AcetamideCAS# 60-35-5 |
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 60-35-5 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 178 | Appearance | Cryst. |
| Formula | C2H5NO | M.Wt | 59.1 |
| Type of Compound | Alkaloids | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Solubility | Soluble in Chloroform,Dichloromethane,Ethyl Acetate,DMSO,Acetone,etc. | ||
| Chemical Name | acetamide | ||
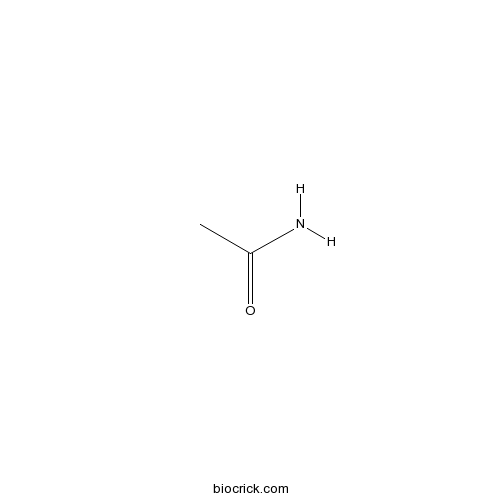
| SMILES | CC(=O)N | ||
| Standard InChIKey | DLFVBJFMPXGRIB-UHFFFAOYSA-N | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | Acetamide (2.88 g/kg/d) can reduce central nervous lesions, but the efficacy is not improved after increasing the dose. |
| Targets | Histone Methyltransferase |
| In vivo | Effects of acetamide at different doses on expression of amino acids in cerebral cortex of rats with acute tetramine poisoning.[Pubmed: 25169228]Zhonghua Lao Dong Wei Sheng Zhi Ye Bing Za Zhi. 2014 Jun;32(6):438-41.To investigate the effects of Acetamide at different doses on the expression of inhibitory amino acids (gamma-aminobutyric acid, GABA) and excitatory amino acid (glutamate, Glu) in the cerebral cortex of rats with acute tetramine (TET) poisoning. |
| Animal Research | Effect of acetamide on histopathology in cerebral cortex of rats with tetramine poisoning.[Pubmed: 24754949]Zhonghua Lao Dong Wei Sheng Zhi Ye Bing Za Zhi. 2014 Apr;32(4):289-92.To observe the effect of different doses of Acetamide on the histopathology in the cerebral cortex of rats with tetramine (TET) poisoning and to provide a basis for the treatment of fluoroAcetamide poisoning with Acetamide. |

Acetamide Dilution Calculator

Acetamide Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 16.9205 mL | 84.6024 mL | 169.2047 mL | 338.4095 mL | 423.0118 mL |
| 5 mM | 3.3841 mL | 16.9205 mL | 33.8409 mL | 67.6819 mL | 84.6024 mL |
| 10 mM | 1.692 mL | 8.4602 mL | 16.9205 mL | 33.8409 mL | 42.3012 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.3384 mL | 1.692 mL | 3.3841 mL | 6.7682 mL | 8.4602 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.1692 mL | 0.846 mL | 1.692 mL | 3.3841 mL | 4.2301 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
- Linoleic acid
Catalog No.:BCN3821
CAS No.:60-33-3
- (6-)ε-Aminocaproic acid
Catalog No.:BCC4888
CAS No.:60-32-2
- Acetylcholine chloride
Catalog No.:BCN2197
CAS No.:60-31-1
- H-Tyr-OH
Catalog No.:BCC3123
CAS No.:60-18-4
- Guanethidine Sulfate
Catalog No.:BCC3789
CAS No.:60-02-6
- EDTA
Catalog No.:BCC7493
CAS No.:60-00-4
- Tagitinin A
Catalog No.:BCN4102
CAS No.:59979-61-2
- Tagitinin F
Catalog No.:BCN4101
CAS No.:59979-57-6
- Carlinoside
Catalog No.:BCN2853
CAS No.:59952-97-5
- Malotilate
Catalog No.:BCC1196
CAS No.:59937-28-9
- 3',4'-dihydro-3'-hydroxy-Xanthyletin
Catalog No.:BCN3680
CAS No.:5993-18-0
- Vicriviroc maleate
Catalog No.:BCC2038
CAS No.:599179-03-0
- Acetyl-Strophanthidin
Catalog No.:BCC8113
CAS No.:60-38-8
- Tetracycline
Catalog No.:BCC9176
CAS No.:60-54-8
- Methimazole
Catalog No.:BCC3812
CAS No.:60-56-0
- Veratramine
Catalog No.:BCN2965
CAS No.:60-70-8
- Antipyrine
Catalog No.:BCC8834
CAS No.:60-80-0
- Phlorizin
Catalog No.:BCN4126
CAS No.:60-81-1
- Phloretin
Catalog No.:BCN4128
CAS No.:60-82-2
- Adenosine cyclophosphate
Catalog No.:BCN2190
CAS No.:60-92-4
- N-Me-DL-Ala-OH.HCl
Catalog No.:BCC2618
CAS No.:600-21-5
- 11Beta-hydroxyprogesterone
Catalog No.:BCN2211
CAS No.:600-57-7
- Oblongine
Catalog No.:BCN4103
CAS No.:60008-01-7
- Glabrene
Catalog No.:BCN6692
CAS No.:60008-03-9
[Effect of acetamide on histopathology in cerebral cortex of rats with tetramine poisoning].[Pubmed:24754949]
Zhonghua Lao Dong Wei Sheng Zhi Ye Bing Za Zhi. 2014 Apr;32(4):289-92.
OBJECTIVE: To observe the effect of different doses of Acetamide on the histopathology in the cerebral cortex of rats with tetramine (TET) poisoning and to provide a basis for the treatment of fluoroAcetamide poisoning with Acetamide. METHODS: Eighty clean Sprague-Dawley rats were randomly divided into five groups: saline control group,dimethylsulfoxide water solution control group,TET poisoning group, Acetamide (2.88 g/kg/d) treatment group, and Acetamide (5.68 g/kg/d) treatment group, with 16 rats in each group. Rats in the poisoning group and treatment groups were poisoned with TET by intragastric administration after fasting; then, saline was injected intramuscularly into rats of the poisoning group, and different doses of Acetamide were injected intramuscularly into rats of treatment groups; the course of treatment was 5 d. At 3 h, 12 h, 48 h, and 7 d after treatment, the cerebral cortex was harvested from rats in each group, and the histopathological changes in the cerebral cortex were evaluated under light and electron microscopes. RESULTS: The light microscopy showed that the TET poisoning group had hypoxia changes in the cerebral cortex, which worsened over time; the treatment groups had reduced hypoxia changes, and the Acetamide (2.88 g/kg/d) treatment group had more reduction than the Acetamide (5.68 g/kg/d) treatment group. The electron microscopy showed that the apoptosis of neuronal cells were the main pathological changes in the TET poisoning group; the treatment groups had reduced apoptotic changes, and the Acetamide (2.88 g/kg/d) treatment group had more reduction than the Acetamide (5.68 g/kg/d) treatment group. CONCLUSION: No pathological changes associated with the synergistic toxic effect of Acetamide and TET are found in the cerebral cortex. Acetamide (2.88 g/kg/d) could reduce central nervous lesions, but the efficacy is not improved after increasing the dose. For patients who cannot be identified with TET or fluoroAcetamide poisoning, Acetamide could be considered for treatment.
[Effects of acetamide at different doses on expression of amino acids in cerebral cortex of rats with acute tetramine poisoning].[Pubmed:25169228]
Zhonghua Lao Dong Wei Sheng Zhi Ye Bing Za Zhi. 2014 Jun;32(6):438-41.
OBJECTIVE: To investigate the effects of Acetamide at different doses on the expression of inhibitory amino acids (gamma-aminobutyric acid, GABA) and excitatory amino acid (glutamate, Glu) in the cerebral cortex of rats with acute tetramine (TET) poisoning. METHODS: Eighty Sprague-Dawley rats (SPF) were randomly divided into five groups, with 16 rats in each group: saline control group, dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO) control group, TET exposure group, high-dose (2.8 g/kg/d) Acetamide treatment group, and super-high-dose (5.6 g/kg/d) Acetamide treatment group. Rats in the exposure group and treatment groups were exposed to TET by intragastric administration after fasting, and were then intramuscularly injected with saline or different doses of Acetamide in the following 5 days. The cortex of the temporal lobe was collected at 3 h, 12 h, 48 h, or 7 d after treatment. The expression levels of GABA and Glu in the cortex of the temporal lobe were determined by average optical density (OD) values in immunohistochemistry. RESULTS: 1) Expression of GABA: The OD value of GABA in TET exposure group started to increase at 12 h after treatment, reached the peak at 48 h, and decreased to the normal level at 7 d. In the high-dose Acetamide treatment group, the increase in OD at 12 h was not so significant as that in the TET exposure group, OD value decreased to the normal level at 48 h and was lower than that in the exposure group, and the changes were more like those in the control groups. In the super-high-dose Acetamide treatment group, OD value began to increase significantly at 3 h and was significantly higher than that in the TET exposure group (P < 0.01), it reached the peak at 12 h, and was restored to the normal value at 48 h. 2) Expression of Glu: The OD value of Glu in TET exposure group at 3 h after treatment was significantly lower than those in the two control groups, it increased gradually from 12 h to 48 h, and recovered to the normal level at the 7th d. The changes in the high-dose Acetamide treatment group were similar to those in the TET exposure group, but became more like those in the control groups after 48 h; the OD value in super-high-dose Acetamide treatment group was significantly higher than that in the TET exposure group at 3 h after treatment (P < 0.01), while no significant difference was found at 12 h; it was significantly lower than those of all other groups at 48 h and 7 d (P < 0.01). CONCLUSIONS: Treatment with high dose of Acetamide has some curative effect on TET poisoning-induced central nervous lesion, while the effect of super-high-dose Acetamide on expression of neurotransmitters is too complex to evaluate.


