Clausena lansium
Clausena lansium
1. The products in our compound library are selected from thousands of unique natural products; 2. It has the characteristics of diverse structure, diverse sources and wide coverage of activities; 3. Provide information on the activity of products from major journals, patents and research reports around the world, providing theoretical direction and research basis for further research and screening; 4. Free combination according to the type, source, target and disease of natural product; 5. The compound powder is placed in a covered tube and then discharged into a 10 x 10 cryostat; 6. Transport in ice pack or dry ice pack. Please store it at -20 °C as soon as possible after receiving the product, and use it as soon as possible after opening.
Natural products/compounds from Clausena lansium
- Cat.No. Product Name CAS Number COA
-
BCN2932
Mauritianin109008-28-8
Instructions
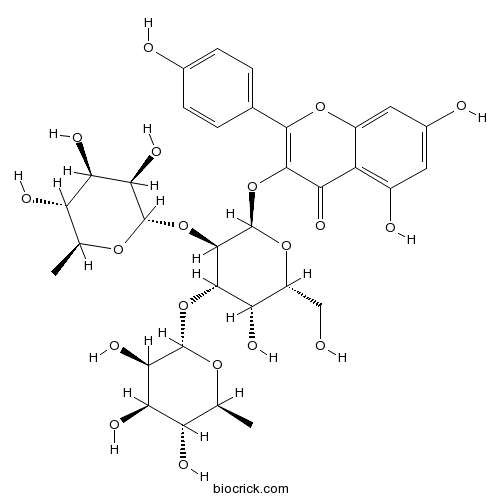
-
BCN5574
Imperatorin482-44-0
Instructions
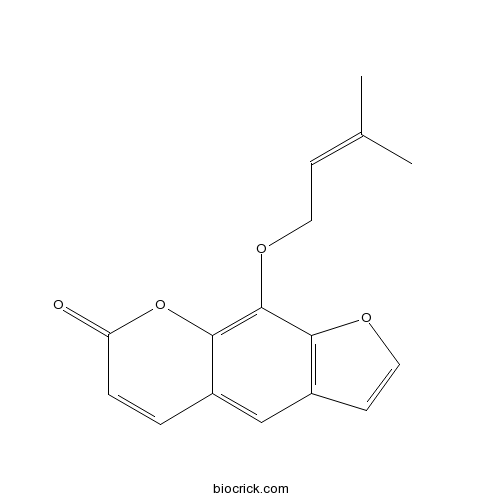
-
BCN3617
Ammijin495-30-7
Instructions
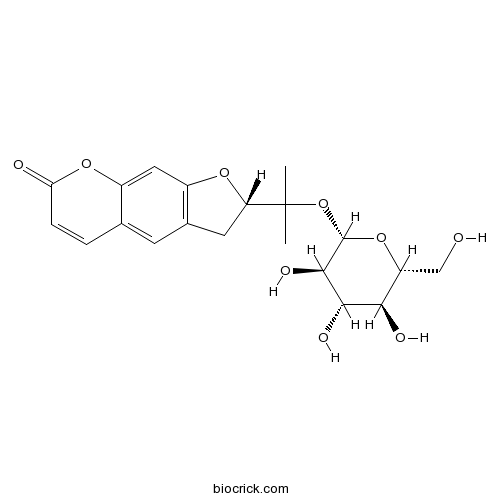
-
BCN2378
Nodakenin495-31-8
Instructions
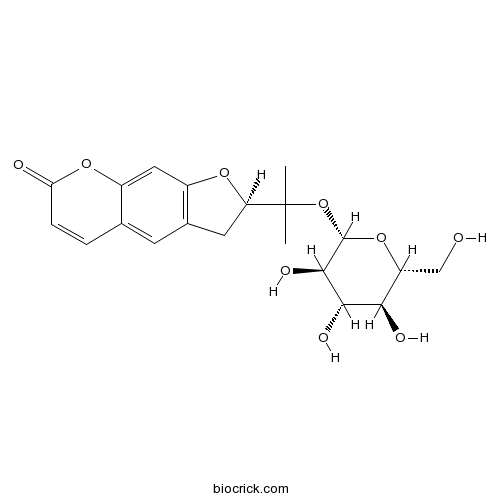
Carbazole alkaloids isolated from the branch and leaf extracts of Clausena lansium.[Pubmed: 30080650]
None
Nematicidal amide alkaloids from the seeds of Clausena lansium.[Pubmed: 29723562]
None
Characterization of santalene synthases using an inorganic pyrophosphatase coupled colorimetric assay.[Pubmed: 29438678]
We developed a colorimetric assay using yeast inorganic pyrophosphatase (IPP1) as a coupling enzyme to measure the activities of terpene synthases. IPP1 hydrolyzes pyrophosphate, the byproduct of terpene synthase catalyzed reactions, into orthophosphate, which can then be quantitated by reacting with molybdic acid to form a blue color compound. As a proof of concept, this method was used to quantitatively characterize three santalene synthases, SaSSy and SspiSSy involved in sandalwood oil biosynthesis, and a phylogenetically distant SanSyn from Clausena lansium. Our study provided the kinetic parameters of all three santalene synthases and demonstrated the validity of the enzyme couple colorimetric assay by the comparison of this assay with the existing GC-MS (Gas Chromatography-Mass Spectrometry) method.
Bioactive Compounds from the Stems of Clausena lansium.[Pubmed: 29240703]
None
Antidiabetic and Lipid-Lowering Effects of the Polyphenol Extracts from the Leaves of Clausena lansium (Lour.) Skeels on Streptozotocin-Induced Type 2 Diabetic Rats.[Pubmed: 29227535]
Clausena lansium (Lour.) Skeels (Wampee) is widely grown in China and considered as a healthy fruit. Its leaves are also considered as traditional herbs. This study analyzed polyphenol compounds in polyphenol extracts of the leaves C. lansium (lour.) Skeels (PEL) and investigated the protective effect of PEL against hyperglycemia and hyperlipidemia in T2DM rats. The result showed that PEL is composed mainly of gallic acid, chlorogenic acid, coffee acid, ferulic acid, and rutin. PEL could obviously relieve some symptoms of T2DM rats, including emaciation, hyperhidrosis, polyphagia, diuresis, liver swelling, kidney, and pancreas hypertrophy, as well as reduce fasting blood glucose. Moreover, the supplementation of PEL significantly ameliorated lipids disorder and protected liver in T2DM rats, including fat accumulation, improvement of lipid distribution and hepatocyte protection. These results indicate that the Oral of PEL have potential effects of against hyperglycemia and hyperlipidemia in diabetic disorders.
Pyrano[3,2-a]carbazole alkaloids as effective agents against ischemic stroke in vitro and in vivo.[Pubmed: 29202406]
A series of pyrano[3,2-a]carbazole alkaloids were designed and synthesized as analogues of Claulansine F (Clau F, 10a) isolated from Clausena lansium. Some of compounds showed strong neuroprotective effects and were promising agents against ischemic stroke. Among these compounds, 7c was the most active in inhibiting the programmed death of PC12 cells and primary cortical neurons. This compound induced neuroprotection following ischemic reperfusion and decreased neurological deficit scores in treated animals. Furthermore, 7c could penetrate the blood-brain barrier (BBB) in rats, and its exposure in the brain was 4.3-fold higher than that in plasma. More importantly, compared to edaravone, 7c exhibited stronger free radical scavenging activity. Our findings suggest that 7c may be promising for further evaluation as an intervention for ischemic stroke.
Clausenlanins A and B, Two Leucine-Rich Cyclic Nonapeptides from Clausena lansium.[Pubmed: 28612198]
None
Proanthocyanidins purified from fruit pericarp of Clausena lansium (Lour.) Skeels as efficient tyrosinase inhibitors: structure evaluation, inhibitory activity and molecular mechanism.[Pubmed: 28128839]
None
Prenylated Coumarins from Heracleum stenopterum, Peucedanum praeruptorum, Clausena lansium, and Murraya paniculata.[Pubmed: 27646268]
None


