2-Amino-3-carboxy-1,4-naphthoquinoneCAS# 173043-38-4 |
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 173043-38-4 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 9859229 | Appearance | Powder |
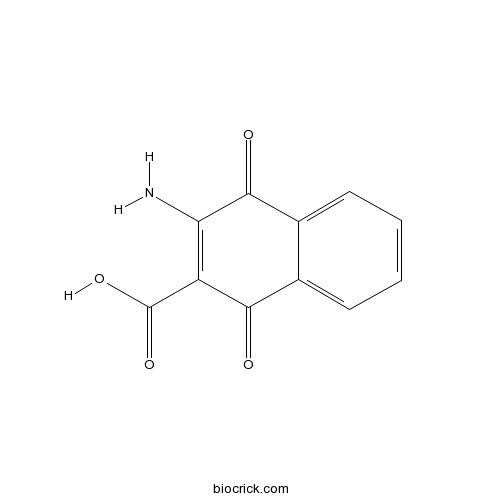
| Formula | C11H7NO4 | M.Wt | 217.18 |
| Type of Compound | Quinones | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Solubility | Soluble in Chloroform,Dichloromethane,Ethyl Acetate,DMSO,Acetone,etc. | ||
| Chemical Name | 3-amino-1,4-dioxonaphthalene-2-carboxylic acid | ||
| SMILES | C1=CC=C2C(=C1)C(=O)C(=C(C2=O)N)C(=O)O | ||
| Standard InChIKey | GXDIXDKPIUJGOV-UHFFFAOYSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C11H7NO4/c12-8-7(11(15)16)9(13)5-3-1-2-4-6(5)10(8)14/h1-4H,12H2,(H,15,16) | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | 2-Amino-3-carboxy-1,4-naphthoquinone is a novel growth stimulator for bifidobacteria, it affects the end-product profile of bifidobacteria through the mediated oxidation of NAD(P)H. |
| Targets | NADPH-oxidase |
| In vitro | Role of 2-amino-3-carboxy-1,4-naphthoquinone, a strong growth stimulator for bifidobacteria, as an electron transfer mediator for NAD(P)(+) regeneration in Bifidobacterium longum.[Pubmed: 10434042]Biochim Biophys Acta. 1999 Aug 5;1428(2-3):241-50.2-Amino-3-carboxy-1,4-naphthoquinone (ACNQ) is a novel growth stimulator for bifidobacteria. The role of ACNQ as a mediator of the electron transfer from NAD(P)H to dioxygen (O(2)) and hydrogen peroxide (H(2)O(2)), proposed in our previous paper, was examined using the cell-free extract and whole cells of Bifidobacterium longum.
|
| Cell Research | 2-Amino-3-carboxy-1,4-naphthoquinone affects the end-product profile of bifidobacteria through the mediated oxidation of NAD(P)H.[Pubmed: 12073135 ]Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2002 Jun;59(1):72-8.Glucose metabolism of bifidobacteria in the presence of 2-Amino-3-carboxy-1,4-naphthoquinone (ACNQ), a specific growth stimulator for bifidobacteria, and ferricyanide (Fe(CN)(6)(3-)) as an extracellular electron acceptor was examined using resting cells of Bifidobacterium longum and Bifidobacterium breve.
|

2-Amino-3-carboxy-1,4-naphthoquinone Dilution Calculator

2-Amino-3-carboxy-1,4-naphthoquinone Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 4.6045 mL | 23.0224 mL | 46.0448 mL | 92.0895 mL | 115.1119 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.9209 mL | 4.6045 mL | 9.209 mL | 18.4179 mL | 23.0224 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.4604 mL | 2.3022 mL | 4.6045 mL | 9.209 mL | 11.5112 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0921 mL | 0.4604 mL | 0.9209 mL | 1.8418 mL | 2.3022 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.046 mL | 0.2302 mL | 0.4604 mL | 0.9209 mL | 1.1511 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
- Graveobioside A
Catalog No.:BCN8570
CAS No.:506410-53-3
- Gancaonin N
Catalog No.:BCN8569
CAS No.:129145-52-4
- Saikogenin D
Catalog No.:BCN8568
CAS No.:5573-16-0
- Vinaginsenoside R8
Catalog No.:BCN8567
CAS No.:156042-22-7
- 3-Feruloyl-1-Sinapoyl sucrose
Catalog No.:BCN8566
CAS No.:98942-06-4
- Periplocoside N
Catalog No.:BCN8565
CAS No.:39946-41-3
- Lancifodilactone F
Catalog No.:BCN8564
CAS No.:850878-47-6
- 3'-Demethylnobiletin
Catalog No.:BCN8563
CAS No.:112448-39-2
- Erigoster B
Catalog No.:BCN8562
CAS No.:849777-61-3
- Acanthopanaxoside B
Catalog No.:BCN8561
CAS No.:915792-03-9
- Glabrolide
Catalog No.:BCN8560
CAS No.:10401-33-9
- Anemarrhenasaponin I
Catalog No.:BCN8559
CAS No.:163047-21-0
- 4'-O-Methylochnaflavone
Catalog No.:BCN8572
CAS No.:49619-87-6
- Perisesaccharide B
Catalog No.:BCN8573
CAS No.:1095261-93-0
- Tectol
Catalog No.:BCN8574
CAS No.:24449-39-6
- Jionoside D
Catalog No.:BCN8575
CAS No.:120406-34-0
- 5,6-Dehydroginsenoside Rd
Catalog No.:BCN8576
CAS No.:1268459-68-2
- Epitheaflagallin 3-O-gallate
Catalog No.:BCN8577
CAS No.:102067-92-5
- Hexamethylquercetagetin
Catalog No.:BCN8578
CAS No.:1251-84-9
- 4-Benzamido-2,5-diethoxybenzenediazonium
Catalog No.:BCN8579
CAS No.:5486-84-0
- Uvarigrin
Catalog No.:BCN8580
CAS No.:200563-11-7
- Isoginsenoside Rh3
Catalog No.:BCN8581
CAS No.:166040-90-0
- Isorosmanol
Catalog No.:BCN8582
CAS No.:93780-80-4
- Ligupurpuroside C
Catalog No.:BCN8583
CAS No.:1194056-33-1
2-Amino-3-carboxy-1,4-naphthoquinone affects the end-product profile of bifidobacteria through the mediated oxidation of NAD(P)H.[Pubmed:12073135]
Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2002 Jun;59(1):72-8.
Glucose metabolism of bifidobacteria in the presence of 2-Amino-3-carboxy-1,4-naphthoquinone (ACNQ), a specific growth stimulator for bifidobacteria, and ferricyanide (Fe(CN)(6)(3-)) as an extracellular electron acceptor was examined using resting cells of Bifidobacterium longum and Bifidobacterium breve. NAD(P)H in the cells is oxidized by ACNQ with the aid of diaphorase activity, and reduced ACNQ donates the electron to Fe(CN)(6)(3-). Exogenous oxidation of NADH by the ACNQ/Fe(CN)(6)(3-) system suppresses the endogenous lactate dehydrogenase reaction competitively, which results in the remarkable generation of pyruvate and a decrease in lactate production. In addition, a decrease in acetate generation is also observed in the presence of ACNQ and Fe(CN)(6)(3-). This phenomenon could not be explained in terms of the fructose-6-phosphate phosphoketolase pathway, but suggests rather that glucose is partially metabolized via the hexose monophosphate pathway. This was verified by NADP(+)-induced reduction of Fe(CN)(6)(3-) in cell-free extracts in the presence of ACNQ. Effects of the ACNQ/Fe(CN)(6)(3-) system on anaerobically harvested cells were also examined. Stoichiometric analysis of the metabolites from the pyruvate-formate lyase pathway suggests that exogenous oxidation of NADH is an efficient method to produce ATP in this pathway.
Role of 2-amino-3-carboxy-1,4-naphthoquinone, a strong growth stimulator for bifidobacteria, as an electron transfer mediator for NAD(P)(+) regeneration in Bifidobacterium longum.[Pubmed:10434042]
Biochim Biophys Acta. 1999 Aug 5;1428(2-3):241-50.
2-Amino-3-carboxy-1,4-naphthoquinone (ACNQ) is a novel growth stimulator for bifidobacteria. The role of ACNQ as a mediator of the electron transfer from NAD(P)H to dioxygen (O(2)) and hydrogen peroxide (H(2)O(2)), proposed in our previous paper, was examined using the cell-free extract and whole cells of Bifidobacterium longum. Continuous monitoring of ACNQ, O(2) and H(2)O(2) by several amperometric techniques has revealed that ACNQ works as a good electron acceptor of NAD(P)H diaphorase and that the reduced form of ACNQ is easily autoxidized and also acts as a better electron donor of NAD(P)H peroxidase than NAD(P)H. The generation of H(2)O(2) by B. longum under aerobic conditions is effectively suppressed in the presence of ACNQ. These ACNQ-mediated reactions would play roles as NAD(P)(+)-regeneration processes. The accumulation of ACNQ in the cytosol has been also suggested. These characteristics of ACNQ seem to be responsible for the growth stimulation of bifidobacteria. Vitamin K(3), which has an extremely low growth-stimulating activity and was used as a reference compound, exhibits much lower activity as an electron transfer mediator. The difference in the activity is discussed in terms of the redox potential and partition property of the quinones.


