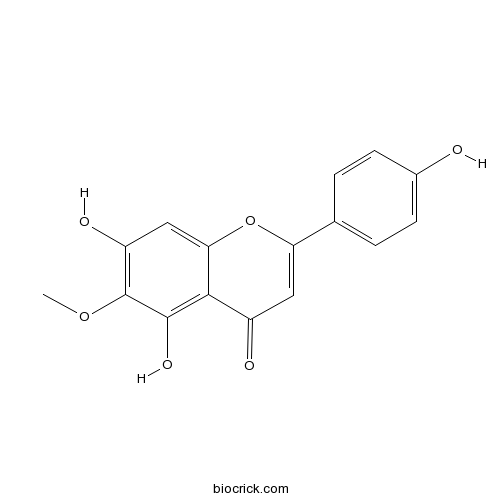
HispidulinPartial positive allosteric modulator at the benzodiazepine receptor CAS# 1447-88-7 |
- LDE225 Diphosphate
Catalog No.:BCC1693
CAS No.:1218778-77-8
- Purmorphamine
Catalog No.:BCC3641
CAS No.:483367-10-8
- LDE225 (NVP-LDE225,Erismodegib)
Catalog No.:BCC5066
CAS No.:956697-53-3
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 1447-88-7 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 5281628 | Appearance | Yellowish powder |
| Formula | C16H12O6 | M.Wt | 300.3 |
| Type of Compound | Flavonoids | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Synonyms | Dinatin | ||
| Solubility | DMSO : 62.5 mg/mL (208.15 mM; Need ultrasonic) H2O : < 0.1 mg/mL (insoluble) | ||
| Chemical Name | 5,7-dihydroxy-2-(4-hydroxyphenyl)-6-methoxychromen-4-one | ||
| SMILES | COC1=C(C=C2C(=C1O)C(=O)C=C(O2)C3=CC=C(C=C3)O)O | ||
| Standard InChIKey | IHFBPDAQLQOCBX-UHFFFAOYSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C16H12O6/c1-21-16-11(19)7-13-14(15(16)20)10(18)6-12(22-13)8-2-4-9(17)5-3-8/h2-7,17,19-20H,1H3 | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | Hispidulin has anti-oxidative, anti-inflammatory, anti-cancer, antiepileptic, neuroprotective, anti-osteoporotic and bone resorption attenuating effects, it targets the VEGF receptor 2-mediated PI3K/Akt/mTOR signaling pathway in endothelial cells, leading to the suppression of pancreatic tumor growth and angiogenesis. Hispidulin can ameliorate high glucose-mediated endothelial dysfunction via inhibiting PKCβII-associated NLRP3 inflammasome activation and NF-κB signaling, it has potential application in the prevention and treatment of diabetic vascular complications. Hispidulin can inhibit platelet aggregation by elevating cAMP levels by a mechanism different from that of theophylline or PGE1. |
| Targets | HIF | AMPK | P-gp | IL Receptor | NF-kB | TNF-α | MAPK | IkB | VEGFR | PI3K | Akt | mTOR | PGE | cAMP | IKK |
| In vitro | Ameliorative effects of hispidulin on high glucose-mediated endothelial dysfunction via inhibition of PKCβII-associated NLRP3 inflammasome activation and NF-κB signaling in endothelial cells[Reference: WebLink]J. Funct. Foods, 2016, 27:392-405.Endothelial dysfunction is closely relevant to atherosclerosis complications in diabetic patients. Hispidulin, a flavone derived from the herb Salvia plebeia R. Br., has numerous biological properties including anti-inflammatory and antioxidative effects, but the underlying mechanism of its anti-inflammatory action remains unclear. This study was designed to investigate the effects of Hispidulin on endothelial homeostasis and its mechanism. Hispidulin, a natural flavone, inhibits human platelet aggregation by increasing cAMP levels.[Pubmed: 2836213]Eur J Pharmacol. 1988 Feb 16;147(1):1-6.Hispidulin, a natural flavone, and theophylline inhibited platelet aggregation triggered by adenosine-5'-monophosphate, arachidonic acid, paf-acether and collagen. |
| In vivo | Protective effect of hispidulin on kainic acid-induced seizures and neurotoxicity in rats.[Pubmed: 25746462]Eur J Pharmacol. 2015 May 15;755:6-15.Hispidulin is a flavonoid compound which is an active ingredient in a number of traditional Chinese medicinal herbs, and it has been reported to inhibit glutamate release. The purpose of this study was to investigate whether Hispidulin protects against seizures induced by kainic acid, a glutamate analog with excitotoxic properties. Hispidulin exerts anti-osteoporotic activity in ovariectomized mice via activating AMPK signaling pathway.[Pubmed: 24338527]Cell Biochem Biophys. 2014 Jun;69(2):311-7.To investigate the effect of Hispidulin on ovariectomy (OVX)-induced bone loss in mice. |
| Kinase Assay | Hispidulin, a small flavonoid molecule, suppresses the angiogenesis and growth of human pancreatic cancer by targeting vascular endothelial growth factor receptor 2-mediated PI3K/Akt/mTOR signaling pathway.[Pubmed: 21087351]Hispidulin inhibits proliferation and enhances chemosensitivity of gallbladder cancer cells by targeting HIF-1α.[Pubmed: 25499970 ]Exp Cell Res. 2015 Mar 15;332(2):236-46.Gallbladder cancer (GBC) is an aggressive malignancy of the bile duct, which is associated with a low (5-year) survival and poor prognosis. The transcription factor HIF-1α is implicated in the angiogenesis, cell survival, epithelial mesenchymal transition (EMT) and invasiveness of GBC. Cancer Sci., 2011, 102(1):219-25.Hispidulin, an active component from Artemisia vestita, a traditional Tibetan medicinal plant, has been shown to possess anti-inflammatory and anti-oxidative activities. However, the functional role of Hispidulin on tumor growth and angiogenesis has not been elucidated. |
| Structure Identification | J Ethnopharmacol. 2015 May 26;166:18-22.Hispidulin, a constituent of Clerodendrum inerme that remitted motor tics, alleviated methamphetamine-induced hyperlocomotion without motor impairment in mice.[Pubmed: 25764963]Previously, we found a patient with an intractable motor tic disorder that could be ameliorated by the ground leaf juice of Clerodendrum inerme (CI). Furthermore, the ethanol extract of CI leaves effectively ameliorated methamphetamine-induced hyperlocomotion (MIH) in mice, an animal model mimicking the hyper-dopaminergic status of tic disorders/Tourette syndrome, schizophrenia, or obsessive-compulsive disorder. Here, we for the first time identified a constituent able to reduce MIH from the CI ethanol extract that might represent a novel lead for the treatment of such disorders. |

Hispidulin Dilution Calculator

Hispidulin Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 3.33 mL | 16.65 mL | 33.3 mL | 66.6001 mL | 83.2501 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.666 mL | 3.33 mL | 6.66 mL | 13.32 mL | 16.65 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.333 mL | 1.665 mL | 3.33 mL | 6.66 mL | 8.325 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0666 mL | 0.333 mL | 0.666 mL | 1.332 mL | 1.665 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0333 mL | 0.1665 mL | 0.333 mL | 0.666 mL | 0.8325 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
Hispidulin is a natural flavone with a broad spectrum of biological activities. Hispidulin is a Pim-1 inhibitor with an IC50 of 2.71 μM.
In Vitro:Hispidulin induces cell death in a dose- and time-dependent manner in HepG2 cells. Hispidulin induces apoptosis through mitochondrial dysfunction, which is characterized by decreased Bcl-2/Bax ratio, disrupted mitochondrial membrane potential and increased release of cytochrome C and activated capase-3[2].
In Vivo:Hispidulin shows significant inhibitory effect on mice tumor size[2]. Hispidulin treatment effectively prevents ovariectomy-induced body weight loss and attenuates ovariectomy-induced bone loss. Hispidulin treatment also decreases trabecular spacing in ovariectomy mice[3]. Intraperitoneally administering hispidulin(10 or 50mg/ kg) to rats 30 min before intraperitoneally injecting kainic acid (15mg/kg) increases seizure latency and decreases seizure score. In addition, hispidulin substantially attenuates kainic acid-induced hippocampal neuronal cell death, and this protective effect is accompanied by the suppression of microglial activation and the production of proinflammatory cytokines such as interleukin-1β, interleukin-6, and tumor necrosis factor-α in the hippocampus[4].
References:
[1]. Chao SW, et al. Total Synthesis of Hispidulin and the Structural Basis for Its Inhibition of Proto-oncogene KinasePim-1. J Nat Prod. 2015 Aug 28;78(8):1969-76.
[2]. Gao H, et al. Hispidulin induces apoptosis through mitochondrial dysfunction and inhibition of P13k/Akt signalling pathway in HepG2 cancer cells. Cell Biochem Biophys. 2014 May;69(1):27-34.
[3]. Zhou R, et al. Hispidulin exerts anti-osteoporotic activity in ovariectomized mice via activating AMPK signaling pathway. Cell Biochem Biophys. 2014 Jun;69(2):311-7.
[4]. Lin TY, et al. Protective effect of hispidulin on kainic acid-induced seizures and neurotoxicity in rats. Eur J Pharmacol. 2015 May 15;755:6-15.
- Olmesartan medoxomil
Catalog No.:BCC2143
CAS No.:144689-63-4
- Olmesartan
Catalog No.:BCC1819
CAS No.:144689-24-7
- (+)-Lyoniresinol
Catalog No.:BCN6248
CAS No.:14464-90-5
- 22-Hydroxy-3-oxoolean-12-en-29-oic acid
Catalog No.:BCN1565
CAS No.:144629-84-5
- GR 113808
Catalog No.:BCC7019
CAS No.:144625-51-4
- CPI-203
Catalog No.:BCC4099
CAS No.:1446144-04-2
- Isomahanine
Catalog No.:BCN3177
CAS No.:144606-95-1
- Schisanlignone D
Catalog No.:BCN3630
CAS No.:144606-84-8
- Schisanlignone C
Catalog No.:BCN3629
CAS No.:144606-83-7
- IRL-1038
Catalog No.:BCC5730
CAS No.:144602-02-8
- Paliperidone
Catalog No.:BCC3834
CAS No.:144598-75-4
- Kanshone H
Catalog No.:BCN7627
CAS No.:1445952-33-9
- Fmoc-D-Cha-OH
Catalog No.:BCC3161
CAS No.:144701-25-7
- Telmisattan
Catalog No.:BCC3863
CAS No.:144701-48-4
- Telmisartan tert-butyl ester
Catalog No.:BCC9161
CAS No.:144702-26-1
- 4F 4PP oxalate
Catalog No.:BCC6678
CAS No.:144734-36-1
- 2-4-Hydroxy-3-methoxyphenyl-7-methoxy-5-benzofuranpropanol
Catalog No.:BCN1564
CAS No.:144735-57-9
- Cyclo(Phe-Val)
Catalog No.:BCN2419
CAS No.:14474-71-6
- Cyclo(Ala-Phe)
Catalog No.:BCN2411
CAS No.:14474-78-3
- Clopidogrel Related Compound B
Catalog No.:BCN2688
CAS No.:144750-52-7
- Brachynoside heptaacetate
Catalog No.:BCN6249
CAS No.:144765-80-0
- L-703,664 succinate
Catalog No.:BCC7437
CAS No.:144776-01-2
- 5-(4-(2-(5-Ethylpyridin-2-yl)ethoxy)benzylidene)thiazolidine-2,4-dione
Catalog No.:BCC8720
CAS No.:144809-28-9
- Deflazacort
Catalog No.:BCC8928
CAS No.:14484-47-0
Hispidulin, a small flavonoid molecule, suppresses the angiogenesis and growth of human pancreatic cancer by targeting vascular endothelial growth factor receptor 2-mediated PI3K/Akt/mTOR signaling pathway.[Pubmed:21087351]
Cancer Sci. 2011 Jan;102(1):219-25.
Hispidulin, an active component from Artemisia vestita, a traditional Tibetan medicinal plant, has been shown to possess anti-inflammatory and anti-oxidative activities. However, the functional role of Hispidulin on tumor growth and angiogenesis has not been elucidated. We found that Hispidulin significantly inhibited human pancreatic tumor growth in xenograft mice when s.c. treated at a dosage of 20 mg/kg daily, and this effect was accompanied with a potent inhibition on angiogenesis. When examining the cytotoxicity of Hispidulin on HUVECs and pancreatic cancer cells in vitro, we found that HUVECs were more susceptible to the treatment, suggesting angiogenesis might be the primary target of Hispidulin. Our results further showed that Hispidulin inhibited vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF)-induced cell migration, invasion, and capillary-like structure formation of HUVECs in a dose-dependent manner. In ex vivo and in vivo angiogenesis assays, we showed that Hispidulin suppressed VEGF-induced microvessel sprouting of rat aortic rings and corneal neovascularization in C57/BL6 mice. To understand the underlying molecular basis, we next examined the effects of Hispidulin on different molecular components in treated HUVECs, and found that Hispidulin suppressed the VEGF-triggered activation of VEGF receptor 2, PI3K, Akt, mTOR, and ribosomal protein S6 kinase, but had little effect on focal adhesion kinase or extracellular signal-regulated kinase at an effective concentration. Taken together, our results indicate that Hispidulin targets the VEGF receptor 2-mediated PI3K/Akt/mTOR signaling pathway in endothelial cells, leading to the suppression of pancreatic tumor growth and angiogenesis.
Hispidulin exerts anti-osteoporotic activity in ovariectomized mice via activating AMPK signaling pathway.[Pubmed:24338527]
Cell Biochem Biophys. 2014 Jun;69(2):311-7.
To investigate the effect of Hispidulin on ovariectomy (OVX)-induced bone loss in mice. Female mice subjected to OVX were treated with Hispidulin for 8 weeks. The total body bone mineral density was measured at the beginning and after the OVX at a time interval of 4 weeks. Micro-computed tomography of the tibia, bone histomorphometric analysis of the femur, and biomechanical analysis of tibia, vertebra, and femoral head were performed to fully evaluate the anti-osteoporotic effect of Hispidulin. Western blot analysis was performed to determine the level of activated AMPK. Hispidulin treatment effectively prevented OVX-induced body weight loss and attenuated OVX-induced bone loss. Hispidulin treatment also decreased trabecular spacing in OVX mice. The suppressing effect of Hispidulin on osteoclast surface and number was also found via histomorphometric analysis. Western blot analysis revealed that Hispidulin significantly elevated the activated AMPK levels. Our findings suggest that Hispidulin exerts anti-osteoporotic and bone resorption attenuating effects via activating the AMPK signaling pathway.
Hispidulin, a natural flavone, inhibits human platelet aggregation by increasing cAMP levels.[Pubmed:2836213]
Eur J Pharmacol. 1988 Feb 16;147(1):1-6.
Hispidulin, a natural flavone, and theophylline inhibited platelet aggregation triggered by adenosine-5'-monophosphate, arachidonic acid, paf-acether and collagen. Hispidulin was 100-fold more potent than theophylline. A threshold concentration of PGE1 did not modify the anti-aggregatory effect of Hispidulin but potentiated the effect of theophylline. A threshold concentration of Hispidulin had no effect on the inhibitory action of theophylline. Hispidulin (100 microM) and theophylline (10 mM) increased the control cAMP level in platelets 4-fold. A threshold concentration of PGE1 had a small effect on Hispidulin-induced cAMP levels but increased the theophylline-induced cAMP levels 3-fold. Theophylline (10 mM)-induced cAMP levels were not modified by Hispidulin. We demonstrate a correlation between the inhibition of platelet aggregation and the increase in cAMP levels induced by Hispidulin. These data suggest that Hispidulin could inhibit platelet aggregation by elevating cAMP levels by a mechanism different from that of theophylline or PGE1.
Hispidulin inhibits proliferation and enhances chemosensitivity of gallbladder cancer cells by targeting HIF-1alpha.[Pubmed:25499970]
Exp Cell Res. 2015 Mar 15;332(2):236-46.
Gallbladder cancer (GBC) is an aggressive malignancy of the bile duct, which is associated with a low (5-year) survival and poor prognosis. The transcription factor HIF-1alpha is implicated in the angiogenesis, cell survival, epithelial mesenchymal transition (EMT) and invasiveness of GBC. In this study, we have investigated the role of HIF-1alpha in the pathobilogy of GBC and effect of Hispidulin on the molecular events controlled by this transcription factor. We observed that Hispidulin caused induction of apoptosis, blockade of growth and cell cycle progression in GBC cells. Our results have demonstrated for the first time that Hispidulin-exerted anti-tumor effect involved the suppression of HIF-1alpha signaling. Hispidulin was found to repress the expression of HIF-1alpha protein dose-dependently without affecting the HIF-1alpha mRNA expression. In addition, the inhibition of HIF-1alpha protein synthesis was revealed to be mediated through the activation of AMPK signaling. Hispidulin also sensitized the tumor cells to Gemcitabine and 5-Fluoroucil by down-regulating HIF-1alpha/P-gp signaling. Given the low cost and exceedingly safe profile, Hispidulin appears to be a promising and novel chemosensitizer for GBC treatment.
Protective effect of hispidulin on kainic acid-induced seizures and neurotoxicity in rats.[Pubmed:25746462]
Eur J Pharmacol. 2015 May 15;755:6-15.
Hispidulin is a flavonoid compound which is an active ingredient in a number of traditional Chinese medicinal herbs, and it has been reported to inhibit glutamate release. The purpose of this study was to investigate whether Hispidulin protects against seizures induced by kainic acid, a glutamate analog with excitotoxic properties. The results indicated that intraperitoneally administering Hispidulin (10 or 50mg/kg) to rats 30 min before intraperitoneally injecting kainic acid (15 mg/kg) increased seizure latency and decreased seizure score. In addition, Hispidulin substantially attenuated kainic acid-induced hippocampal neuronal cell death, and this protective effect was accompanied by the suppression of microglial activation and the production of proinflammatory cytokines such as interleukin-1beta, interleukin-6, and tumor necrosis factor-alpha in the hippocampus. Moreover, Hispidulin reduced kainic acid-induced c-Fos expression and the activation of mitogen-activated protein kinases in the hippocampus. These data suggest that Hispidulin has considerable antiepileptic, neuroprotective, and antiinflammatory effects on kainic acid-induced seizures in rats.
Hispidulin, a constituent of Clerodendrum inerme that remitted motor tics, alleviated methamphetamine-induced hyperlocomotion without motor impairment in mice.[Pubmed:25764963]
J Ethnopharmacol. 2015 May 26;166:18-22.
ETHNOPHARMACOLOGICAL RELEVANCE: Previously, we found a patient with an intractable motor tic disorder that could be ameliorated by the ground leaf juice of Clerodendrum inerme (CI). Furthermore, the ethanol extract of CI leaves effectively ameliorated methamphetamine-induced hyperlocomotion (MIH) in mice, an animal model mimicking the hyper-dopaminergic status of tic disorders/Tourette syndrome, schizophrenia, or obsessive-compulsive disorder. Here, we for the first time identified a constituent able to reduce MIH from the CI ethanol extract that might represent a novel lead for the treatment of such disorders. MATERIALS AND METHODS: The ethanol extract of CI was sub-divided into n-hexane, dichloromethane, n-butanol and water fractions. Using MIH alleviation as a bioassay, active compounds were identified in these fractions using silica gel chromatography, recrystallization and proton NMR spectroscopy. RESULTS: The dichloromethane and n-hexane fractions were active in the bioassay. Further subfractionation and re-crystallization resulted in an active compound that was identified to be Hispidulin by proton NMR spectroscopy. Hispidulin significantly alleviated MIH in mice at doses that did not affect their spontaneous locomotor activity or performance in the rotarod test, a measure for motor coordination. CONCLUSIONS: Hispidulin is a flavonoid that has been isolated from several plants and reported to have anti-oxidative, anti-inflammatory and anti-cancer activities. Here, we for the very first time found that Hispidulin can also alleviate MIH at doses that did not impair motor activity, suggesting a therapeutic potential of Hispidulin in hyper-dopaminergic disorders.
The flavone hispidulin, a benzodiazepine receptor ligand with positive allosteric properties, traverses the blood-brain barrier and exhibits anticonvulsive effects.[Pubmed:15231642]
Br J Pharmacol. 2004 Jul;142(5):811-20.
The functional characterization of Hispidulin (4',5,7-trihydroxy-6-methoxyflavone), a potent benzodiazepine (BZD) receptor ligand, was initiated to determine its potential as a modulator of central nervous system activity. After chemical synthesis, Hispidulin was investigated at recombinant GABA(A)/BZD receptors expressed by Xenopus laevis oocytes. Concentrations of 50 nm and higher stimulated the GABA-induced chloride currents at tested receptor subtypes (alpha(1-3,5,6)beta(2)gamma(2)S) indicating positive allosteric properties. Maximal stimulation at alpha(1)beta(2)gamma(2)S was observed with 10 microm Hispidulin. In contrast to diazepam, Hispidulin modulated the alpha(6)beta(2)gamma(2)S-GABA(A) receptor subtype. When fed to seizure-prone Mongolian gerbils (Meriones unguiculatus) in a model of epilepsy, Hispidulin (10 mg kg(-1) body weight (BW) per day) and diazepam (2 mg kg(-1) BW per day) markedly reduced the number of animals suffering from seizures after 7 days of treatment (30 and 25% of animals in the respective treatment groups, vs 80% in the vehicle group). Permeability across the blood-brain barrier for the chemically synthesized, (14)C-labelled Hispidulin was confirmed by a rat in situ perfusion model. With an uptake rate (K(in)) of 1.14 ml min(-1) g(-1), measurements approached the values obtained with highly penetrating compounds such as diazepam. Experiments with Caco-2 cells predict that orally administered Hispidulin enters circulation in its intact form. At a concentration of 30 microm, the flavone crossed the monolayer without degradation as verified by the absence of glucuronidated metabolites.
Constituents of sage (Salvia officinalis) with in vitro affinity to human brain benzodiazepine receptor.[Pubmed:12624814]
Planta Med. 2003 Feb;69(2):113-7.
Benzodiazepine receptor binding assay-guided fractionation of the methanol extract from sage leaves ( Salvia officinalis L.) revealed three flavones and two abietane diterpenes functioning as benzodiazepine receptor-active components. Structural elucidation of the isolated pure compounds was performed by UV, EI-MS, ESI(pos)-MS/MS, as well as 1H- and 13C-NMR techniques. The flavones apigenin, Hispidulin and cirsimaritin competitively inhibited 3H-flumazenil binding to the benzodiazepine receptor with IC50 values of 30, 1.3 and 350 microM, respectively. In addition, the affinities of the newly discovered diterpene receptor ligands, i. e., 7-methoxyrosmanol and galdosol, were characterized. 7-Methoxyrosmanol exhibited an IC50 value of 7.2 microM and galdosol showed the strongest binding activity to the benzodiazepine receptor with an IC50 value of 0.8 microM.


