2-AllylphenolCAS# 1745-81-9 |
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

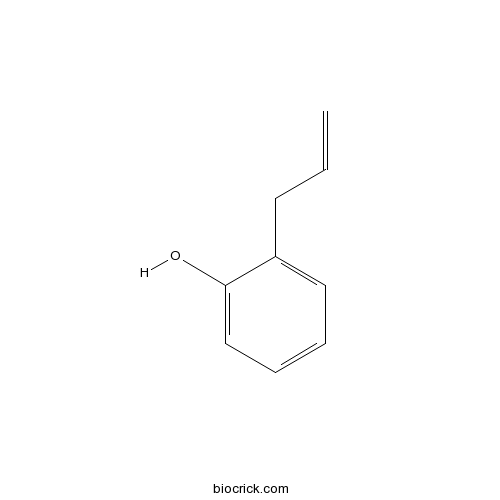
| Cas No. | 1745-81-9 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 15624 | Appearance | Powder |
| Formula | C9H10O | M.Wt | 134 |
| Type of Compound | N/A | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Solubility | Soluble in Chloroform,Dichloromethane,Ethyl Acetate,DMSO,Acetone,etc. | ||
| Chemical Name | 2-prop-2-enylphenol | ||
| SMILES | C=CCC1=CC=CC=C1O | ||
| Standard InChIKey | QIRNGVVZBINFMX-UHFFFAOYSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C9H10O/c1-2-5-8-6-3-4-7-9(8)10/h2-4,6-7,10H,1,5H2 | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||

2-Allylphenol Dilution Calculator

2-Allylphenol Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 7.4627 mL | 37.3134 mL | 74.6269 mL | 149.2537 mL | 186.5672 mL |
| 5 mM | 1.4925 mL | 7.4627 mL | 14.9254 mL | 29.8507 mL | 37.3134 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.7463 mL | 3.7313 mL | 7.4627 mL | 14.9254 mL | 18.6567 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.1493 mL | 0.7463 mL | 1.4925 mL | 2.9851 mL | 3.7313 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0746 mL | 0.3731 mL | 0.7463 mL | 1.4925 mL | 1.8657 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
- alpha-Spinasterol glucoside
Catalog No.:BCN1120
CAS No.:1745-36-4
- Tipranavir
Catalog No.:BCC2002
CAS No.:174484-41-4
- Sanggenol A
Catalog No.:BCN3602
CAS No.:174423-30-4
- Amiloride HCl dihydrate
Catalog No.:BCC5068
CAS No.:17440-83-4
- Riluzole
Catalog No.:BCC3849
CAS No.:1744-22-5
- Tsugaric acid A
Catalog No.:BCN2980
CAS No.:174391-64-1
- Picropodophyllotoxin
Catalog No.:BCN2585
CAS No.:17434-18-3
- Astragaloside
Catalog No.:BCN5959
CAS No.:17429-69-5
- Caohuoside E
Catalog No.:BCN8198
CAS No.:174286-23-8
- Epimedin K
Catalog No.:BCN8201
CAS No.:174286-13-6
- Apigenin 7-O-(2G-rhamnosyl)gentiobioside
Catalog No.:BCN1524
CAS No.:174284-20-9
- Pancixanthone A
Catalog No.:BCN7379
CAS No.:174232-30-5
- SDZ 220-581
Catalog No.:BCC1939
CAS No.:174575-17-8
- SDZ 220-040
Catalog No.:BCC6992
CAS No.:174575-40-7
- SB 218795
Catalog No.:BCC7037
CAS No.:174635-53-1
- SB-222200
Catalog No.:BCC1926
CAS No.:174635-69-9
- Talnetant
Catalog No.:BCC1981
CAS No.:174636-32-9
- Phalloidin
Catalog No.:BCC7945
CAS No.:17466-45-4
- AN-2690
Catalog No.:BCC1360
CAS No.:174671-46-6
- CH 275
Catalog No.:BCC5913
CAS No.:174688-78-9
- 2-Amino-6-methoxybenzothiazole
Catalog No.:BCC8542
CAS No.:1747-60-0
- Ginsenoside Rh4
Catalog No.:BCN3503
CAS No.:174721-08-5
- Carabrone
Catalog No.:BCN1121
CAS No.:1748-81-8
- Fmoc-Hyp(Bzl)-OH
Catalog No.:BCC3255
CAS No.:174800-02-3
Metabolism of fungicide 2-allylphenol in Rhizoctonia cerealis.[Pubmed:24530843]
Ecotoxicol Environ Saf. 2014 Apr;102:136-41.
2-Allylphenol is a biomimetic synthetic fungicide that mimics the compound ginkgol found in gingko fruit (Gingko biloba L.). This systemic fungicide can effectively suppress a wide range of plant diseases, including wheat sharp eyespot (Rhizoctonia cerealis). However, its degradation in environment after application is still unknown. To understand this fungicide degradation, major metabolites of 2-Allylphenol in R. cerealis were examined. The parent and metabolites of 2-Allylphenol were detected and quantified in the mycelia and liquid medium. Results showed that 2-Allylphenol was metabolized and bio-transformed by R. cerealis, and four metabolites were found, including 2-(2-hydroxyphenyl) acetic acid (M1), 2-(2, 3-dihydroxypropyl) phenol (M2), 2-(2-hydroxypropyl)-phenol (M3) and 2-(3-hydroxypropyl)-phenol (M4). Based on the results, we propose that the biodegradation pathway is that 2-Allylphenol is rapidly oxidized into metabolite M2 and hydrolyzed into M3 and M4, which formed M2, and carboxylation of M2 to 2-hydroxy-3-(2-hydroxyphenyl) propionic acid which undergo hydrolyzation and decarboxylation to form M1. 2-Allylphenol can be bio-transformed to new compounds by R. cerealis, suggesting the existence of microbe metabolic pathways for 2-Allylphenol.
Inhibitory effect of bionic fungicide 2-allylphenol on Botrytis cinerea (Pers. ex Fr.) in vitro.[Pubmed:19685448]
Pest Manag Sci. 2009 Dec;65(12):1337-43.
BACKGROUND: 2-Allylphenol is a registered fungicide in China to control fungal diseases on tomato, strawberry and apple. It is synthetic and structurally resembles the active ingredient ginkgol isolated from Ginkgo biloba L. bark. 2-Allylphenol has been used in China for 10 years. However, its biochemical mode of action remains unclear. An in vitro study was conducted on the biochemical mechanism of 2-allyphenol inhibiting Botrytis cinerea (Pers. ex Fr.). RESULTS: The inhibition was approximately 3 times stronger when the fungus was grown on non-fermentable source, glycerol, than that on a fermentable carbon source, glucose. Inhibition of B. cinerea and Magnaporthe oryzae (Hebert) Barr mycelial growth was markedly potentiated in the presence of salicylhydroxamic acid (SHAM), an inhibitor of mitochondrial alternative oxidase. Furthermore, at 3 h after treatment with 2-Allylphenol, oxygen consumption had recovered, but respiration was resistant to potassium cyanide and sensitive to SHAM, indicating that 2-Allylphenol had the ability to induce cyanide-resistant respiration. The mycelium inhibited in the presence of 2-Allylphenol grew vigorously after being transferred to a fungicide-free medium, indicating that 2-Allylphenol is a fungistatic compound. Adenine nucleotide assay showed that 2-Allylphenol depleted ATP content and decreased the energy charge values, which confirmed that 2-Allylphenol is involved in the impairment of the ATP energy generation system. CONCLUSION: These results suggested that 2-Allylphenol induces cyanide-resistant respiration and causes ATP decrease, and inhibits respiration by an unidentified mechanism.
Synthesis of 2,3-Dihydrobenzofurans via the Palladium Catalyzed Carboalkoxylation of 2-Allylphenols.[Pubmed:28392926]
Org Chem Front. 2016 Oct 1;3(10):1314-1318.
A new Pd-catalyzed alkene carboalkoxylation strategy for the preparation of 2,3-dihydrobenzofurans is described. This method effects the coupling of readily available 2-Allylphenol derivatives with aryl triflates to generate a wide range of functionalized 2,3-dihydrobenzofurans in good yields and diastereoselectivities (up to >20:1). Use of newly developed reaction conditions that promote anti-heteropalladation of the alkene is essential in order to generate products in high yield.
Acid-promoted direct electrophilic trifluoromethylthiolation of phenols.[Pubmed:25627036]
Org Biomol Chem. 2015 Mar 14;13(10):3103-15.
The electrophilic aromatic ring trifluoromethylthiolation of various substituted phenols was accomplished using PhNHSCF3 (N-trifluoromethylsulfanyl)aniline, (1) in the presence of BF3.Et2O (2) or triflic acid as the promoter. The functionalization was exclusively para-selective; phenols unsubstituted in both the ortho- and para positions solely gave the para-substituted SCF3-products in all cases, while para-substituted phenols gave the ortho-substituted SCF3-products. 3,4-Dialkyl substituted phenols yielded the corresponding products according to the Mills-Nixon effect, and estrone and estradiol furnished biologically interesting SCF3-analogues. The highly reactive catechol and pyrogallol substrates gave the expected products smoothly in the presence of BF3.Et2O, whereas less reactive phenols required triflic acid. 2-Allylphenol gave the expected p-SCF3 analogue, which underwent an addition/cyclization sequence and furnished a new di-trifluoromethylthio substituted 2,3-dihydrobenzofuran derivative. Some additional transformations of 4-(trifluoromethylthio)phenol with NBS, NIS, HNO3, HNO3/H2SO4 and 4-bromobenzyl bromide were performed giving bromo-, iodo-, nitro- and benzyl substituted products. The latter derivative underwent Suzuki-Miyaura coupling with phenylboronic acid.


