Clerodendrum indicum
Clerodendrum indicum
1. The products in our compound library are selected from thousands of unique natural products; 2. It has the characteristics of diverse structure, diverse sources and wide coverage of activities; 3. Provide information on the activity of products from major journals, patents and research reports around the world, providing theoretical direction and research basis for further research and screening; 4. Free combination according to the type, source, target and disease of natural product; 5. The compound powder is placed in a covered tube and then discharged into a 10 x 10 cryostat; 6. Transport in ice pack or dry ice pack. Please store it at -20 °C as soon as possible after receiving the product, and use it as soon as possible after opening.
Natural products/compounds from Clerodendrum indicum
- Cat.No. Product Name CAS Number COA
-
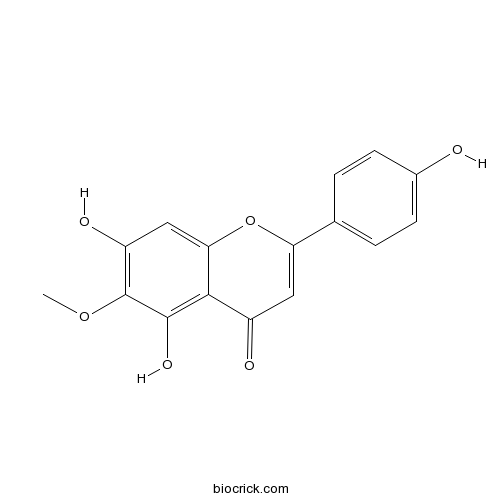
BCN6250
Hispidulin1447-88-7
Instructions
-
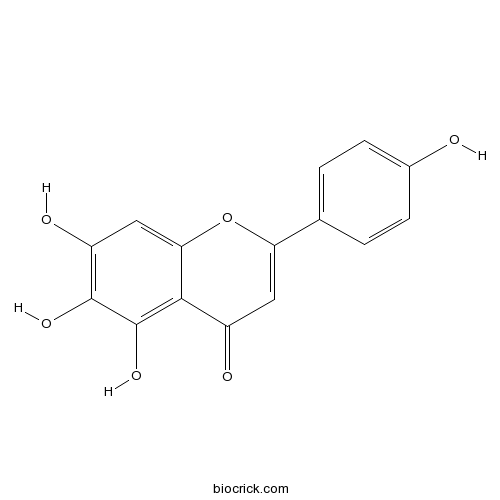
BCN5380
Scutellarein529-53-3
Instructions
Cytotoxic activity of the chemical constituents of Clerodendrum indicum and Clerodendrum villosum roots.[Pubmed: 29397094]
The roots of two Thai medicinal plants, Clerodendrum indicum and Clerodendrum villosum are found in traditional medicine practices. The aim of this research was to preliminarily study the cytotoxicity of extracts of their roots, and the parts that possessed cytotoxic activity were separated on a chromatograph to identify their active compounds.
Network pharmacology-based virtual screening of natural products from Clerodendrum species for identification of novel anti-cancer therapeutics.[Pubmed: 28070575]
Plant-derived natural products (NPs) play a vital role in the discovery of new drug molecules and these are used for development of novel therapeutic drugs for a specific disease target. Literature review suggests that natural products possess strong inhibitory efficacy against various types of cancer cells. Clerodendrum indicum and Clerodendrum serratum are reported to have anticancer activity; therefore a study was carried out to identify selective anticancer agents from these plants species. In this report, we employed a docking weighted network pharmacological approach to understand the multi-therapeutics potentiality of C. indicum and C. serratum against various types of cancer. A library of 53 natural products derived from these plants was compiled from the literature and three dimensional space analyses were performed in order to establish the drug-likeness of the NPs library. Further, an NPs-cancer network was built based on docking. We predicted five compounds, namely apigenin 7-glucoside, hispidulin, scutellarein-7-O-beta-d-glucuronate, acteoside and verbascoside, to be potential binding therapeutics for cancer target proteins. Apigenin 7-glucoside and hispidulin were found to have maximum binding interactions (relationship) with 17 cancer drug targets in terms of docking weighted network pharmacological analysis. Hence, we used an integrative approach obtained from network pharmacology for identifying combinatorial drug actions against the cancer targets. We believe that our present study may provide important clues for finding novel drug inhibitors for cancer.
Antiplasmodial activities of a Thai traditional antipyretic formulation, Bencha-Loga-Wichian: A comparative study between the roots and their substitutes, the stems.[Pubmed: 27396349]
Bencha-Loga-Wichian (BLW) is a polyherbal antipyretic formulation that is comprised of Capparis micracantha, Clerodendrum indicum, Ficus racemosa, Harrisonia perforata, and Tiliacora triandra. A traditional medical textbook has documented the use of this formulation for the treatment of many types of fever, including malaria-like fever. Traditionally, BLW is composed of the root parts of those plants. However, in current practice, the stem parts are frequently substituted. Thus, this study aimed to evaluate the antiplasmodial activities of BLW and compare the efficacy between the stem and root parts.
Large Scale Screening of Ethnomedicinal Plants for Identification of Potential Antibacterial Compounds.[Pubmed: 26985889]
The global burden of bacterial infections is very high and has been exacerbated by increasing resistance to multiple antibiotics. Antibiotic resistance leads to failed treatment of infections, which can ultimately lead to death. To overcome antibiotic resistance, it is necessary to identify new antibacterial agents. In this study, a total of 662 plant extracts (diverse parts) from 222 plant species (82 families, 177 genera) were screened for antibacterial activity using the agar cup plate method. The aqueous and methanolic extracts were prepared from diverse plant parts and screened against eight bacterial (two Gram-positive and six Gram-negative) species, most of which are involved in common infections with multiple antibiotic resistance. The methanolic extracts of several plants were shown to have zones of inhibition ≥ 12 mm against both Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria. The minimum inhibitory concentration was calculated only with methanolic extracts of selected plants, those showed zone of inhibition ≥ 12 mm against both Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria. Several extracts had minimum inhibitory concentration ≤ 1 mg/mL. Specifically Adhatoda vasica, Ageratum conyzoides, Alangium salvifolium, Alpinia galanga, Andrographis paniculata, Anogeissus latifolia, Annona squamosa, A. reticulate, Azadirachta indica, Buchanania lanzan, Cassia fistula, Celastrus paniculatus, Centella asiatica, Clausena excavate, Cleome viscosa, Cleistanthus collinus, Clerodendrum indicum, Croton roxburghii, Diospyros melanoxylon, Eleutherine bulbosa, Erycibe paniculata, Eryngium foetidum, Garcinia cowa, Helicteres isora, Hemidesmus indicus, Holarrhena antidysenterica, Lannea coromandelica, Millettia extensa, Mimusops elengi, Nyctanthes arbor-tristis, Oroxylum indicum, Paederia foetida, Pterospermum acerifolium, Punica granatum, Semecarpus anacardium, Spondias pinnata, Terminalia alata and Vitex negundo were shown to have significant antimicrobial activity. The species listed here were shown to have anti-infective activity against both Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria. These results may serve as a guide for selecting plant species that could yield the highest probability of finding promising compounds responsible for the antibacterial activities against a broad spectrum of bacterial species. Further investigation of the phytochemicals from these plants will help to identify the lead compounds for drug discovery.
Phytochemical investigation and in vitro antinociceptive activity of Clerodendrum indicum leaves.[Pubmed: 22866546]
The crude ethanolic extracts of Clerodendrum indicum Linn. leaves were investigated for possible antinociceptive activity using acetic acid induced writhing model in mice. Phytochemical analysis was also carried out according to the standard procedures to identify the presence of different phytoconstituents in the ethanolic extract of the plant leaves. The study results showed 38.91 and 55.24% inhibition of writhings in the tested mice when ethanolic extract of Clerodendrum indicum Linn. leaves at doses of 250 and 500 mg kg(-1) body weight was given intraperitoneally, respectively. The study results were also compared with antinociceptive activity of the standard drug, Diclofenac sodium (68.37% inhibition) used at 25 mg kg(-1) body weight. At the above doses, the crude ethanolic extract of the plant showed significant antinociceptive activity in dose dependent fashion in acetic acid-induced writhing model in mice. The inhibition of writhings was calculated in respective to control group and it was found that p-values (<0.0001) obtained in all cases were extremely statistically significant. However, the phytochemical analysis showed the presence of alkaloid, steroid, saponin, tannin, reducing sugar and gum. The results suggest that crude ethanolic extracts of Clerodendrum indicum leaves possess significant antinociceptive properties justifying its folkloric use as analgesics and further research is necessary to isolate the principle phytochemical constituent(s) responsible for this activity.
Chemical and biological investigation of some Clerodendrum species cultivated in Egypt.[Pubmed: 20738216]
Phytochemical investigation of Clerodendrum chinense (Osbeck) Mabberley (Lamiaceae) cultivated in Egypt and evaluation for anti-inflammatory, analgesic, and antipyretic effects of the methanol and chloroform extracts of Clerodendrum chinense, Clerodendrum indicum (L.) Kuntze, Clerodendrum glabrum E. Meyer.
Medicinal plants from Nepal; II. Evaluation as inhibitors of lipid peroxidation in biological membranes.[Pubmed: 10197748]
In an ethnopharmacological screening of selected Nepalese medicinal plants, the inhibitory effect on lipid peroxidation of 36 methanolic extracts of 28 different plant species were evaluated using bovine brain phospholipid liposomes as model membranes. The most potent inhibitor with an IC50 value of 0.93 microg/ml was the extract obtained from the bark of Clerodendrum indicum. The extracts obtained from Aglaia roxburghiana fruits, Euonymus pendulus barks and Emblica officinalis fruits were also active and inhibited lipid peroxidation with IC50 values of 10, 12 and 13 microg/ml, respectively. The most active extracts were from indigenous plants traditionally used to treat inflammatory diseases.


