipose-derived stem cells to support the development of the mouse follicles. Our findings suggest that co-encapsulation of ADSCs with early-stage follicles supports follicular development, through secretion of cytokines that promote follicular survival, antrum formation, and meiotic competence. The unique 3D culture system that supports the survival of both cell types has translational implications, as ADSCs could be used as an autologous source for in vitro maturation of early-stage human follicles.
Altered umbilical sex steroids in preterm infants born small for gestational age.[Pubmed:30895831]
J Matern Fetal Neonatal Med. 2019 Mar 21:1-181.
BACKGROUND: Boys born small for gestational age (SGA) are at increased risk of testicular dysgenesis syndrome, and girls born SGA face the risk of polycystic ovary syndrome later in life. Our aim was to study whether neonates born SGA have an altered profile of steroid hormones at birth. MATERIALS AND METHODS: A total of 168 singletons (99 boys, 69 girls) born at 32.0-36.9 gestational weeks were recruited to a population-based, university hospital, single-center study. Of these, 31 infants (17 boys, 14 girls) were born SGA. The concentrations of dehydroepiandrosterone sulfate (DHEAS), Androstenedione, testosterone, dihydrotestosterone, estrone, estradiol, cortisone, and cortisol were analyzed in umbilical cord serum with mass spectrometry. RESULTS: Girls born SGA had higher levels of Androstenedione than girls born appropriate for gestational age (AGA) (4.0 versus 2.6 nmol/L, p = 0.002). Boys born SGA had lower levels of estrone than boys born AGA (33 822 versus 62 471 pmol/L, p = 0.038). Infants born SGA had lower levels of cortisone than infants born AGA, both in girls (340 versus 579 nmol/L, p = 0.010) and in boys (308 versus 521 nmol/L, p = 0.045). Furthermore, boys born SGA had a higher cortisol/cortisone ratio than boys born AGA (0.41 versus 0.25, p = 0.028). Gestational age correlated with DHEAS (boys r = 0.48, p = 0.000, girls r = 0.35, p = 0.013), and cortisol (boys r = 0.48, p = 0.000, girls r = 0.29, p = 0.039). CONCLUSIONS: In moderate-to-late preterm infants born SGA we observed a different steroid hormone profile in cord serum. Girls born SGA show increased levels of Androstenedione and boys born SGA show decreased levels of estrone in cord serum, which could be related to placental aromatase deficiency in intrauterine growth restriction.


